Combined Use of C- and X-Band SAR Data for Subsidence Monitoring in an Urban Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological and Hydrogeological Setting
3. Available Data
3.1. Interferometric Data
3.2. Stratigraphical Information and Borehole Classification System
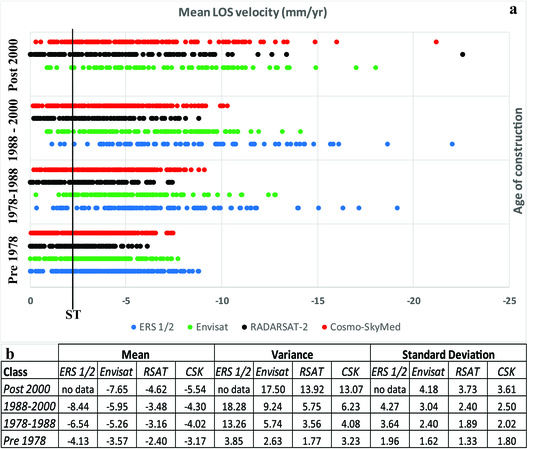
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Regional Scale Analysis
4.2. Local and Building Scale Analysis
4.2.1. Movement Detection of Recently Built Buildings
4.2.2. Buildings with Trend Changes
4.2.3. Relation between InSAR Displacements and Urbanization
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, S.; Samsonov, S.; Yin, H.; Ye, S.; Cao, Y. Time-series analysis of subsidence associated with rapid urbanization in Shanghai, China measured with SBAS InSAR method. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, M.; Bozzano, F.; Strappaveccia, C.; Baiocchi, V.; Prestininzi, A. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of the influence of anthropic pressure on subsidence in a sedimentary basin near Rome. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4223–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcari, M.; Albano, M.; Saroli, M.; Tolomei, C.; Lancia, M.; Moro, M.; Stramondo, S. Subsidence Detected by Multi-Pass Differential SAR Interferometry in the Cassino Plain (Central Italy): Joint Effect of Geological and Anthropogenic Factors? Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9676–9690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Lei, K.; Ke, Y.; Duan, G.; Zhou, C. Spatial correlation between land subsidence and urbanization in Beijing, China. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 2637–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yu, D.; Yin, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, S. Modelling the anthropogenic impacts on fluvial flood risks in a coastal mega-city: A scenario-based case study in Shanghai, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 136, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, L.; Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Moretti, S. PSInSAR analysis in the Pisa Urban Area (Italy): A case study of subsidence related to stratigraphical factors and urbanization. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, K.E.; Belliss, S.E.; Samsonov, S.V.; McNeill, S.J.; Glassey, P.J. A review of the status of satellite remote sensing and image processing techniques for mapping natural hazards and disasters. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansosti, E.; Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Lanari, R. Space-borne radar interferometry techniques for the generation of deformation time series: An advanced tool for Earth’s surface displacement analysis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, O.I.; Saeidi, V.; Pradhan, B.; Yusuf, Y.A. Advanced differential interferometry synthetic aperture radar techniques for deformation monitoring: A review on sensors and recent research development. Geocarto Int. 2014, 29, 536–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent scatterer interferometry: A review. ISPRS J Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Cigna, F.; Moretti, S. Multi-temporal mapping of land subsidence at basin scale exploiting Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: Case study of Gioia Tauro plain (Italy). J. Maps 2012, 8, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, L.; Teatini, P.; Strozzi, T. Natural versus anthropogenic subsidence of Venice. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Ventisette, C.; Solari, L.; Raspini, F.; Ciampalini, A.; Di Traglia, F.; Moscatelli, M.; Pagliaroli, A.; Moretti, S. Use of PSInSAR data to map highly compressible soil layers. Geol. Acta 2015, 13, 309–323. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini, S.; Moretti, S. Analysis of recent ground subsidence in the Sibari plain (Italy) by means of satellite SAR interferometry-based methods. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 4550–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scifoni, S.; Bonano, M.; Marsella, M.; Sonnessa, A.; Tagliafierro, V.; Manunta, M.; Lanari, R.; Ojha, C.; Sciotti, M. On the joint exploitation of long-term DInSAR time series and geological information for the investigation of ground settlements in the town of Roma (Italy). Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 182, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peduto, D.; Cascini, L.; Arena, L.; Ferlisi, S.; Fornaro, G.; Reale, D. A general framework and related procedures for multiscale analyses of DInSAR data in subsiding urban areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 186–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, T. Time-series InSAR applications over urban areas in China. IEEE J-STARS 2011, 4, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J. Land subsidence and ground fissures in Xi’an, China 2005–2012 revealed by multi-band InSAR time-series analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Bonano, M.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, T.; Wang, H. The Use of C-/X-Band Time-Gapped SAR Data and Geotechnical Models for the Study of Shanghai’s Ocean-Reclaimed Lands through the SBAS-DInSAR Technique. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, R.; Márquez, Y.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Delgado, J.; Blanco, P.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Martínez, M.; Herrera, G.; Mulas, J. Mapping ground subsidence induced by aquifer overexploitation using advanced Differential SAR Interferometry: Vega Media of the Segura River (SE Spain) case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Tomás, R.; Monells, D.; Centolanza, G.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Vicente, F.; Navarro, V.D.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Sanabria, M.; Cano, M.; et al. Analysis of subsidence using TerraSAR-X data: Murcia case study. Eng. Geol. 2010, 116, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, R.; Romero, R.; Mulas, J.; Marturià, J.J.; Mallorquí, J.J.; López-Sánchez, J.M.; Herrera, G.; Gutiérrez, F.; González, P.J.; Fernández, J.; et al. Radar interferometry techniques for the study of ground subsidence phenomena: A review of practical issues through cases in Spain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notti, D.; Mateos, R.M.; Monserrat, O.; Devanthéry, N.; Peinado, T.; Roldán, F.J.; Fernández-Chacón, F.; Galve, J.P.; Lamas, F.; Azañón, J.M. Lithological control of land subsidence induced by groundwater withdrawal in new urban areas (Granada Basin, SE Spain). Multiband DInSAR monitoring. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 2317–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Loupasakis, C.; Rozos, D.; Moretti, S. Advanced interpretation of land subsidence by validating multi-interferometric SAR data: The case study of the Anthemountas basin (Northern Greece). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. 2013, 13, 2425–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Loupasakis, C.; Rozos, D.; Adam, N.; Moretti, S. Ground subsidence phenomena in the Delta municipality region (Northern Greece): Geotechnical modeling and validation with Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 28, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikos, S.; Ioannis, P.; Constantinos, L.; Paraskevas, T.; Anastasia, K.; Charalambos, K. Land subsidence rebound detected via multi-temporal InSAR and ground truth data in Kalochori and Sindos regions, Northern Greece. Eng. Geol. 2016, 209, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, T.H.; Amelung, F.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Rocca, F.; Dokka, R.; Sella, G.; Kim, S.W.; Wdowinski, S.; Withman, D. Space geodesy: Subsidence and flooding in New Orleans. Nature 2006, 441, 587–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelung, F.; Galloway, D.L.; Bell, J.W.; Zebker, H.A.; Laczniak, R.J. Sensing the ups and downs of Las Vegas: InSAR reveals structural control of land subsidence and aquifer-system deformation. Geology 1999, 27, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, S.V.; Tiampo, K.F.; Feng, W. Fast subsidence in downtown of Seattle observed with satellite radar. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2016, 4, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.K.; Doubre, C.; Weber, C.; Gourmelen, N.; Masson, F. Recent land subsidence caused by the rapid urban development in the Hanoi region (Vietnam) using ALOS InSAR data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.S.; Chang, C.P.; Nguyen, X.T.; Yhokha, A. TerraSAR-X Data for High-Precision Land Subsidence Monitoring: A Case Study in the Historical Centre of Hanoi, Vietnam. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Gumilar, I.; Andreas, H.; Murdohardono, D.; Fukuda, Y. On causes and impacts of land subsidence in Bandung Basin, Indonesia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Amelung, F.; Abidin, H.; Hong, S.H. Sinking cities in Indonesia: ALOS PALSAR detects rapid subsidence due to groundwater and gas extraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heleno, S.I.; Oliveira, L.G.; Henriques, M.J.; Falcão, A.P.; Lima, J.N.; Cooksley, G.; Ferretti, A.; Fonseca, A.M.; Lobo-Ferreira, J.P.; Fonseca, J.F. Persistent scatterers interferometry detects and measures ground subsidence in Lisbon. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2152–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalão, J.; Nico, G.; Lollino, P.; Conde, V.; Lorusso, G.; Silva, C. Integration of InSAR Analysis and Numerical Modeling for the Assessment of Ground Subsidence in the City of Lisbon, Portugal. IEEE J-STARS 2016, 9, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascucci, V. Neogene evolution of the Viareggio basin, Northern Tuscany (Italy). GeoActa 2005, 4, 123–138. [Google Scholar]
- Amorosi, A.; Rossi, V.; Sarti, G.; Mattei, R. Coalescent valley fills from the late Quaternary record of Tuscany (Italy). Quat. Int. 2013, 288, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguzzi, M.; Amorosi, A.; Colalongo, M.L.; Ricci Lucchi, M.; Rossi, V.; Sarti, G.; Vaiani, S.C. Late Quaternary climatic evolution of the Arno coastal plain (Western Tuscany, Italy) from subsurface data. Sediment. Geol. 2007, 202, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorosi, A.; Sarti, G.; Rossi, V.; Fontana, V. Anatomy and sequence stratigraphy of the late Quaternary Arno valley fill (Tuscany, Italy). Adv. Appl. Seq. Stratigr. Italy 2008, 1, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Amorosi, A.; Ricci Lucchi, M.; Rossi, V.; Sarti, G. Climate change signature of small-scale parasequences from Lateglacial–Holocene transgressive deposits of the Arno valley fill. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2009, 273, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeck, K.; Antonioli, F.; Anzidei, M.; Ferranti, L.; Leoni, G.; Scicchitano, G.; Silenzi, S. Sea level change along the Italian coast during the Holocene and projections for the future. Quat. Int. 2011, 232, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, V.; Amorosi, A.; Sarti, G.; Potenza, M. Influence of inherited topography on the Holocene sedimentary evolution of coastal systems: An example from Arno coastal plain (Tuscany, Italy). Geomorphology 2011, 135, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarti, G.; Rossi, V.; Amorosi, A. Influence of Holocene stratigraphic architecture on ground surface settlements: A case study from the City of Pisa (Tuscany, Italy). Sediment. Geol. 2012, 281, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burland, J.; Jamiolkowski, M.B.; Viggiani, C. Leaning Tower of Pisa: Behaviour after stabilization operations. Int. J. Geoeng. Case Hist. 2009, 1, 156–169. [Google Scholar]
- Relazione Generale e Allegati Tecnici del Piano Strutturale del Comune di Pisa; Comune di Pisa: Pisa, Italy, 1997; Available online: http://www.comune.pisa.it/doc/sit-pisa/nuovo_prg/relaz.htm (accessed on 27 October 2016).
- Grassi, S.; Cortecci, G. Hydrogeology and geochemistry of the multilayered confined aquifer of the Pisa plain (Tuscany–central Italy). Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butteri, M.; Doveri, M.; Giannecchini, R.; Gattai, P. Hydrogeologic-hydrogeochemical multidisciplinary study of the confined gravelly aquifer in the coastal Pisan Plain between the Arno River and Scolmatore Canal (Tuscany). Mem. Descr. Carta Geol. d’It. 2010, XC, 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A small-baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, F.; Elefante, S.; Imperatore, P.; Zinno, I.; Manunta, M.; De Luca, C.; Lanari, R. SBAS-DInSAR Parallel Processing for Deformation Time-Series Computation. IEEE J-STARS 2014, 7, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonano, M.; Manunta, M.; Pepe, A.; Paglia, L.; Lanari, R. From previous C-band to new X-band SAR systems: Assessment of the DInSAR mapping improvement for deformation time-series retrieval in urban areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1973–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manunta, M.; Marsella, M.; Zeni, G.; Sciotti, M.; Atzori, S.; Lanari, R. Two-scale surface deformation analysis using the SBAS-DInSAR technique: A case study of the city of Rome, Italy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1665–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arangio, S.; Calò, F.; Di Mauro, M.; Bonano, M.; Marsella, M.; Manunta, M. An application of the SBAS-DInSAR technique for the assessment of structural damage in the city of Rome. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2013, 10, 1469–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Lanari, R. On the extension of the minimum cost flow algorithm for phase unwrapping of multitemporal differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, F.; Ardizzone, F.; Castaldo, R.; Lollino, P.; Tizzani, P.; Guzzetti, F.; Lanari, R.; Angeli, M.; Pontoni, F.; Manunta, M. Enhanced landslide investigations through advanced DInSAR techniques: The Ivancich case study, Assisi, Italy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 142, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovenga, F.; Wasowski, J.; Nitti, D.O.; Nutricato, R.; Chiaradia, M.T. Using COSMO/SkyMed X-band and ENVISAT C-band SAR interferometry for landslides analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Frodella, W.; Bardi, F.; Bianchini, S.; Moretti, S. The effectiveness of high-resolution LiDAR data combined with PSInSAR data in landslide study. Landslides 2016, 13, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschetti, G.; Lanari, R. Synthetic Aperture Radar Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Solari, L.; Ciampalini, A.; Bianchini, S.; Moretti, S. PSInSAR analysis in urban areas: A case study in the Arno coastal plain (Italy). Rend. Online Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 2016, 41, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuti, P.; Casagli, N.; Farina, P.; Marks, F.; Ferretti, A.; Menduni, G. Land subsidence in the Arno River Basin studied through SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Land Subsidence, Shanghai, China, 23–28 October 2005; Volume 1, pp. 407–416. [Google Scholar]
- Rosi, A.; Tofani, V.; Agostini, A.; Tanteri, L.; Stefanelli, C.T.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Subsidence mapping at regional scale using persistent scatters interferometry (PSI): The case of Tuscany region (Italy). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K.; Peck, R.B. Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Peduto, D.; Nicodemo, G.; Maccabiani, J.; Ferlisi, S. Multi-scale analysis of settlement-induced building damage using damage surveys and DInSAR data: A case study in The Netherlands. Eng. Geol. 2017, 218, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, S.; Pratesi, F.; Nolesini, T.; Casagli, N. Building deformation assessment by means of persistent scatterer interferometry analysis on a landslide-affected area: The Volterra (Italy) case study. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4678–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratesi, F.; Tapete, D.; Terenzi, G.; Del Ventisette, C.; Moretti, S. Rating health and stability of engineering structures via classification indexes of InSAR Persistent Scatterers. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 40, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratesi, F.; Tapete, D.; Del Ventisette, C.; Moretti, S. Mapping interactions between geology, subsurface resource exploitation and urban development in transforming cities using InSAR Persistent Scatterers: Two decades of change in Florence, Italy. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 77, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solari, L.; Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Zinno, I.; Bonano, M.; Manunta, M.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Combined Use of C- and X-Band SAR Data for Subsidence Monitoring in an Urban Area. Geosciences 2017, 7, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7020021
Solari L, Ciampalini A, Raspini F, Bianchini S, Zinno I, Bonano M, Manunta M, Moretti S, Casagli N. Combined Use of C- and X-Band SAR Data for Subsidence Monitoring in an Urban Area. Geosciences. 2017; 7(2):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolari, Lorenzo, Andrea Ciampalini, Federico Raspini, Silvia Bianchini, Ivana Zinno, Manuela Bonano, Michele Manunta, Sandro Moretti, and Nicola Casagli. 2017. "Combined Use of C- and X-Band SAR Data for Subsidence Monitoring in an Urban Area" Geosciences 7, no. 2: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7020021
APA StyleSolari, L., Ciampalini, A., Raspini, F., Bianchini, S., Zinno, I., Bonano, M., Manunta, M., Moretti, S., & Casagli, N. (2017). Combined Use of C- and X-Band SAR Data for Subsidence Monitoring in an Urban Area. Geosciences, 7(2), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7020021