Effects of Solids Accumulation on Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Substrate, Plant Growth and Performance of a Mediterranean Horizontal Flow Treatment Wetland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Design
2.2. Weather Data
2.3. Water Quality
2.4. Accumulated Material Characterization and Vegetation Study
2.5. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Weather Data
3.2. Water Quality
3.3. Accumulated Material Characterization
3.4. Phragmites australis Growth
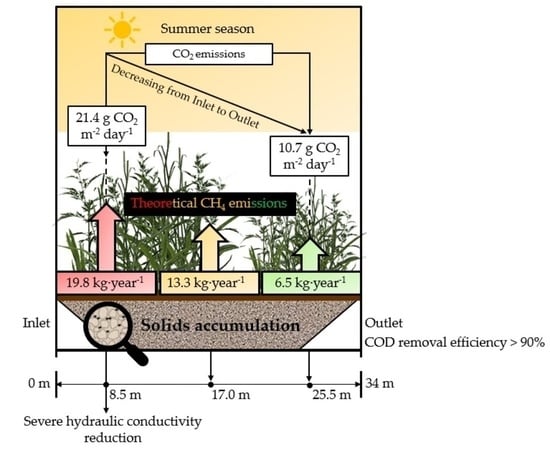
3.5. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vymazal, J. The use constructed wetlands with horizontal sub-surface flow for various types of wastewaters. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. The use of hybrid constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment with special attention to nitrogen removal: A review of a recent development. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4795–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbera, A.C.; Borin, M.; Ioppolo, A.; Cirelli, G.L.; Maucieri, C. Carbon dioxide emissions from horizontal sub-surface constructed wetlands in the Mediterranean Basin. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 64, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maucieri, C.; Barbera, A.C.; Vymazal, J.; Borin, M. A review on the main affecting factors of greenhouse gases emission in constructed wetlands. Agr. For. Meteorol. 2017, 236, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, D.; Ferrante, M.; Copat, C.; Grasso, A.; Milani, M.; Sacco, A.; Licciardello, F.; Cirelli, G.L. Metal removal processes in a pilot hybrid constructed wetland for the treatment of semi-synthetic stormwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, A.; Cirelli, G.L.; Ventura, D.; Barbagallo, S.; Licciardello, F. Hydraulic performance of horizontal constructed wetlands for stormwater treatment: A pilot-scale study in the Mediterranean. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 169, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mander Ülo Dotro, G.; Ebie, Y.; Towprayoon, S.; Chiemchaisri, C.; Nogueira, S.F.; Jamsranjav, B.; Kasak, K.; Truu, J.; Tournebize, J.; Mitsch, W.J. Greenhouse gas emission in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 66, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liikanen, A.; Huttunen, J.T.; Karjalainen, S.M.; Heikkinen, K.; Väisänen, T.S.; Nykänen, H.; Martikainen, P.J. Temporal and seasonal changes in greenhouse gas emissions from a constructed wetland purifying peat mining runoff waters. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 26, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altor, A.E.; Mitsch, W.J. Pulsing hydrology, methane emissions and carbon dioxide fluxes in created marshes: A 2-year ecosystem study. Wetlands 2008, 28, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemanová, K.; Picek, T.; Dušek, J.; Edwards, K.; Šantrůčková, H. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus tranformations are related to age of a constructed wetland. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 207, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzakpasu, M.; Scholz, M.; Harrington, R.; Jordan, S.N.; McCarthy, V. Characterising infiltration and contaminant migration beneath earthen-lined integrated constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 41, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzakpasu, M.; Scholz, M.; Harrington, R.; McCarthy, V.; Jordan, S. Groundwater quality impacts from a full-scale integrated constructed wetland. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2014, 34, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, F.A.; Lee, K.E.; Goh, C.T.; Mokhtar, M.; Latif, M.T.; Goh, T.L.; Simon, N. The use of constructed wetlands in sequestrating carbon: An overview. Nat. Environ. Pol. Tech. 2017, 16, 813–819. [Google Scholar]
- Vymazal, J. Removal of BOD5 in constructed wetlands with horizontal sub-surface flow: Czech experience. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Does clogging affect long-term removal of organics and suspended solids in gravel-based horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands? Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardello, F.; Sacco, A.; Barbagallo, S.; Ventura, D.; Cirelli, G.L. Evaluation of different methods to assess the hydraulic behavior in horizontal treatment wetlands. Water 2020, 12, 2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, M.; Marzo, A.; Toscano, A.; Consoli, S.; Cirelli, G.L.; Ventura, D.; Barbagallo, S. Evapotranspiration from horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands planted with different perennial plant species. Water 2019, 11, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Rice, E.W. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, R.; Bagarello, V.; Barbagallo, S.; Iovino, M.; Marzo, A.; Toscano, A. Evaluation of clogging in full-scale subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 95, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA-AWWA-WEF. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Hammerle, A.; Zeeman, M.; Wohlfahrt, G. On the calculation of daytime CO2 fluxes measured by automated closed transparent chambers. Agr. For. Meteorol. 2018, 263, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbera, A.C.; Borin, M.; Cirelli, G.L.; Toscano, A.; Maucieri, C. Comparison of carbon balance in Mediterranean pilot constructed wetlands vegetated with different C4 plant species. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 2372–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories. In The National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme; Eggleston, H.S., Buendia, L., Miwa, K., Ngara, T., Tanabe, K., Eds.; The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Hayama, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes, M.G.; Güereca, L.P.; Molina, L.T.; Noyola, A. Methane emissions from stabilization ponds for municipal wastewater treatment in Mexico. J. Int. Environ. Sci. 2015, 12, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IPCC 2013. Supplement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories: Wetlands; Hiraishi, T., Krug, T., Tanabe, K., Srivastava, N., Baasansuren, J., Fukuda, M., Troxler, T.G., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Ye, C.; Chen, X.; Xie, B.; Huang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, M. Effects of plant species on soil microbial processes and CH4 emission from constructed wetlands. Environ. Pol. 2013, 174, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; An, P.; Krishnakumar, B.; Zhao, L.; Sun, L.; Mizuochi, M.; Inamori, Y. Effect of plant harvest on methane emission from two constructed wetlands designed for the treatment of wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picek, T.; Čížková, H.; Dušek, J. Greenhouse gas emissions from a constructed wetland-Plants as important sources of carbon. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 31, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ström, L.; Lamppa, A.; Christensen, T.R. Greenhouse gas emissions from a constructed wetland in southern Sweden. Wet. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 15, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verville, J.H.; Hobbie, S.E.; Chapin, F.S.; Hooper, D.U. Response of tundra CH4 and CO2 flux to manipulation of temperature and vegetation. Biogeochemistry 1998, 41, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, S.; Huang, Z.; Cui, L.; Wang, X. Evaluation of organic matter removal efficiency and microbial enzyme activity in vertical-flow constructed wetland systems. Environments 2016, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzo, A.; Ventura, D.; Cirelli, G.L.; Aiello, R.; Vanella, D.; Rapisarda, R.; Barbagallo, S.; Consoli, S. Hydraulic reliability of a horizontal wetland for wastewater treatment in Sicily. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedescoll, A.; Uggetti, E.; Llorens, E.; Granés, F.; García, D.; García, J. Practical method based on saturated hydraulic conductivity used to assess clogging in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, C.C.; Adams, D.D.; Downes, M.T. Methane Emissions from Constructed Wetlands Treating Agricultural Wastewaters. J. Environ. Qual. 1997, 26, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.E.; Gustavsson, A.M.; Öquist, M.G.; Svensson, B.H. Methane emissions from a constructed wetland treating wastewater—Seasonal and spatial distribution and dependence on edaphic factors. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3960–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søvik, A.K.; Augustin, J.; Heikkinen, K.; Huttunen, J.T.; Necki, J.M.; Karjalainen, S.M.; Kløve, B.; Liikanen, A.; Mander, Ü.; Puustinen, M.; et al. Emission of the Greenhouse Gases Nitrous Oxide and Methane from Constructed Wetlands in Europe. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 35, 2360–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais-Landry, G.; Maranger, R.; Brisson, J.; Chazarenc, F. Greenhouse gas production and efficiency of planted and artificially aerated constructed wetlands. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Capel, V.; Castro, A.; Ruiz, I.; Soto, M. Anaerobic biodegradation tests and gas emissions from subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3044–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maucieri, C.; Borin, M.; Milani, M.; Cirelli, G.L.; Barbera, A.C. Plant species effect on CO2 and CH4 emissions from pilot constructed wetlands in Mediterranean area. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 134, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselles-Osorio, A.; Puigagut, J.; Segú, E.; Vaello, N.; Granés, F.; García, D.; García, J. Solids accumulation in six full-scale subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Water Quality Parameter | HF In (mg·L−1) (±SD, n = 12) | HF Out (mg·L−1) (±SD, n = 12) | Removal Efficiency (%) (±SD, n = 12) |
|---|---|---|---|
| COD | 164.4 (±17.1) | 38.4 (±13.1) | 76.6 (±7.3) |
| BOD5 | 129.11 (±28.5) | 8.2 (±4.3) | 93.6 (±1.8) |
| TSS | 62.2 (±39.4) | 4 (±5.8) | 99 (±0.8) |
| N-NH4 | 12.8 (±10.6) | 0.1 (±0.1) | 99 (±0.4) |
| Total N | 76 (±28.5) | 26.9 (25.8) | 74.3 (±30) |
| Total P | 16.6 (±9.1) | 10.2 (±11.1) | 54 (±15) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sacco, A.; Sciuto, L.; Licciardello, F.; Cirelli, G.L.; Milani, M.; Barbera, A.C. Effects of Solids Accumulation on Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Substrate, Plant Growth and Performance of a Mediterranean Horizontal Flow Treatment Wetland. Environments 2023, 10, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10020030
Sacco A, Sciuto L, Licciardello F, Cirelli GL, Milani M, Barbera AC. Effects of Solids Accumulation on Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Substrate, Plant Growth and Performance of a Mediterranean Horizontal Flow Treatment Wetland. Environments. 2023; 10(2):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10020030
Chicago/Turabian StyleSacco, Alessandro, Liviana Sciuto, Feliciana Licciardello, Giuseppe L. Cirelli, Mirco Milani, and Antonio C. Barbera. 2023. "Effects of Solids Accumulation on Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Substrate, Plant Growth and Performance of a Mediterranean Horizontal Flow Treatment Wetland" Environments 10, no. 2: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10020030
APA StyleSacco, A., Sciuto, L., Licciardello, F., Cirelli, G. L., Milani, M., & Barbera, A. C. (2023). Effects of Solids Accumulation on Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Substrate, Plant Growth and Performance of a Mediterranean Horizontal Flow Treatment Wetland. Environments, 10(2), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10020030