Chemical Analysis of Fluorobenzenes via Multinuclear Detection in the Strong Heteronuclear J-Coupling Regime
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. NMR Spectroscopy
2.3. Gaussian Calculations
2.4. Data Processing
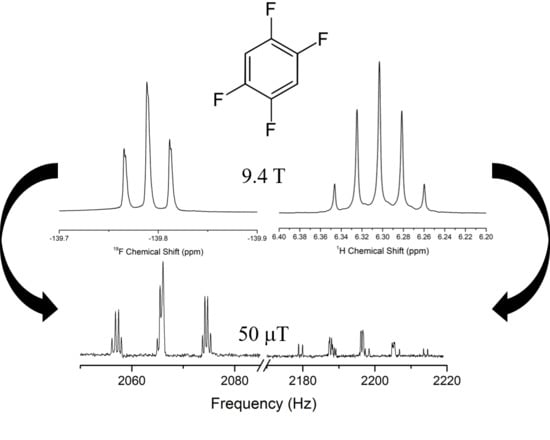
3. Results
3.1. Fit Quality of Simulated Spectra
3.2. Evalutation of the Larmor Frequencies Derived from the JCS
3.3. Evalutation of the J-Couplings Derived from the JCS
3.4. Evaluation of the Chemical Shift Derived from the JCS
4. Discussion
4.1. Quantitation of JCS
4.2. Pople Notation in the Strong Heteronuclear J-Coupling Regime
4.3. Homonuclear J-Coupling Effects in JCS
4.4. Determination of the Relative J-Coupling Signs
4.5. General Trends in the J-Couplings of Fluorobenzenes
4.6. LF and High Field Subspectra
4.7. Chemical Shift Resolution at LF
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobsen, N.E. NMR Spectroscopy Explained: Simplified Theory, Applications and Examples for Organic Chemistry and Structural Biology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 1–688. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhmutov, V.I. Solid-State NMR in Materials Science: Principles and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 1–288. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G. (Ed.) NMR of Proteins and Small Biomolecules; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 326, pp. 1–246. [Google Scholar]
- Abragam, A. The Principles of Nuclear Magnetism; Oxford University Press: Oxford, England, 1961; pp. 1–599. [Google Scholar]
- Duer, M.J. Introduction to Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy; Blackwell Science Ltd: Malden, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–368. [Google Scholar]
- Slichter, C.P. Principles of Magnetic Resonance; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 1–658. [Google Scholar]
- Reisch, M. Helium shortage looms. Chem. Eng. News 2017, 95, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Reisch, M. Helium shortages will persist. Chem. Eng. News 2019, 97, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.; Blümich, B. NMR spectroscopy with compact instruments. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 83, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootveld, M.; Percival, B.; Gibson, M.; Osman, Y.; Edgar, M.; Molinari, M.; Mather, M.L.; Casanova, F.; Wilson, P.B. Progress in low-field benchtop NMR spectroscopy in chemical and biochemical analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1067, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murali, N.; Krishnan, V.V. A primer for nuclear magnetic relaxation in liquids. Concepts Magn. Reson. 2003, 17A, 86–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, E.; Hansen, E.A.; Diehl, P.; Kellerhals, H. NMR Subspectral Analysis Applied to Polyfluorobenzenes C6HnF6−n. IV. 1,2,4-Trifluorobenzene. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 51, 1839–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.W. Pure Shift NMR Spectroscopy. Emagres 2014, 3, 295–309. [Google Scholar]
- Appelt, S.; Häsing, F.W.; Sieling, U.; Gordji-Nejad, A.; Gloggler, S.; Blümich, B. Paths from weak to strong coupling in NMR. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 023420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelt, S.; Häsing, F.W.; Kühn, H.; Blümich, B. Phenomena in J-coupled nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in low magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Appelt, S.; Häsing, F.W.; Kühn, H.; Sieling, U.; Blümich, B. Analysis of molecular structures by homo—And hetero-nuclear J-coupled NMR in ultra-low field. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 440, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelt, S.; Kühn, H.; Häsing, F.W.; Blümich, B. Chemical analysis by ultrahigh-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance in the Earths magnetic field. Nat. Phys. 2006, 2, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halse, M.E.; Callaghan, P.T. A dynamic nuclear polarization strategy for multi-dimensional Earth’s field NMR spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 2008, 195, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halse, M.E.; Callaghan, P.T.; Feland, B.C.; Wasylishen, R.E. Quantitative analysis of Earth’s field NMR spectra of strongly-coupled heteronuclear systems. J. Magn. Reson. 2009, 200, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trahms, L.; Burghoff, M. NMR at very low fields. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 28, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghoff, M.; Hartwig, S.; Trahms, L.; Bernarding, J. Nuclear magnetic resonance in the nanoTesla range. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 054103. [Google Scholar]
- McDermott, R.; Trabesinger, A.H.; Muck, M.; Hahn, E.L.; Pines, A.; Clarke, J. Liquid-state NMR and scalar couplings in microtesla magnetic fields. Science 2002, 295, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, J.N.; Coy, A.; Dykstra, R.; Eccles, C.D.; Hunter, M.W.; Callaghan, P.T. Two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy in Earth’s magnetic field. J. Magn. Reson. 2006, 182, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Hwang, S.M.; Yu, K.K.; Kim, K. Two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy of 13C methanol at less than 5 μT. J. Magn. Reson. 2014, 246, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabesinger, A.H.; McDermott, R.; Lee, S.; Mück, M.; Clarke, J.; Pines, A. SQUID-Detected Liquid State NMR in Microtesla Fields. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, G.J. Nuclear magnetism of liquid systems in the earth field range. Phys. Rep. 1980, 58, 213–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernarding, J.; Buntkowsky, G.; Macholl, S.; Hartwig, S.; Burghoff, M.; Trahms, L. J-Coupling Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Liquids in nT Fields. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 714–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Krause, H.-J.; Hartwig, S.; Burghoff, M.; Trahms, L. Liquid state nuclear magnetic resonance at low fields using a nitrogen cooled superconducting quantum interference device. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 182503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, S.; Chen, H.; Deng, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, K.L.; Liu, C.W.; Liu, C.I.; Yang, H.; Horng, H.; Chieh, J.J.; et al. Microtesla NMR and High Resolution MR Imaging Using High- Tc SQUIDs. ITAS 2013, 23, 1602404. [Google Scholar]
- Buckenmaier, K.; Rudolph, M.; Back, C.; Misztal, T.; Bommerich, U.; Fehling, P.; Koelle, D.; Kleiner, R.; Mayer, H.A.; Scheffler, K. SQUID-Based Detection of Ultra-Low-Field Multinuclear NMR of Substances Hyperpolarized Using Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buckenmaier, K.; Scheffler, K.; Plaumann, M.; Fehling, P.; Bernarding, J.; Rudolph, M.; Back, C.; Koelle, D.; Kleiner, R.; Hövener, J.-B.; et al. Multiple Quantum Coherences Hyperpolarized at Ultra-Low Fields. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2019, 20, 2823–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Krause, H.-J.; Braginski, A.I.; Burghoff, M.; Trahms, L. Nuclear magnetic resonance in the earth’s magnetic field using a nitrogen-cooled superconducting quantum interference device. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 072505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Jin, Y.; Li, S.; Ren, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, G.; Zheng, D. Detection of nuclear magnetic resonance in the microtesla range using a high Tcdc-SQUID. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 400, 052041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamans, B.C.; Andreychenko, A.; Heerschap, A.; Wijmenga, S.S.; Tessari, M. NMR at earth’s magnetic field using para-hydrogen induced polarization. J. Magn. Reson. 2011, 212, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.-Q.; Liu, C.; Dong, H.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Krause, H.-J.; Xie, X.-M.; Offenhäusser, A. Time-Domain Frequency Correction Method for Averaging Low-Field NMR Signals Acquired in Urban Laboratory Environment. ChPhL 2012, 29, 107601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom Mann, P.; Clark, S.; Cahill, S.T.; Campbell, C.D.; Harris, M.T.; Hibble, S.; To, T.; Worrall, A.; Stewart, M. Implementation of Earth’s Field NMR Spectroscopy in an Undergraduate Chemistry Laboratory. J. Chem. Educ. 2019, 96, 2326–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.-H.; Yang, H.-C.; Horng, H.-E.; Yang, S.Y.; Chen, H.H.; Hwang, D.W.; Hwang, L.-P. Sensitive J-coupling spectroscopy using high—Tc superconducting quantum interference devices in magnetic fields as low as microteslas. Supercon. Sci. Technol. 2009, 22, 045008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, S.-H.; Chen, M.-J.; Yang, H.-C.; Lee, S.-Y.; Chen, H.-H.; Horng, H.-E.; Yang, S.-Y. A study of J-coupling spectroscopy using the Earth’s field nuclear magnetic resonance inside a laboratory. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2010, 81, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.S.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.-J.; Hwang, S.-m.; Kim, J.-M.; Yu, K.K.; Kwon, H.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, Y.-H. Application of the double relaxation oscillation superconducting quantum interference device sensor to micro-tesla 1 H nuclear magnetic resonance experiments. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 110, 053906. [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua, G.; Biancalana, V.; Baranga, A.B.-A.; Dancheva, Y.; Rossi, C. Microtesla NMR J-coupling spectroscopy with an unshielded atomic magnetometer. J. Magn. Reson. 2016, 263, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chizhik, V.I.; Kupriyanov, P.A.; Mozzhukhin, G.V. NMR in Magnetic Field of the Earth: Pre-Polarization of Nuclei with Alternating Magnetic Field. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2014, 45, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, J.W.; Budker, D. Zero- to Ultralow-Field NMR. eMagRes 2016, 5, 1395–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Kaseman, D.C.; Magnelind, P.E.; Widgeon Paisner, S.; Yoder, J.L.; Alvarez, M.; Urbaitis, A.V.; Janicke, M.T.; Nath, P.; Espy, M.A.; Williams, R.F. Design and Implementation of a J-coupled Spectrometer for Multidimensional Structure and Relaxation Detection at Low Magnetic Fields. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 054103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, M.; Zeinali, F.; Mojally, M.; Hughes, C.; Riaz, S.; Weaver, G.W. NMR spectral analysis of second-order 19F-19F, 19F-1H and 13C-19F coupling constants in pentafluorobenzene and tetrafluoro-4-(morpholino)pyridine using ANATOLIA. J. Fluor. Chem. 2019, 224, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, V.; Ernst, L.; Lustig, E. The complete 13C 19F, and 1H spectral analysis of the fluorobenzenes C6HnF6−n. III. The remaining members of the series; INDO MO calculations of JFH, JFF, JCH, and JCF. J. Magn. Reson. 1977, 27, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb, H.E.; Kotlyar, V.; Nudelman, A. NMR chemical shifts of common laboratory solvents as trace impurities. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7512–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Rev. A.03; Gaussian: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Frisch, M.J. Calculation of Nuclear Spin−Spin Coupling Constants of Molecules with First and Second Row Atoms in Study of Basis Set Dependence. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2006, 2, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, S.A.; Yates, J.R.; Pickard, C.J.; Mauri, F. A first principles theory of nuclear magnetic resonance J-coupling in solid-state systems. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 204107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hogben, H.J.; Krzystyniak, M.; Charnock, G.T.P.; Hore, P.J.; Kuprov, I. Spinach—A software library for simulation of spin dynamics in large spin systems. J. Magn. Reson. 2011, 208, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntioinen, S.; Laatikainen, R. Solvent effects on the 1H-1H, 1H-19F and 19F-19F coupling constants of fluorobenzene and 1,2-difluorobenzene. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1992, 30, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrenson, I.J. High-resolution fluorine magnetic resonance spectra of some pentafluorophenyl derivatives. J. Chem. Soc. 1965, 0, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, S.; Espinosa, J.F.; Parella, T. IPAP–HSQMBC: Measurement of long-range heteronuclear coupling constants from spin-state selective multiplets. J. Magn. Reson. 2010, 207, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, S.; Espinosa, J.F.; Parella, T. Accurate measurement of small heteronuclear coupling constants from pure-phase α/β HSQMBC cross-peaks. J. Magn. Reson. 2011, 213, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurí, J.; Nolis, P.; Parella, T. Efficient and fast sign-sensitive determination of heteronuclear coupling constants. J. Magn. Reson. 2013, 236, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelt, S.; Häsing, F.W.; Kühn, H.; Perlo, J.; Blümich, B. Mobile High Resolution Xenon Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in the Earth’s Magnetic Field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 197602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katz, I.; Shtirberg, L.; Shakour, G.; Blank, A. Earth field NMR with chemical shift spectral resolution: Theory and proof of concept. J. Magn. Reson. 2012, 219, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.K.; Becker, E.D.; Cabral De Menezes, S.M.; Granger, P.; Hoffman, R.E.; Zilm, K.W. Further conventions for NMR shielding and chemical shifts (IUPAC Recommendations 2008). eMagRes 2007, 33, 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- Diehl, P.; Pople, J. The analysis of complex nuclear magnetic resonance spectra: II. Some further systems with one strong coupling constant. Mol. Phys. 1960, 3, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pople, J.; Schaefer, T. The analysis of complex nuclear magnetic resonance spectra: I. Systems with one pair of strongly coupled nuclei. Mol. Phys. 1960, 3, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S. Relative Signs of Spin-Spin Interactions in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. J. Chem. Phys. 1958, 28, 358–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S. Relative Signs of Spin-Spin Interactions in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. II. J. Chem. Phys. 1960, 32, 1700–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessenden, R.; Waugh, J. Strong Coupling in Nuclear Resonance Spectra. II. Field Dependence of Some Unsymmetrical Three-Spin Spectra. J. Chem. Phys. 1959, 31, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowsky, H.; Holm, C.; Saika, A.; Williams, G. Electron Coupling of Nuclear Spins. I. Proton and Fluorine Magnetic Resonance Spectra of Some Substituted Benzenes1,2. JPC 1957, 79, 4596–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.; Gutowsky, H. Determination of the Signs of Nuclear Spin-Spin Indirect Coupling Constants. J. Chem. Phys. 1956, 25, 1288–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, E.; Maxwell, D. Spin echo measurements of nuclear spin coupling in molecules. Phys. Rev. 1952, 88, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.A.; Gutowsky, H.S. Electron Coupling of Nuclear Spins. II. Molecular Orbital Interpretation of Coupling Constants Observed in Fluorobenzenes. J. Chem. Phys. 1959, 30, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, V.; Lincoln, D.N. The complete 13 C, 19 F and 1 H spectral analysis of the fluorobenzenes C6HnF6∼-n.I.1,3,5-trifluorobenzene. J. Magn. Reson. 1975, 18, 374–382. [Google Scholar]
- Lustig, E.; Duy, N.; Diehl, P.; Kellerhals, H. NMR Subspectral Analysis Applied to Polyfluorobenzenes C6HnF6–n. II. 1,2,3,4-Tetrafluorobenzene. J. Chem. Phys. 1968, 48, 5001–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, W.G.; Wells, E.J. NMR spectrum of para-difluorobenzene. I. Mol. Spectrosc. 1964, 14, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Compound | Parameters Optimized | B0 (µT) | 19F Relaxation Rates (Hz) | 1H Relaxation Rates (Hz) | RSS | R-Factor (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene+ Hexafluorobenzene | 3 | 51.64 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.26 | 14 |
| Monofluorobenzene | 12 | 51.55 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 9.0 |
| 1,2-Difluorobenzene | 12 | 51.56 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 13 |
| 1,3-Difluorobenzene | 12 | 51.59 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.98 | 19 |
| 1,4-Difluorobenzene | 9 | 51.56 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 11 |
| 1,2,4-Trifluorobenzene | 18 | 51.58 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 1.01 | 24 |
| 1,2,4,5-Tetrafluorobenzene | 9 | 51.57 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.89 | 19 |
| Pentafluorobenzene | 12 | 51.56 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.37 | 15 |
| Compound | 3J1,2 | 4J1,3 | 5J1,4 | 4J1,5 | 3J1,6 | 3J2,3 | 4J2,4 | 5J2,5 | 4J2,6 | 3J3,4 | 4J3,5 | 5J3,6 | 3J4,5 | 4J4,6 | 3J5,6 | R-Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monofluorobenzene Exp | 9.12 | 5.77 | 0.15 | 5.77 | 9.12 | 8.38 | 1.13 | 0.53 | 2.90 | 7.56 | 1.90 | 0.53 | 7.56 | 1.13 | 8.38 | 9 |
| Monofluorobenzene Lit 1 | 9.18 | 5.76 | 0.35 | 5.76 | 9.18 | 8.36 | 1.06 | 0.42 | 2.77 | 7.45 | 1.82 | 0.42 | 7.45 | 1.06 | 8.36 | 12 |
| Monofluorobenzene Calc | 10.81 | 5.31 | −2.02 3 | 5.31 | 10.81 | 10.82 | −0.21 3 | 1.17 | 0.36 | 9.91 | 0.36 | 1.17 | 9.91 | −0.21 3 | 10.81 | 65 |
| 1,2-Difluorobenzene Exp | −20.81 | 8.11 | −1.41 | 4.51 | 10.72 | 10.72 | 4.51 | −1.41 | 8.11 | 8.27 | 1.59 | 0.23 | 7.57 | 1.59 | 8.27 | 13 |
| 1,2-Difluorobenzene Lit 1 | −20.82 | 8.06 | −1.39 | 4.53 | 10.85 | 10.85 | 4.53 | −1.40 | 8.06 | 8.30 | 1.61 | 0.26 | 7.61 | 1.61 | 8.30 | 13 |
| 1,2-Difluorobenzene Calc | −13.98 | 8.39 | −3.42 | 4.12 | 13.03 | 13.03 | 4.12 | −3.42 | 8.39 | 10.70 | 0.35 | 1.00 | 10.12 | 0.35 | 10.70 | 95 |
| 1,3-Difluorobenzene Exp | 9.42 | 6.62 | −0.81 | 6.62 | 8.43 | 9.42 | 2.44 | 0.32 | 2.44 | 8.43 | 6.62 | −0.81 | 8.42 | 0.87 | 8.42 | 19 |
| 1,3-Difluorobenzene Lit 1 | 9.42 | 6.52 | −0.81 | 6.63 | 8.43 | 9.42 | 2.44 | 0.32 | 2.44 | 8.43 | 6.63 | −0.81 | 8.43 | 0.87 | 8.43 | 20 |
| 1,3-Difluorobenzene Calc | 11.5 | 5.14 | −2.81 | 6.17 | 10.38 | 11.5 | 1.44 | 1.06 | 1.44 | 10.38 | 6.17 | −2.82 | 10.38 | −0.22 3 | 10.38 | 76 |
| 1,4-Difluorobenzene Exp | 8.07 | 4.14 | 17.65 | 4.14 | 8.07 | 9.09 | 4.14 | 0.00 | 3.15 | 8.07 | 3.15 | 0.00 | 8.07 | 4.14 | 9.09 | 11 |
| 1,4-Difluorobenzene Lit 1 | 8.09 | 4.16 | 17.65 | 4.16 | 8.09 | 9.09 | 4.16 | 0.34 | 3.24 | 8.09 | 3.24 | 0.34 | 8.09 | 4.16 | 9.09 | 13 |
| 1,4-Difluorobenzene Calc | 9.89 | 3.99 | 21.95 | 3.99 | 9.86 | 11.64 | 3.99 | 1.12 | 2.11 | 9.82 | 2.11 | 1.12 | 9.86 | 3.99 | 11.65 | 110 |
| 1,2,4-Trifluorobenzene Exp | −20.01 | 6.30 | 15.02 | 3.30 | 10.06 | 10.67 | 3.14 | −2.03 | 8.86 | 8.32 | 3.06 | 0.37 | 7.82 | 5.09 | 9.19 | 24 |
| 1,2,4-Trifluorobenzene Lit 1 | −20.42 | 6.35 | 15.09 | 3.31 | 10.09 | 10.65 | 3.19 | −2.01 | 8.98 | 8.38 | 3.08 | 0.34 | 7.86 | 5.09 | 9.22 | 26 |
| 1,2,4-Trifluorobenzene Calc | −13.86 | 6.87 | 19.87 | 3.05 | 12.47 | 13.34 | 2.14 | −3.87 | 9.34 | 10.55 | 2.14 | 1.09 | 9.64 | 4.94 | 11.80 | 160 |
| 1,2,4,5-Tetrafluorobenzene Exp | −20.74 | 7.40 | 13.22 | −0.50 | 10.05 | 10.05 | −0.50 | 13.22 | 7.40 | 10.05 | 7.40 | 0.50 | −20.74 | 7.40 | 10.05 | 19 |
| 1,2,4,5-Tetrafluorobenzene Lit 1 | −20.74 | 7.45 | 13.33 | −0.22 | 10.06 | 10.06 | −0.22 | 13.33 | 7.45 | 10.06 | 7.45 | 0.53 | −20.74 | 7.45 | 10.06 | 26 |
| 1,2,4,5-Tetrafluorobenzene Calc | −14.67 | 8.00 | 18.54 | −4.65 | 12.98 | 12.98 | −4.65 | 13.13 | 8.00 | 12.98 | 8.00 | 1.35 | −14.67 | 8.00 | 12.98 | 110 |
| Pentafluorobenzene Exp | −21.10 | 1.3 | 9.1 | −2.30 | 10.31 | −18.95 | −0.65 | 9.10 | 6.93 | −18.95 | 1.3 | −2.70 | −21.10 | 6.93 | 10.31 | 15 |
| Pentafluorobenzene Lit 1 | −20.57 | 1.21 | 8.78 | −2.04 | 10.41 | −18.75 | −1.23 | 8.78 | 7.00 | −18.75 | 1.23 | −2.65 | −20.57 | 7.00 | 10.41 | 25 |
| Pentafluorobenzene Lit 2 | −21.78 | 1.24 | 8.74 | −2.17 | 10.02 | −20.11 | −1.20 | 8.74 | 6.87 | −20.11 | 1.24 | −2.70 | −21.78 | 6.87 | 10.02 | 46 |
| Pentafluorobenzene Calc | −14.86 | 3.55 | 12.78 | −6.33 | 13.6 | −12.48 | −0.89 | 12.78 | 7.67 | −12.48 | 3.55 | −4.19 | −14.86 | 7.67 | 13.6 | 120 |
| Compound | High Field and JCS 19F δiso (ppm) | R-Factor (19F δiso = 0 ppm) (%) | R-Factor (correct 19F δiso) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene + Hexafluorobenzene | −163.2 | 92 | 14 |
| Monofluorobenzene | −112.9 | 10 | 9 |
| 1,2-Difluorobenzene | −138.4 | 26 | 13 |
| 1,3-Difluorobenzene | −109.9 | 31 | 12 |
| 1,4-Difluorobenzene | −119.6 | 28 | 11 |
| 1,2,4-Trifluorobenzene | −143.5 −133.5 −115.7 | 54 | 24 |
| 1,2,4,5-Tetrafluorobenzene | −139.7 | 83 | 19 |
| Pentafluorobenzene | −162.5 −154.2 −139.2 | 90 | 15 |
| Compound | 1H-19F Stoichiometric | 1H-19F Experimental | 1H-19F Simulated | Experimental Error (%) | Simulated Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene + Hexafluorobenzene | 1.00 | 1.16 [0.963] | 1.12 [0.930] | 15.6 [3.69] | 11.7 [6.92] |
| Monofluorobenzene | 5.00 | 7.04 [5.86] | 5.62 [4.68] | 40.8 [17.3] | 12.4 [6.37] |
| 1,2-Difluorobenzene | 2.00 | 2.26 [1.88] | 2.25 [1.87] | 12.9 [5.99] | 12.2 [6.49] |
| 1,3-Difluorobenzene | 2.00 | 2.20 [1.84] | 2.26 [1.88] | 10.1 [8.27] | 12.7 [6.09] |
| 1,4-Difluorobenzene | 2.00 | 2.37 [1.98] | 2.24 [1.87] | 18.7 [1.14] | 12.2 [6.53] |
| 1,2,4-Trifluorobenzene | 1.00 | 0.979 [0.815] | 1.11 [0.928] | 2.14 [18.5] | 11.4 [7.20] |
| 1,2,4,5-Tetrafluorobenzene | 0.500 | 0.687 [0.572] | 0.568 [0.473] | 37.4 [14.5] | 13.7 [5.30] |
| Pentafluorobenzene | 0.200 | 0.292 [0.243] | 0.229 [0.191] | 46.0 [21.7] | 14.7 [4.41] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaseman, D.C.; Janicke, M.T.; Frankle, R.K.; Nelson, T.; Angles-Tamayo, G.; Batrice, R.J.; Magnelind, P.E.; Espy, M.A.; Williams, R.F. Chemical Analysis of Fluorobenzenes via Multinuclear Detection in the Strong Heteronuclear J-Coupling Regime. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3836. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113836
Kaseman DC, Janicke MT, Frankle RK, Nelson T, Angles-Tamayo G, Batrice RJ, Magnelind PE, Espy MA, Williams RF. Chemical Analysis of Fluorobenzenes via Multinuclear Detection in the Strong Heteronuclear J-Coupling Regime. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(11):3836. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113836
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaseman, Derrick C., Michael T. Janicke, Rachel K. Frankle, Tammie Nelson, Gary Angles-Tamayo, Rami J. Batrice, Per E. Magnelind, Michelle A. Espy, and Robert F. Williams. 2020. "Chemical Analysis of Fluorobenzenes via Multinuclear Detection in the Strong Heteronuclear J-Coupling Regime" Applied Sciences 10, no. 11: 3836. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113836
APA StyleKaseman, D. C., Janicke, M. T., Frankle, R. K., Nelson, T., Angles-Tamayo, G., Batrice, R. J., Magnelind, P. E., Espy, M. A., & Williams, R. F. (2020). Chemical Analysis of Fluorobenzenes via Multinuclear Detection in the Strong Heteronuclear J-Coupling Regime. Applied Sciences, 10(11), 3836. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113836