Preparation of Palm Oil Ash Nanoparticles: Taguchi Optimization Method by Particle Size Distribution and Morphological Studies
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
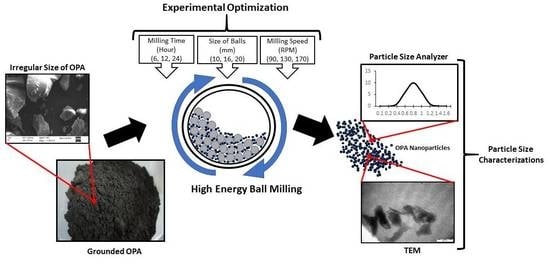
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of Experiment
2.2. Materials Characterization
2.2.1. Particle Size Measurement
2.2.2. Morphology Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Parameters Optimization
3.2. The Influence of the Studied Parameters on the Responses
3.3. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Approach
3.4. Characteristic of Palm Oil Ash Morphology and Particle Size Distribution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hameed, B.H.; Ahmad, A.A.; Aziz, N. Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics of acid dye adsorption on activated palm ash. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 133, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Ismail, M.E.; Muhammad, B. Influence of elevated temperatures on physical and compressive strength properties of concrete containing palm oil fuel ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2358–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boey, P.-L.; Ganesan, S.; Lim, S.-X.; Lim, S.-L.; Maniam, G.P.; Khairuddean, M. Utilization of BA (boiler ash) as catalyst for transesterification of palm olein. Energy 2011, 36, 5791–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khankhaje, E.; Hussin, M.W.; Mirza, J.; Rafieizonooz, M.; Salim, M.R.; Siong, H.C.; Warid, M.N.M. On blended cement and geopolymer concretes containing palm oil fuel ash. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Islam, M.M.; Mo, K.H.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z. Durability properties of sustainable concrete containing high volume palm oil waste materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khankhaje, E.; Rafieizonooz, M.; Salim, M.R.; Khan, R.; Mirza, J.; Siong, H.C. Sustainable clean pervious concrete pavement production incorporating palm oil fuel ash as cement replacement. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.H.; Hashim, M.A. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of zinc on ash particles derived from oil palm waste. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2002, 77, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainudin, N.F.; Lee, K.T.; Kamaruddin, A.H.; Bhatia, S.; Mohamed, A.R. Study of adsorbent prepared from oil palm ash (OPA) for flue gas desulfurization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 45, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Fizree, H.M.; Bhat, A.H.; Jawaid, M.; Abdullah, C.K. Development and characterization of epoxy nanocomposites based on nano-structured oil palm ash. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 53, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Fizree, H.M.; Jawaid, M.; Alattas, O.S. Preparation and characterization of nano structured materials from oil palm ash: A bio-agricultural waste from oil palm mill. BioResources 2011, 6, 4537–4546. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Rus Mahayuni, A.R.; Rudi, D.; Almulali, M.Z.; Abdullah, C.K. Characterization of various organic waste nanofillers obtained from oil palm ash. BioResources 2012, 7, 5771–5780. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, J.E.; Cervantes, J.; Esparza, R.; Rosas, G. Iron nanoparticles produced by high-energy ball milling. J. Nanopart. Res. 2007, 9, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, L.; Colangelo, F.; Cioffi, R.; Rea, I.; Stefano, L.D. A Mechanochemical Approach to Porous Silicon Nanoparticles Fabrication. Materials 2011, 4, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salah, N.; Habib, S.S.; Khan, Z.H.; Memic, A.; Azam, A.; Alarfaj, E.; Zahed, N.; Al-Hamedi, S. High-energy ball milling technique for ZnO nanoparticles as antibacterial material. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, H. Critical rotation speed for ball-milling. Powder Technol. 1999, 104, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enqvist, E.; Ramanenka, D.; Marques, P.A.; Gracio, J.; Emami, N. The effect of ball milling time and rotational speed on ultra high molecular weight polyethylene reinforced with multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutuk, S. Influence of milling parameters on particle size of ulexite material. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.G.; Anandhan, S. Influence of planetary ball milling parameters on the mechano-chemical activation of fly ash. Powder Technol. 2015, 281, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitonde, V.; Karnik, S.; Davim, J.P. Taguchi multiple-performance characteristics optimization in drilling of medium density fibreboard (MDF) to minimize delamination using utility concept. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 196, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.p.; Tarng, Y. Design optimization of cutting parameters for turning operations based on the Taguchi method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1998, 84, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fan, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, A. Effect of carbon black nanoparticles from the pyrolysis of discarded tires on the performance of asphalt and its mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hubenthal, F.; Blázquez Sánchez, D.; Träger, F. Determination of morphological parameters of supported gold nanoparticles: Comparison of AFM combined with optical spectroscopy and theoretical modeling versus TEM. Appl. Sci. 2012, 2, 566–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcay, K.; Sirkecioğlu, A.; Tatlıer, M.; Savaşçı, Ö.T.; Erdem-Şenatalar, A. Wet ball milling of zeolite HY. Powder Technol. 2004, 142, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, O.; Pamtoks, H.; Omolayo, M.P.; Adelana, R.A. Taguchi Optimization of Process Parameters on the Hardness and Impact Energy of Aluminium Alloy Sand Castings. Leonardo J. Sci. 2013, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Külekcı, M.K. Analysis of process parameters for a surface-grinding process based on the Taguchi method. Mater. Tehnol. 2013, 47, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Goya, G.F. Handling the particle size and distribution of Fe3O4 nanoparticles through ball milling. Solid State Commun. 2004, 130, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, R. Mechanical activation of fly ash: Effect on reaction, structure and properties of resulting geopolymer. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 1–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, E.; Hamey, R.; Scarlett, B. Production of pigment nanoparticles using a wet stirred mill with polymeric media. China Particuol. 2004, 2, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkwanyana, S.; Loveday, B. Addition of pebbles to a ball-mill to improve grinding efficiency—Part 2. Miner. Eng. 2018, 128, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerstenau, D.W.; Lutch, J.J.; De, A. The effect of ball size on the energy efficiency of hybrid high-pressure roll mill/ball mill grinding. Powder Technol. 1999, 105, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kwon, J.; Kim, K.; Mun, M. Optimum choice of the make-up ball sizes for maximum throughput in tumbling ball mills. Powder Technol. 2013, 246, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kharisma, A.; Murphiyanto, R.D.J.; Perdana, M.K.; Kasih, T.P. Application of Taguchi method and ANOVA in the optimization of dyeing process on cotton knit fabric to reduce re-dyeing process. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; p. 012023. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczyk, M. Application of Taguchi and Anova methods in selection of process parameters for surface roughness in precision turning of titanium. Adv. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Chattopadhyaya, S.; Hloch, S. Multi response optimization of process parameters based on Taguchi—Fuzzy model for coal cutting by water jet technology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 56, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, B.; Tavandashti, M.P.; Zandrahimi, M. Particle size characterization of nanoparticles–A practicalapproach. Iran. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 8, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Aqeel Ashraf, M.; Peng, W.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. Effects of Size and Aggregation/Agglomeration of Nanoparticles on the Interfacial/Interphase Properties and Tensile Strength of Polymer Nanocomposites. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pishvaei, M.; Farshchi, T.F. Synthesis of high solid content polyacrylate/nanosilica latexes via miniemulsion polymerization. Iran. Polym. J. 2010, 19, 707–716. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdimamaghani, M.; Pourvala, T.; Motamedi, E.; Fathi, B.; Vashaee, D.; Tayebi, L. Synthesis and characterization of encapsulated nanosilica particles with an acrylic copolymer by in situ emulsion polymerization using thermoresponsive nonionic surfactant. Materials 2013, 6, 3727–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Parameter | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milling Time | 6 h | 12 h | 24 h |
| Milling speed | 100 rpm | 130 rpm | 170 rpm |
| Size of stainless-steel ball | 10 mm | 16 mm | 20 mm |
| Experiment | Milling Time (hour) | Milling Speed (rpm) | Size of Balls (mm) | Mean Particle Size (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 h | 100 rpm | 10 mm | 0.48 ± 0.06 |
| 2 | 6 h | 130 rpm | 16 mm | 0.41 ± 0.07 |
| 3 | 6 h | 170 rpm | 20 mm | 0.23 ± 0.06 |
| 4 | 12 h | 100 rpm | 16 mm | 0.28 ± 0.09 |
| 5 | 12 h | 130 rpm | 20 mm | 0.19 ± 0.04 |
| 6 | 12 h | 170 rpm | 10 mm | 0.15 ± 0.08 |
| 7 | 24 h | 100 rpm | 20 mm | 0.11 ± 0.07 |
| 8 | 24 h | 130 rpm | 10 mm | 0.13 ± 0.04 |
| 9 | 24 h | 170 rpm | 16 mm | 0.09 ± 0.07 |
| Experiment | Milling Time | Milling Speed | Size of Balls | SN Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.92 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | −0.31 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0.43 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.32 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1.51 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1.20 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3.94 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3.39 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | −0.28 |
| Level | Milling Time | Milling Speed | Size of Balls |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.34422 | 1.72604 * | 1.83909 |
| 2 | 1.01416 | 1.53138 | −0.09304 |
| 3 | 2.3507 * | 0.45170 | 1.96308 * |
| Delta ∆ | 2.00652 | 1.27434 | 2.05612 |
| Rank | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Parameter | DoF | Sum of Square | Means Square | F-Test | Contribution (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milling Time | 2 | 6.2614 | 3.1307 | 4.80 | 34.08 |
| Milling Speed | 2 | 2.8275 | 1.4138 | 2.17 | 15.39 |
| Size of Balls | 2 | 7.9762 | 3.9881 | 6.11 | 43.42 |
| Error | 2 | 1.3053 | 0.6527 | 7.11 | |
| Total | 8 | 18.3704 | 100 |
| Parameter | Level | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Milling Time | 3 | 24 h |
| Milling Speed | 1 | 100 rpm |
| Size of balls | 3 | 20 mm |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizal, S.; Abdullah, C.K.; Olaiya, N.G.; Sri Aprilia, N.A.; Zein, I.; Surya, I.; Abdul Khalil, H.P.S. Preparation of Palm Oil Ash Nanoparticles: Taguchi Optimization Method by Particle Size Distribution and Morphological Studies. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030985
Rizal S, Abdullah CK, Olaiya NG, Sri Aprilia NA, Zein I, Surya I, Abdul Khalil HPS. Preparation of Palm Oil Ash Nanoparticles: Taguchi Optimization Method by Particle Size Distribution and Morphological Studies. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(3):985. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030985
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizal, Samsul, C. K. Abdullah, N. G. Olaiya, N. A. Sri Aprilia, Ikramullah Zein, Indra Surya, and H. P. S. Abdul Khalil. 2020. "Preparation of Palm Oil Ash Nanoparticles: Taguchi Optimization Method by Particle Size Distribution and Morphological Studies" Applied Sciences 10, no. 3: 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030985
APA StyleRizal, S., Abdullah, C. K., Olaiya, N. G., Sri Aprilia, N. A., Zein, I., Surya, I., & Abdul Khalil, H. P. S. (2020). Preparation of Palm Oil Ash Nanoparticles: Taguchi Optimization Method by Particle Size Distribution and Morphological Studies. Applied Sciences, 10(3), 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030985