Ruthenium–Thymine Acetate Binding Modes: Experimental and Theoretical Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
2.2. Experimental Procedure
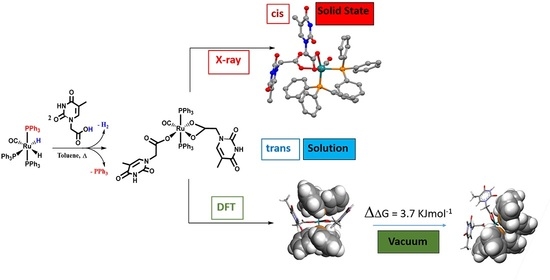
2.2.1. Synthesis of Complex. κ1O)-THA κ2(O,O)-THAc-[Ru(CO)(PPh3)2], 2
2.2.2. Synthesis of Complexes mer–κ1(O)THAc-[RuH(CO)(PPh3)3] (3a, 3b) + trans(P,P)-κ2(O,O)THAc -[RuH(CO)(PPh3)2], 4
2.3. Reactions of 1 with Acetic Acid
2.4. X-ray Crystallography
2.5. Computational Details
3. Results
3.1. Reactions of [Ru(CO)H2(PPh3)3] 1 with THAcOH
3.2. Studies on the Reaction Path: Isolation of the Intermediates mer–κ1(O)-THAc [Ru(CO)H(PPh3)3] 3a, 3b and trans(P,P)-[κ2(O,O)-THAc-[Ru(CO)H(PPh3)2] 4
3.3. DFT Theoretical Calculations
3.4. Reactions of 1 with AcOH and DFT Calculations
3.5. Intra or Inter-Molecular Bonding Network?
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergamo, A.; Masi, A.; Peacock, A.F.A.; Habtemariam, A.; Sadler, P.J.; Sava, G. In vivo tumour and metastasis reduction and in vitro effects on invasion assays of the ruthenium RM175 and osmium AFAP51 organometallics in the mammary cancer model. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2010, 104, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessio, E. Thirty Years of the Drug Candidate NAMI-A and the Myths in the Field of Ruthenium Anticancer Compounds: A Personal Perspective. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 12, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, T.S.; Santos, F.; Côrte-Real, L.; Marques, F.; Robalo, M.P.; Amorim Madeira, P.J.; Garcia, M.H. Biological activity and cellular uptake of [Ru(η5-C5H5)(PPh3)(Me2bpy)][CF3SO3] complex. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 122, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allardyce, C.S.; Dyson, P.J. Ruthenium in Medicine: Current Clinical Uses and Future Prospects. Platin. Metals Rev. 2001, 45, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Gasser, G.; Ott, I.; Metzler-Nolte, N. Organometallic anticancer compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frezza, M.; Hindo, S.; Chen, D.; Davenport, A.; Schmitt, S.; Tomco, D.; Ping Dou, Q. Novel metals and metal complexes as platforms for cancer therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 1813–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Silva, D.O.; Pinto, D. Anticancer Natural Coumarins as Lead Compounds for the Discovery of New Drugs. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 312–323. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamo, A.; Gaiddon, C.; Schellens, J.H.; Beijnen, J.H.; Sava, G. Approaching tumour therapy beyond platinum drugs: Status of the art and perspectives of ruthenium drug candidates. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 106, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messori, L.; Merlino, A. Ruthenium metalation of proteins: The X-ray structure of the complexformed between NAMI-A and hen egg white lysozyme. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 6128–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motswainyana, W.M.; Ajibade, P.A. Anticancer Activities of Mononuclear Ruthenium(II) Coordination Complexes. Adv. Chem. 2015, 2015, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dragutan, I.; Dragutan, V.; Demonceau, A. The Expanding Chemistry of the Ruthenium Complexes. Molecules 2015, 20, 17244–17274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Wang, F.; Habtemariam, A.; Luo, Q.; Li, X.; Wu, K.; Sadler, P.J.; Xiong, S. Organometallic ruthenium anticancer complexes inhibit human glutathione-S-transferase π. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 128, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Shamsi, F.; Azam, A. Editorial of Special Issue Ruthenium Complex: The Expanding Chemistry of the Ruthenium Complexes. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 772–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostova, I. Ruthenium complexes as anticancer agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 1085–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadler, P.J.; Guo, Z. Metal complexes in medicine: Design and mechanism of action. Pure Appl. Chem. 1998, 70, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ang, W.H.; Dyson, P.J. Classical and Non-Classical Ruthenium-Based Anticancer Drugs: Towards Targeted Chemotherapy. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 2006, 4003–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.J. Ruthenium metallopharmaceuticals. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003, 236, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, N.V. On the enzymatic activity of albumin. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2015, 41, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J.; Villa, M.D.; Rodriguez, V.; Cutillas, N.; Vicente, C.; Lopez, G.; Bautista, D. A novel Metal-binding mode of thymine nucleobases: N(3) and O(4) chelation. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 548–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sletten, E. Metal binding to nucleic acid—A journey from the beginning. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2016, 452, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, B. Multiplicity of metal ion binding patterns to nucleobases. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2000, 200–202, 487–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Lima, A.; Castro Pereira, F.; Pinheiro Almeida, M.A.; Santos Mello, F.M.; Carvalho Pires, W.; Monteiro Pinto, T.; Delella, F.K.; Felisbino, S.L.; Moreno, V.; Azevedo Batista, A.; et al. Novel piplartine-containing ruthenium complexes: Synthesis, cell growth inhibition, apoptosis induction and ROS production on HCT116 cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105865. [Google Scholar]
- Lippert, B.; Sanz Miguel, P.J. The Renaissance of Metal−Pyrimidine Nucleobase Coordination Chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; van Beijnum, J.R.; Casini, A.; Nazarov, A.A.; Wagnieres, G.; van den Bergh, H.; Dyson, P.J.; Griffioen, A.W. Organometallic ruthenium(II) arene compounds with antiangiogenic activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3895–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, T. The hydrogen bond in the solid state. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 48–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, B. Rare iminol tautomer of 1-methylthymine through metal coordination at N(3). Inorg. Chim. Acta 1981, 55, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schollhorn, H.; Thewalt, U.; Lippert, B. Metal-Stabilized Rare Tautomers of Nucleobases. 2.′2-Oxo-4-hydroxo Form of Uracil: Crystal Structures and Solution Behavior of Two Platinum (II) Complexes Containing Imino1 Tautomers of l-Methyluracile. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 7213–7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, B.; Neugebauer, D. Simultaneous Binding of Two Different Transition Metals to the DNA Model Base I-Methylthymine: The X-ray Structure of Bis[bis(p-1-methylthyminato-N3,04)-cis-diammineplatinum (II)] Silver Nitrate Pentahydrate. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1980, 46, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, B. Effects of metal-ion binding on nucleobase pairing: Stabilization, prevention and mismatch formation. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1997, 21, 3971–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruning, W.; Ascaso, I.; Freisinger, E.; Sabat, M.; Lippert, B. Metal-stabilized rare tautomers of nucleobases. 8. Promotion of rare cytosine tautomer upon complex formation with (dien)M2_ (M_/Pt, Pd). Inorg. Chim. Acta 2002, 339, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samouei, H.; Miloserdov, F.M.; Escudero-Adan, E.C.; Grushin, V.V. Solid-state structure and solution reactivity of [(Ph3P)4Ru(H)2] and related Ru(II) complexes used in catalysis: A reinvestigation. Oragnometallics 2014, 33, 7279–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SMART & SAINT Software Reference Manuals, Version 5.051 (Windows NT Version); Bruker Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1998.
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS Program for Empirical Absorption Correction; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Altomare, A.; Cascarano, G.; Giacovazzo, C.; Guagliardi, A.; Moliterni, A.G.G.; Burla, M.C.; Polidori, G.; Camalli, M.; Siliqi, D. SIRWARE: A universal data exchange format for crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1996, 52, C79. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXTL Plus (Windows NT Version) Structure Determination Package, Version 5.1; Bruker Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, H.-J.; Knowles, P.J.; Knizia, G.; Manby, F.R.; Schütz, M. Molpro: A general-purpose quantum chemistry program package. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2012, 2, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, P.J.; Wadt, W.R. Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for the transition-metal atoms Sc to Hg. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density–functional thermochemistry III: The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samouei, H.; Grushin, V.V. New, Highly Efficient, Simple, Safe, and Scalable Synthesis of [1-(Carboxy-methyl)-thymine; (Ph3P)3Ru(CO)(H)2]. Organometallics 2013, 32, 4440–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynam, J.M.; Welby, C.E.; Whitwood, A.C. Exploitation of a Chemically Non-innocent Acetate Ligand in the Synthesis and Reactivity of Ruthenium Vinylidene Complexes. Organometallics 2009, 28, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welby, C.E.; Eschemann, T.O.; Unsworth, C.A.; Smith, E.J.; Thatcher, R.J.; Whitwood, A.C.; Lynam, J.M. Ruthenium Acetate Complexes as Versatile Probes of Metal-Ligand Interactions: Insight into the Ligand Effects of Vinylidene, Carbene, Carbonyl, Nitrosyl and Isocyanide. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2012, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akitt, J.W.; Mann, B.E. NMR and Chemistry. An Introduction to Modern NMR Spectroscopy, 4th ed.; Stamley Thornes: Cheltenham, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, M.; George, M.W.; Moore, J.N.; Pattison, D.I.; Perutz, R.N.; Virrels, I.G.; Ye, T.-Q. Ultrafast reductive elimination of Hydrogen from a metal carbonyl dihydride complex; A study by time-resolved and visible spectroscopy. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1997, 17, 2857–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procacci, B.; Duckett, S.B.; George, M.W.; Hanson-Heine, M.W.D.; Horwath, R.; Perutz, R.N.; Sun, X.-Z.; Vuong, K.Q.; Welch, J.A. Competing Pathways in the Photochemistry of Ru(H)2(CO)(PPh3)3. Organometallics 2018, 37, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao-Chang, L.; Feng, W.; Ding, J.C. 1-(Carboxy-methyl)-hymine. Acta Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 1611. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanein, K.; Zamora, F.; Castillo, O.; Amo-Ochoa, P. Supramolecular interactions in Cobalt (II)–nucleobases complexes: A methyl matter. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2016, 452, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawinecki, R.; Kuczek, A.; Kolehmainen, E.; Osmialowski, B.; Krygowski, T.M.; Kauppinen, R. Influence of bond fixation in Benzo-annulated N-salicyldeneanilines and their ortho-C(=O)X derivatives (X=CH3, NH2, OCH3) on tautomeric equilibria in solution. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 4498–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanein, K.; Castillo, O.; Gómez-García, C.J.; Zamora, F.; Amo-Ochoa, P. Asymmetric and Symmetric Dicopper(II) Paddle-Wheel Units with Modified Nucleobases. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 5485–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendier, L.; Sabo-Etienne, S. Borane–Mediated Carbon Dioxide Reduction at Ruthenium: Formation of C1 and C2 Compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1671–1674. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, S.D.; Uttley, M.F. Complexes of the platinum metals. Part II. Carboxylato (triphenylphosphine) derivatives of ruthenium, osmium, rhodium, and iridium. Dalton Trans. 1973, 18, 1912–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, J.; Freeman, N.J. β-diketone interaction. Part 5: Solvent effect on the keto-enol equilibrium. J. Mol. Struct. 1987, 161, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, S. Variety in the coordination modes of β-dicarbonyl compounds in metal complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1986, 70, 51–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, V.R.S.; Freire, M.; Barbosa, D.P.; Bezerra, L.; Bomfim, D.R.; Moreira, M.B.; Soares, J.A.; Ellena, J.; Batista, A.A. Ru(II)-thyminate complexes: New metallodrug candidates against tumor cells. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 6794–6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, R.S.; Bomfim, L.M.; Oliveira, K.M.; Moreirab, D.R.M.; Soares, M.B.P.; Ellena, J.; Bezerra, D.P.; Batista, A.A. Ru(II) complexes containing uracil nucleobase analogs with cytotoxicity against tumor cells. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 198, 110751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza Oliveira, M.; Dantas de Santana, A.A.; Correa, R.S.; Botelho, M.; Soares, P.; Batista, A.A.; Bezerra, D.P. Ru(II)-Thymine Complex Causes Cell Growth Inhibition and Induction of Caspase-Mediated Apoptosis in Human Promyelocytic Leukemia HL-60 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1609–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.S.; Tokmakoff, A. Identification of Lactam-Lactim Tautomers of Aromatic Heterocycles in Aqueous Solution Using 2D IR Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 3, 3302–3306. [Google Scholar]


 Expected intermolecular Watson-Crick H-interactions Å NH-OC between two adjacent THAc rings.
Expected intermolecular Watson-Crick H-interactions Å NH-OC between two adjacent THAc rings.  OC(O)-H (C5H5-P) between the κ1-THAc C(O)O and the proton belonging to a phenyl of PPh3 of the adjacent molecule O6-H45 (2.51) O-H31 (2.44) N2H-O7 (2.12) N4H-O4 (2.05).
OC(O)-H (C5H5-P) between the κ1-THAc C(O)O and the proton belonging to a phenyl of PPh3 of the adjacent molecule O6-H45 (2.51) O-H31 (2.44) N2H-O7 (2.12) N4H-O4 (2.05).  π–π stacking between two aromatic rings (3.6 Å) of THAc ring belonging to opposite molecules.
π–π stacking between two aromatic rings (3.6 Å) of THAc ring belonging to opposite molecules.
 Expected intermolecular Watson-Crick H-interactions Å NH-OC between two adjacent THAc rings.
Expected intermolecular Watson-Crick H-interactions Å NH-OC between two adjacent THAc rings.  OC(O)-H (C5H5-P) between the κ1-THAc C(O)O and the proton belonging to a phenyl of PPh3 of the adjacent molecule O6-H45 (2.51) O-H31 (2.44) N2H-O7 (2.12) N4H-O4 (2.05).
OC(O)-H (C5H5-P) between the κ1-THAc C(O)O and the proton belonging to a phenyl of PPh3 of the adjacent molecule O6-H45 (2.51) O-H31 (2.44) N2H-O7 (2.12) N4H-O4 (2.05).  π–π stacking between two aromatic rings (3.6 Å) of THAc ring belonging to opposite molecules.
π–π stacking between two aromatic rings (3.6 Å) of THAc ring belonging to opposite molecules.










| Solvent, rfx | Ru/AcH Ratio | Time (min) | Species | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHCl3 | 1:2 | 240 | 7 | 65 |
| CDCl3 r.t. | 1:1 | 14 h (r.t); | 5 + 6 | 50 (6) + 38 (5) |
| CDCl3 | 1:2 | 30 | 7 | 50 (7) |
| CH2Cl2 | 1:2 | 40 | 5 | 70 |
| toluene | 1:1 | 240 | 5 + 6 | 70 (5) + 30 (6) |
| CPME | 1:2 | 40 | 7 | 70 (7) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bordoni, S.; Cerini, S.; Tarroni, R.; Monari, M.; Micheletti, G.; Boga, C. Ruthenium–Thymine Acetate Binding Modes: Experimental and Theoretical Studies. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3113. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073113
Bordoni S, Cerini S, Tarroni R, Monari M, Micheletti G, Boga C. Ruthenium–Thymine Acetate Binding Modes: Experimental and Theoretical Studies. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(7):3113. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073113
Chicago/Turabian StyleBordoni, Silvia, Stefano Cerini, Riccardo Tarroni, Magda Monari, Gabriele Micheletti, and Carla Boga. 2021. "Ruthenium–Thymine Acetate Binding Modes: Experimental and Theoretical Studies" Applied Sciences 11, no. 7: 3113. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073113
APA StyleBordoni, S., Cerini, S., Tarroni, R., Monari, M., Micheletti, G., & Boga, C. (2021). Ruthenium–Thymine Acetate Binding Modes: Experimental and Theoretical Studies. Applied Sciences, 11(7), 3113. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073113