Black Layers of Decay and Color Patterns on Heritage Limestone as Markers of Environmental Change
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section


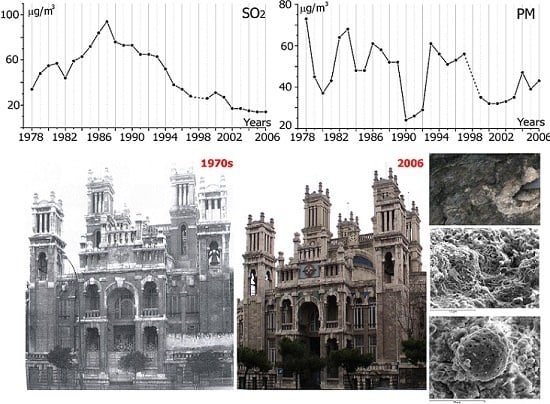
2.1. Environs and Climate

2.2. Layers of Black Decay

| Sample Type | N° | XL* | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black crust | BC1 | 45 | Façade: church (North) |
| BC2 | 46 | Wall: facing west | |
| Particulate matter | PM1 | - | Façade: NW main entrance |
| PM2 | - | Wall: facing north | |
| Layers of black decay (spherical particle analysis) | SP1 | 46 | Wall: facing north |
| SP2 | 57 | Wall: facing north | |
| SP3 | 57 | Wall: facing north | |
| SP4 | 46 | Wall: facing north | |
| SP5 | 55 | Façade: main entrance (South) | |
| SP6 | 57 | Façade: main entrance (South) | |
| SP7 | 57 | Façade: main entrance (South) | |
| SP8 | 55 | Façade: main entrance (South) | |
| SP9 | 63 | Façade: NW wing | |
| SP10 | 62 | Façade: NW wing | |
| SP11 | 64 | Façade: NW wing | |
| SP12 | 59 | Façade: NW wing |
2.3. Comparison of Color Patterns

3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterisation of Layers of Black Decay
3.1.1. Black Crust and Spherical Particles

| Location | (a) | (b) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Ø (μm) | Surface | Major Elements | Shape | Ø (μm) | Major Elements | |||
| Church | Metallic | 4,0 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 4,0 | Si, Al | ||
| 14,3 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 4,3 | Ca, Ti | ||||
| 21,9 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 4,6 | Ti | ||||
| 4,3 | Rough | Ca, Ti | Hemispherical (rather dense) | 4,6 | Ca, Fe | ||||
| 15,2 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 4,7 | Fe | ||||
| 24,2 | Smooth | C, Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 5,0 | C, Si | ||||
| 20,8 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 5,1 | Si | ||||
| 5,0 | Smooth | C, Si | Spherical (dense) | 5,6 | C | ||||
| 7,3 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 6,0 | Si, Al, Fe | ||||
| 13,7 | Smooth | C, Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 6,0 | Fe | ||||
| Main entrance | Metallic | 8,0 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 6,0 | Si, Al | ||
| 7,6 | Rough | Fe | Spherical (dense) | 6,4 | Si, Al | ||||
| 18,0 | Rough | Fe, Ca | Spherical (dense) | 6,9 | Si, Ca, Fe | ||||
| 4,6 | Rough | Ti | Hemispherical (rather dense) | 7,0 | Si, Al | ||||
| 4,6 | Rough | Ca, Fe | Spherical (dense) | 7,3 | Si, Al | ||||
| 18,0 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 7,4 | Fe | ||||
| 4,7 | Smooth | Fe | Spherical (dense) | 7,6 | Fe | ||||
| 19,0 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 7,6 | Ca, Si | ||||
| 7,4 | Smooth | Fe | Spherical (dense) | 7,9 | Fe | ||||
| 6,4 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 7,9 | Fe | ||||
| Carbonaceous | 13,2 | Smooth | C | Hemispherical (rather dense) | 8,0 | Si, Al | |||
| Metallic (A) | 7,0 | Rather rough | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 8,3 | C | |||
| Carbonaceous (B) | 5,6 | Rough | C | Hemispherical (porous) | 8,3 | Fe, Si, Mg | |||
| Metallic (A) | 10,2 | Rough | Ca, S | Spherical (dense) | 8,9 | Fe | |||
| Metallic (B) | 7,6 | Rather rough | Ca, Si | Spherical (dense) | 9,2 | Ca, Fe, S | |||
| Metallic (C) | 22,9 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 10,2 | Ca, S | |||
| Metallic (D) | 9,2 | Rather rough | Ca, Fe, S | Spherical (dense) | 10,4 | Fe | |||
| Metallic | 6,0 | Smooth | Si, Al, Fe | Spherical (dense) | 13,2 | C | |||
| Naves | NW (N) | Metallic | 6,0 | Rough | Fe | Spherical (dense) | 13,3 | Si, Al | |
| 10,4 | Rough | Fe | Spherical (dense) | 13,7 | C, Si, Al | ||||
| 6,9 | Rough | Si, Ca, Fe | Spherical (dense) | 14,3 | Si, Al | ||||
| NE (N) | Carbonaceous | 56,3 | Rough | C | Hemispherical (porous) | 15,0 | C | ||
| 24,6 | Rough | C | Hemispherical (porous) | 15,2 | Si, Al | ||||
| Metallic | 15,4 | Rough | Fe | Spherical (dense) | 15,4 | Fe | |||
| 6,00 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 18,0 | Fe, Ca | ||||
| NE (S) | Metallic | 8,9 | Rough | Fe | Spherical (dense) | 18,0 | Si, Al | ||
| 5,1 | Smooth | Si | Spherical (dense) | 19,0 | Si, Al | ||||
| 7,9 | Rough | Fe | Spherical (dense) | 20,8 | Si, Al | ||||
| SE (N) | Metallic | 7,9 | Rough | Fe | Spherical (dense) | 21,9 | Si, Al | ||
| 13,3 | Smooth | Si, Al | Spherical (dense) | 22,9 | Si, Al | ||||
| Carbonaceous | 8,3 | Smooth | C | Hemispherical (rather dense) | 24,2 | C, Si, Al | |||
| 15,0 | Smooth | C | Hemispherical (rather dense) | 24,6 | C | ||||
| Metallic | 8,3 | Rough | Fe, Si, Mg | Spherical (dense) | 56,3 | C | |||

3.1.2. Settled Dust

| - | Anion (mg/L) | Cation (mg/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorides | Nitrates | Sulfates | Sodium | Magnesium | Calcium | |
| PM1 (façade) | 20.5 | 73.7 | 1152 | 22.5 | - | 563 |
| PM2 (wall) | 55.9 | 107.9 | 940 | 27.5 | 11.4 | 442 |
3.2. Climate Change in the Environs and Its Effect on Color Patterns
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonazza, A.; Sabbioni, C.; Ghedini, N. Quantitative data on carbon fractions in interpretation of black crusts and soiling on European built heritage. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, C.M.; Brimblecombe, P. Past and future colouring patterns of historic stone buildings. Mater. Constr. 2008, 58, 143–160. [Google Scholar]
- Sablier, M.; Garrigues, P. Cultural heritage and its environment: An issue of interest for Environmental Science and Pollution Research. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5769–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cultrone, G.; Arizzi, A.; Sebastián, E.; Rodríguez-Navarro, C. Sulfation of calcitic and dolomitic lime mortars in the presence of diesel particulate matter. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylona, S.; Saltbones, J.; Semb, A.; Schaug, J. Trends in sulfur quality data in Europe. In Proceedings of the 1990 International Conference on Acidic Deposition: Its Nature and Impacts, Glasgow, UK, 16–21 September 1990.
- Searle, D.; Mitchell, D.; Halsey, D.; Dews, S.; Smith, J. The effects of coal and diesel particulates on the weathering loss of two major building stones in the United Kingdom: A comparative microcatchment study. In Proceedings of 9th International Congress on Deterioration and Conservation of Stone, Venice, Italy, 19–24 June 2000; pp. 391–400.
- Rodriguez-Navarro, C.; Sebastian, E. Role of particulate matter from vehicle exhaust on porous building stones (limestone) sulfation. Total Environ. 1996, 187, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fort, R.; Alvarez de Buergo, M.; López de Azcona, M.C.; Mingarro, F. The efficiency of urban remodelling in reducing the effects of atmospheric pollution on monuments. In Air Pollution and Cultural Heritage; Sáiz-Jiménez, C., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2004; pp. 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Ghedini, N.; Ozga, I.; Bonazza, A.; Dilillo, M.; Cachier, H.; Sabbioni, C. Atmospheric aerosol monitoring as a strategy for the preventive conservation of urban monumental heritage: The Florence Baptistery. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5979–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbota, H.; Young, C.; Strlič, M. Pollution monitoring at heritage sites in developing and emerging economies. Stud. Conserv. 2013, 58, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, C.M.; Brimblecombe, P. Effect of Long-Term Changes in Air Pollution and Climate on the Decay and Blackening of European Stone Buildings; Prikryl, R., Smith, B.J., Eds.; Geological Society, London, Special Publications: London, UK, 2007; Volume 271, pp. 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Fronteau, G.; Schneider-Thomachot, C.; Chopin, E.; Barbin, V.; Mouze, D.; Pascal, A. Black-Crust Growth and Interaction with Underlying Limestone Microfacies; Prikryl, R., Smith, B.J., Eds.; Geological Society, London, Special Publications: London, UK, 2010; Volume 333, pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Camuffo, D.; Del Monte, M.; Sabbioni, C. Origin and growth mechanisms of the sulfated crusts on urban limestone. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1983, 19, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornbush, M.; Viles, H. Integrated digital photography and image processing for the quantification of colouration on soiled limestone surfaces in Oxford, England. J. Cult. Herit. 2004, 5, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzi, L.; Giussani, B.; Rizzo, B.; Corti, C.; Pozzi, A.; Dossi, C. Monuments as sampling surfaces of recent traffic pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbioni, C.; Zappia, G.; Riontino, C.; Blanco-Varela, M.T.; Aguilera, J.; Puertas, F.; van Belen, K.; Toumbakari, E.E. Atmosferic deterioration of ancient and modern hydraulic mortars. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakok, T.; Chang, S.G.; Harker, A.B. Sulfates as pollution particulates: Catalytic formation on carbon (soot) particles. Science 1974, 186, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfiore, C.M.; Barca, D.; Bonazza, A.; Comite, V.; La Russa, M.F.; Pezzino, A.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Sabbioni, C. Application of spectrometric analysis to the identification of pollution sources causing cultural heritage damage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8848–8859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Russa, M.F.; Belfiore, C.M.; Comite, V.; Barca, D.; Bonazza, A.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Crisci, G.M.; Pezzino, A. Geochemical study of black crusts as a diagnostic tool in cultural heritage. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 113, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barca, D.; Comite, V.; Belfiore, C.M.; Bonazza, A.; La Russa, M.F.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Crisci, G.M.; Pezzino, A.; Sabbioni, C. Impact of air pollution in deterioration of carbonate building materials in Italian urban environments. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 48, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghedini, N.; Sabbioni, C.; Bonazza, A.; Gobbi, G.; Zappia, G. A quantitative methodology for carbon speciation in black crusts on monuments. In Air Pollution and Cultural Heritage; Sáiz-Jiménez, C., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2004; pp. 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, C.I.; Tang, W.; Finger, S.; Etyemezian, V.; Striegel, M.F.; Sherwood, S.I. Soiling patterns on a tall limestone building: Changes over 60 years. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toniolo, L.; Zerbi, C.M.; Bugini, R. Black layers on historical architecture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanting, R.W. Black smoke and soiling. In Aerosols; Lewis Publishers: Chelsea, MI, USA, 1986; pp. 923–932. [Google Scholar]
- Cachier, H.; Sarda-Estève, R.; Oikonomou, K.; Sciare, J.; Bonazza, A.; Sabbioni, C.; Reyes, J. Aerosolcharacterization and sources in different European urban atmospheres: Paris, Seville, Florence and Milan. In Air Pollution and Cultural Heritage; Sáiz-Jiménez, C., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2004; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield, T.; Hamilton, R.; Ellis, B.; Newby, P. Diesel particulates emissions and the implications for the soiling of buildings. Environmentalist 1991, 11, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, D.E.; Mitchell, D.J. The effect of coal and diesel particulates on the weathering loss of Portland Limestone in an urban environment. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, C.M.; Brimblecombe, P.; Esbert, R.M.; Alonso, F.J. Color changes in architectural limestones from pollution and cleaning. COLOR Res. Appl. 2007, 32, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L. Practical Petrographic classification of Limestones. Bull. Am. Assoc. Pet. 1959, 43, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Monserrat, E.M.; Varas, M.J.; Fort, R.; Álvarez de Buergo, M.A. Assessment of different methods for cleaning the limestone facades of the former workers Hospital of Madrid, Spain. Stud. Conserv. 2011, 56, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fort, R.; Álvarez de Buergo, M.; Pérez-Monserrat, E.M.; Gomez-Heras, M.; Varas, M.J.; Freire, D.M. Evolution in the use of natural building stone in Madrid, Spain. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2013, 46, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artíñano, B.; Pujadas, M.; Plaza, J.; Crespí, S.N.; Cabal, H.; Aceña, B.; Terés, J. Air pollution episodes inthe Madrid airshed. In Transport and Transformation of Pollutants in the Troposphere; Borrel, P.M., Borrell, P., Cvitas, T., Seiler, W., Eds.; SPB Academic Publishing: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1994; pp. 294–297. [Google Scholar]
- Artıñ́ano, B.; Salvador, P.; Alonso, D.G.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A. Anthropogenic and natural influence on the PM10 and PM2.5 aerosol in Madrid (Spain). Analysis of high concentration episodes. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 125, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzón, A.; Moragues, A.; Acha, C. Seasonal analysis of air pollution levels in Madrid. Total Environ. 1999, 235, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzón, A.; Guerrero, M.J. Valuation of social and health effects of transport-related air pollution in Madrid (Spain). Total Environ. 2004, 334, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querol, X.; Mantilla, E.; Ruiz, C.R.; Lopez-Soler, A.; Juan, R. Seasonal evolution of suspended particles around a large coal-fired power station: Chemical characterization. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, P.; Artıñ́ano, B.; Alonso, D.G.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A. Identification and characterisation of sources of PM10 in Madrid (Spain) by statistical methods. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid Salud. Available online: http://www.madridsalud.es (accessed on 4 November 2015).
- Inicio—Ayuntamiento de Madrid. Available online: http://www.munimadrid.es (accessed on 4 November 2015).
- Royal Decree 2482/1986: Especificaciones de gasolinas, gasóleos y fuelóleos en concordancia con las de la CEE (BOE 291, 05-12-86). Available online: https://www.boe.es/boe/dias/1986/12/05/pdfs/A40110-40113.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2015). (In Spanish)
- Brimblecombe, P.; Grossi, C.M.; Harris, I. Climate change critical to cultural heritage. In Survival and Sustainability; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J. Global Climate Change: Every Cultural Site at Risk? Available online: http://www.icomos.org/risk/world_report/2006-2007/pdf/H@R_2006-2007_50_Special_Focus_GCC_Every_Site_Risk.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2015).
- Friedman, G.M. Identification of carbonate minerals by staining methods. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1959, 29, 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Pache, F.; Alonso, F.J.; Esbert, R.M. La microscopía electrónica de barrido aplicada al estudio de partículas sólidas de contaminación depositadas sobre la piedra monumental. Ing. Civ. 1996, 101, 26–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bonazza, A.; Sabbioni, C.; Ghedini, N.; Favoni, O.; Zappia, G. Carbon data in black crusts on European monuments. In Air Pollution and Cultural Heritage; Sáiz-Jiménez, C., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2004; pp. 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage (CIE). Colorimetry: Recommendations on Uniform Color Spaces, Color Difference Equations and Psychometric Color Terms. CIE: Vienna, Austria, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Olaru, M.; Aflori, M.; Simionescu, B.; Doroftei, F.; Stratulat, L. Effect of SO2 dry deposition on porous dolomitic limestones. Materials 2010, 3, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleugels, G.; Dewolfs, R.; Van Grieken, R. On the memory effect of limestone for air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 1993, 27, 1931–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, K.; Schiavon, N. Cause of sulfate attack on concrete, render and stone indicated by sulfur isotope ratios. Nature 1989, 342, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbioni, C. Characterization of atmospheric particles on monuments by scanning electron mocroscopy/energy dispersive X-ray analyses. Electron Microsc. 1992, 2, 773–777. [Google Scholar]
- Labrada-Delgado, G.; Aragon-Pina, A.; Campos-Ramos, A.; Castro-Romero, T.; Amador-Munoz, O.; Villalobos-Pietrini, R. Chemical and morphological characterization of PM 2.5 collected during MILAGRO campaign using scanning electron microscopy. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2012, 3, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, M. Les Aerosoles Antropogenes et L’Alteration de la Pierre; École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Laboratoire de Conservation de La Pierre: Lausanne, Switzerland, 1990. (in French) [Google Scholar]
- Brimblecombe, P; Grossi, C.M. Aesthetic thresholds and blackening of stone buildings. Total Environ. 2005, 349, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittelson, D.B. Engine and nanoparticles: A review. J. Aerosols Sci. 1998, 29, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, C.M.; Esbert, R.M.; Díaz-Pache, F. Degradación y durabilidad de materiales rocosos de edificación en ambientes urbanos. Mater. Constr. 1998, 48, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbioni, C.; Zappia, G. Characterization of particles emitted by domestic heating units fueled by distilled oil. Atmos. Environ. A Gen. Top. 1993, 27, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, E.M. Stone in Architecture: Properties, Durability in Man’s Environment; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Esbert, R.M.; Díaz-Pache, F.; Grossi, C.M.; Alonso, F.J.; Ordaz, J. Airborne particulate matter around the Cathedral of Burgos (Castilla y León, Spain). Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Covert, D.S.; Larson, T.V.; Waggoner, A.P. Chemical properties of tropospheric sulfur aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 1978, 12, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzman, B.; Kendall, M.; Watt, J.; Williams, I. Characterisation of airborne particles in London by computer-controlled scanning electron microscopy. Total Environ. 1999, 241, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Heras, M.; Benavente, D.; Fort, R.; Alvarez de Buergo, M. A note on soluble salt minerals from pigeon droppings as potential contributors to the decay of stone base cultural heritage. Eur. J. Mineral. 2004, 16, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cámara, B.; de Buergo, M.A.; Fort, R.; Ascaso, C.; Gomez-Heras, M.; de los Rios, A. Another Source of Soluble Salts in Urban Environments due to Recent Social Behaviour Patter in Historical Centres; Rogerio-Candelera, M.A., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2014; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Cámara, B.; Alvarez de Buergo, M.; Fort, R. Crystallization processes derived from the interaction of urine and dolostone. In Proceedings of the 2015 EGU General Assembly, Wien, Austria, 12–17 April 2015.
- Smith, B.J.; McCabe, S.; McAllister, D.; Adamson, C.; Viles, H.A.; Curran, J.M. A commentary on climate change, stone decay dynamics and the “greening” of natural stone buildings: New perspectives on “deep wetting”. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, M.; Rovelli, G.; D’Angelo, L.; Perrone, M.G.; Sangiorgi, G.; Bolzacchini, E.; Ferrero, L. Experimental Measurements of Particulate Matter Deliquescence and Crystallization Relative Humidity: Application in Heritage Climatology. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perez-Monserrat, E.M.; Varas-Muriel, M.J.; Alvarez De Buergo, M.; Fort, R. Black Layers of Decay and Color Patterns on Heritage Limestone as Markers of Environmental Change. Geosciences 2016, 6, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences6010004
Perez-Monserrat EM, Varas-Muriel MJ, Alvarez De Buergo M, Fort R. Black Layers of Decay and Color Patterns on Heritage Limestone as Markers of Environmental Change. Geosciences. 2016; 6(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences6010004
Chicago/Turabian StylePerez-Monserrat, Elena Mercedes, Maria Jose Varas-Muriel, Monica Alvarez De Buergo, and Rafael Fort. 2016. "Black Layers of Decay and Color Patterns on Heritage Limestone as Markers of Environmental Change" Geosciences 6, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences6010004
APA StylePerez-Monserrat, E. M., Varas-Muriel, M. J., Alvarez De Buergo, M., & Fort, R. (2016). Black Layers of Decay and Color Patterns on Heritage Limestone as Markers of Environmental Change. Geosciences, 6(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences6010004