Investigating the Role of Shell Thickness and Field Cooling on Saturation Magnetization and Its Temperature Dependence in Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3 Core/Shell Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural and Morphological Analysis
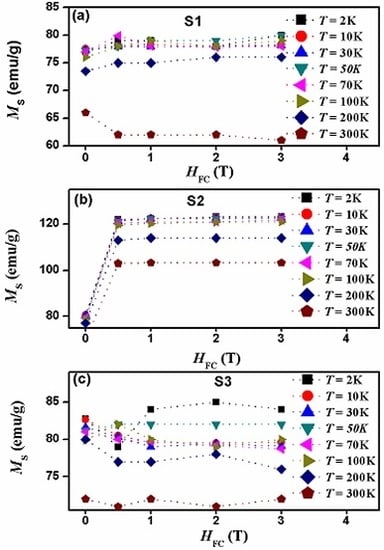
3.2. Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gubin, S.P.; Koksharov, Y.A.; Khomutov, G.B.; Yurkov, G.Y. Magnetic nanoparticles: Preparation, structure and properties. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2005, 74, 489–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, I.M.; Issa, B.; Haik, Y. The role of aggregation of ferrite nanoparticles on their magnetic properties. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 3882–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubbe, A.S.; Bergmann, C.; Riess, H.; Schriver, F.; Reichardt, P.; Possinger, K.; Matthias, M.; Dorken, B.; Herrmann, F.; Gürtler, R.; et al. Clinical experiences with magnetic drug targeting: A phase I study with 4′-epidoxorubicin in 14 patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 4686–4693. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Larsen, B.A.; Haag, M.A.; Serkova, N.J.; Shroyer, K.R.; Stoldt, C.R. Controlled aggregation of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the development of molecular magnetic resonance imaging probes. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 265102–265108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, B.; Obaidat, I.M.; Albiss, B.A.; Haik, Y. Magnetic nanoparticles: Surface effects and properties related to biomedicine applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21266–21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaidat, I.M.; Issa, B.; Haik, Y. Magnetic properties of magnetic nanoparticles for efficient hyperthermia. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Liu, F.; Ma, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z. Nanoparticle-based systems for T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10591–10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, A.; Honda, H.; Kobayashi, T. Cancer immunotherapy based on intracellular hyperthermia using magnetite nanoparticles: A novel concept of “heat-controlled necrosis” with heat shock protein expression. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2006, 55, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, S.; Jouini, N.; Fievet, F.; Stephan, O.; Marhic, C.; Richard, M.; Villain, F.; Chartier dit Moulin, C.; Brice, S.; Sainctavit, P. Influence of the synthesis parameters on the cationic distribution of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles obtained by forced hydrolysis in polyol medium. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 345, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Haneda, K.; Seki, M.; Iijima, T. Morphology and magnetic properties of ultrafine ZnFe2O4 particles. Appl. Phys. A 1990, 50, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, T.; Haneda, K.; Sato, T.; Ikeda, S.; Asano, H. Cation distribution in ZnFe2O4 fine particles studied by neutron powder diffraction. Solid State Commun. 1992, 81, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyadevan, B.; Tohji, K.; Nakatsuka, K. Structure analysis of coprecipitated ZnFe2O4 by extended X-ray-absorption fine structure. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 6325–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdeh, H.H.; Ho, J.C.; Oliver, S.A.; Willey, R.J.; Oliveri, G.; Busca, G. Magnetic properties of partially-inverted zinc ferrite aerogel powders. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 1851–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovec, D.; Kodre, A.; Arčon, I.; Drofenik, M. Structure of manganese zinc ferrite spinel nanoparticles prepared with co-precipitation in reversed microemulsions. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovec, D.; Kodre, A.; Arčon, I.; Drofenik, M. The structure of compositionally constrained zinc-ferrite spinel nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, R.H.; Berkowitz, A.E.; McNiff, E.J., Jr.; Foner, S. Surface spin disorder in NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, R.H.; Berkowitz, A.E.; McNiff, E.J., Jr.; Foner, S. Surface spin disorder in ferrite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 5552–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, R.H.; Berkowitz, A.E. Atomic-scale magnetic modeling of oxide nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 6321–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazeau, F.; Dubois, E.; Hennion, M.; Perzynski, R.; Raikher, Y. Quasi-elastic neutron scattering on γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Europhys. Lett. 1997, 40, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennion, M.; Bellouard, C.; Mirebeau, I.; Dormann, J.L.; Nogues, M. Dual spin dynamics of small fe particles. Europhys. Lett. 1994, 25, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellouard, C.; Mirebeau, I.; Hennion, M. Magnetic correlations of fine ferromagnetic particles studied by small-angle neutron scattering. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 53, 5570–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosensweig, R.E. Heating magnetic fluid with alternating magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 252, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondeck, C.L.; Habib, A.H.; Ohodnicki, P.; Miller, K.; Sawyer, C.A.; Chaudhary, P.; McHenry, M.E. Theory of magnetic fluid heating with an alternating magnetic field with temperature dependent materials properties for self-regulated heating. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 07B324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayek, C.; Manna, K.; Bhattacharjee, G.; Murugavel, P.; Obaidat, I.M. Investigating size- and temperature-dependent coercivity and saturation magnetization in PEG coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Magnetochemistry 2017, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, I.M.; Issa, B.; Albiss, B.A.; Haik, Y. Temperature dependence of saturation magnetization and coercivity in Mn0.5Zn0.5Gd0.02Fe1.98O4 ferrite nanoparticles. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 92, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairan, A.; Khan, M.; Khan, U.; Iqbal, M.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Temperature-dependent magnetic response of antiferromagnetic doping in cobalt ferrite nanostructures. Nanomaterials 2017, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, B.N.; Doshi, A.S.; Prabhu, R.; Venkataramani, N.; Prasad, S.; Krishnan, R. Temperature dependence of FMR and magnetization in nanocrystalline zinc ferrite thin films. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 055928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajonrit, J.; Wongpratat, U.; Kidkhunthod, P.; Pinitsoontorn, S.; Maensiri, S. Effects of Co doping on magnetic and electrochemical properties of BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 449, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, S.; Lee, K.; Jo, Y.; Yoon, S.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Lee, K.; Lee, J.; Jung, M. Interface effect of magnetic properties in Ni nanoparticles with a hcp core and fcc shell structure. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 6126–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, F.S.; Bartolome, F.; Petroff, F.; Bartolome, J.; Garcia, M.; Deranlot, C.; Jaffres, M.; Martinez, H.; Bencok, P.; Wilhelm, F.; et al. Tuning the magnetic anisotropy of Co nanoparticles by metal capping. Europhys. Lett. 2006, 76, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skomski, R.; Coey, J.M.D. Giant energy product in nanostructured two-phase magnets. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 48, 15812–15816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, E.E.; Jiang, J.S.; Bader, S.D. Hard/soft magnetic heterostructures: Model exchange-spring magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Sun, S.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Liu, J.P. Tailoring magnetic properties of core/shell nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Li, J.; Liu, J.P.; Wang, Z.L.; Sun, S. Exchange-coupled nanocomposite magnets by nanoparticle self-assembly. Nature 2002, 420, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, Y.; Antony, J.; Sharma, A.; Nutting, J.; Sikes, D.; Meyer, D. Iron/iron oxide core-shell nanoclusters for biomedical applications. J. Nanopart. Res. 2006, 8, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosvenor, A.P.; Kobe, B.A.; McIntyre, N.S. Examination of the oxidation of iron by oxygen using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and QUASESTM. Surf. Sci. 2004, 565, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, I.M.; Nayek, C.; Manna, K.; Bhattacharya, G.; Al-Omari, I.; Gismelseed, A. Investigating exchange bias and coercivity in Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3 core/shell nanoparticles of fixed core diameter and variable shell thicknesses. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.M.; Imhoff, D.; Yu-Zhang, K.; Leprince-Wang, Y. Effect of field cooling on magnetic properties of ultrafine CoO/Co particles. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2005, 81, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, K.; Mumtaz, A.; Hasanain, S.K.; Bertino, M.F. Temperature dependent coercivity and magnetization of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 2199–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneller, E.F.; Luborsky, F.E. Particle size dependence of coercivity and remanence of single-domain particles. J. Appl. Phys. 1963, 34, 656–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, X.; Garcia del Muro, M.; Tejada, J.; Pfeiffer, H.; Gornert, P.; Sinn, E. Magnetic study of M-type doped barium ferrite nanocrystalline powders. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 74, 3333–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bloch, F. Zur theorie des ferromagnetismus. Z. Phys. 1930, 61, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, E.D.; Bennett, L.H.; Watson, R.E. Extension of the Bloch T3/2 law to magnetic nanostructures: Bose-Einstein condensation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 147210–147212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senz, V.; Röhlsberger, R.; Bansmann, J.; Leupold, O.; Meiwes-Broer, K.-H. Temperature dependence of the magnetization in Fe islands on W(110): Evidence for spin-wave quantization. New J. Phys. 2003, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, P.V.; Linderoth, S.; Lindgard, P.A. Finite-size effects in the magnetic properties of ferromagnetic clusters. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1992, 104–107, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, P.V.; Linderoth, S.; Lindgard, P.A. Finite-size modifications of the magnetic properties of clusters. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 48, 7259–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linderoth, S.; Balcells, L.; Labarta, A.; Tejada, J.; Hendriksen, P.V.; Sethi, S.A. Magnetization and mossbauer studies of ultrafine Fe-C particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1993, 124, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggeman, A.S.; Petford-Long, A.K.; Dobson, P.J.; Wiggins, J.; Bromwich, T.; Dunin-Borkowski, R.; Kasama, T. Synthesis and characterisation of silica encapsulated cobalt nanoparticles and nanoparticle chains. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 301, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bianco, L.; Fiorani, D.; Testa, A.M.; Bonetti, E. Exchange bias in the nanogranular Fe/Feoxide system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 290–291, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogues, J.; Sort, J.; Langlais, V.; Skumryev, V.; Surinach, S.; Munoz, J.S.; Baro, M.D. Exchange bias in nanostructures. Phys. Rep. 2015, 422, 65–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommareddi, N.S.; Tata, M.; John, V.T.; McPherson, G.L.; Herman, M.F.; Lee, Y.-S.; O’Connor, C.J.; Akkara, J.A.; Kaplan, D.L. Synthesis of superparamagnetic polymer–ferrite composites using surfactant microstructures. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morup, S.; Topsoe, H.J. Mössbauer studies of thermal excitations in magnetically ordered microcrystals. Appl. Phys. 1976, 11, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, H.M.I.; Moyo, T.; Ezekiel, I.P.; Osman, N.S.E. Structural and magnetic properties of Sr0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 nanoferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 365, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, D.; Vélez-Fort, E.; García, D.A.; García, R.; Litrán, R.; Barrera-Solano, C.; Ramírez-del-Solar, M.; Domínguez, M. Size and surface effects in the magnetic properties of maghemite and magnetite coated nanoparticles. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 4407–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubin, S.P. (Ed.) Magnetic Nanoparticles; Wiley-VCH: Berlin, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-3-527-40790-3. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, C.R.; Aquino, R.; Sousa, M.H.; Rechenberg, H.R.; Goya, G.F.; Tourinho, F.A.; Depeyrot, J. Low temperature experimental investigation of finite-size and surface effects in CuFe2O4 nanoparticles of ferrofluids. J. Metastab. Nanocryst. Mater. 2004, 20–21, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, K.; Mitra, S.; Kumar, P.A. Deviation from Bloch T3/2 law in ferrite nanoparticles. Europhys. Lett. 2006, 75, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.A.; Mandal, K. Effect of spatial confinement on spin-wave spectrum: Low temperature deviation from Bloch T3/2 law in Co nanoparticles. arXiv, 2007; arXiv:cond-mat/0701152. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, P.; Thakur, A.; Singh, M. Effect of nanoparticles on the magnetic properties of Mn-Zn soft ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, L.D.; Kolesnichenko, V.; Caruntu, D.; Chou, N.H.; O’Connor, C.J.; Spinu, L. Magnetic properties of ultrafine cobalt ferrite particles. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 93, 7486–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morup, S. Comment on “Deviation from the Bloch T3/2 law in ferrite nanoparticles” by K. Mandal et al. Europhys. Lett. 2007, 77, 27003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajra, P.; Basu, S.; Dutta, S.; Brahma, P.; Chakravorty, D. Exchange bias in ferrimagnetic–antiferromagnetic nanocomposite produced by mechanical attrition. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 2269–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Shell Thickness (nm) | Fitted Parameters at ZFC | αB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 (emu/g) | T0 (K) | |||
| S1 | 1 | 77.5 (±0.4) | 852 (±15) | 2.0 |
| S2 | 3 | 79.9 (±0.1) | 689 (±10) | 2.5 |
| S3 | 5 | 82.8 (±0.2) | 580 (±5) | 3.0 |
| HFC (T) | Fitted Parameters | αB | |
|---|---|---|---|
| M0 (emu/g) | TC (K) | ||
| 0.5 | 78.0 ± 0.1 | 443 ± 5 | 4.0 |
| 1 | 78.7 ± 0.14 | 452 ± 2.6 | 3.8 |
| 2 | 78.1 ± 0.6 | 412 ± 9.9 | 4.9 |
| 3 | 78.3 ± 0.2 | 427 ± 3 | 4.6 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obaidat, I.M.; Nayek, C.; Manna, K. Investigating the Role of Shell Thickness and Field Cooling on Saturation Magnetization and Its Temperature Dependence in Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3 Core/Shell Nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7121269
Obaidat IM, Nayek C, Manna K. Investigating the Role of Shell Thickness and Field Cooling on Saturation Magnetization and Its Temperature Dependence in Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3 Core/Shell Nanoparticles. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(12):1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7121269
Chicago/Turabian StyleObaidat, Ihab M., Chiranjib Nayek, and Kaustuv Manna. 2017. "Investigating the Role of Shell Thickness and Field Cooling on Saturation Magnetization and Its Temperature Dependence in Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3 Core/Shell Nanoparticles" Applied Sciences 7, no. 12: 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7121269
APA StyleObaidat, I. M., Nayek, C., & Manna, K. (2017). Investigating the Role of Shell Thickness and Field Cooling on Saturation Magnetization and Its Temperature Dependence in Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3 Core/Shell Nanoparticles. Applied Sciences, 7(12), 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7121269