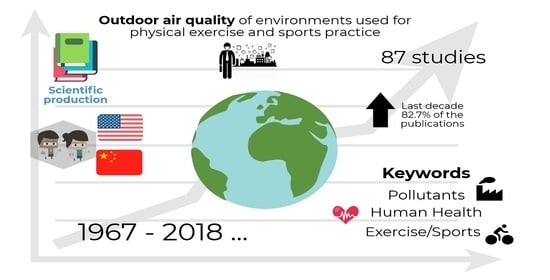
Outdoor Air Quality of Environments Used for Exercise and Sports Practice: An Analysis of Scientific Production through Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Publications
3.2. The Authors
3.3. Journals
4. Discussion
4.1. Publications
4.2. Authors, Institutions, and Countries
4.3. Journals
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuoco, F.C.; Stabile, L.; Buonanno, G.; Trassiera, C.V.; Massimo, A.; Russi, A.; Mazaheri, M.; Morawska, L.; Andrade, A. Indoor air quality in naturally ventilated Italian classrooms. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1652–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stabile, L.; Massimo, A.; Canale, L.; Russi, A.; Andrade, A.; Dell’Isola, M. The effect of ventilation strategies on indoor air quality and energy consumptions in classrooms. Buildings 2019, 9, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrade, A.; Dominski, F.H.; Pereira, M.L.; de Liz, C.M.; Buonanno, G. Fitness centers demonstrate CO2 concentration levels above recommended standards. Acta Sci. Health Sci. 2018, 40, e35768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.; Dominski, F.H.; Pereira, M.L.; de Liz, C.M.; Buonanno, G. Infection risk in gyms during physical exercise. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 19675–19686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, M.; Mannucci, P.M.; Harari, S.; Pontoni, F.; Croci, E. The health and economic burden of air pollution. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 931–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.M.; Shiroma, E.J.; Lobelo, F.; Puska, P.; Blair, S.N.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: An analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy. Lancet 2012, 380, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Health Risks: Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, A.; Vilarino, G.T.; Bevilacqua, G.G. What is the effect of strength training on pain and sleep in patients with fibromyalgia? Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 96, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebel, K.; Ding, D.; Chey, T.; Stamatakis, E.; Brown, W.J.; Bauman, A.E. Effect of moderate to vigorous physical activity on all-cause mortality in middle-aged and older Australians. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; LeBlanc, A.G. Systematic review of the health benefits of physical activity and fitness in school-aged children and youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.M.; American College of Sports Medicine. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: Guidance for prescribing exercise. Med. Sci. Sports. Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tainio, M.; de Nazelle, A.J.; Götschi, T.; Kahlmeier, S.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Thiago, H.S.; Paul, K.; James, W. Can air pollution negate the health benefits of cycling and walking? Prev. Med. 2016, 87, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrade, A.; Dominski, F.H. Indoor air quality of environments used for physical exercise and sports practice: Systematic review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 15, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlisle, A.; Sharp, N. Exercise and outdoor ambient air pollution. Br. J. Sports Med. 2001, 35, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajian, M.; Mohaghegh, S. Indoor Air Pollution in Exercise Centers. IJMTFM 2015, 5, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Pope, C.A., 3rd; Brook, J.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, Council on the Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, and Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity and Metabolism. Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: An update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 121, 2331–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, S.H.; Van Hee, V.C.; Bergen, S.; Szpiro, A.A.; DeRoo, L.A.; London, S.J.; Sandler, D.P.; Julian, D.M.; Joel, D.K. Long-term air pollution exposure and blood pressure in the sister study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauderman, W.J.; Urman, R.; Avol, E.; Berhane, K.; McConnell, R.; Rappaport, E.; Roger, C.; Fred, L. Association of improved air quality with lung development in children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.K.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, Z.; Chung, K.F. Mechanistic impact of outdoor air pollution on asthma and allergic diseases. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, L.V.; Koehle, M.S. The health effects of exercising in air pollution. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Rui, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Jian, Z.; Yindong, T. Sources of atmospheric pollution: A bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2017, 112, 1025–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.; Dominski, F.H.; Coimbra, D.R. Scientific production on indoor air quality of environments used for physical exercise and sports practice: Bibliometric analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, D.R.; Dominski, F.H.; Correia, C.K.; Andrade, A. Scientific production in Sports Science Journals: Bibliometric analysis. Rev. Bras. Med. Esport. 2019, 25, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brimblecombe, P.; Grossi, C.M. The bibliometrics of atmospheric environment. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibzadeh, F.; Yadollahie, M. Are shorter article titles more attractive for citations? Crosssectional study of 22 scientific journals. Croat. Med. J. 2010, 51, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McConnell, R.; Berhane, K.; Gilliland, F.; London, S.J.; Islam, T.; Gauderman, W.J.; Edward, A.; Helene, G.M.; John, M.P. Asthma in exercising children exposed to ozone: A cohort study. Lancet 2002, 359, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Xing, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, Y.; Kebin, H.; Lixin, F.; Jiming, H. Quantifying the air pollutants emission reduction during the 2008 Olympic Games in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2490–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Rueda, D.; de Nazelle, A.; Tainio, M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. The health risks and benefits of cycling in urban environments compared with car use: Health impact assessment study. BMJ 2011, 343, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rich, D.Q.; Kipen, H.M.; Huang, W.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Ohman-Strickland, P.; Hu, M.; Philipp, C.; Diehl, S.R.; et al. Association between changes in air pollution levels during the Beijing Olympics and biomarkers of inflammation and thrombosis in healthy young adults. JAMA 2012, 307, 2068–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panis, L.I.; De Geus, B.; Vandenbulcke, G.; Willems, H.; Degraeuwe, B.; Bleux, N.; Vinit, M.; Isabelle, T.; Romain, M. Exposure to particulate matter in traffic: A comparison of cyclists and car passengers. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Primbs, T.; Tao, S.; Simonich, S.L.M. Atmospheric particulate matter pollution during the 2008 Beijing Olympics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5314–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Xie, S. Assessment of traffic-related air pollution in the urban streets before and during the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games traffic control period. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5682–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.D.; Brauer, M.; Frank, L.D. Healthy neighborhoods: Walkability and air pollution. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1752–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, L.; Nawrot, T.S.; De Geus, B.; Meeusen, R.; Degraeuwe, B.; Bernard, A.; Sughis, M.; Nemery, B.; Panis, L.I. Subclinical responses in healthy cyclists briefly exposed to traffic-related air pollution: An intervention study. Environ. Health 2010, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wayne, W.S.; Wehrle, P.F.; Carroll, R.E. Oxidant air pollution and athletic performance. JAMA 1967, 199, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zell, H.; Quarcoo, D.; Scutaru, C.; Vitzthum, K.; Uibel, S.; Schöffel, N.; Mache, S.; Groneberg, D.A.; Spallek, M.F. Air pollution research: Visualization of research activity using density-equalizing mapping and scientometric benchmarking procedures. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2010, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falagas, M.E.; Zarkali, A.; Karageorgopoulos, D.E.; Bardakas, V.; Mavros, M.N. The impact of article length on the number of future citations: A bibliometric analysis of general medicine journals. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e49476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole-Hunter, T.; Weichenthal, S.; Kubesch, N.; Foraster, M.; Carrasco-Turigas, G.; Bouso, L.; Martínez, D.; Westerdahl, D.; de Nazalle, A.; Nieuwenhijsen, M. Impact of traffic-related air pollution on acute changes in cardiac autonomic modulation during rest and physical activity: A cross-over study. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheridan, G.; Wisken, E.; Hing, C.; Smith, T. A bibliometric analysis assessing temporal changes in publication and authorship characteristics in The Knee from 1996 to 2016. Knee 2018, 25, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geminiani, A.; Ercoli, C.; Feng, C.; Caton, J.G. Bibliometrics study on authorship trends in periodontal literature from 1995 to 2010. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.C.; Hu, Y.H.; Lin, W.C.; Tsai, C.F.; Ke, S.W. Research impact of general and funded papers: A citation analysis of two ACM international conference proceeding series. Online Information Rev. 2016, 40, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shapira, P. Is there a relationship between research sponsorship and publication impact? An analysis of funding acknowledgments in nanotechnology papers. PLoS ONE. 2015, 10, e0117727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyvik, S.; Reymert, I. Research collaboration in groups and networks: Differences across academic fields. Scientometrics 2017, 113, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweileh, W.M.; Al-Jabi, S.W.; Sa’ed, H.Z.; Sawalha, A.F. Outdoor air pollution and respiratory health: A bibliometric analysis of publications in peer-reviewed journals (1900–2017). Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2018, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dragos, C.M.; Dragos, S.L. Bibliometric approach of factors affecting scientific productivity in environmental sciences and ecology. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolle, S.R.; Thyavanahalli, S.H. Global research on air pollution between 2005 and 2014: A bibliometric study. Collect. Build. 2016, 35, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Mean | Median | Minimum | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of title | 15.12 | 14 | 6 | 34 |
| Number of keywords | 5.13 | 5 | 0 | 11 |
| Number of tables | 3.07 | 3 | 0 | 9 |
| Number of figures | 3.77 | 3 | 0 | 30 |
| Number of References | 41.39 | 39 | 5 | 149 |
| Length (pages) | 11.942 | 9 | 4 | 204 |
| Number of citations WoS | 22.70 | 7 | 0 | 418 |
| Number of citations WoS by year | 2.68 | 1.33 | 0 | 24.59 |
| Citations in all databases | 24.17 | 7 | 0 | 427 |
| Usage Count | 28.57 | 19 | 0 | 243 |
| Title | Journal | Author/Year of Publication | Wos Citations/Average by Year | Pollutants Investigated | Exercise/Sport Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asthma in exercising children exposed to ozone: a cohort study | Lancet | McConnell et al. (2002) [26] | 462 / 24.32 | PM10, PM2.5, O3, NO2 | Sports |
| Quantifying the air pollutants emission reduction during the 2008 Olympic Games in Beijing | Environmental Science & Technology | Wang et al. (2010) [27] | 215 / 19.55 | SO2, NOx, PM10, NMVOC | The 2008 Olympic Games |
| The health risks and benefits of cycling in urban environments compared with car use: health impact assessment study | British Medical Journal | Rojas-Rueda et al. (2011) [28] | 203 / 20.30 | PM2.5 | Transport—cyclism |
| Association Between Changes in Air Pollution Levels During the Beijing Olympics and Biomarkers of Inflammation and Thrombosis in Healthy Young Adults | Journal of the American Medical Association | Rich et al. (2012) [29] | 195 / 21.67 | PM2.5, SO2, NO2, CO, O3 | The 2008 Olympic Games |
| Exposure to particulate matter in traffic: A comparison of cyclists and car passengers | Atmospheric Environment | Panis et al. (2010) [30] | 185 / 16.82 | PNC, PM2.5 and PM10 | Transport—cyclism |
| Atmospheric Particulate MatterPollution during the 2008 Beijing Olympics | Environmental Science & Technology | Wang et al. (2009) [31] | 113/9.42 | PM10, PM 2.5, PM 2.5-10 | The 2008 Olympic Games |
| Assessment of traffic-related air pollution in the urban streets before and during the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games traffic control period | Atmospheric Environment | Wang and Xie (2009) [32] | 97/8.08 | PM10, CO, NO2, O3 | The 2008 Olympic Games |
| Healthy neighborhoods: Walkability and air pollution | Environmental Health Perspectives | Marshall et al. (2009) [33] | 97 / 8.08 | NO, O3 | Physical activity |
| Subclinical responses in healthy cyclists briefly exposed to traffic-related air pollution: An intervention study | Environmental Health | Jacobs et al. (2010) [34] | 87 / 7.91 | PM10, PM2.5, UFP | Transport - cyclism |
| Oxidant Air Pollution and Athletic Performance | Journal of the American Medical Association | Wayne et al. (1967) [35] | 79 / 1.46 | CO | Sport - Running |
| Funding Agency | Countries | Number of Studies Funded |
|---|---|---|
| National Natural Science Foundation of China | China | 11 |
| Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development | Brazil | 5 |
| Beijing Council of Science and Technology | China | 3 |
| Chinese Academy of Sciences | China | 3 |
| German Research Foundation (DFG) | Germany | 3 |
| National Basic Research Program of China | China | 3 |
| São Paulo Research Foundation | Brazil | 3 |
| Belgian science policy under the Science for Sustainable Development program | Belgium | 2 |
| The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences | United States | 2 |
| Health Canada | Canada | 2 |
| Universidad de Los Andes | Colombia | 2 |
| Study Characteristics | Until 2008 | After 2008 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 15 (14.2%) | n = 91 (85.8%) | ||
| Journal impact factor | 8.95 | 4.38 | 0.145 |
| Citations in WoS | 42.80 | 19.22 | 0.446 |
| Citations in WoS/year | 2.31 | 2.71 | 0.149 |
| Usage count WoS ** | 7.85 | 31.75 | <0.01 |
| N. of Authors ** | 3.93 | 6.86 | <0.01 |
| N. of Institutions ** | 1.87 | 3.68 | <0.01 |
| N. of countries * | 1.13 | 1.76 | 0.017 |
| Length of study (pages) ** | 7.67 | 12.65 | <0.01 |
| Length of title * | 13.26 | 15.43 | 0.042 |
| N. of Tables | 2.80 | 3.11 | 0.284 |
| N. of Figures | 2.93 | 3.91 | 0.231 |
| N. of Keywords | 4.37 | 5.22 | 0.118 |
| N. of References ** | 22.60 | 44.48 | <0.01 |
| Number of Publications | Journals | FI | Country of Journals | Journal Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | Atmospheric Environment | 4.01 | Netherlands | Environmental Science, Earth and Planetary Sciences |
| 8 | Science of the Total Environment | 5.58 | Netherlands | Environmental Science |
| 5 | Environmental Science & Technology | 7.14 | EUA | Chemistry, Environmental Sciences and Medicine |
| 4 | Environmental Health Perspectives | 7.73 | EUA | Environmental Science, Medicine |
| 4 | Environment International | 7.94 | United Kingdom | Environmental Science |
| 4 | Environmental Research | 5.02 | EUA | Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology, Environmental Science |
| 3 | Aerosol and Air Quality Research | 2.73 | Taiwan | Environmental Science |
| 3 | Environmental Health | 4.43 | - | Environmental Science |
| 3 | Archives of Environmental Health | - | EUA | Environmental Science |
| 3 | Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine | 1.59 | EUA | Medicine |
| 3 | Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise | 4.47 | EUA | Health Professions, Medicine |
| 3 | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 2.46 | Switzerland | Environmental Science |
| 3 | PLoS ONE | 2.77 | EUA | Agricultural and Biological Sciences Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology Medicine |
| 2 | Inhalation Toxicology | 1.73 | United Kingdom | Environmental Science Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics |
| 2 | International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity | 6.03 | United Kingdom | Health Professions Medicine Nursing |
| 2 | Journal of the American Medical Association | 51.27 | EUA | Medicine |
| 1 | 43 journals | 0.128 until 51.27 | 7 countries | - |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrade, A.; Dominski, F.H.; Vilarino, G.T. Outdoor Air Quality of Environments Used for Exercise and Sports Practice: An Analysis of Scientific Production through Bibliometric Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4540. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104540
Andrade A, Dominski FH, Vilarino GT. Outdoor Air Quality of Environments Used for Exercise and Sports Practice: An Analysis of Scientific Production through Bibliometric Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4540. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104540
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrade, Alexandro, Fábio Hech Dominski, and Guilherme Torres Vilarino. 2021. "Outdoor Air Quality of Environments Used for Exercise and Sports Practice: An Analysis of Scientific Production through Bibliometric Analysis" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4540. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104540
APA StyleAndrade, A., Dominski, F. H., & Vilarino, G. T. (2021). Outdoor Air Quality of Environments Used for Exercise and Sports Practice: An Analysis of Scientific Production through Bibliometric Analysis. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4540. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104540