Application of Response Surface Methodology for Optimisation of Simultaneous UHPLC-PDA Determination of Oleanolic and Ursolic Acids and Standardisation of Ericaceae Medicinal Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Standards
2.2. UHPLC Equipment
2.3. Plant Material and Sample Preparation
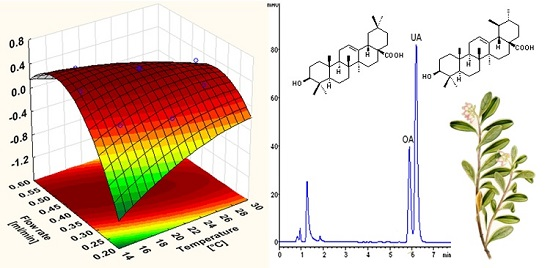
2.4. Experimental Design and Data Treatment
2.5. Validation of the Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Extraction Solvent
3.2. Optimisation of the Chromatographic Conditions
3.3. Validation of the Method
3.4. Method Application to Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J. Pharmacology of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 49, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checker, R.; Sandur, S.K.; Sharma, D.; Patwardhan, R.S.; Jayakumar, S.; Kohli, V.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Sainis, K.B. Potent Anti-inflammatory activity of ursolic acid, a triterpenoid antioxidant, is mediated through suppression of NF-kB, AP-1 and NF-AT. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolska, K.I.; Grudniak, A.M.; Fiecek, B.; Kraczkiewicz-Dowjat, A.; Kurek, A. Antibacterial activity of oleanolic and ursolic acids and their derivatives. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2010, 5, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, A.; Nadkowska, P.; Pliszka, S.; Wolska, K.I. Modulation of antibiotic resistance in bacterial pathogens by oleanolic acid and ursolic acid. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.J.; Yin, M.C. Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory protection of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid in PC12 cells. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, H174–H178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Murakami, A.; Ohigashi, H. Ursolic acid: An anti- and pro-inflammatory triterpenoid. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwery, O.; Onstein, R.E.; Bouchenak-Khelladi, Y.; Xing, Y.; Carter, R.J.; Linder, H.P. As old as the mountains: The radiation of the Ericaceae. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Sheng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J. Variation of oleanolic and ursolic acid in the flesh of persimmon fruit among different cultivars. Molecules 2010, 15, 6580–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumoska, K.; Simonovska, B.; Albreht, A.; Vovk, I. TLC and TLC-MS screening of ursolic, oleanolic and betulinic acids in plant extracts. J. Planar. Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 2013, 26, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicsak, G.; Veres, K.; Kallai, M.; Mathe, I. Gas chromatographic method for routine determination of oleanolic and ursolic acids in medicinal plants. Chromatographia 2003, 58, 295–299. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S. Determination of free isomeric oleanolic acid and ursolic acid in Pterocephalus hookeri by capillary zone electrophoresis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesellier, E.; Destandau, E.; Grigoras, C.; Fougere, L.; Elfakir, C. Fast separation of triterpenoids by supercritical fluid chromatography/evaporative light scattering detector. J. Chromatogr. A. 2012, 1268, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Chen, X.Q. A comparative study of the separation of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid in Prunella vulgaris by high-performance liquid chromatography and cyclodextrin-modified micellar electrokinetic chromatography. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2009, 6, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogianni, V.G.; Exarchou, V.; Troganis, A.; Gerothanassis, I.P. Rapid and novel discrimination and quantification of oleanolic and ursolic acids in complex plant extracts using two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy—Comparison with HPLC methods. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2009, 635, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, K.; Zhao, E.Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, L.; Yang, X.; Xie, X. Determination of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid in Chinese medicinal plants using HPLC with PAH polymeric C18. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2013, 9, S19–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszewska, M. Optimization and validation of an HPLC-UV method for analysis of corosolic, oleanolic, and ursolic acids in plant material: Application to Prunus serotina Ehrh. Acta Chromatogr. 2008, 20, 643–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X.; You, J.; Suo, Y. Determination of triterpenic acids in fruits by a novel high performance liquid chromatography method with high sensitivity and specificity. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójciak-Kosior, M.; Sowa, I.; Kocjan, R.; Nowak, R. Effect of different extraction techniques on quantification of oleanolic and ursolic acid in Lamii albi flos. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 44, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Chen, W. Determination of oleanolic and ursolic acids in different parts of Perilla frutescens by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2008, 19, 1429–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.-P.; Zhang, R.-F.; Zhang, X.-H.; Zhu, J.-H.; Huang, J.-Z. Separation of three triterpene acids in leaves of Diospyros kaki by high performance liquid chromatography using hydroxy-propyl-β-cyclodextrin as mobile phase modifier. J. Liq. Chromatogr. R. T. 2011, 34, 1340–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Guo, H. Determination of oleanolic and ursolic acid in Chinese herbs using HPLC and γ-CD as mobile phase modifier. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 3023–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Suo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; You, J.; Ji, Z.; Wang, A.; Han, L.; Lv, H.; Ye, Y. Rapid, Selective, and Sensitive Analysis of triterpenic acids in Hippophae rhamnoides L. using HPLC with pre-column fluorescent derivatization and identification with post-column APCI-MS. J. Liq. Chromatogr. R. T. 2015, 38, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-L.; You, J.-M.; Song, C.-H.; Xia, L.; Zheng, J.; Suo, Y.-R. Development of a new HPLC method with precolumn fluorescent derivatization for rapid, selective and sensitive detection of triterpenic acids in fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2972–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhang, X.; You, J.; Song, C.; Sun, Z.; Xia, L.; Suo, Y. Highly sensitive and selective pre-column derivatization high-performance liquid chromatography approach for rapid determination of triterpenes oleanolic and ursolic acids and application to Swertia species: Optimization of triterpenic acids extraction and pre-column derivatization using response surface methodology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 688, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Fen, W.; Lei, C.; Xiao, W.; Sun, H. Study on determination of pentacyclic triterpenoids in Chaenomeles by HPLC–ELSD. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2009, 47, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Lv, L.; Wang, X.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, G. Simultaneous determination of oleanolic and ursolic acids in rat plasma by HPLC–MS: Application to a pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of different combinations of QingGanSanJie decoction extracts. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 53, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnut, S.M.; Salisbury, J.J. The role of UHPLC in pharmaceutical development. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampofo-Yeboah, A.; Lambrechts, H.; Brink, D.; Hiten, F.; Afriyie-Gyawu, E. Analysis of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid, potential antifertility agents in moringa (Moringa oleifera) seed. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. A 2013, 3, 989–999. [Google Scholar]
- Guillarme, D.; Nguyen, D.T.-T.; Rudaz, S.; Veuthey, J.-L. Method transfer for fast liquid chromatography in pharmaceutical analysis: Application to short columns packed with small particle. Part I: Isocratic separation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 66, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; Bruns, R.E.; da Silva, E.G.P.; dos Santos, W.N.L.; Quintella, C.M.; David, J.M.; de Andrade, J.B.; Breitkreitz, M.C.; Jardim, I.C.S.F.; Neto, B.B. Statistical designs and response surface techniques for the optimization of chromatographic systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1158, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, R.H.; Montgomery, D.C.; Anderson-Cook, C.M. Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Derringer, G.; Suich, R. Simultaneous optimization of several response variables. J. Qual. Technol. 1980, 12, 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/UCM073384.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2014).
- Corley, J. Best practices in establishing detection and quantification limits for pesticide residues in foods. In Handbook of Residue Analytical Methods for Agrochemicals; Lee, P.W., Aizawa, H., Barefoot, A.C., Murphy, J.J., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, I.J.; Ko, Y.I.; Kim, Y.M.; Han, S.K. Solubilization of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid by cosolvency. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1997, 20, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, P.; Hosseiny, S.S.; Szczotka, M.; Jordan, V.; Schlitter, K. Rapid solubility determination of the triterpenes oleanolic acid and ursolic acid by UV-spectroscopy in different solvents. Phytochem. Lett. 2009, 2, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewska, M.A.; Michel, P. Antioxidant activity of inflorescences, leaves and fruits of three Sorbus species in relation to their polyphenolic composition. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 1507–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, J. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction followed by RP-HPLC for the simultaneous determination of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid in the fruits of Chaenomeles sinensis. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Guo, W. Comparative determination of ursolic acid and oleanolic acid of Macrocarpium officinalis (Sieb. et Zucc.) Nakai by RP-HPLC. Ind. Crops Prod. 2008, 28, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-H.; Su, Q.; Zang, Z.-H. Simultaneous determination of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid by RP-HPLC in the leaves of Eriobotrya japonica Lindl. J. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 2, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa, I.; Wójciak-Kosior, M.; Rokicka, K.; Kocjan, R.; Szymczak, G. Application of solid phase extraction with the use of silica modified with polyaniline film for pre-treatment of samples from plant material before HPLC determination of triterpenic acids. Talanta 2014, 122, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbaguidi, F.; Accrombessi, G.; Moudachirou, M.; Quetin-Leclercq, J. HPLC quantification of two isomeric triterpenic acids isolated from Mitracarpus scaber and antimicrobial activity on Dermatophilus congolensis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 39, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, F.V., Jr.; Bidiingmeyer, B.A. Influence of temperature on column efficiency in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 2024–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundstedt, T.; Seifert, E.; Abramo, L.; Thelin, B.; Nyström, Å.; Pettersen, J.; Bergman, R. Experimental design and optimization. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 1988, 42, 3–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giriraj, P.; Sivakkumar, T. Development and validation of a rapid chemometrics assisted RP-HPLC with PDA detection method for the simultaneous estimation of pyridoxine HCl and doxylamine succinate in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form. Chromatogr. Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiani, A.; Malavasi, G.; Palla, G.; Marseglia, A.; Tognolini, M.; Bruni, R. A simple GC–MS method for the screening of betulinic, corosolic, maslinic, oleanolic and ursolic acid contents in commercial botanicals used as food supplement ingredients. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, S.; Trojan, H.; Kopp, T.; Laszczyk, M.N.; Scheffler, A. Pentacyclic triterpene distribution in various plants—Rich sources for a new group of multi-potent plant extracts. Molecules 2009, 14, 2016–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szakiel, A.; Pączkowski, C.; Koivuniemi, H.; Huttunen, S. Comparison of the triterpenoid content of berries and leaves of lingonberry Vaccinium vitis-idaea from Finland and Poland. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4994–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szakiel, A.; Pączkowski, C.; Huttunen, S. Triterpenoid content of berries and leaves of bilberry Vaccinium myrtillus from Finland and Poland. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11839–11849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Run | Levels | Factors | Responses | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | FR | T (°C) | FR (mL/min) | ST (min) | Rs | D | |
| 1 | +1 | +1 | 27.0 | 0.50 | 4.583 | 1.29 | 0.000 |
| 2 | +1 | −1 | 27.0 | 0.30 | 7.591 | 1.49 | 0.228 |
| 3 | −1 | +1 | 17.0 | 0.50 | 5.561 | 1.42 | 0.442 |
| 4 | −1 | −1 | 17.0 | 0.30 | 9.265 | 1.71 | 0.000 |
| 5 | −1.41 | 0 | 15.0 | 0.40 | 7.244 | 1.59 | 0.382 |
| 6 | +1.41 | 0 | 29.1 | 0.40 | 5.501 | 1.36 | 0.316 |
| 7 | 0 | −1.41 | 22.0 | 0.26 | 9.620 | 1.66 | 0.000 |
| 8 | 0 | +1.41 | 22.0 | 0.54 | 4.660 | 1.31 | 0.141 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 22.0 | 0.40 | 6.282 | 1.50 | 0.479 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 22.0 | 0.40 | 6.289 | 1.49 | 0.466 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 22.0 | 0.40 | 6.283 | 1.49 | 0.466 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 22.0 | 0.40 | 6.286 | 1.49 | 0.466 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 22.0 | 0.40 | 6.289 | 1.49 | 0.466 |
| Response 1 | Reduced Response Model | R2 | Adjusted R2 2 | F-Value 3 | p-Value 4 | CV (%) 5 | Adequate Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST | 6.31 − 0.64T − 1.72FR + 0.42FR2 + 0.17TFR | 0.9993 | 0.9989 | 1960.31 | <0.0001 | 0.91% | 135.50 |
| Rs | 1.49 − 0.08T − 0.01T2 − 0.12FR + 0.02TFR | 0.9984 | 0.9976 | 1268.19 | <0.0001 | 0.40% | 113.43 |
| D | 0.47 − 0.04T + 0.05FR − 0.07T2 − 0.02FR2 − 0.17TFR | 0.9887 | 0.9806 | 122.57 | <0.0001 | 9.29% | 25.61 |
| Response 1 | Predicted Values | Experimental Values | Error 2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ST (min) | 6.090 | 6.200 | 1.81 |
| Rs | 1.490 | 1.500 | 0.67 |
| D | 0.495 | 0.490 | 1.01 |
| Analyte | Linearity Range (μg/mL) | Linear Regression (n) 1 | r | F-Test Value for Linear Fit 2 | LOD 3 [ng/mL (ng)] | LOQ 4 [ng/mL (ng)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA | 1.49–149.40 | y = 3.3355 x (6) | 0.99998 | 144923.04 | 47 (0.141) | 374 (1.122) |
| UA | 3.24–324.30 | y = 3.3535 x (6) | 0.99998 | 155563.173 | 51 (0.153) | 405 (1.215) |
| Authors | Method | Column | Mobile Phase | FR 1 (mL/min) | T 2 (°C) | ST 3 (min) | LOD 4 (ng) | Rs 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zou and Chen [19] | HPLC-PDA | Kromasil 100 C18 (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | MeOH:0.5% aqueous H3PO4 (88:12, v/v) | 1.0 | 25 | 19.5 | 7.8–8.4 | 2.5 |
| Fan et al. [20] | HPLC-PDA | Zorbax Eclipse XDB-C18 (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | MeOH:0.2% aqueous AcOH (85:15, v/v) + HP-β-CD (10 mmol/L) | 1.0 | 35 | 11.5 | 20.8–22.3 | 2.0 |
| Zhang et al. [15] | HPLC-UV | Ultimate XB-PAH (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | MeCN:water (85:15, v/v) | 1.0 | 25 | 16.9 | 2.1–3.3 | >3.4 |
| Sowa et al. [41] | HPLC-PDA | Supelco Discovery C18 (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | MeCN:water:1% H3PO4 (90:10:0.5 v/v/v) | 0.8 | 10 | 9.6 | 2.8–3.0 | 1.6 |
| Olszewska [16] | HPLC-UV | Nucleodur Gravity C18 (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | MeOH:1% aqueous H3PO4 (90:10, v/v) | 0.6 | 20 | 25.0 | 0.7–1.0 | 1.5 |
| Ampofo- Yeboah et al. [28] | UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS | Waters Acquity BEH C18 (100 × 2.1mm, 2.1 μm) | MeOH:10 mmol aqueous ammonium acetate (75:25, v/v) | 0.38 | 50 | 7.2 | 0.6 | 1.5 |
| present | UHPLC-PDA | Zorbax Eclipse XDB C18 (100 × 3.0, 1.8 μm) | MeOH:1% aqueous H3PO4 (90:10, v/v) | 0.44 | 18 | 6.2 | 0.1–0.2 | 1.5 |
| Analyte | Precision (RSD %) 1 | Accuracy 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level (μg/mL) | Intra-Day Variability | Inter-day Variability | Spiked Level (μg/mL) | Recovery (RSD, %) | |||
| tR | Peak Area | tR | Peak Area | ||||
| OA | 149.40 | 0.04 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 1.56 | 5 | 95.98 (1.78) |
| 52.70 | 0.12 | 0.65 | 0.44 | 1.79 | 50 | 98.32 (2.23) | |
| 14.94 | 0.14 | 1.14 | 0.39 | 2.16 | 100 | 96.75 (2.13) | |
| UA | 324.30 | 0.04 | 0.43 | 0.49 | 1.02 | 10 | 96.78 (2.38) |
| 198.11 | 0.09 | 0.93 | 0.37 | 1.33 | 100 | 97.47 (1.91) | |
| 32.43 | 0.13 | 1.22 | 0.43 | 2.46 | 200 | 97.83 (2.48) | |
| Species | OA (mg/g) 1 | UA (mg/g) 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Arctostaphylos uva ursi | 4.47 ± 0.022 D | 18.61 ± 0.233 D |
| Gaultheria procumbens | 1.58 ± 0.049 B | 5.76 ± 0.043 C |
| Vaccinium myrtillus | 1.78 ± 0.003 C | 1.30 ± 0.034 A |
| Vaccinium vitis idaea | 0.74 ± 0.008 A | 2.50 ± 0.021 B |
| Species | OA (mg/g) 1 | FOA 2 | UA (mg/g) 1 | FUA 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arctostaphylos uva ursi | 3.06 ± 0.087 D | 1.46 | 14.37 ± 0.305 D | 1.30 |
| Gaultheria procumbens | 0.84 ± 0.012 B | 1.88 | 3.71 ± 0.067 C | 1.55 |
| Vaccinium myrtillus | 1.13 ± 0.035 C | 1.57 | 0.81 ± 0.019 A | 1.60 |
| Vaccinium vitis idaea | 0.38 ± 0.018 A | 1.95 | 1.57 ± 0.039 B | 1.59 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Owczarek, A.; Kuźma, Ł.; Wysokińska, H.; Olszewska, M.A. Application of Response Surface Methodology for Optimisation of Simultaneous UHPLC-PDA Determination of Oleanolic and Ursolic Acids and Standardisation of Ericaceae Medicinal Plants. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6090244
Owczarek A, Kuźma Ł, Wysokińska H, Olszewska MA. Application of Response Surface Methodology for Optimisation of Simultaneous UHPLC-PDA Determination of Oleanolic and Ursolic Acids and Standardisation of Ericaceae Medicinal Plants. Applied Sciences. 2016; 6(9):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6090244
Chicago/Turabian StyleOwczarek, Aleksandra, Łukasz Kuźma, Halina Wysokińska, and Monika Anna Olszewska. 2016. "Application of Response Surface Methodology for Optimisation of Simultaneous UHPLC-PDA Determination of Oleanolic and Ursolic Acids and Standardisation of Ericaceae Medicinal Plants" Applied Sciences 6, no. 9: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6090244
APA StyleOwczarek, A., Kuźma, Ł., Wysokińska, H., & Olszewska, M. A. (2016). Application of Response Surface Methodology for Optimisation of Simultaneous UHPLC-PDA Determination of Oleanolic and Ursolic Acids and Standardisation of Ericaceae Medicinal Plants. Applied Sciences, 6(9), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6090244