Reliability and Agreement of Three Devices for Measuring Implant Stability Quotient in the Animal Ex Vivo Model
Abstract
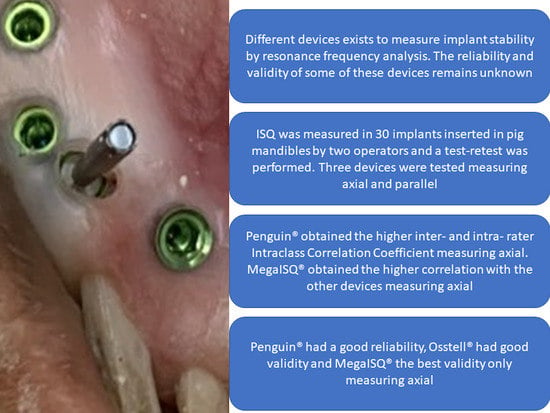
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turkyilmaz, I.; Sennerby, L.; Tumer, C.; Yenigul, M.; Avci, M. Stability and marginal bone level measurements ofunsplinted implants used for mandibular overdentures: A 1-year randomized prospective clinical study comparingearly and conventional loading protocols. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2006, 17, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huwiler, M.; Pjeturson, B.E.; Bosshardt, D.D.; Salvi, G.E.; Lang, N.P. Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA) in relation to jaw bone characteristics during early healing. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2007, 18, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trisi, P.; Perfetti, G.; Baldoni, E.; Berardi, D.; Colagiovanni, M.; Scogna, G. Implant micromotion is related to peak insertion torque and bone density. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, W.; Klein, D.; Karl, M. Micromotion of dental implants: Basic mechanical considerations. J. Med. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brizuela-Velasco, A.; Alvarez-Arenal, A.; Gil-Mur, F.J.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Chávarri-Prado, D.; Chento-Valiente, Y.; Dieguez-Pereira, M. Relationship between torque and resonance frequency measurements, performed by resonance frequency analysis, in micromobility of dental implants: An in vitro study. Implant Dent. 2015, 24, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanetti, E.M.; Ciaramella, S.; Calì, M.; Pascoletti, G.; Martorelli, M.; Asero, R.; Watts, D.C. Modal analysis for implant stability assessment: Sensitivity of this methodology for different implant designs. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atsumi, M.; Park, S.H.; Wang, H.L. Methods used to assess implant stability: Current status. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2007, 22, 743–754. [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio, C.; Lang, N.P.; Rangert, B. Validity and clinical significance of biomechanical testing of implant/bone interface. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2006, 17 (Suppl. S2), 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Shin, Y.H.; Park, J.H.; Shim, J.H.; Shin, S.W.; Lee, J.Y. The reliability of anycheck device related to healing abutment diameter. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2020, 12, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brizuela-Velasco, A.; Chávarri-Prado, D. The functional loading of implants increases their stability: A retrospective clinical study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santamaría-Arrieta, G.; Brizuela-Velasco, A.; Fernández-González, F.J.; Chávarri-Prado, D.; Chento-Valiente, Y.; Solaberrieta, E.; Chávarri-Prado, D.; Chento-Valiente, Y.; Solaberrieta, E. Biomechanical evaluation of oversized drilling technique on primary implant stability measured by insertion torque and resonance frequency analysis. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2016, 1, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buyukguclu, G.; Ozkurt-Kayahan, Z.; Kazazoglu, E. Reliability of the Osstell implant stability quotient and Penguin resonance frequency analysis to evaluate implant stability. Implant Dent. 2018, 27, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanos, G.E.; Bastardi, D.J.; Kakar, A.; Moore, R.; Delgado-Ruiz, R.A.; Javed, F. In vitro comparison of resonance frequency analysis devices to evaluate implant stability of narrow diameter implants at varying drilling speeds in dense artificial bone blocks. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bural, C.; Dayan, C.; Geçkili, O. Initial stability measurements of implants using a new magnetic resonance frequency analyzer with titanium transducers: An ex vivo study. J. Oral Implantol. 2020, 46, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, M.R. Resonance Frequency Analysis: Agreement and correlation of implant stability quotients between three commercially available instruments. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Pyo, S.W.; Cho, H.J.; An, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Koo, K.T.; Lee, Y.M. Comparison of implant stability measurements between a resonance frequency analysis device and a modified damping capacity analysis device: An in vitro study. J. Periodontal. Implant Sci. 2020, 50, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker, W.; Hujoel, P.; Becker, B.E. Resonance frequency analysis: Comparing two clinical instruments. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, C.P.; Lang, N.P. Factors influencing resonance frequency analysis assessed by Osstell mentor during implant tissue integration: I. Instrument positioning, bone structure, implant length. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2010, 21, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kästel, I.; de Quincey, G.; Neugebauer, J.; Sader, R.; Gehrke, P. Does the Manual Insertion Torque of Smartpegs Affect the Outcome of Implant Stability Quotients (ISQ) During Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA)? Int. J. Implant Dent. 2019, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Device | Technique | ISQ | Difference with Mean ISQ Values 62.1 (59.2 to 65) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OSSTELL® Beacon | parallel | 62.2 (59.5 to 64.9) | 0.1 (−0.1 to 0.1) |
| perpendicular | 60.6 (58.0 to 63.3) | −1.5 (−1.7 to −1.15) | |
| PENGUIN® | parallel | 66.3 (62.4 to 70.1) | 4.2 (3.25 to 5.1) |
| perpendicular | 63.1 (60.0 to 66.3) | 1 (0.85 to 1.3) | |
| MEGAISQ® | parallel | 60.1 (57.5 to 62.6) | −2 (−2.4 to −1.65) |
| perpendicular | 60.2 (57.5 to 62.8) | −1.9 (−2.2 to −1.65) |
| Reliability | ICC Classification | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INTER-RATER | INTRA-RATER | |||
| METHOD | ICC (95% CI) | ICC (95% CI) | ||
| OSSTELL®B parallel | 0.37 (0.40 to 0.64) | poor | 0.65 (0.38 to 0.81) | moderate |
| OSSTELL®B perpendicular | 0.20 (−0.17 to 0.52) | poor | 0.47 (0.13 to 0.71) | poor |
| PENGUIN® parallel | 0.86 (0.72 to 0.93) | good | 0.85 (0.70 to 0.92) | good |
| PENGUIN® perpendicular | 0.57 (0.26 to 0.77) | moderate | 0.78 (0.56 to 0.89) | good |
| MEGAISQ® parallel | 0.26 (−0.11 to 0.57) | poor | 0.60 (0.26 to 0.79) | moderate |
| MEGAISQ® perpendicular | −0.01 (−0.38 to 0.36) | poor | 0.57 (0.27 to 0.77) | moderate |
| Osstell® Beacon Parallel | Osstell® Beacon Perpend. | PENGUIN® Parallel | PENGUIN® Perpend. | MEGAISQ® Parallel | MEGAISQ® Perpend. | TOTAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSSTELL® Beacon parallel | 1 | 0.723 ** | 0.667 ** | 0.555 ** | 0.766 ** | 0.405 ** | 4.12 |
| OSSTELL® Beacon perpend. | 0.723 ** | 1 | 0.575 ** | 0.652 ** | 0.653 ** | 0.525 ** | 4.13 |
| PENGUIN® parallel | 0.667 ** | 0.575 ** | 1 | 0.760 ** | 0.691 ** | 0.298 * | 3.99 |
| PENGUIN® perpend. | 0.555 ** | 0.652 ** | 0.760 ** | 1 | 0.675 ** | 0.404 ** | 4.05 |
| MEGAISQ® parallel | 0.766 ** | 0.653 ** | 0.691 ** | 0.675 ** | 1 | 0.449 ** | 4.23 |
| MEGAISQ® perpend. | 0.405 ** | 0.525 ** | 0.298 * | 0.404 ** | 0.449 ** | 1 | 3.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blazquez-Hinarejos, M.; Saka-Herrán, C.; Diez-Alonso, V.; Ayuso-Montero, R.; Velasco-Ortega, E.; Lopez-Lopez, J. Reliability and Agreement of Three Devices for Measuring Implant Stability Quotient in the Animal Ex Vivo Model. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083453
Blazquez-Hinarejos M, Saka-Herrán C, Diez-Alonso V, Ayuso-Montero R, Velasco-Ortega E, Lopez-Lopez J. Reliability and Agreement of Three Devices for Measuring Implant Stability Quotient in the Animal Ex Vivo Model. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(8):3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083453
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlazquez-Hinarejos, Monica, Constanza Saka-Herrán, Victor Diez-Alonso, Raul Ayuso-Montero, Eugenio Velasco-Ortega, and Jose Lopez-Lopez. 2021. "Reliability and Agreement of Three Devices for Measuring Implant Stability Quotient in the Animal Ex Vivo Model" Applied Sciences 11, no. 8: 3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083453
APA StyleBlazquez-Hinarejos, M., Saka-Herrán, C., Diez-Alonso, V., Ayuso-Montero, R., Velasco-Ortega, E., & Lopez-Lopez, J. (2021). Reliability and Agreement of Three Devices for Measuring Implant Stability Quotient in the Animal Ex Vivo Model. Applied Sciences, 11(8), 3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083453