Synergistically-Enhanced Thermal Conductivity of Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Materials by Expanded Graphite and Carbon Nanotube
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Treatment of Expandable Graphite and MWCNT
2.3. Preparation of Hybrid Fillers
2.4. Preparation of Thermal Conductivity Enhanced SSPCMs
2.5. Characterization
2.5.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.5.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5.3. Thermal Conductivity Test
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Morphology of Fillers
3.2. Thermal Conductivity
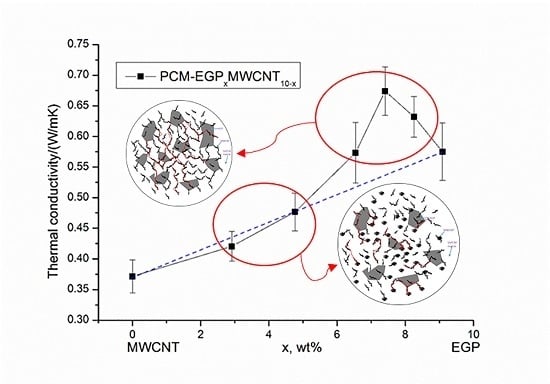
3.3. Synergistic Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, C.Y.; Tian, Y. Review on thermal energy storage with phase change materials (pcms) in building applications. Appl. Energy 2012, 92, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.M.; Khudhair, A.M.; Razack, S.A.K.; Al-Hallaj, S. A review on phase change energy storage: Materials and applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 1597–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Salehi-Khojin, A.; Zhong, W.-H. Enhancement of fluid thermal conductivity by the addition of single and hybrid nano-additives. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 462, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hwang, Y.; Radermacher, R. Review of cold storage materials for air conditioning application. Int. J. Refrig. 2012, 35, 2053–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaipekli, A.; Biçer, A.; Sarı, A.; Tyagi, V.V. Thermal characteristics of expanded perlite/paraffin composite phase change material with enhanced thermal conductivity using carbon nanotubes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 134, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J. Preparation and melting/freezing characteristics of cu/paraffin nanofluid as phase-change material (pcm). Energy Fuel 2010, 24, 1894–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.-L.; Zhu, F.-R.; Yu, S.-B.; Zhu, L.; Cao, Z.; Sun, L.-X.; Deng, G.-R.; Yan, W.-P.; Zhang, L. Effects of copper nanowires on the properties of an organic phase change material. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cell 2012, 105, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, P.; Li, M. Preparation and thermal characterization of paraffin/metal foam composite phase change material. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintakrinda, K.; Weinstein, R.D.; Fleischer, A.S. A direct comparison of three different material enhancement methods on the transient thermal response of paraffin phase change material exposed to high heat fluxes. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2011, 50, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xie, H.; Li, Y.; Xin, Z. Pw based phase change nanocomposites containing γ-Al2O3. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 102, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.J.; Gao, J.Y. Preparation and thermophysical properties of nanoparticle-in-paraffin emulsion as phase change material. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 2009, 36, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesumathy, S.; Udayakumar, M.; Suresh, S. Experimental study of enhanced heat transfer by addition of cuo nanoparticle. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 48, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Khodadadi, J.M. An experimental investigation of enhanced thermal conductivity and expedited unidirectional freezing of cyclohexane-based nanoparticle suspensions utilized as nano-enhanced phase change materials (nepcm). Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2012, 62, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xie, H.; Xin, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, L. Enhancing thermal conductivity of palmitic acid based phase change materials with carbon nanotubes as fillers. Sol. Energy 2010, 84, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-N.; Ger, M.-D.; Liu, Y.-M.; Fan, Y.-C.; Wen, N.-T.; Lin, C.-K.; Pu, N.-W. Improving the thermal conductivity and shape-stabilization of phase change materials using nanographite additives. Carbon 2013, 51, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Ling, Z.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Z. Rt100/expand graphite composite phase change material with excellent structure stability, photo-thermal performance and good thermal reliability. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cell 2015, 140, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Drzal, L.T. High latent heat storage and high thermal conductive phase change materials using exfoliated graphite nanoplatelets. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cell 2009, 93, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarı, A.; Karaipekli, A. Thermal conductivity and latent heat thermal energy storage characteristics of paraffin/expanded graphite composite as phase change material. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, R. Preparation and thermal characterization of expanded graphite/paraffin composite phase change material. Carbon 2010, 48, 2538–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Py, X.; Olives, R.; Mauran, S. Paraffin/porous-graphite-matrix composite as a high and constant power thermal storage material. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2001, 44, 2727–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A.; Farid, M.; Selman, J.; Al-Hallaj, S. Thermal conductivity enhancement of phase change materials using a graphite matrix. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2006, 26, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Sellan, D.P.; Pettes, M.T.; Kong, X.; Ji, J.; Shi, L.; Ruoff, R.S. Enhanced thermal conductivity of phase change materials with ultrathin-graphite foams for thermal energy storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xie, H.; Xin, Z. Thermal properties of paraffin based composites containing multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Thermochim. Acta 2009, 488, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.-W.; Fang, X.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Xiao, Y.-Q.; Yu, Z.-T.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.-C.; Cen, K.-F. Effects of various carbon nanofillers on the thermal conductivity and energy storage properties of paraffin-based nanocomposite phase change materials. Appl. Energy 2013, 110, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrali, M.; Latibari, S.T.; Mehrali, M.; Metselaar, H.S.C.; Silakhori, M. Shape-stabilized phase change materials with high thermal conductivity based on paraffin/graphene oxide composite. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 67, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. A nano-graphite/paraffin phase change material with high thermal conductivity. Appl. Energy 2013, 106, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Fan, L.-W.; Ding, Q.; Wang, X.; Yao, X.-L.; Hou, J.-F.; Yu, Z.-T.; Cheng, G.-H.; Hu, Y.-C.; Cen, K.-F. Increased thermal conductivity of eicosane-based composite phase change materials in the presence of graphene nanoplatelets. Energy Fuel 2013, 27, 4041–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarı, A. Form-stable paraffin/high density polyethylene composites as solid–liquid phase change material for thermal energy storage: Preparation and thermal properties. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, J.P.; Yang, R. Preparation, stability and mechanical property of shape-stabilized phase change materials. Energy Build. 2014, 77, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R. Flame retardance property of shape-stabilized phase change materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cell 2015, 140, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMaadeed, M.; Labidi, S.; Krupa, I.; Karkri, M. Effect of expanded graphite on the phase change materials of high density polyethylene/wax blends. Thermochim. Acta 2015, 600, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolciak, P.; Karkri, M.; Al-Maadeed, M.A.; Krupa, I. Thermal characterization of phase change materials based on linear low-density polyethylene, paraffin wax and expanded graphite. Renew. Energy 2016, 88, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-L.; Zhang, R.-M.; Xie, K.; Liu, N.; Wang, J. Heat conduction enhanced shape-stabilized paraffin/hdpe composite pcms by graphite addition: Preparation and thermal properties. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cell 2010, 94, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Feng, B.; Gong, K. Preparation and performance of shape stabilized phase change thermal storage materials with high thermal conductivity. Energy Convers. Manag. 2002, 43, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, R.; Lin, K. Influence of additives on thermal conductivity of shape-stabilized phase change material. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cell 2006, 90, 1692–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.J.; Wang, S.G.; Zhang, Q. Thermal and electrical transport in multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Phys. Lett. A 2004, 329, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Shi, L.; Majumdar, A.; McEuen, P.L. Thermal transport measurements of individual multiwalled nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 215502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.P.; Ramesh, P.; Sun, X.B.; Bekyarova, E.; Itkis, M.E.; Haddon, R.C. Enhanced thermal conductivity in a hybrid graphite nanoplatelet-carbon nanotube filler for epoxy composites. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4740–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Materials | Density (g/cm3) | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Specific Heat (J/gK) | Melting Point °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | 0.94~0.96 | 0.44 | 2.3 | 130 |
| SBS | 0.92~0.95 | 0.16 | 1.9 | - |
| Paraffin | 0.915 | 0.14 | 2.5 | 20–25 |
| EGP [20] | 1.8 | 100 | 0.71 | - |
| WMCNT [36,37] * | 1.8 | 200/3000 | 0.71 | - |
| Sample | Composition (Mass Ratio) | Filler Content/(wt %) | Density/(×103 kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCM | SBS/HDPE/paraffin = 30/10/60 | 0 | 0.800 |
| PCM-1EGP | PCM/EGP = 100/1 | 0.99 | 0.800 |
| PCM-3EGP | PCM/EGP = 100/3 | 2.91 | 0.810 |
| PCM-5EGP | PCM/EGP = 100/5 | 4.76 | 0.822 |
| PCM-7EGP | PCM/EGP = 100/7 | 6.54 | 0.834 |
| PCM-10EGP | PCM/EGP = 100/10 | 9.09 | 0.849 |
| PCM-12EGP | PCM/EGP = 100/12 | 10.71 | 0.858 |
| PCM-1MWCNT | PCM/MWCNT = 100/1 | 0.99 | 0.807 |
| PCM-3MWCNT | PCM/MWCNT = 100/3 | 2.91 | 0.824 |
| PCM-5MWCNT | PCM/MWCNT = 100/5 | 4.76 | 0.832 |
| PCM-7MWCNT | PCM/MWCNT = 100/7 | 6.54 | 0.859 |
| PCM-10MWCNT | PCM/MWCNT = 100/10 | 9.09 | 0.870 |
| PCM-EGP9MWCNT1 | PCM/EGP/MWCNT = 100/9/1 | 9.09 | 0.855 |
| PCM-EGP8MWCNT2 | PCM/EGP/MWCNT = 100/8/2 | 9.09 | 0.866 |
| PCM-EGP7MWCNT3 | PCM/EGP/MWCNT = 100/7/3 | 9.09 | 0.867 |
| PCM-EGP5MWCNT5 | PCM/EGP/MWCNT = 100/5/5 | 9.09 | 0.860 |
| PCM-EGP3MWCNT7 | PCM/EGP/MWCNT = 100/3/7 | 9.09 | 0.861 |
| Sample | Cp/(J/gK) |
|---|---|
| PCM | 2.42 ± 0.19 |
| PCM-1EGP | 2.38 ± 0.15 |
| PCM-3EGP | 2.22 ± 0.14 |
| PCM-5EGP | 2.23 ± 0.10 |
| PCM-7EGP | 2.28 ± 0.13 |
| PCM-10EGP | 2.35 ± 0.17 |
| PCM-12EGP | 2.34 ± 0.17 |
| PCM-1MWCNT | 2.33 ± 0.11 |
| PCM-3MWCNT | 2.31 ± 0.10 |
| PCM-5MWCNT | 2.37 ± 0.15 |
| PCM-7MWCNT | 2.31 ± 0.14 |
| PCM-10MWCNT | 2.34 ± 0.12 |
| PCM-EGP9MWCNT1 | 2.31 ± 0.16 |
| PCM-EGP8MWCNT2 | 2.30 ± 0.15 |
| PCM-EGP7MWCNT3 | 2.27 ± 0.14 |
| PCM-EGP5MWCNT5 | 2.32 ± 0.11 |
| PCM-EGP3MWCNT7 | 2.36 ± 0.17 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.-P.; Yang, R. Synergistically-Enhanced Thermal Conductivity of Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Materials by Expanded Graphite and Carbon Nanotube. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7060574
Liu Z-P, Yang R. Synergistically-Enhanced Thermal Conductivity of Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Materials by Expanded Graphite and Carbon Nanotube. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(6):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7060574
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhang-Peng, and Rui Yang. 2017. "Synergistically-Enhanced Thermal Conductivity of Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Materials by Expanded Graphite and Carbon Nanotube" Applied Sciences 7, no. 6: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7060574
APA StyleLiu, Z. -P., & Yang, R. (2017). Synergistically-Enhanced Thermal Conductivity of Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Materials by Expanded Graphite and Carbon Nanotube. Applied Sciences, 7(6), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7060574