The Impact of Aluminium Salt Dosing for Chemical Phosphorus Removal on the Settleability of Activated Sludge
Abstract
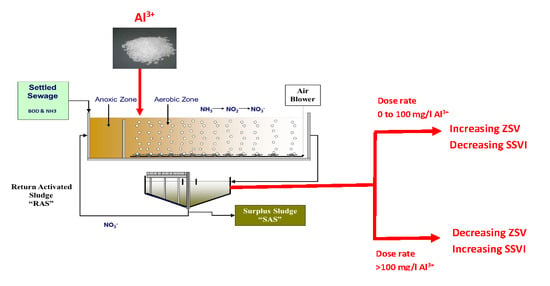
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Jar Tests Protocol
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscope
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Aluminium Dosing on Activated Sludge Morphology
3.2. Effects of Aluminium Dosing on ZSV and SSVI
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ojo, P.; Ifelebuegu, A.O. The impact of alum on the bulking of a full scale activated sludge plant. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Bio-Informatics and Environmental Engineering, Rome, Italy, 18–19 August 2016; Institute of Research Engineers and Doctors: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Haandel, A.C.V.; Lubbe, J.G.M.V. Handbook of Biological Wastewater Treatment: Design and Optimisation of Activated Sludge System, 2nd ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, D.; Richard, M.G.; Daigger, G.T. Manual on the Causes and Control of Activated Sludge Bulking and Foaming and Other Solids Separation Problems, 3rd ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, A.M.P.; Pagilla, K.R.; Heijnen, J.J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Bulking filamentous sludge: A Critical Review. J. Water Res. 2004, 38, 793–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leven, L.; Wijnbladh, E.; Tuvesson, M.; Kragelund CHalin, S. Control of Microthrix Parvicella and Sludge Bulking by Zone in a Full-Scale WWTP. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rittmann, B.E.; McCarty, P.L. Environmental Biotechnology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wilen, B.M.; Jin, B.; Lant, P. The influence of key constituents in activated sludge on surface and flocculating properties. Water Res. 2003, 37, 127–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Yang, S.F. Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. J. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, B.Q.; Droppo, I.G.; Leppard, G.G.; Liss, S.N. Effect of solids retention time on structure and characteristics of sludge flocs in sequencing batch reactors. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Gregory, J. Coagulation by hydrolysing metal salts. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100–102, 475–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbain, V.; Block, J.C.; Manem, J. Bio-flocculation in activated sludge: An analytical approach. Water Res. 1993, 27, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmann, B.E.; Laspidou, C.S. A unified theory for extracellular polymeric substances, soluble microbial products, and active and inert biomass. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, G.P.; Yu, H.Q.; Li, X.Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: A Review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggs, C.A.; Lant, P.A. Activated sludge flocculation: On-line determination of floc size and the effect of shear. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2542–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Wilen, B.M.; Lant, P. A comprehensive insight into floc characteristics and their impact on compressibility and settleability of activated sludge. Chem. Eng. 2003, 95, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.; She, Z.; Chang, Q.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Yang, N. Effect of salinity on extracellular polymeric substances of activated sludge from an anoxic-anaerobic sequencing batch reactor. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2789–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, M.J.; Tom, L.A.; Sobeck, D.C. Case study I: Application of the divalent cation bridging theory to improve bio-floc properties and industrial activated sludge system performance and direct addition of divalent cations. Water Environ. Res. 2004, 76, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, M.J.; Novak, J.T. Dewatering and settling of activated sludge’s: The case for using cation analysis. Water Environ. Res. 1997, 69, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.B.; Yan, S.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) producing bacterial strains of municipal wastewater sludge: Isolation, molecular identification, EPS characterization and performance for sludge settling and dewatering. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2253–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.S.; Wen, Y.; Cao, A.S.; Huang, J.S.; Zhou, Q.; Somasundaran, P. The influence of additives (Ca2+, Al3+ and Fe3+) on the interaction energy and loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of activated sludge and their flocculation mechanisms. Bio-Resour. Technol. 2012, 114, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakii, K.; Kitamura, S.; Shirakashi, T.; Kuriyama, M. Effect of calcium ion on sludge characteristics. J. Ferment. Technol. 1985, 63, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Orf, M.; Laquidara, M.; Muller, C.; Park, C.; Novak, J. Adjusting floc cations to improve effluent quality: The case of aluminium addition at Sioux City wastewater treatment facility. In Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, WEFTEC 2004: Session 41–50, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–6 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, R.I.; Vesilind, P.A. Sludge volume index-what is it? J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1969, 41, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar]
- White, M.J.D. Design and control of secondary settlement tanks. Water Pollut. Control 1976, 75, 459–467. [Google Scholar]
- Bye, C.M.; Dold, P.L. Sludge volume index settleability measures: Effect for solids characteristics and test parameters. J. Water Environ. Res. 1998, 70, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesilind, P.A. Theoretical considerations: Design of prototype thickeners from batch settling tests. Water Sewage Works 1968, 115, 302–307. [Google Scholar]
- Ekama, G.A.; Barnard, J.L.; Gunthert, F.W.; Krebs, P.; McCorquadale, J.A.; Parker, D.S.; Wahlberg, E.J. Secondary Settling Tanks, Theory, Modelling, Design and Operation; International Association of Water Quality, Scientific Report No. 6; International Association of Water Quality: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, T.; Stephenson, T. Development of a jar testing protocol for chemical phosphorus removal in activated sludge using statistical experimental design. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1730–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agridiotis, V.; Forster, C.F.; Carliell-Marquet, C. Addition of Al and Fe salts during treatment of paper mill effluents to improve activated sludge settlement characteristics. Bio-Resour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2926–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerardi, M.H. Settleability Problems and Loss of Solids in the Activated Sludge Process; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Eikelboom, D.E.; Andreadakis, A.; Andreasen, K. Survey of filamentous populations in nutrient removal plants in four European countries. J. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 37, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Liang, W.; Tan, H.; Yao, C.; Zhang, N.; Lu, L. Effects of calcium and magnesium addition on the start-up of sequencing batch reactor using bio-floc technology treating solid aquaculture waste. Aqua-Cult. Eng. 2013, 57, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, B.; Tomlinson, E. Bulking of Activated Sludge, 1st ed.; Ellis Horwood for the Water Research Centre: Chichester, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Burton, F. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal, Reuse; Metcalf and Eddy, INC.: Wakefield, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhasselt, A.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. Estimation of sludge sedimentation parameters from single batch settling curves. Water Res. 2000, 34, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forster, C.F. Aspects of the behaviour of filamentous microbes in activated sludge. Water Environ. J. 1996, 10, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haas, G.A.; Wentzel, M.C.; Ekama, G.A. The use of simultaneous chemical precipitation in modified activated sludge systems exhibiting biological excess phosphate removal-Part 1: Literature review. Water SA 2000, 26, 439–452. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, G.P.; Yu, H.Q.; Li, X.Y. Stability of sludge flocs under shear conditions: Roles of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 93, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, M.J.; Sobeck, D.C. Examination of three theories for mechanisms of cation-induced bio-flocculation. Water Res. 2002, 36, 527–538. [Google Scholar]
- Piirtola, L.; Uusitalo RVesilind, A. Effect of mineral materials and cations on activated and alum sludge settling. Water Res. 2000, 34, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, L.H.; Gotfredsen, A.K.; Agerkk, M.L.; Nielsen, P.H.; Keiding, K. Effect of colloidal stability on clarification and dewatering of activated sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 34, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.; Forster, C.F. Bulking in activated sludge plants treating paper mill wastewaters. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, F.; Gurakan, G.C.; Sanin, F.D. Monovalent cations and their influence on activated sludge floc chemistry, structure, and physical characteristics. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 100, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Parameter | Control | Dosing Concentration (mg/L) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alum Dosed | |||||||||||
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 80 | 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | |
| Mean ZSV (m/h) | 1.49 | 1.59 | 1.71 | 1.84 | 2 | 2.11 | 2.12 | 2.06 | 1.52 | 1.43 | 1.33 |
| Mean SSVI (mL/g) | 87.43 | 80.8 | 73.41 | 68.8 | 63.24 | 58.36 | 58.55 | 69.24 | 80.78 | 100.1 | 105.5 |
| Mean X (g/L) | 2.52 | 2.65 | 2.73 | 2.8 | 2.86 | 2.92 | 2.99 | 3.09 | 3.3 | 3.55 | 3.76 |
| SD ZSV (m/h) | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.36 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.15 |
| SD SSVI (mL/g) | 32.95 | 29.01 | 27.04 | 24.02 | 21.95 | 19.4 | 22.33 | 23.74 | 24.1 | 14.64 | 15.5 |
| SD X (g/L) | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.2 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.16 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ojo, P.; Ifelebuegu, A.O. The Impact of Aluminium Salt Dosing for Chemical Phosphorus Removal on the Settleability of Activated Sludge. Environments 2018, 5, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5080088
Ojo P, Ifelebuegu AO. The Impact of Aluminium Salt Dosing for Chemical Phosphorus Removal on the Settleability of Activated Sludge. Environments. 2018; 5(8):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5080088
Chicago/Turabian StyleOjo, Peter, and Augustine O. Ifelebuegu. 2018. "The Impact of Aluminium Salt Dosing for Chemical Phosphorus Removal on the Settleability of Activated Sludge" Environments 5, no. 8: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5080088
APA StyleOjo, P., & Ifelebuegu, A. O. (2018). The Impact of Aluminium Salt Dosing for Chemical Phosphorus Removal on the Settleability of Activated Sludge. Environments, 5(8), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5080088