Target Tracking Based on a Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Guidance Law by Fixed-Wing UAV
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. UAV Dynamic Model
2.2. Relative Motion Model
3. Target Tracking Based on Sliding Model Control
3.1. Loitering Algorithm
3.2. Sliding Manifold Designing
3.3. Guidance Law
3.4. Stability Analysis
4. Simulation Results
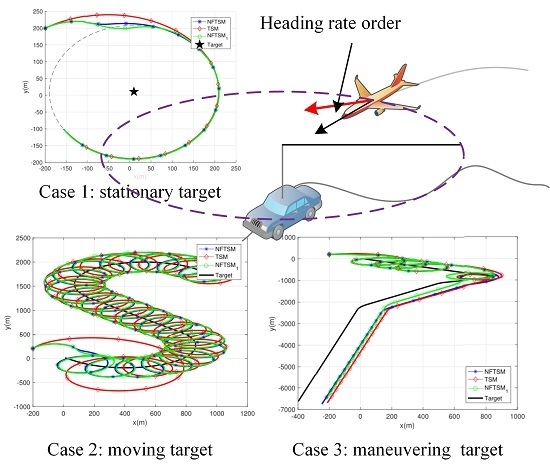
4.1. Stationary Target
4.2. Constant Speed Target
4.3. Maneuvering Target
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| SMC | Sliding Model Control |
| NFTSM | Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode |
| TSM | Terminal Sliding Mode |
| EKF | Extended Kalman Filter |
| , | UAV horizontal position |
| , | UAV airspeed and heading angle |
| , | UAV groundspeed and course angle |
| , , , | The motion state of target |
| L | Distance from target to UAV |
| Desired separation distance | |
| r | Distance error |
| Azimuth angle of UAV in target-frame | |
| Auxiliary parameter about azimuth angle | |
| , , | Auxiliary heading angle of UAV, target and wind |
| Steady value of UAV | |
| Heading angle error | |
| s | Sliding manifold |
| ℓ | Auxiliary parameter about distance error |
| , ,, , | NFTSM manifold parameters |
| , , | NFTSM fast reaching law parameters |
| UAV command |
References
- Rucco, A.; Aguiar, A.P.; Pereira, F.L.; de Sousa, J.B. A Predictive Path-Following Approach for Fixed-Wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Presence of Wind Disturbances. In Proceedings of the Robot 2015: Second Iberian Robotics Conference, Lisbon, Portugal, 19–21 November 2015; pp. 623–634. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Xin, B.; Peng, Z. A memetic algorithm for path planning of curvature-constrained UAVs performing surveillance of multiple ground targets. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2014, 27, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, J. Connectivity Maintenance Based on Multiple Relay UAVs Selection Scheme in Cooperative Surveillance. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Bao, Z.; Wang, R.; Qiao, S.; Zhou, Y. Quantum Wind Driven Optimization for Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle Path Planning. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 1457–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujit, P.B.; Saripalli, S.; Sousa, J.B. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Path Following: A Survey and Analysis of Algorithms for Fixed-Wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicless. IEEE Control Syst. 2014, 34, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. Circling over a Target with Relative Side Bearing. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2016, 39, 1454–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Huang, R.; Vaughn, A.; Xiao, X.; Hedrick, J.K.; Zennaro, M.; Sengupta, R. Strategies of path-planning for a UAV to track a ground vehicle. In Proceedings of the AINS Conference, Menlo Park, CA, USA, 30 June–1 July 2003; Volume 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shames, I.; Dasgupta, S.; Fidan, B.; Anderson, B.D.O. Circumnavigation Using Distance Measurements Under Slow Drift. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2012, 57, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Kim, S.; Shin, H.S.; White, B.A.; Tsourdos, A.; Rabbath, C.A. Rendezvous and standoff target tracking guidance using differential geometry. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2013, 69, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frew, E.W.; Lawrence, D.A.; Dixon, C.; Elston, J.; Pisano, W.J. Lyapunov guidance vector fields for unmanned aircraft applications. In Proceedings of the 2007 American Control Conference, New York, NY, USA, 9–13 July 2007; pp. 371–376. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, P.; Wang, H.; Su, Z. Cooperative path planning with applications to target tracking and obstacle avoidance for multi-UAVs. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 54, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, M.; Goodrich, M.A.; Griffiths, S.; Eldredge, A.; Beard, R.W. Target acquisition, localization, and surveillance using a fixed-wing mini-UAV and gimbaled camera. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 2600–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, H.H. Game-theoretical persistent tracking of a moving target using a unicycle-type mobile vehicle. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6222–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Oh, H.; Tsourdos, A. Nonlinear model predictive coordinated standoff tracking of a moving ground vehicle. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2013, 36, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevost, C.G.; Thériault, O.; Desbiens, A.; Poulin, E.; Gagnon, E. Receding horizon model-based predictive control for dynamic target tracking: A comparative study. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 10–13 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Narkiewicz, J.P.; Kopyt, A.; Radyisyewski, P.; Malecki, T. Optimal selection of UAV for ground target tracking. In Proceedings of the AIAA Modeling and Simulation Technologies Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 22–26 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.K.; Wang, J.; Paw, Y.C.; Ng, T.Y. Tracking of a moving ground target by a quadrotor using a backstepping approach based on a full state cascaded dynamics. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 47, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, H.H. Cooperative Tracking a Moving Target Using Multiple Fixed-wing UAVs. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2016, 81, 505–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Kim, S.; Tsourdos, A.; White, B.A. Decentralised standoff tracking of moving targets using adaptive sliding mode control for UAVs. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2014, 76, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, V.; Fidan, B.; Ordóñez, R.; Köksal, M.İ. A target tracking approach for nonholonomic agents based on artificial potentials and sliding mode control. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2012, 134, 061004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modirrousta, A.; Sohrab, M.; Dehghan, S.M.M. A modified guidance law for ground moving target tracking with a class of the fast adaptive second-order sliding mode. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2016, 38, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinkun, L. Sliding Mode Control Design And MATLAB Simulation: The Basic Theory and Design Method; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Harl, N.; Balakrishnan, S. Impact time and angle guidance with sliding mode control. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2012, 20, 1436–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Song, S.; Zhou, H. Adaptive nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode guidance law with impact angle constraints. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2016, 14, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.X.; Fang, J.C. An adaptive three-dimensional nonlinear path following method for a fix-wing micro aerial vehicle. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2012, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Jia, Y. Combined vector field approach for 2D and 3D arbitrary twice differentiable curved path following with constrained UAVs. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2016, 83, 133–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Shalom, Y.; Li, X.R.; Kirubarajan, T. Estimation with Applications to Tracking and Navigation: Theory Algorithms and Software; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Karsaz, A.; Ahari, A.A. Backward input estimation algorithm for tracking maneuvering target. In Proceedings of the 2016 24th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Shiraz, Iran, 10–12 May 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 745–750. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Hovakimyan, N. Cooperative target tracking in balanced circular formation: Multiple UAVs tracking a ground vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2013 American Control Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 17–19 June 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 5386–5391. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Yu, X.; Shirinzadeh, B.; Man, Z. Continuous finite-time control for robotic manipulators with terminal sliding mode. Automatica 2005, 41, 1957–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, J. Nonsingular fast terminal sliding-mode control for nonlinear dynamical systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2011, 21, 1865–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradshteyn, I.S.; Ryzhik, I.M. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, H.K. Noninear Systems, 3rd ed.; Publishing House of Electronics Indystry: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]










| Initial Condition | Value |
|---|---|
| Sampling time, (s) | 0.5 |
| UAV initial position, (m) | [−200,200] |
| Constant airspeed, (m/s) | 13 |
| Maximum turn rate, | 5 |
| Desired distance, (m) | 200 |
| Target initial position, (m) | [10,10] |
| Target initial velocity, (m/s) | 2 |
| Wind speed, (m/s) | [0.1,0.2] |
| Algorithm | Coefficient | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NFTSM | , | , | , | , | |
| , | , | , | |||
| TSM | , | , | , | ||
| , | , | , | , | ||
| , | , | , | |||
| Algorithm | Case () | Simulation Time (s) | Convergence Time (s) | Distance Error r (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NFTSM | 80 | 31.2 | less than 0.0001 | |
| TSM | 80 | 80 | −0.742 | |
| 80 | 37.3 | less than 0.0001 | ||
| NFTSM | 100 | 72.9 | less than 0.0001 | |
| TSM | 100 | 100 | no convergence | |
| 100 | 100 | shock |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, K.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y. Target Tracking Based on a Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Guidance Law by Fixed-Wing UAV. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040333
Wu K, Cai Z, Zhao J, Wang Y. Target Tracking Based on a Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Guidance Law by Fixed-Wing UAV. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(4):333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040333
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Kun, Zhihao Cai, Jiang Zhao, and Yingxun Wang. 2017. "Target Tracking Based on a Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Guidance Law by Fixed-Wing UAV" Applied Sciences 7, no. 4: 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040333
APA StyleWu, K., Cai, Z., Zhao, J., & Wang, Y. (2017). Target Tracking Based on a Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Guidance Law by Fixed-Wing UAV. Applied Sciences, 7(4), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040333