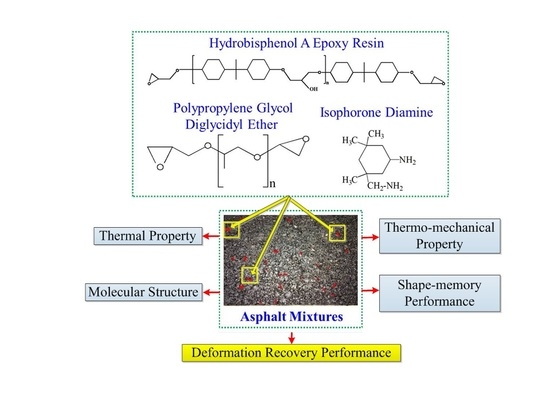
Analysis of Preparation and Properties on Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin Used for Asphalt Mixtures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin (SM-HEP)
2.3. Preparation of the Asphalt Mixture Mixed with the Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin (SM-HEP)
2.4. Test Methods
2.4.1. Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC)
2.4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.4.3. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
2.4.4. Tensile-Recovery Shape Memory Test
2.4.5. Deformation Recovery Test
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Controllable Preparation Result of the Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin (SM-HEP)
3.2. The Thermal Property of the Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin Used for Asphalt Mixtures (SM-HEP-AM)
3.3. The Molecular Structure of the Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin Used for Asphalt Mixtures (SM-HEP-AM)
3.4. The Thermo-Mechanical Property of the Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin Used for Asphalt Mixtures (SM-HEP-AM)
3.5. The Shape-Memory Performance of the Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin Used for Asphalt Mixtures (SM-HEP-AM)
3.6. The Deformation Recovery Performance of the Asphalt Mixtures with and without the Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin Used for Asphalt Mixtures (SM-HEP-AM)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Si, W.; Zhou, X.; Ma, B.; Li, N. The mechanism of different thermoregulation types of composite shape-stabilized phase change materials used in asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, T.; Soltani, M.; Karim, M. Experimental characterization of rutting performance of Polyethylene Terephthalate modified asphalt mixtures under static and dynamic loads. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 65, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Yuan, Q.; Ni, F. Analysis of factors on asphalt pavement rut development based on measured load and temperature gradient. China J. Highw. Transp. 2012, 25, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; You, Z.; Wei, K; Huang, X. Determination of specific heat capacity on composite shape-stabilized phase change materials and asphalt mixtures by heat exchanges system. Materials 2016, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Adhikari, S.; Chang, Y.; Ren, J.; Liu, J.; You, Z. Preparation of composite shape-stabilized phase change materials for highway pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 42, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Si, W.; Ren, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Li, J. Exploration of road temperature-adjustment material in asphalt mixture. Road Mater. Pavement 2014, 15, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Study on application of PCM in asphalt mixture. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 168–170, 2625–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sireesh, S. Rutting behavior of geocell reinforced base layer overlying weak sand subgrades. Procedia Eng. 2016, 143, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. Chapter 9—Predictions of rutting on asphalt pavements. Struct. Behav. Asph. Pavements 2016, 17, 601–648. [Google Scholar]
- Shafabakhsh, G.; Ani, O.J. Experimental investigation of effect of Nano TiO2/SiO2 modified bitumen on the rutting and fatigue performance of asphalt mixtures containing steel slag aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziari, H.; Behbahani, H.; Kamboozia, N.; Ameri, M. New achievements on positive effects of nanotechnology zyco-soil on rutting resistance and stiffness modulus of glasphalt mix. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, M.; Nitin, S.Y.; Ken, G.; Roxanne, L.; Zach, J. Shape-memory polymer networks with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for remote activation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 3166–3176. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Huang, W.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Purnawali, H. Cooling-/water-responsive shape memory hybrids. Compos. Sci Technol. 2012, 72, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florence, P.; Antoniya, T.; Philippe, D.; Raquez, J. Shape-memory polymers for multiple applications in the materials world. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 80, 268–294. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe, A.; Desfaits, A.; Salazkin, I.; Yahia, L.; Sokolowski, W.; Raymond, J. Cold hibernated elastic memory foams for endovascular interventions. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, K.; Dunn, M.; Liu, Y.; Finch, D.; Lake, M.; Munshi, N. Shape memory polymer nanocomposites. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 5115–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretsch, T.; Ecker, M.; Schildhauer, M.; Maskos, M. Switchable information carriers based on shape memory polymer. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7757–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, M.; Pretsch, T. Multifunctional poly(ester urethane) laminates with encoded information. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandman, S.; Zhu, X. Biodegradable shape-memory polymers for biomedical applications. In Shape Memory Polymers for Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 219–245. [Google Scholar]
- Karger, J.; Kéki, S. Recent advances in shape memory epoxy resins and composites. In Multifunctionality of Polymer Composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 822–841. [Google Scholar]
- Fritzsche, N.; Pretsch, T. Programming of Temperature-Memory Onsets in a Semicrystalline Polyurethane Elastomer. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 5952–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothe, M.; Pretsch, T. Bidirectional actuation of a thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 14491–14497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amber, J.; Gyaneshwar, P.; Baur, J.W. Strain rate-and temperature-dependent tensile properties of an epoxy-based, thermosetting, shape memory polymer (Veriflex-E). Mech. Time-Depend. Mat. 2012, 16, 205–221. [Google Scholar]
- Loredana, S. Shape memory epoxy foams: New materials for aerospace applications. Mater. Sci. Forum 2012, 706, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, P.; Sain, M.; Yan, N. Synthesis and characterization of an extractive-based bio-epoxy resin from beetle infested pinus contorta bark. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3483–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, Y. Revealing triple-shape memory effect by polymer bilayers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 1823–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Highway Ministry of Transport. Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering; China Communication Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Menozzi, A.; Garcia, A.; Partl, M.; Schuetz, P. Induction healing of fatigue damage in asphalt test samples. Constr Build. Mater. 2015, 74, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Rousseau, I. Facile tailoring of thermal transition temperatures of epoxy shape memory polymers. Polymer 2009, 50, 1852–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowski, W.; Tan, S. Advanced self-deployable structures for space applications. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2007, 44, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Zhu, G.; Tang, Y.; Liu, T.; Xie, J. The effects of crosslink density on thermo-mechanical properties of shape-memory hydro-epoxy resin. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 2903–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Zhu, G.; Tang, Y.; Tian, G.; Xie, J. Thermomechanical properties of shape-memory hydro-epoxy resin. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 055022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Specimen | AL-3040 (mol) | JH-230 (mol) | IPDA (mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| JH-230 0.02 | 0.98 | 0.02 | 0.5 |
| JH-230 0.04 | 0.96 | 0.04 | 0.5 |
| JH-230 0.05 | 0.95 | 0.05 | 0.5 |
| JH-230 0.06 | 0.94 | 0.06 | 0.5 |
| JH-230 0.08 | 0.92 | 0.08 | 0.5 |
| JH-230 0.10 | 0.90 | 0.10 | 0.5 |
| Specimen | AL-3040 (mol) | JH-230 (mol) | IPDA (mol) | Tg-Fitted (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JH-230-0.0274 | 0.9726 | 0.0274 | 0.5 | 60 |
| JH-230-0.0407 | 0.9593 | 0.0407 | 0.5 | 55 |
| JH-230-0.0540 | 0.9460 | 0.0540 | 0.5 | 50 |
| JH-230-0.0678 | 0.9322 | 0.0678 | 0.5 | 45 |
| JH-230-0.0805 | 0.9805 | 0.0805 | 0.5 | 40 |
| Specimen | AL-3040 (mol) | JH-230 (mol) | IPDA (mol) | Tg-Fitted (°C) | Tg-Measured (Uppercase) (°C) | Error Bars (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JH-230-0.0353 | 0.9647 | 0.0353 | 0.5 | 60 | 60.9 | 1.0 |
| JH-230-0.0463 | 0.9537 | 0.0463 | 0.5 | 55 | 55.5 | 0.7 |
| JH-230-0.0574 | 0.9426 | 0.0574 | 0.5 | 50 | 49.4 | 0.5 |
| JH-230-0.0685 | 0.9315 | 0.0685 | 0.5 | 45 | 44.8 | 0.4 |
| JH-230-0.0796 | 0.9204 | 0.0796 | 0.5 | 40 | 39.0 | 0.8 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, B.; Zhou, X.; Wei, K.; Bo, Y.; You, Z. Analysis of Preparation and Properties on Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin Used for Asphalt Mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7060523
Ma B, Zhou X, Wei K, Bo Y, You Z. Analysis of Preparation and Properties on Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin Used for Asphalt Mixtures. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(6):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7060523
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Biao, Xueyan Zhou, Kun Wei, Yanzhen Bo, and Zhanping You. 2017. "Analysis of Preparation and Properties on Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin Used for Asphalt Mixtures" Applied Sciences 7, no. 6: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7060523
APA StyleMa, B., Zhou, X., Wei, K., Bo, Y., & You, Z. (2017). Analysis of Preparation and Properties on Shape Memory Hydrogenated Epoxy Resin Used for Asphalt Mixtures. Applied Sciences, 7(6), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7060523