Laser Ablation ICP-MS Analysis of Chemically Different Regions of Rat Prostate Gland with Implanted Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Chemical Analysis of a Prostate Gland
1.2. Mineral Compounds in Prostate Gland Cancer
1.3. ROI Concept
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Material
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Instrumentation
2.4. Sample Treatment
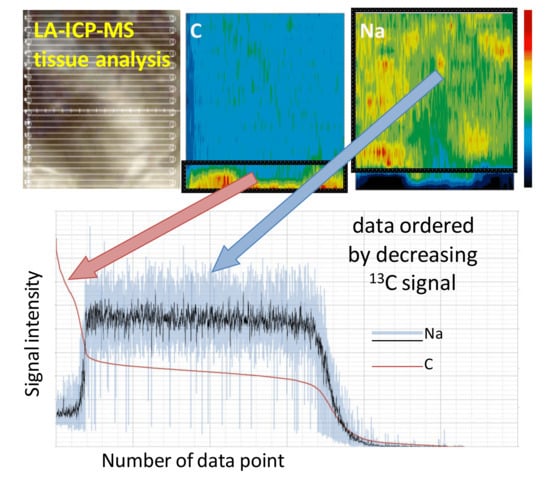
2.5. Data Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.J.; Minas, T.Z.; Ambs, S. Analysis of Tumor Biology to Advance Cancer Health Disparity Research. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panigrahi, G.K.; Praharaj, P.P.; Kittaka, H.; Mridha, A.R.; Black, O.M.; Singh, R.; Mercer, R.; van Bokhoven, A.; Torkko, K.C.; Agarwal, C.; et al. Exosome proteomic analyses identify inflammatory phenotype and novel biomarkers in African American prostate cancer patients. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1110–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frattaroli, J.; Weidner, G.; Dnistrian, A.M.; Kemp, C.; Daubenmier, J.J.; Marlin, R.O.; Crutchfield, L.; Yglecias, L.; Carroll, P.R.; Ornish, D. Clinical Events in Prostate Cancer Lifestyle Trial: Results From Two Years of Follow-Up. Urology 2008, 72, 1319–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.H. Nutrition and prostate cancer: An overview. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2014, 14, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Navarro Rosenblatt, D.A.; Chan, D.S.; Vieira, A.R.; Vieira, R.; Greenwood, D.C.; Vatten, L.J.; Norat, T. Dairy products, calcium, and prostate cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 87–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lippman, S.M.; Klein, E.A.; Goodman, P.J.; Lucia, M.S.; Thompson, I.M.; Ford, L.G.; Parnes, H.L.; Minasian, L.M.; Gaziano, J.M.; Hartline, J.A.; et al. Effect of Selenium and Vitamin E on Risk of Prostate Cancer and Other Cancers. JAMA 2009, 301, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swami, S.; Krishnan, A.V.; Feldman, D. Vitamin D Metabolism and Action in the Prostate: Implications for Health and Disease. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 347, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregg, J.R.; Zheng, J.; Lopez, D.S.; Reichard, C.; Browman, G.; Chapin, B.; Kim, J.; Davis, J.; Daniel, C.R. Diet quality and Gleason grade progression among localised prostate cancer patients on active surveillance. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, L.C.; Franklin, R.B. A comprehensive review of the role of zinc in normal prostate function and metabolism; and its implications in prostate cancer. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 611, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nyman, D.W.; Stratton, M.S.; Kopplin, M.J.; Dalkin, B.L.; Nagle, R.B.; Gandolfi, A.J. Selenium and selenomethionine levels in prostate cancer patients. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2004, 28, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doble, P.A.; Miklos, G.L.G. Distributions of manganese in diverse human cancers provide insights into tumour radioresistance. Metallomics 2018, 10, 1191–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bishop, D.P.; Clases, D.; Fryer, F.; Williams, E.; Wilkins, S.; Hare, D.J.; Cole, N.; Karst, U.; Doble, P.A. Elemental bio-imaging using laser ablation-triple quadrupole-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2016, 31, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiziler, A.R.; Aydemir, B.; Guzel, S.; Alici, B.; Ataus, S.; Tuna, M.B.; Durak, H.; Kilic, M. May the level and ratio changes of trace elements be utilized in identification of disease progression and grade in prostatic cancer? Trace Elem. Electrolytes 2010, 27, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaichick, V.; Zaichick, S. Use of INAA and ICP-MS for the assessment of trace element mass fractions in adult and geriatric prostate. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2014, 301, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaichick, V.; Zaichick, S. Ratios of Cadmium/Trace Element Contents in Prostate Gland as Carcinoma’s Markers. Canc. Ther. Oncol. Int. J. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, R.G.; Palumbo, A.; Souza, P.A.V.R.; Pereira, G.R.; Canellas, C.G.L.; Anjos, M.J.; Nasciutti, L.E.; Lopes, R.T. Elemental concentration analysis in prostate tissues using total reflection X-ray fluorescence. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 95, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.P.; Dwivedi, S.; Dhakad, U.; Murthy, R.C.; Choubey, V.K.; Goel, A.; Sankhwar, S.N. Status and Interrelationship of Zinc, Copper, Iron, Calcium and Selenium in Prostate Cancer. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 31, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinceti, M.; Venturelli, M.; Sighinolfi, C.; Trerotoli, P.; Bonvicini, F.; Ferrari, A.; Bianchi, G.; Serio, G.; Bergomi, M.; Vivoli, G. Case-control study of toenail cadmium and prostate cancer risk in Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 373, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daragó, A.; Sapota, A.; Nasiadek, M.; Klimczak, M.; Kilanowicz, A. The effect of zinc and selenium supplementation mode on their bioavailability in the rat prostate. Should administration be joint or separate? Nutrients 2016, 8, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, K.H.; Bradley, D.A.; Looi, L.M. Elevated trace element concentrations in malignant breast tissues. Br. J. Radiol. 1997, 70, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durak, I.; Kavutcu, M.; Canbolat, O.; Işik, A.U.; Akyol, O. Concentrations of some major and minor elements in larynx tissues with and without cancer. Biometals 1994, 7, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Motley, S.S.; Smith, J.A.; Concepcion, R.; Barocas, D.; Byerly, S.; Fowke, J.H. Blood magnesium, and the interaction with calcium, on the risk of high-grade prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Ebraheem, A.; Farquharson, M.J.; Ryan, E. The evaluation of biologically important trace metals in liver, kidney and breast tissue. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christudoss, P.; Selvakumar, R.; Fleming, J.J.; Gopalakrishnan, G. Zinc status of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate carcinoma. Indian J. Urol. 2011, 27, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapota, A.; Daragó, A.; Taczalski, J.; Kilanowicz, A. Disturbed homeostasis of zinc and other essential elements in the prostate gland dependent on the character of pathological lesions. BioMetals 2009, 22, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachara, B.A.; Marchaluk-Wiśniewska, E.; Maciag, A.; Pepliński, J.; Skokowski, J.; Lambrecht, W. Decreased selenium concentration and glutathione peroxidase activity in blood and increase of these parameters in malignant tissue of lung cancer patients. Lung 1997, 175, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Wang, C.; Yu, W.; Fan, W.; Wang, S.; Shen, N.; Wu, P.; Li, X.; Wang, F. Selenium Exposure and Cancer Risk: An Updated Meta-analysis and Meta-regression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.-Y.; Chu, Y.-J.; Gong, X.-L.; Hou, C.; Li, W.-G.; Gong, H.-M.; Xie, J.-R. Regional variation of cancer mortality incidence and its relation to selenium levels in China. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1985, 7, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daragó, A.; Sapota, A.; Duda-Szymańska, J. Levels of cadmium, zinc, copper and selenium in subjects with diagnosed prostate cancer. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2003, 54, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Venkateswaran, V.; Fleshner, N.E.; Klotz, L.H. Modulation of cell proliferation and cell cycle regulators by vitamin E in human prostate carcinoma cell lines. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 1578–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalabopoulos, K.; Kotsalos, A.; Batistatou, A.; Charalabopoulos, A.; Vezyraki, P.; Peschos, D.; Kalfakakou, V.; Evangelou, A. Selenium in serum and neoplastic tissue in breast cancer: Correlation with CEA. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Wennemuth, G. Ca2+ clearance mechanisms in cancer cell lines and stromal cells of the prostate. Prostate 2014, 74, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.D.; Whitley, B.M.; Hoyo, C.; Grant, D.J.; Schwartz, G.G.; Presti, J.C.; Iraggi, J.D.; Newman, K.A.; Gerber, L.; Taylor, L.A.; et al. Dietary calcium and risk for prostate cancer: A case- control study among US veterans. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2012, 9, E39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skrajnowska, D.; Bobrowska-Korczak, B.; Tokarz, A. Disorders of mechanisms of calcium metabolism control as potential risk factors of prostate cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 4229–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Kaaks, R.; Linseisen, J.; Rohrmann, S. Dietary calcium and magnesium intake in relation to cancer incidence and mortality in a German prospective cohort (EPIC-Heidelberg). Cancer Causes Control 2011, 22, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonithon-Kopp, C.; Kronborg, O.; Giacosa, A.; Räth, U.; Faivre, J. Calcium and fibre supplementation in prevention of colorectal adenoma recurrence: A randomised intervention trial. Lancet 2000, 356, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banas, A.; Kwiatek, W.M.; Banas, K.; Gajda, M.; Pawlicki, B.; Cichocki, T. Correlation of concentrations of selected trace elements with Gleason grade of prostate tissues. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 15, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ludwig, H.; Evstatiev, R.; Kornek, G.; Aapro, M.; Bauernhofer, T.; Buxhofer-Ausch, V.; Fridrik, M.; Geissler, D.; Geissler, K.; Gisslinger, H.; et al. Iron metabolism and iron supplementation in cancer patients. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2015, 127, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torti, S.V.; Torti, F.M. Iron and cancer: More ore to be mined. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Z.; Dai, L.L.; Song, Y.N.; Kang, Y.; Si, J.M.; Xia, J.; Liu, Y.F. Regulatory effect of iron regulatory protein-2 on iron metabolism in lung cancer. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 5514–5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theophanides, T.; Anastassopoulou, J. Copper and carcinogenesis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 42, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denoyer, D.; Clatworthy, S.A.S.; Masaldan, S.; Meggyesy, P.M.; Cater, M.A. Heterogeneous copper concentrations in cancerous human prostate tissues. Prostate 2015, 75, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.; Lago, L.; Gonzalez De Vega, R.; Bray, L.; Hare, D.J.; Clases, D.; Doble, P.A.; Adlard, P.A. Characterising the spatial and temporal brain metal profile in a mouse model of tauopathy. Metallomics 2020, 12, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusch, A.; Depboylu, C.; Palm, C.; Wu, B.; Höglinger, G.U.; Schäfer, M.K.H.; Becker, J.S. Cerebral Bioimaging of Cu, Fe, Zn, and Mn in the MPTP Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease Using Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 21, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franklin, K.; Paxinos, G. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; ISBN 9780123742445. [Google Scholar]
- Opačić, M.; Ristić, A.J.; Sokić, D.; Baščarević, V.; Raičević, S.; Savić, S.; Zorović, M.; Živin, M.; Simon, V.; Spasojević, I.; et al. Regional distribution of cytochrome c oxidase activity and copper in sclerotic hippocampi of epilepsy patients. Brain Behav. 2020, 11, e01986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvernoy, H.M.; Cattin, F.; Risold, P.-Y. The Human Hippocampus Functional Anatomy, Vascularization and Serial Sections with MRI, 3rd ed.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fingerhut, S.; Sperling, M.; Holling, M.; Niederstadt, T.; Allkemper, T.; Radbruch, A.; Heindel, W.; Paulus, W.; Jeibmann, A.; Karst, U. Gadolinium-based contrast agents induce gadolinium deposits in cerebral vessel walls, while the neuropil is not affected: An autopsy study. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiner, S.; Schweikert, A.; Van Malderen, S.J.M.; Schoeberl, A.; Neumayer, S.; Jilma, P.; Peyrl, A.; Koellensperger, G. Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Trace Elements at the Single-Cell Level for Clinical Practice. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 8207–8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaly, N.; Pugh, J.A.; Kalber, T.L.; Bunch, J.; Miller, A.D.; McLeod, C.W.; Bell, J.D. Imaging of gadolinium spatial distribution in tumor tissue by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2010, 12, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radbruch, A.; Richter, H.; Fingerhut, S.; Martin, L.F.; Xia, A.; Henze, N.; Paulus, W.; Sperling, M.; Karst, U.; Jeibmann, A. Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain in a Large Animal Model: Comparison of Linear and Macrocyclic Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents. Invest. Radiol. 2019, 54, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bücker, P.; Richter, H.; Radbruch, A.; Sperling, M.; Brand, M.; Holling, M.; Van Marck, V.; Paulus, W.; Jeibmann, A.; Karst, U. Deposition patterns of iatrogenic lanthanum and gadolinium in the human body depend on delivered chemical binding forms. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 63, 126665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uca, Y.O.; Hallmann, D.; Hesse, B.; Seim, C.; Stolzenburg, N.; Pietsch, H.; Schnorr, J.; Taupitz, M. Microdistribution of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents in Atherosclerotic Plaques Determined by LA-ICP-MS and SR-μXRF Imaging. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2021, 23, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajnóg, A.; Hanć, A.; Barałkiewicz, D.; Gryszczyńska, B.; Majewski, W.; Iskra, M. Bioimaging of macro- and microelements in blood vessels with calcified plaque in atherosclerosis obliterans by LA-ICP-MS. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M-M, P.; Weiskirchen, R.; Gassler, N.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Becker, J.S. Novel Bioimaging Techniques of Metals by Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry for Diagnosis Of Fibrotic and Cirrhotic Liver Disorders. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornwilard, M.M.; Merle, U.; Weiskirchen, R.; Becker, J.S. Bioimaging of copper deposition in Wilson’s diseases mouse liver by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry imaging (LA-ICP-MSI). Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 354–355, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-García, L.J.; Gokhan Elci, S.; Vachet, R.W. Reconstruction, analysis, and segmentation of LA-ICP-MS imaging data using Python for the identification of sub-organ regions in tissues. Analyst 2020, 145, 3705–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterholt, T.; Salber, D.; Matusch, A.; Becker, J.S.; Palm, C. IMAGENA: Image Generation and Analysis—An interactive software tool handling LA-ICP-MS data. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 307, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbach, K.; Holbrook, T.; Reemtsma, T.; Wagner, S. Effective processing and evaluation of chemical imaging data with respect to morphological features of the zebrafish embryo. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.F.S.; Theiner, S.; Meibom, A.; Koellensperger, G.; Keppler, B.K.; Dyson, P.J. Application of imaging mass spectrometry approaches to facilitate metal-based anticancer drug research. Metallomics 2017, 9, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.S.; Matusch, A.; Wu, B. Bioimaging mass spectrometry of trace elements—recent advance and applications of LA-ICP-MS: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 835, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matusch, A.; Bauer, A.; Becker, J.S. Element imaging in formalin fixed slices of human mesencephalon. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 307, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.S.; Breuer, U.; Hsieh, H.F.; Osterholt, T.; Kumtabtim, U.; Wu, B.; Matusch, A.; Caruso, J.A.; Qin, Z. Bioimaging of metals and biomolecules in mouse heart by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and secondary ion mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9528–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oros-Peusquens, A.M.; Matusch, A.; Becker, J.S.; Shah, N.J. Automatic segmentation of tissue sections using the multielement information provided by LA-ICP-MS imaging and k-means cluster analysis. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 307, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagielska, A.; Ruszczyńska, A.; Wagner, B.; Bulska, E.; Skrajnowska, D.; Bobrowska-Korczak, B. ICP-MS analysis of diet supplementation influence on the elemental content of rat prostate gland. Mon. Chem. Chem. Mon. 2019, 150, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jagielska, A.; Ruszczyńska, A.; Bulska, E.; Wagner, B. The impact of sample preparation on the elemental composition of soft tissues assessed by laser ablation ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, L.A. Nomenclature in evaluation of analytical methods including detection and quantification capabilities. Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 36, T189–T195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, B.; Czajka, A. Non-invasive approximation of elemental composition of historic inks by LA-ICP-MS measurements of bathophenanthroline indicators. Talanta 2021, 222, 121520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.K.; Pitschmann, A.; Ahmad, N. Resveratrol-zinc combination for prostate cancer management. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costello, L.C.; Franklin, R.B. The clinical relevance of the metabolism of prostate cancer; zinc and tumor suppression: Connecting the dots. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krone, C.A.; Harms, L.C.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Giovannucci, E.L. Re: Zinc supplement use and risk of prostate cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 1556–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolenko, V.; Teper, E.; Kutikov, A.; Uzzo, R. Zinc and zinc transporters in prostate carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2013, 10, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sapota, A.; Daragó, A.; Skrzypińska-Gawrysiak, M.; Nasiadek, M.; Klimczak, M.; Kilanowicz, A. The bioavailability of different zinc compounds used as human dietary supplements in rat prostate: A comparative study. Biometals 2014, 27, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, E.; Laskow, T.C.; Buchser, W.J.; Pitt, B.R.; Basse, P.H.; Butterfield, L.H.; Kalinski, P.; Lotze, M.T. Zinc in innate and adaptive tumor immunity. J. Transl. Med. 2010, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, E. Zinc deficiency, DNA damage and cancer risk. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2004, 15, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainburg, T.; McInnes, L.; Gentner, T.Q. Parametric umap embeddings for representation and semisupervised learning. Neural Comput. 2021, 33, 2881–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukmanov, R.A.; Riedo, A.; Wacey, D.; Ligterink, N.F.W.; Grimaudo, V.; Tulej, M.; de Koning, C.; Neubeck, A.; Wurz, P. On Topological Analysis of fs-LIMS Data. Implications for in Situ Planetary Mass Spectrometry. Front. Artif. Intell. 2021, 4, 668163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Dietary Group | Concentration of Element/g·L−1 | Dose of Element/mg/Day/Rat | Chemical Form in Aqueous Suspension |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn-suppl (n = 12) | 4.6 | 1.85 | ZnSO4·7H2O |
| Cu-suppl (n = 12) | 0.639 | 0.256 | CuSO4·5H2O |
| Se-suppl (n = 14) | 0.018 | 0.0072 | Na2SeO4 |
| Fe-suppl (n = 10) | 7.5 | 3.0 | FeSO4·7H2O |
| Ca-suppl (n = 11) | 75 | 30 | CaCl2·6H2O |
| Standard (n = 11) | - | - | - |
| ICP-MS | LA-ICP-MS | ICP-MS [68] |
|---|---|---|
| RF power | 1350 W | 1350 W |
| Carrier gas flow rate (Ar) | 0.9 L/min | 0.9 L/min |
| Dwell time | 5 ms | 50 ms |
| Readings | 12,000 | 3 |
| Sweeps | 1 | 1 |
| Replicates | 1 | 3 |
| Monitored isotopes: | 13C, 23Na, 26Mg, 27Al, 31P, 32S, 34S, 35Cl, 39K, 44Ca, 57Fe, 65Cu, 66Zn, 78Se, 88Sr, 202Hg, 208Pb | 23Na, 24Mg, 39K, 43Ca, 57Fe, 63Cu, 66Zn, 82Se, 88Sr, 208Pb |
| Laser Ablation | ||
| Ablation mode | multi-line ablation | |
| Number of ablation lines | 15 | |
| Laser energy | 0.5 mJ | |
| Laser shot frequency | 20 Hz | |
| Spot size | 100 μm | |
| Space between lines | 100 μm | |
| Scan rate | 50 μm/s | |
| Shutter delay | 20 s | |
| Ablation time per sample | 1020 s |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruszczyńska, A.; Skrajnowska, D.; Jagielska, A.; Bobrowska-Korczak, B.; Wagner, B. Laser Ablation ICP-MS Analysis of Chemically Different Regions of Rat Prostate Gland with Implanted Cancer Cells. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031474
Ruszczyńska A, Skrajnowska D, Jagielska A, Bobrowska-Korczak B, Wagner B. Laser Ablation ICP-MS Analysis of Chemically Different Regions of Rat Prostate Gland with Implanted Cancer Cells. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(3):1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031474
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuszczyńska, Anna, Dorota Skrajnowska, Agata Jagielska, Barbara Bobrowska-Korczak, and Barbara Wagner. 2022. "Laser Ablation ICP-MS Analysis of Chemically Different Regions of Rat Prostate Gland with Implanted Cancer Cells" Applied Sciences 12, no. 3: 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031474
APA StyleRuszczyńska, A., Skrajnowska, D., Jagielska, A., Bobrowska-Korczak, B., & Wagner, B. (2022). Laser Ablation ICP-MS Analysis of Chemically Different Regions of Rat Prostate Gland with Implanted Cancer Cells. Applied Sciences, 12(3), 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031474