Type 1 Diabetes: Interferons and the Aftermath of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Enteroviral Infection
Abstract
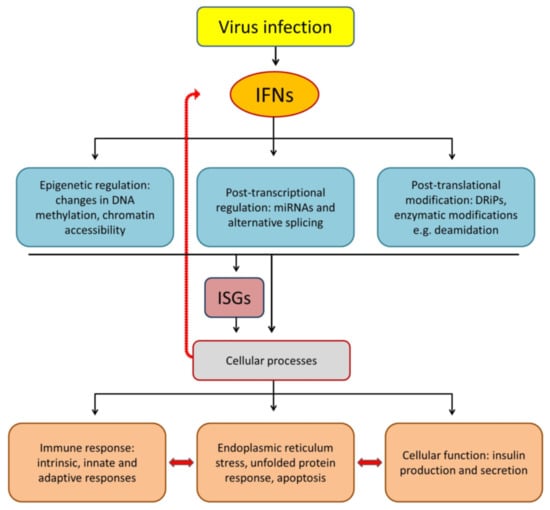
:1. Introduction
2. IFNs as a Key Link between Environmental and Genetic Risk Factors of Autoimmune T1D
3. IFNs Induce Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Unfolded Protein Response and Apoptosis
4. IFNs May Promote the Expression of Neo-Antigens in Beta Cells
5. Epigenetic Modulation of Cellular Responses by IFNs
6. IFN-Mediated Antiviral Responses May Determine the Fate of Infected Cells
7. IFNs as Regulators of Cell Mediated Immunity
8. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pugliese, A. Autoreactive T cells in type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2881–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanter, M.; Sork, H.; Tuomela, S.; Flodström-Tullberg, M. Genetic and Environmental Interaction in Type 1 Diabetes: A Relationship Between Genetic Risk Alleles and Molecular Traits of Enterovirus Infection? Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eizirik, D.; Pasquali, L.; Cnop, M. Pancreatic β-cells in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Different pathways to failure. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.J.; Willcox, A.; Bone, A.J.; Foulis, A.K.; Morgan, N.G. The prevalence of enteroviral capsid protein vp1 immunostaining in pancreatic islets in human type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anagandula, M.; Richardson, S.J.; Oberste, M.S.; Sioofy-Khojine, A.B.; Hyoty, H.; Morgan, N.G.; Korsgren, O.; Frisk, G. Infection of human islets of Langerhans with two strains of Coxsackie B virus serotype 1: Assessment of virus replication, degree of cell death and induction of genes involved in the innate immunity pathway. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulis, A.K.; Farquharson, M.A.; Meager, A. Immunoreactive alpha-interferon in insulin-secreting beta cells in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 1987, 2, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogvold, L.; Edwin, B.; Buanes, T.; Frisk, G.; Skog, O.; Anagandula, M.; Korsgren, O.; Undlien, D.; Eike, M.C.; Richardson, S.J.; et al. Detection of a low-grade enteroviral infection in the islets of langerhans of living patients newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2015, 64, 1682–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sioofy-Khojine, A.B.; Lehtonen, J.; Nurminen, N.; Laitinen, O.H.; Oikarinen, S.; Huhtala, H.; Pakkanen, O.; Ruokoranta, T.; Hankaniemi, M.M.; Toppari, J.; et al. Coxsackievirus B1 infections are associated with the initiation of insulin-driven autoimmunity that progresses to type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poma, A.; Genoni, A.; Broccolo, F.; Denaro, M.; Pugliese, A.; Basolo, F.; Toniolo, A. Immune Transcriptome of Cells Infected with Enterovirus Strains Obtained from Cases of Type 1 Diabetes. Microorganisms 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.; Morgan, N. Enteroviral infections in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes: New insights for therapeutic intervention. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshebani, A.; Olsson, A.; Westman, J.; Tuvemo, T.; Korsgren, O.; Frisk, G. Effects on isolated human pancreatic islet cells after infection with strains of enterovirus isolated at clinical presentation of type 1 diabetes. Virus Res. 2007, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindersson, M.; Elshebani, A.; Orn, A.; Tuvemo, T.; Frisk, G. Simultaneous type 1 diabetes onset in mother and son coincident with an enteroviral infection. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Publ. Pan Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2005, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairn, C.; Galbraith, D.; Taylor, K.; Clements, G. Enterovirus variants in the serum of children at the onset of Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 1999, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya-Suri, V.; Schlosser, M.; Zimmermann, K.; Rjasanowski, I.; Gürtler, L.; Mentel, R. Enterovirus RNA sequences in sera of schoolchildren in the general population and their association with type 1-diabetes-associated autoantibodies. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champsaur, H.; Dussaix, E.; Samolyk, D.; Fabre, M.; Bach, C.; Assan, R. Diabetes and Coxsackie virus B5 infection. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 1980, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Horta, O.; Bello, M.; Cabrera-Rode, E.; Suárez, J.; Más, P.; García, I.; Abalos, I.; Jofra, R.; Molina, G.; Díaz-Díaz, O.; et al. Echovirus 4 and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Autoimmunity 2001, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otonkoski, T.; Roivainen, M.; Vaarala, O.; Dinesen, B.; Leipälä, J.; Hovi, T.; Knip, M. Neonatal Type I diabetes associated with maternal echovirus 6 infection: A case report. Diabetologia 2000, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paananen, A.; Ylipaasto, P.; Rieder, E.; Hovi, T.; Galama, J.; Roivainen, M. Molecular and biological analysis of echovirus 9 strain isolated from a diabetic child. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Clements, G.; Riding, M.; Collins, P.; Bottazzo, G.; Taylor, K. Simultaneous onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus in identical infant twins with enterovirus infection. Diabet. Med. A J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 1998, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, W.C.; Rawlinson, W.D.; Craig, M.E. Enterovirus infection and type 1 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational molecular studies. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2011, 342, d35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stene, L.; Oikarinen, S.; Hyöty, H.; Barriga, K.; Norris, J.; Klingensmith, G.; Hutton, J.; Erlich, H.; Eisenbarth, G.; Rewers, M. Enterovirus infection and progression from islet autoimmunity to type 1 diabetes: The Diabetes and Autoimmunity Study in the Young (DAISY). Diabetes 2010, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Werf, N.v.d.; Kroese, F.G.M.; Rozing, J.; Hillebrands, J.L. Viral Infections as Potential Triggers of Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2007, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, M.; Nair, S.; Stein, H.; Rawlinson, W. Viruses and type 1 diabetes: A new look at an old story. Pediatric Diabetes 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppieters, K.; Boettler, T.; Herrath, M.v. Virus infections in type 1 diabetes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, U.; Herrath, M.v. Do viral infections protect from or enhance type 1 diabetes and how can we tell the difference? Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tracy, S.; Drescher, K.; Jackson, J.; Kim, K.; Kono, K. Enteroviruses, type 1 diabetes and hygiene: A complex relationship. Rev. Med. Virol. 2010, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifie, E.; Russell, M.A.; Dhayal, S.; Leete, P.; Sebastiani, G.; Nigi, L.; Dotta, F.; Marjomaki, V.; Eizirik, D.L.; Morgan, N.G.; et al. Unexpected subcellular distribution of a specific isoform of the Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor, CAR-SIV, in human pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2344–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oikarinen, M.; Tauriainen, S.; Honkanen, T.; Vuori, K.; Karhunen, P.; Vasama-Nolvi, C.; Oikarinen, S.; Verbeke, C.; Blair, G.E.; Rantala, I.; et al. Analysis of pancreas tissue in a child positive for islet cell antibodies. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulte, B.; Bakkers, J.; Lanke, K.; Melchers, W.; Westerlaken, C.; Allebes, W.; Aanstoot, H.; Bruining, G.; Adema, G.; Kuppeveld, F.V.; et al. Detection of enterovirus RNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of type 1 diabetic patients beyond the stage of acute infection. Viral Immunol. 2010, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylipaasto, P.; Klingel, K.; Lindberg, A.M.; Otonkoski, T.; Kandolf, R.; Hovi, T.; Roivainen, M. Enterovirus infection in human pancreatic islet cells, islet tropism in vivo and receptor involvement in cultured islet beta cells. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiltunen, M.; Hyöty, H.; Knip, M.; Ilonen, J.; Reijonen, H.; Vähäsalo, P.; Roivainen, M.; Lönnrot, M.; Leinikki, P.; Hovi, T.; et al. Islet Cell Antibody Seroconversion in Children Is Temporally Associated with Enterovirus Infections. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 175, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatoni, A.; Baj, A.; Bianchi, G.; Federico, G.; Colombo, M.; Toniolo, A. Intrafamilial spread of enterovirus infections at the clinical onset of type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnrot, M.; Salminen, K.; Knip, M.; Savola, K.; Kulmala, P.; Leinikki, P.; Hyypiä, T.; Akerblom, H.; Hyöty, H. Enterovirus RNA in serum is a risk factor for beta-cell autoimmunity and clinical type 1 diabetes: A prospective study. Childhood Diabetes in Finland (DiMe) Study Group. J. Med. Virol. 2000, 61, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wagenknecht, L.; Roseman, J.; Herman, W. Increased incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus following an epidemic of Coxsackievirus B5. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1991, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, D.; Taylor, K. Seasonal incidence of diabetes mellitus. Br. Med. J. 1969, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laitinen, O.H.; Honkanen, H.; Pakkanen, O.; Oikarinen, S.; Hankaniemi, M.M.; Huhtala, H.; Ruokoranta, T.; Lecouturier, V.; Andre, P.; Harju, R.; et al. Coxsackievirus B1 is associated with induction of beta-cell autoimmunity that portends type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2014, 63, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oikarinen, S.; Tauriainen, S.; Hober, D.; Lucas, B.; Vazeou, A.; Sioofy-Khojine, A.; Bozas, E.; Muir, P.; Honkanen, H.; Ilonen, J.; et al. Virus antibody survey in different European populations indicates risk association between coxsackievirus B1 and type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2014, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vehik, K.; Lynch, K.F.; Wong, M.C.; Tian, X.; Ross, M.C.; Gibbs, R.A.; Ajami, N.J.; Petrosino, J.F.; Rewers, M.; Toppari, J.; et al. Prospective virome analyses in young children at increased genetic risk for type 1 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Calvo, T.; Sabouri, S.; Anquetil, F.; Herrath, M.v. The Viral Paradigm in Type 1 Diabetes: Who Are the Main Suspects? Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.; Basu, T.; Kim, C. Lower Incidence Rate of Type 1 Diabetes after Receipt of the Rotavirus Vaccine in the United States, 2001–2017. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burke, R.; Tate, J.; Jiang, B.; Parashar, U. Rotavirus and Type 1 Diabetes-is there a connection? A synthesis of the evidence. J. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, P.; Lakshmikanth, T.; Laitinen, O.; Utorova, R.; Jacobson, S.; Oikarinen, M.; Domsgen, E.; Koivunen, M.; Chaux, P.; Devard, N.; et al. A preclinical study on the efficacy and safety of a new vaccine against Coxsackievirus B1 reveals no risk for accelerated diabetes development in mouse models. Diabetologia 2015, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, V.M.; Hankaniemi, M.M.; Svedin, E.; Sioofy-Khojine, A.; Oikarinen, S.; Hyoty, H.; Laitinen, O.H.; Hytonen, V.P.; Flodstrom-Tullberg, M. A Coxsackievirus B vaccine protects against virus-induced diabetes in an experimental mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stone, V.; Hankaniemi, M.; Laitinen, O.; Sioofy-Khojine, A.; Lin, A.; Lozano, I.D.; Mazur, M.; Marjomäki, V.; Loré, K.; Hyöty, H.; et al. A hexavalent Coxsackievirus B vaccine is highly immunogenic and has a strong protective capacity in mice and nonhuman primates. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccone, P.; Fehervari, Z.; Phillips, J.; Dunne, D.; Cooke, A. Parasitic worms and inflammatory diseases. Parasite Immunol. 2006, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodansky, H.; Staines, A.; Stephenson, C.; Haigh, D.; Cartwright, R. Evidence for an environmental effect in the aetiology of insulin dependent diabetes in a transmigratory population. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1992, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oilinki, T.; Otonkoski, T.; Ilonen, J.; Knip, M.; Miettinen, P. Prevalence and characteristics of diabetes among Somali children and adolescents living in Helsinki, Finland. Pediatric Diabetes 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderström, U.; Aman, J.; Hjern, A. Being born in Sweden increases the risk for type 1 diabetes - a study of migration of children to Sweden as a natural experiment. Acta Paediatr. (Oslo, Nor. 1992) 2012, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viskari, H.; Ludvigsson, J.; Uibo, R.; Salur, L.; Marciulionyte, D.; Hermann, R.; Soltesz, G.; Füchtenbusch, M.; Ziegler, A.; Kondrashova, A.; et al. Relationship between the incidence of type 1 diabetes and maternal enterovirus antibodies: Time trends and geographical variation. Diabetologia 2005, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viskari, H.; Ludvigsson, J.; Uibo, R.; Salur, L.; Marciulionyte, D.; Hermann, R.; Soltesz, G.; Füchtenbusch, M.; Ziegler, A.; Kondrashova, A.; et al. Relationship between the incidence of type 1 diabetes and enterovirus infections in different European populations: Results from the EPIVIR project. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiskari, T.; Kondrashova, A.; Viskari, H.; Kaila, M.; Haapala, A.; Aittoniemi, J.; Virta, M.; Hurme, M.; Uibo, R.; Knip, M.; et al. Allergic sensitization and microbial load--a comparison between Finland and Russian Karelia. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, S.; Yoshida, H.; Moodley, D.; LeBoité, H.; Rothamel, K.; Raj, T.; Ye, C.; Chevrier, N.; Zhang, S.; Feng, T.; et al. Parsing the Interferon Transcriptional Network and Its Disease Associations. Cell 2016, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefan-Lifshitz, M.; Karakose, E.; Cui, L.; Ettela, A.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, W.; Tomer, Y. Epigenetic Modulation of β Cells by Interferon-α via PNPT1/mir-26a/TET2 Triggers Autoimmune Diabetes. JCI Insight 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, K.; Richardson, S.J.; Leete, P.; Morgan, N.G.; Korsgren, O.; Flodstrom-Tullberg, M. Induction of an antiviral state and attenuated coxsackievirus replication in type III interferon-treated primary human pancreatic islets. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7646–7654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Willcox, A.; Richardson, S.J.; Bone, A.J.; Foulis, A.K.; Morgan, N.G. Analysis of islet inflammation in human type 1 diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 155, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.J.; Rodriguez-Calvo, T.; Gerling, I.C.; Mathews, C.E.; Kaddis, J.S.; Russell, M.A.; Zeissler, M.; Leete, P.; Krogvold, L.; Dahl-Jorgensen, K.; et al. Islet cell hyperexpression of HLA class I antigens: A defining feature in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2448–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junior, A.D.; Sampaio, N.; Rehwinkel, J. A Balancing Act: MDA5 in Antiviral Immunity and Autoinflammation. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of Type I Interferon Responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlee, M.; Hartmann, G. Discriminating Self From Non-Self in Nucleic Acid Sensing. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouin, A.; Gretteau, P.; Wehbe, M.; Renois, F.; N’Guyen, Y.; Lévêque, N.; Vu, M.; Tracy, S.; Chapman, N.; Bruneval, P.; et al. Enterovirus Persistence in Cardiac Cells of Patients With Idiopathic Dilated Cardiomyopathy Is Linked to 5’ Terminal Genomic RNA-Deleted Viral Populations With Viral-Encoded Proteinase Activities. Circulation 2019, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, P.; Messner, R. Molecular Mechanisms of Coxsackievirus Persistence in Chronic Inflammatory Myopathy: Viral RNA Persists Through Formation of a Double-Stranded Complex Without Associated Genomic Mutations or Evolution. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 10113–10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chia, J. The Role of Enterovirus in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, S.; Thomsen, A. Sensing of RNA Viruses: A Review of Innate Immune Receptors Involved in Recognizing RNA Virus Invasion. J. Virol. 2012, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pichlmair, A.; Sousa, C.R.e. Innate Recognition of Viruses. Immunity 2007, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geravandi, S.; Liu, H.; Maedler, K. Enteroviruses and T1D: Is It the Virus, the Genes or Both which Cause T1D. Microorganisms 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichlmair, A.; Schulz, O.; Tan, C.; Näslund, T.; Liljeström, P.; Weber, F.; Sousa, C.R.e. RIG-I-mediated Antiviral Responses to Single-Stranded RNA Bearing 5’-phosphates. Science 2006, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pichlmair, A.; Schulz, O.; Tan, C.P.; Rehwinkel, J.; Kato, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S.; Way, M.; Schiavo, G.; Reis e Sousa, C. Activation of MDA5 Requires Higher-Order RNA Structures Generated during Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10761–10769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peisley, A.; Lin, C.; Wu, B.; Orme-Johnson, M.; Liu, M.; Walz, T.; Hur, S. Cooperative Assembly and Dynamic Disassembly of MDA5 Filaments for Viral dsRNA Recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Diao, F.; Lei, C.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Tien, P.; et al. The Adaptor Protein MITA Links Virus-Sensing Receptors to IRF3 Transcription Factor Activation. Immunity 2008, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, B.; Cheng, G. Modulation of the Interferon Antiviral Response by the TBK1/IKKi Adaptor Protein TANK. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, J.; Coyne, C. Mechanisms of MAVS Regulation at the Mitochondrial Membrane. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newby, B.; Mathews, C. Type I Interferon Is a Catastrophic Feature of the Diabetic Islet Microenvironment. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foulis, A.K.; Farquharson, M.A.; Hardman, R. Aberrant expression of class II major histocompatibility complex molecules by B cells and hyperexpression of class I major histocompatibility complex molecules by insulin containing islets in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1987, 30, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, M.; Krogvold, L.; Kuric, E.; Dahl-Jørgensen, K.; Skog, O. Expression of Interferon-Stimulated Genes in Insulitic Pancreatic Islets of Patients Recently Diagnosed With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2016, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colli, M.; Ramos-Rodríguez, M.; Nakayasu, E.; Alvelos, M.; Lopes, M.; Hill, J.; Turatsinze, J.; Brachène, A.C.d.; Russell, M.; Raurell-Vila, H.; et al. An Integrated Multi-Omics Approach Identifies the Landscape of Interferon-α-Mediated Responses of Human Pancreatic Beta Cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colli, M.; Hill, J.; Marroquí, L.; Chaffey, J.; Santos, R.D.; Leete, P.; Brachène, A.C.d.; Paula, F.; Beeck, A.O.d.; Castela, A.; et al. PDL1 Is Expressed in the Islets of People With Type 1 Diabetes and Is Up-Regulated by interferons-α and-γ via IRF1 Induction. EBioMedicine 2018, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, S.; Yuan, X.; Lin, Z.; Huang, Z. HLA-DQB1 and HLA-DRB1 Variants Confer Susceptibility to Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults: Relative Predispositional Effects Among Allele Groups. Genes 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farina, F.; Picascia, S.; Pisapia, L.; Barba, P.; Vitale, S.; Franzese, A.; Mozzillo, E.; Gianfrani, C.; Pozzo, G.G.D. HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1 Alleles, Conferring Susceptibility to Celiac Disease and Type 1 Diabetes, Are More Expressed Than Non-Predisposing Alleles and Are Coordinately Regulated. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kallionpää, H.; Elo, L.; Laajala, E.; Mykkänen, J.; Ricaño-Ponce, I.; Vaarma, M.; Laajala, T.; Hyöty, H.; Ilonen, J.; Veijola, R.; et al. Innate Immune Activity Is Detected Prior to Seroconversion in Children With HLA-conferred Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility. Diabetes 2014, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Chen, Q.; Su, S.; Zhang, P.; Kurosaka, K.; Caspi, R.; Michalek, S.; Rosenberg, H.; Zhang, N.; Oppenheim, J. Eosinophil-derived Neurotoxin Acts as an Alarmin to Activate the TLR2-MyD88 Signal Pathway in Dendritic Cells and Enhances Th2 Immune Responses. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, L.; Palucka, A.; Arce, E.; Cantrell, V.; Borvak, J.; Banchereau, J.; Pascual, V. Interferon and Granulopoiesis Signatures in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Blood. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bovin, L.; Rieneck, K.; Workman, C.; Nielsen, H.; Sørensen, S.; Skjødt, H.; Florescu, A.; Brunak, S.; Bendtzen, K. Blood Cell Gene Expression Profiling in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Discriminative Genes and Effect of Rheumatoid Factor. Immunol. Lett. 2004, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domsgen, E.; Lind, K.; Kong, L.; Huhn, M.H.; Rasool, O.; van Kuppeveld, F.; Korsgren, O.; Lahesmaa, R.; Flodstrom-Tullberg, M. An IFIH1 gene polymorphism associated with risk for autoimmunity regulates canonical antiviral defence pathways in Coxsackievirus infected human pancreatic islets. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oram, R.A.; Patel, K.; Hill, A.; Shields, B.; McDonald, T.J.; Jones, A.; Hattersley, A.T.; Weedon, M.N. A Type 1 Diabetes Genetic Risk Score Can Aid Discrimination Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in Young Adults. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Funabiki, M.; Kato, H.; Miyachi, Y.; Toki, H.; Motegi, H.; Inoue, M.; Minowa, O.; Yoshida, A.; Deguchi, K.; Sato, H.; et al. Autoimmune Disorders Associated With Gain of Function of the Intracellular Sensor MDA5. Immunity 2014, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gateva, V.; Sandling, J.; Hom, G.; Taylor, K.; Chung, S.; Sun, X.; Ortmann, W.; Kosoy, R.; Ferreira, R.; Nordmark, G.; et al. A Large-Scale Replication Study Identifies TNIP1, PRDM1, JAZF1, UHRF1BP1 and IL10 as Risk Loci for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jean-Baptiste, V.; Xia, C.; Clare-Salzler, M.; Horwitz, M. Type 1 Diabetes and Type 1 Interferonopathies: Localization of a Type 1 Common Thread of Virus Infection in the Pancreas. EBioMedicine 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, J.; Zou, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Pan, F.; Ye, D. Meta-analysis of TYK2 Gene Polymorphisms Association With Susceptibility to Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marroqui, L.; Santos, R.D.; Fløyel, T.; Grieco, F.; Santin, I.; Beeck, A.O.d.; Marselli, L.; Marchetti, P.; Pociot, F.; Eizirik, D. TYK2, a Candidate Gene for Type 1 Diabetes, Modulates Apoptosis and the Innate Immune Response in Human Pancreatic β-Cells. Diabetes 2015, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brachène, A.C.d.; Castela, A.; Beeck, A.O.d.; Mirmira, R.; Marselli, L.; Marchetti, P.; Masse, C.; Miao, W.; Leit, S.; Evans-Molina, C.; et al. Pre-clinical Evaluation of TYK2 Inhibitors for Human Beta Cell Protection in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marroqui, L.; Santos, R.D.; Beeck, A.O.d.; Brachène, A.C.d.; Marselli, L.; Marchett, P.; Eizirik, D. Interferon-α Mediates Human Beta Cell HLA Class I Overexpression, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis, Three Hallmarks of Early Human Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetologia 2017, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brozzi, F.; Nardelli, T.R.; Lopes, M.; Millard, I.; Barthson, J.; Igoillo-Esteve, M.; Grieco, F.A.; Villate, O.; Oliveira, J.M.; Casimir, M.; et al. Cytokines induce endoplasmic reticulum stress in human, rat and mouse beta cells via different mechanisms. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Majoros, A.; Platanitis, E.; Kernbauer-Hölzl, E.; Rosebrock, F.; Müller, M.; Decker, T. Canonical and Non-Canonical Aspects of JAK-STAT Signaling: Lessons From Interferons for Cytokine Responses. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdul-Sater, A.A.; Majoros, A.; Plumlee, C.R.; Perry, S.; Gu, A.D.; Lee, C.; Shresta, S.; Decker, T.; Schindler, C. Different STAT Transcription Complexes Drive Early and Delayed Responses to Type I IFNs. J. Immunol. (Baltimore Md. 1950) 2015, 195, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fung, T.S.; Torres, J.; Liu, D.X. The Emerging Roles of Viroporins in ER Stress Response and Autophagy Induction during Virus Infection. Viruses 2015, 7, 2834–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, P.; Ron, D. The Unfolded Protein Response: From Stress Pathway to Homeostatic Regulation. Science 2011, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Tian, M.; Ding, C.; Yu, S. The C/EBP Homologous Protein (CHOP) Transcription Factor Functions in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Microbial Infection. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Z.; Shen, L.; Ma, H.; Yang, J.; Yang, D.; Chen, H.; Wei, J.; Lu, Q.; Wang, D.; Xiang, W.; et al. Involvement of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated C/EBP Homologous Protein Activation in Coxsackievirus B3-Induced Acute Viral Myocarditis. Circ. Heart Fail. 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delbrel, E.; Soumare, A.; Naguez, A.; Label, R.; Bernard, O.; Bruhat, A.; Fafournoux, P.; Tremblais, G.; Marchant, D.; Gille, T.; et al. HIF-1α Triggers ER Stress and CHOP-mediated Apoptosis in Alveolar Epithelial Cells, a Key Event in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, J.; Scheuner, D.; Wang, S.; Han, J.; Kodali, V.; Li, P.; Nguyen, J.; George, J.; Davis, C.; Wu, S.; et al. The IRE1α/XBP1s Pathway Is Essential for the Glucose Response and Protection of β Cells. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanase, N.; Hata, K.; Shimo, K.; Hayashida, M.; Evers, B.; Mizuguchi, J. Requirement of c-Jun NH2-terminal Kinase Activation in Interferon-Alpha-Induced Apoptosis Through Upregulation of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) in Daudi B Lymphoma Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozzi, F.; Gerlo, S.; Grieco, F.; Juusola, M.; Balhuizen, A.; Lievens, S.; Gysemans, C.; Bugliani, M.; Mathieu, C.; Marchetti, P.; et al. Ubiquitin D Regulates IRE1α/c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) Protein-dependent Apoptosis in Pancreatic Beta Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lombardi, A.; Tomer, Y. Interferon Alpha Impairs Insulin Production in Human Beta Cells via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Gao, B.; Ye, L.; Han, X.; Wang, W.; Kong, L.; Fang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein (HBx) Activates ATF6 and IRE1-XBP1 Pathways of Unfolded Protein Response. Virus Res. 2007, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colli, M.L.; Paula, F.M.; Marselli, L.; Marchetti, P.; Roivainen, M.; Eizirik, D.L.; Op de Beeck, A. Coxsackievirus B Tailors the Unfolded Protein Response to Favour Viral Amplification in Pancreatic beta Cells. J. Innate Immun. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlitz, G.; Jagus, R.; Elroy-Stein, O. Phosphorylation of Initiation factor-2 Alpha Is Required for Activation of Internal Translation Initiation During Cell Differentiation. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kracht, M.; Lummel, M.v.; Nikolic, T.; Joosten, A.; Laban, S.; Slik, A.v.d.; Veelen, P.v.; Carlotti, F.; Koning, E.d.; Hoeben, R.; et al. Autoimmunity Against a Defective Ribosomal Insulin Gene Product in Type 1 Diabetes. Nat. Med. 2017, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, R.; Haan, A.D.; Zaldumbide, A.; Koning, E.D.; Ru, A.D.; Veelen, P.V.; Lummel, M.V.; Roep, B. Human Islets and Dendritic Cells Generate Post-Translationally Modified Islet Autoantigens. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marré, M.; James, E.; Piganelli, J. β Cell ER Stress and the Implications for Immunogenicity in Type 1 Diabetes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babon, J.A.; DeNicola, M.E.; Blodgett, D.M.; Crevecoeur, I.; Buttrick, T.S.; Maehr, R.; Bottino, R.; Naji, A.; Kaddis, J.; Elyaman, W.; et al. Analysis of self-antigen specificity of islet-infiltrating T cells from human donors with type 1 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.; Rihanek, M.; Hohenstein, A.; Nakayama, M.; Michels, A.; Gottlieb, P.; Haskins, K.; Delong, T. Hybrid Insulin Peptides Are Autoantigens in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2019, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arribas-Layton, D.; Guyer, P.; Delong, T.; Dang, M.; Chow, I.; Speake, C.; Greenbaum, C.; Kwok, W.; Baker, R.; Haskins, K.; et al. Hybrid Insulin Peptides Are Recognized by Human T Cells in the Context of DRB1*04:01. Diabetes 2020, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiles, T.; Powell, R.; Michel, R.; Beard, K.; Hohenstein, A.; Bradley, B.; Reisdorph, N.; Haskins, K.; Delong, T. Identification of Hybrid Insulin Peptides (HIPs) in Mouse and Human Islets by Mass Spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delong, T.; Wiles, T.; Baker, R.; Bradley, B.; Barbour, G.; Reisdorph, R.; Armstrong, M.; Powell, R.; Reisdorph, N.; Kumar, N.; et al. Pathogenic CD4 T Cells in Type 1 Diabetes Recognize Epitopes Formed by Peptide Fusion. Science 2016, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marre, M.; McGinty, J.; Chow, I.; DeNicola, M.; Beck, N.; Kent, S.; Powers, A.; Bottino, R.; Harlan, D.; Greenbaum, C.; et al. Modifying Enzymes Are Elicited by ER Stress, Generating Epitopes That Are Selectively Recognized by CD4+ T Cells in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2018, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Duque, S.; Azoury, M.E.; Colli, M.L.; Afonso, G.; Turatsinze, J.V.; Nigi, L.; Lalanne, A.I.; Sebastiani, G.; Carre, A.; Pinto, S.; et al. Conventional and Neo-antigenic Peptides Presented by beta Cells Are Targeted by Circulating Naive CD8+ T Cells in Type 1 Diabetic and Healthy Donors. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fradin, D.; Fur, S.L.; Mille, C.; Naoui, N.; Groves, C.; Zelenika, D.; McCarthy, M.; Lathrop, M.; Bougnères, P. Association of the CpG Methylation Pattern of the Proximal Insulin Gene Promoter With Type 1 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Miao, F.; Paterson, A.D.; Lachin, J.M.; Zhang, L.; Schones, D.E.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Tompkins, J.D.; Genuth, S.; et al. Epigenomic Profiling Reveals an Association Between Persistence of DNA Methylation and Metabolic Memory in the DCCT/EDIC Type 1 Diabetes Cohort. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramos-Rodríguez, M.; Raurell-Vila, H.; Colli, M.; Alvelos, M.; Subirana-Granés, M.; Juan-Mateu, J.; Norris, R.; Turatsinze, J.; Nakayasu, E.; Webb-Robertson, B.; et al. The Impact of Proinflammatory Cytokines on the β-cell Regulatory Landscape Provides Insights Into the Genetics of Type 1 Diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, M.; Redick, S.; Blodgett, D.; Richardson, S.; Leete, P.; Krogvold, L.; Dahl-Jørgensen, K.; Bottino, R.; Brissova, M.; Spaeth, J.; et al. HLA Class II Antigen Processing and Presentation Pathway Components Demonstrated by Transcriptome and Protein Analyses of Islet β-Cells From Donors With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2019, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, Y.; Kim, J.; Okamoto, H.; Ni, M.; Wei, Y.; Adler, C.; Murphy, A.; Yancopoulos, G.; Lin, C.; Gromada, J. RNA Sequencing of Single Human Islet Cells Reveals Type 2 Diabetes Genes. Cell Metab. 2016, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.W.; Ho, A.; Alshabee-Akil, A.; Hardikar, A.A.; Kay, T.W.; Rawlinson, W.D.; Craig, M.E. Coxsackievirus B5 Infection Induces Dysregulation of microRNAs Predicted to Target Known Type 1 Diabetes Risk Genes in Human Pancreatic Islets. Diabetes 2016, 65, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engelmann, I.; Alidjinou, E.; Bertin, A.; Bossu, J.; Villenet, C.; Figeac, M.; Sane, F.; Hober, D. Persistent Coxsackievirus B4 Infection Induces microRNA Dysregulation in Human Pancreatic Cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelmann, I.; Alidjinou, E.; Bertin, A.; Sane, F.; Hober, D. miRNAs in Enterovirus Infection. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieco, F.; Sebastiani, G.; Juan-Mateu, J.; Villate, O.; Marroqui, L.; Ladrière, L.; Tugay, K.; Regazzi, R.; Bugliani, M.; Marchetti, P.; et al. MicroRNAs miR-23a-3p, miR-23b-3p, and miR-149-5p Regulate the Expression of Proapoptotic BH3-Only Proteins DP5 and PUMA in Human Pancreatic β-Cells. Diabetes 2017, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacob, A.; Smith, C. Intron Retention as a Component of Regulated Gene Expression Programs. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meertens, L.; Hafirassou, M.; Couderc, T.; Bonnet-Madin, L.; Kril, V.; Kümmerer, B.; Labeau, A.; Brugier, A.; Simon-Loriere, E.; Burlaud-Gaillard, J.; et al. FHL1 Is a Major Host Factor for Chikungunya Virus Infection. Nature 2019, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, M.; Eugster, A.; Walther, D.; Daehling, N.; Riethausen, S.; Kuehn, D.; Klingel, K.; Beyerlein, A.; Zillmer, S.; Ziegler, A.; et al. Incomplete Immune Response to Coxsackie B Viruses Associates With Early Autoimmunity Against Insulin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, K.; Svedin, E.; Domsgen, E.; Kapell, S.; Laitinen, O.H.; Moll, M.; Flodstrom-Tullberg, M. Coxsackievirus counters the host innate immune response by blocking type III interferon expression. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, S.; Smithee, S.; Alhazmi, A.; Chapman, N. Coxsackievirus can persist in murine pancreas by deletion of 5’ terminal genomic sequences. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.J.; Leete, P.; Bone, A.J.; Foulis, A.K.; Morgan, N.G. Expression of the enteroviral capsid protein VP1 in the islet cells of patients with type 1 diabetes is associated with induction of protein kinase R and downregulation of Mcl-1. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, N.G.; Richardson, S.J. Enteroviruses as causative agents in type 1 diabetes: Loose ends or lost cause? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. Tem 2014, 25, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiecki, M.; Colonna, M. The Multifaceted Biology of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouse, J.; Kalinke, U.; Oxenius, A. Regulation of antiviral T cell responses by type I interferons. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouse, J.; Bedenikovic, G.; Wiesel, M.; Ibberson, M.; Xenarios, I.; Laer, D.V.; Kalinke, U.; Vivier, E.; Jonjic, S.; Oxenius, A. Type I Interferons Protect T Cells Against NK Cell Attack Mediated by the Activating Receptor NCR1. Immunity 2014, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, C.; Peng, R.; Chernatynskaya, A.; Yuan, L.; Carter, C.; Valentine, J.; Sobel, E.; Atkinson, M.; Clare-Salzler, M. Increased IFN-α-producing Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells (pDCs) in Human Th1-mediated Type 1 Diabetes: pDCs Augment Th1 Responses Through IFN-α Production. J. Immunol. (Baltimore Md. 1950) 2014, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, J.; Simoni, Y.; Furio, L.; Beaudoin, L.; Agerberth, B.; Barrat, F.; Lehuen, A. Crosstalk between neutrophils, B-1a cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells initiates autoimmune diabetes. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, P.; Denis, C.; Soulas, C.; Bourbon-Caillet, C.; Lopez, J.; Arnoux, T.; Bléry, M.; Bonnafous, C.; Gauthier, L.; Morel, A.; et al. Anti-NKG2A mAb Is a Checkpoint Inhibitor That Promotes Anti-tumor Immunity by Unleashing Both T and NK Cells. Cell 2018, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ntali, G.; Kassi, E.; Alevizaki, M. Endocrine sequelae of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Horm. (Athens Greece) 2017, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekoua, M.P.; Dechaumes, A.; Sane, F.; Alidjinou, E.K.; Moutairou, K.; Yessoufou, A.; Hober, D. Enteroviral Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes: The Role of Natural Killer Cells. Microorganisms 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallionpää, H.; Somani, J.; Tuomela, S.; Ullah, U.; Albuquerque, R.d.; Lönnberg, T.; Komsi, E.; Siljander, H.; Honkanen, J.; Härkönen, T.; et al. Early Detection of Peripheral Blood Cell Signature in Children Developing β-Cell Autoimmunity at a Young Age. Diabetes 2019, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Son, M.; Jung, M.; Choi, S.; Cho, D.; Kim, T. IL-32γ Induces Chemotaxis of Activated T Cells via Dendritic Cell-Derived CCL5. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akhbari, P.; Richardson, S.J.; Morgan, N.G. Type 1 Diabetes: Interferons and the Aftermath of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Enteroviral Infection. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091419
Akhbari P, Richardson SJ, Morgan NG. Type 1 Diabetes: Interferons and the Aftermath of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Enteroviral Infection. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(9):1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091419
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkhbari, Pouria, Sarah J Richardson, and Noel G Morgan. 2020. "Type 1 Diabetes: Interferons and the Aftermath of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Enteroviral Infection" Microorganisms 8, no. 9: 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091419
APA StyleAkhbari, P., Richardson, S. J., & Morgan, N. G. (2020). Type 1 Diabetes: Interferons and the Aftermath of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Enteroviral Infection. Microorganisms, 8(9), 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091419