Reviewing the Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: From Waste Generation and Anaerobic Process to Its Perspectives
Abstract
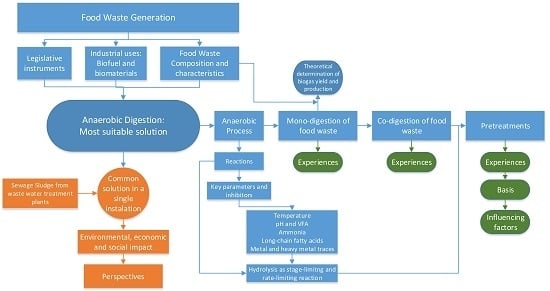
:1. Introduction
FW Characterisation
2. Industrial uses of FW, Different from Anaerobic Digestion
2.1. Biomaterials Production
2.2. Energy Production
3. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste
3.1. AD Process
3.1.1. Hydrolysis as Stage-Limiting and Rate-Limiting Reaction in AD
Temperature and pH
Substrate Structure
Particle Size
3.2. Key Parameters
3.2.1. Temperature
3.2.2. VFA and pH
3.2.3. Carbon, Nitrogen and C/N Ratio
3.2.4. Ammonia Content and Formation
3.2.5. Long-Chain Fatty Acids
3.2.6. Metal and Heavy Metals Traces
3.3. Anaerobic Mono-Digestion of FW
4. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste
Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage Sludge
5. Pre-Treatments for Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste
5.1. Mechanical and Physical Pre-Treatment
5.2. Chemical Pre-Treatments
5.3. Thermal Pre-Treatments
5.4. Biological Pre-Treatments
6. Environmental Impacts of Anaerobic Digestion of FW with Sewage Sludge
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Anaerobic Digestion |
| AM | Animal Manure |
| BMP | Biochemical Methane Potential |
| CoAD | Anaerobic Co-digestion |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| EU | European Union |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| FL | Food Loose |
| FSC | Food Supply Chain |
| FW | Food Waste |
| HTG | Hydrothermal Gasification |
| LCFA | Long Chain Fatty Acids |
| LPCH | Lipids, Proteins and Carbohydrates |
| OFMSW | Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste |
| OM | Organic Matter |
| TBMP | Theoretical Biochemical Methane Potential |
| TS | Total Solids |
| SS | Sewage Sludge |
| VFA | Volatile Fatty Acids |
| VS | Volatile Solids |
| WWTP | Waste Water Treatment Plants |
References
- Girotto, F.; Alibardi, L.; Cossu, R. Food waste generation and industrial uses: A review. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Food Loss Prevention in Perishable Crops—Contents; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt, J.; Barthel, M.; Macnaughton, S. Food waste within food supply chains: Quantification and potential for change to 2050. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 3065–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, S.L.H.; Lo, I.M.C. Reviewing the anaerobic digestion and co-digestion process of food waste from the perspectives on biogas production performance and environmental impacts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 24435–24450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzby, J.C.; Hyman, J. Total and per capita value of food loss in the United States. Food Policy 2012, 37, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, R.; Ishikawa, M. Prevention and Recycling of Food Wastes in Japan: Policies and Achievements; Kobe University: Kobe, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Health and Food Safety. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/departments/health-and-food-safety_en (accessed on 20 September 2018).
- Monier, V.; Mudgal, S.; Escalon, V.; O’Connor, C.; Gibon, T.; Anderson, G.; Montoux, H.; Reisinger, H.; Dolley, P.; Ogilvie, S. Preparatory Study on Food Waste Across EU 27; European Commission (DG ENV) Directorate C-Industry: Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bräutigam, K.-R.; Jörissen, J.; Priefer, C. The extent of food waste generation across EU-27: Different calculation methods and the reliability of their results. Waste Manag. Res. 2014, 32, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nellman, C.; MacDevette, M.; Manders, T.; Eickhout, B.; Svihus, B.; Prins, A. The Environmental Food Crisis–The Environment’s Role in Averting Future Food Crises; UNEP Rapid Response, U.N. Environ. Programme GRID-Arendal Nor; UNEP/Earthprint: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Papargyropoulou, E.; Lozano, R.; Steinberger, J.K.; Wright, N.; bin Ujang, Z. The food waste hierarchy as a framework for the management of food surplus and food waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 76, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernstad, A.; la Cour Jansen, J. Review of comparative LCAs of food waste management systems—Current status and potential improvements. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 2439–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaya, W.; Gheewala, S.H. Life cycle assessment of MSW-to-energy schemes in Thailand. J. Clean. Prod. 2007, 15, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.H.; Lim, T.Z.; Tan, R.B.H. Food waste conversion options in Singapore: Environmental impacts based on an LCA perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, J.; Boldrin, A.; Christensen, T.H. Anaerobic digestion and digestate use: Accounting of greenhouse gases and global warming contribution. Waste Manag. Res. 2009, 27, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sustainable Management of Food|US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sustainable-management-food (accessed on 8 January 2018).
- The Council of The European Union. Council Directive 1999/31/EC of 26 April 1999 on the Landfill of Waste; Council of the European Union: Luxembourg, 1999; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- The European Parliament and the Council of The European Union. DIRECTIVE 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cossu, R. From triangles to cycles. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2915–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, J.; Scott, E.; Weusthuis, R.; Mooibroek, H. Bio-Refinery as the Bio-Inspired Process to Bulk Chemicals. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uçkun Kiran, E.; Trzcinski, A.P.; Ng, W.J.; Liu, Y. Bioconversion of food waste to energy: A review. Fuel 2014, 134, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, Y.; An, M.-Z.; Tang, Y.-Q.; Syo, T.; Osaka, N.; Morimura, S.; Kida, K. Production of fuel ethanol and methane from garbage by high-efficiency two-stage fermentation process. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2009, 108, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M. Bioenergy conversion studies of organic fraction of MSW: Kinetic studies and gas yield—organic loading relationships for process optimisation. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 95, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Xiao, G.; Peng, L.; Su, H.; Tan, T. The anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and cattle manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, K.; Ezaki, Y. Open L-lactic acid fermentation of food refuse using thermophilic Bacillus coagulans and fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of microflora. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Ren, N. Bioconversion of Kitchen Garbage to Lactic Acid by Two Wild Strains of Lactobacillus Species. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2005, 40, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; Ji, K.S.; Baik, Y.H.; Kwak, W.S.; McCaskey, T.A. Lactic acid fermentation of food waste for swine feed. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1858–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Oh, B.R.; Shin, H.-J.; Eom, C.-Y.; Kim, S.W. Statistical optimization of enzymatic saccharification and ethanol fermentation using food waste. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.-Q.; Koike, Y.; Liu, K.; An, M.-Z.; Morimura, S.; Wu, X.-L.; Kida, K. Ethanol production from kitchen waste using the flocculating yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain KF-7. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S. Biohydrogen production by anaerobic fermentation of food waste. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2004, 29, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, R.; Elmashad, H.; Sun, H.; Ying, Y. Effect of food to microorganism ratio on biohydrogen production from food waste via anaerobic fermentation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 6968–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, C.O.; Perez, E.; Horvath, I.T.; Sheldon, R.A.; Poliakoff, M. Valorization of Biomass: Deriving More Value from Waste. Science 2012, 337, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, S.L.H.; Lo, I.M.C.; Woon, K.S.; Yan, D.Y.S. Life cycle assessment of waste treatment strategy for sewage sludge and food waste in Macau: Perspectives on environmental and energy production performance. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Su, H.; Baeyens, J.; Tan, T. Reviewing the anaerobic digestion of food waste for biogas production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovidou, E.; Ohandja, D.-G.; Gronow, J.; Voulvoulis, N. The Household Use of Food Waste Disposal Units as a Waste Management Option: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 1485–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovidou, E.; Ohandja, D.-G.; Voulvoulis, N. Food waste co-digestion with sewage sludge—Realising its potential in the UK. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 112, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straka, F.; Jenicek, P.; Zabranska, J.; Dohanyos, M.; Kuncarova, M. Anaerobic Fermentation of Biomass and Wastes with Respect to Sulfur and Nitrogen Contents in Treated Materials. In Proceedings of the 11th International Waste Management and Landifill Symposium; Environmental Sanitary Engineering Centre (CISA): Sardinia, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Gavala, H.N.; Skiadas, I.V.; Mladenovska, Z.; Ahring, B.K. Improving anaerobic sewage sludge digestion by implementation of a hyper-thermophilic prehydrolysis step. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belitz, H.D.; Grosch, W.; Schieberle, P. Food Chemistry 4th Revised and Extended Edition; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 315–327. [Google Scholar]
- Christ, O.; Wilderer, P.A.; Angerhöfer, R.; Faulstich, M. Mathematical modeling of the hydrolysis of anaerobic processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carucci, G.; Carrasco, F.; Trifoni, K.; Majone, M.; Beccari, M. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Industry Wastes: Effect of Codigestion on Methane Yield. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Xu, K.-Q.; Li, Y.-Y.; Inamori, Y. Evaluation of hydrogen and methane production from municipal solid wastes with different compositions of fat, protein, cellulosic materials and the other carbohydrates. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 15711–15718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, M.; Holmström, D.; Bohn, I.; Bisaillon, M.; Morgan-Sagastume, F.; Lagerkvist, A. Impact of physical pre-treatment of source-sorted organic fraction of municipal solid waste on greenhouse-gas emissions and the economy in a Swedish anaerobic digestion system. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naroznova, I.; Møller, J.; Scheutz, C. Characterisation of the biochemical methane potential (BMP) of individual material fractions in Danish source-separated organic household waste. Waste Manag. 2016, 50, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agyeman, F.O.; Tao, W. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and dairy manure: Effects of food waste particle size and organic loading rate. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lee, Y.-W.; Jahng, D. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and piggery wastewater: Focusing on the role of trace elements. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5048–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Su, H.; Tan, T. Batch and semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of food waste in a dual solid–liquid system. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 145, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Elmashad, H.; Hartman, K.; Wang, F.; Liu, G.; Choate, C.; Gamble, P. Characterization of food waste as feedstock for anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Ge, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Pang, Y. Characteristics and anaerobic digestion performances of kitchen wastes. Kezaisheng Nengyuan Renew. Energy Resour. 2010, 28, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, A. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste with MSW incineration plant fresh leachate: Process performance and synergistic effects. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Lian, S.; Zheng, L. Effects of thermal pre-treatment on anaerobic co-digestion of municipal biowastes at high organic loading rate. Chemosphere 2014, 101, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Li, S.; Yuan, H.; Zou, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Chufo, A.; Jaffar, M.; Li, X. Evaluating biomethane production from anaerobic mono- and co-digestion of food waste and floatable oil (FO) skimmed from food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 185, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabella, N.; Castellani, V.; Sala, S. Current options for the valorization of food manufacturing waste: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuessl, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Schneller, A. Opportunities in Bio-Based Building Blocks for Polycondensates and Vinyl Polymers; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 49–70. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y. Efficient production of optically pure l -lactic acid from food waste at ambient temperature by regulating key enzyme activity. Water Res. 2015, 70, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassan, M.A.; Yee, L.-N.; Yee, P.L.; Ariffin, H.; Raha, A.R.; Shirai, Y.; Sudesh, K. Sustainable production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from renewable oil-palm biomass. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, A.; Othman, N.; Baharuddin, A.S.; Mokhtar, M.N.; Tabatabaei, M. Enhancing the Halal Food Industry by Utilizing Food Wastes to Produce Value-added Bioproducts. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 121, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagliano, G.; Ventorino, V.; Panico, A.; Pepe, O. Integrated systems for biopolymers and bioenergy production from organic waste and by-products: A review of microbial processes. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refaat, A.A. Biofuels from Waste Materials. In Comprehensive Renewable Energy; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 217–261. ISBN 978-0-08-087873-7. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparatos, A.; Stromberg, P.; Takeuchi, K. Biofuels, ecosystem services and human wellbeing: Putting biofuels in the ecosystem services narrative. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 142, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, A.; Boscaro, D.; Dalla Venezia, F.; Correale Santacroce, F.; Pezzuolo, A.; Sartori, L.; Bolzonella, D. Biogas from Residual Grass: A Territorial Approach for Sustainable Bioenergy Production. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 2747–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscaro, D.; Pezzuolo, A.; Sartori, L.; Marinello, F.; Mattioli, A.; Bolzonella, D.; Grigolato, S. Evaluation of the energy and greenhouse gases impacts of grass harvested on riverbanks for feeding anaerobic digestion plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 4099–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirozzi, D.; Ausiello, A.; Strazza, R.; Trofa, M.; Zuccaro, G.; Toscano, G. Exploitation of agricultural biomasses to produce ii-generation biodiesel. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakci, M. The potential of restaurant waste lipids as biodiesel feedstocks. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaakob, Z.; Mohammad, M.; Alherbawi, M.; Alam, Z.; Sopian, K. Overview of the production of biodiesel from Waste cooking oil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Polo, C.; Cledera-Castro, M. del M. An optimized water reuse and waste valorization method for a sustainable development of poultry slaughtering plants. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 2702–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alptekin, E.; Canakci, M.; Sanli, H. Biodiesel production from vegetable oil and waste animal fats in a pilot plant. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2146–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanavati, H.; Nahvi, I.; Karimi, K. Organic fraction of municipal solid waste as a suitable feedstock for the production of lipid by oleaginous yeast Cryptococcus aerius. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekmecelioglu, D.; Uncu, O.N. Kinetic modeling of enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated kitchen wastes for enhancing bioethanol production. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoeberl, M.; Werkmeister, R.; Faulstich, M.; Russ, W. Biobutanol from food wastes—fermentative production, use as biofuel an the influence on the emissions. Procedia Food Sci. 2011, 1, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.P.T.; Kaushik, R.; Parshetti, G.K.; Mahmood, R.; Balasubramanian, R. Food waste-to-energy conversion technologies: Current status and future directions. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, U. Process and technological aspects of municipal solid waste gasification. A review. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muangrat, R.; Onwudili, J.A.; Williams, P.T. Reactions of different food classes during subcritical water gasification for hydrogen gas production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 2248–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.S.K.; Pfaltzgraff, L.A.; Herrero-Davila, L.; Mubofu, E.B.; Abderrahim, S.; Clark, J.H.; Koutinas, A.A.; Kopsahelis, N.; Stamatelatou, K.; et al. Food waste as a valuable resource for the production of chemicals, materials and fuels. Current situation and global perspective. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagos, K.; Zong, J.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Lu, X. Anaerobic co-digestion process for biogas production: Progress, challenges and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, C.; Rounsefell, B.; Grinham, A.; Clarke, W.; Udy, J. Anaerobic digestion of harvested aquatic weeds: Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes), cabomba (Cabomba caroliniana) and salvinia (Salvinia molesta). Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.K.; Park, S.C.; Chang, H.N. Biochemical methane potential and solid state anaerobic digestion of Korean food wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 1995, 52, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chynoweth, D.P.; Turick, C.E.; Owens, J.M.; Jerger, D.E.; Peck, M.W. Biochemical methane potential of biomass and waste feedstocks. Biomass Bioenergy 1993, 5, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.J.; Esteban, M.B.; Márquez, M.C.; Ramos, P. Biodegradable municipal solid waste: Characterization and potential use as animal feedstuffs. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata-Alvarez, J.; Llabrés, P.; Cecchi, F.; Pavan, P. Anaerobic digestion of the Barcelona central food market organic wastes: Experimental study. Bioresour. Technol. 1992, 39, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallathambi Gunaseelan, V. Anaerobic digestion of biomass for methane production: A review. Biomass Bioenergy 1997, 13, 83–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, T.; Tauseef, S.M.; Abbasi, S.A. Biogas Energy; Springer: New York, NY, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4614-1039-3. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, G.; Frunzo, L.; Giordano, A.; Liotta, F.; Panico, A.; Pirozzi, F. Anaerobic co-digestion of organic wastes. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jahng, D. Long-term anaerobic digestion of food waste stabilized by trace elements. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appels, L.; Assche, A.V.; Willems, K.; Degrève, J.; Impe, J.V.; Dewil, R. Peracetic acid oxidation as an alternative pre-treatment for the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4124–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gujer, W.; Zehnder, A.J.R. Conversion Processes in Anaerobic Digestion. Water Sci. Technol. 1983, 15, 127–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, E. Estudio Comparativo de la Digestión Anaerobia Mesófila y Termófila de Fangos Urbanos. Estado del arte, Parámetros de Operación y Modelado Matemático del Sistema; Universidad de Navarra: San Sebastán, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, N.M.G.; Droste, R.L.; Kennedy, K.J. Evaluation of continuous mesophilic, thermophilic and temperature phased anaerobic digestion of microwaved activated sludge. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2822–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeken, A.; Hamelers, B. Effect of temperature on hydrolysis rates of selected biowaste components. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 69, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, F.R. The biochemistry of anaerobic digestion. In Biomethane: Production and Uses; Roger Bowskil Printing Ltd.: Exeter, UK, 1980; pp. 41–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.G. An Introduction to Chemical Engineering Kinetics & Reactor Design; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1977; ISBN 978-0-471-39609-3. [Google Scholar]
- Palmowski, L.M.; Müller, J.A.; Palmowski, L.M.; Müller, J.A. Influence of the size reduction of organic waste on their anaerobic digestion. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lettinga, G.; Field, J.; van Lier, J.; Zeeman, G.; Huishoff Pol, L.W. Advanced anaerobic wastewater treatment in the near future. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Sanders, W. Assessment of the anaerobic biodegradability of macropollutants. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2004, 3, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izumi, K.; Okishio, Y.; Nagao, N.; Niwa, C.; Yamamoto, S.; Toda, T. Effects of particle size on anaerobic digestion of food waste. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2010, 64, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.S.; Kim, D.H.; Hyun, S.H. Effect of particle size and sodium ion concentration on anaerobic thermophilic food waste digestion. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, W.T.M. Anaerobic Hydrolysis during Digestion of Complex Substrates; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, J.A.; Ferguson, J.F. Solubilization of Particulate Organic Carbon during the Acid Phase of Anaerobic Digestion. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1981, 53, 352–366. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, W.T.M.; Geerink, M.; Lettinga, G. Anaerobic hydrolysis kinetics of particulate substrates. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavilin, V.A.; Rytov, S.V.; Lokshina, L.Y. A description of hydrolysis kinetics in anaerobic degradation of particulate organic matter. Bioresour. Technol. 1996, 56, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadavid-Rodríguez, L.S.; Horan, N. Methane production and hydrolysis kinetics in the anaerobic degradation of wastewater screenings. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaseelan, V.N. Biochemical methane potential of fruits and vegetable solid waste feedstocks. Biomass Bioenergy 2004, 26, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokela, J.P.Y.; Vavilin, V.A.; Rintala, J.A. Hydrolysis rates, methane production and nitrogen solubilisation of grey waste components during anaerobic degradation. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavilin, V.A.; Fernandez, B.; Palatsi, J.; Flotats, X. Hydrolysis kinetics in anaerobic degradation of particulate organic material: An overview. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffiere, P.; Loisel, D.; Bernet, N.; Delgenes, J.-P. Towards new indicators for the prediction of solid waste anaerobic digestion properties. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Smith, L.H.; McCarty, P.L. Methane fermentation of selected lignocellulosic materials. Biomass 1990, 21, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panico, A.; d’Antonio, G.; Esposito, G.; Frunzo, L.; Iodice, P.; Pirozzi, F.; Panico, A.; d’Antonio, G.; Esposito, G.; Frunzo, L.; et al. The Effect of Substrate-Bulk Interaction on Hydrolysis Modeling in Anaerobic Digestion Process. Sustainability 2014, 6, 8348–8363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeh, A.-I.; Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, S.H. Effect of particle size on the rate of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, P.N. A model of some aspects of microbial degradation of particulate substrates. J. Ferment. Technol. 1987, 65, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwietniewska, E.; Tys, J. Process characteristics, inhibition factors and methane yields of anaerobic digestion process, with particular focus on microalgal biomass fermentation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlostathis, S.G.; Giraldo-Gomez, E. Kinetics of anaerobic treatment: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Control 1991, 21, 411–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.; Borja, R.; Weiland, P.; Travieso, L.; Martín, A. Effect of substrate concentration and temperature on the anaerobic digestion of piggery waste in a tropical climate. Process Biochem. 2001, 37, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmashad, H. Effect of temperature and temperature fluctuation on thermophilic anaerobic digestion of cattle manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 95, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Oh, B.R.; Chun, Y.N.; Kim, S.W. Effects of temperature and hydraulic retention time on anaerobic digestion of food waste. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 102, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jules, B.; van, L.; Salih, R.; Gatze, L. High-rate anaerobic wastewater treatment under psychrophilic and thermophilic conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallert, C.; Winter, J. Mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of source-sorted organic wastes: Effect of ammonia on glucose degradation and methane production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 48, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schink, B.; Stams, A.J.M. Syntrophism Among Prokaryotes. In The Prokaryotes; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 471–493. ISBN 978-3-642-30122-3. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Miao, H.; Huang, Z.; Gao, S.; Ruan, W. In situ volatile fatty acids influence biogas generation from kitchen wastes by anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 163, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyukkamaci, N.; Filibeli, A. Volatile fatty acid formation in an anaerobic hybrid reactor. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1491–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, B.; Scherer, P. The roles of acetotrophic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens during anaerobic conversion of biomass to methane: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, J.; Shimizu, T.; Kanno, T.; Kobayashi, M. Dynamic behavior in response to pH shift during anaerobic acidogenesis with a chemostat culture. Biotechnol. Tech. 1999, 13, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.H.P.; Liu, H. Effect of pH on hydrogen production from glucose by a mixed culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 82, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, J.-I.; Shimizu, T.; Tada, K.; Kanno, T.; Kobayashi, M. Selective production of organic acids in anaerobic acid reactor by pH control. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 82, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Park, S.Y.; Zhu, J. Solid-state anaerobic digestion for methane production from organic waste. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G.; Han, X. Optimizing feeding composition and carbon–nitrogen ratios for improved methane yield during anaerobic co-digestion of dairy, chicken manure and wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 120, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, O.P.; Visvanathan, C. Effect of C/N ratio and ammonia-N accumulation in a pilot-scale thermophilic dry anaerobic digester. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 113, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.; Iyer, K.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.J. Ammonia removal in anaerobic digestion by biogas stripping: An evaluation of process alternatives using a first order rate model based on experimental findings. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 178, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yenigün, O.; Demirel, B. Ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion: A review. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Li, Y. Evaluation of methane production and macronutrient degradation in the anaerobic co-digestion of algae biomass residue and lipid waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, H.; Brune, D. Anaerobic co-digestion of algal sludge and waste paper to produce methane. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, C.J.; Humphreys, P.N. The anaerobic treatment of a ligno-cellulosic substrate offering little natural pH buffering capacity. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Peng, L.; Su, H. The effect of a buffer function on the semi-continuous anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 139, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauterböck, B.; Ortner, M.; Haider, R.; Fuchs, W. Counteracting ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion by removal with a hollow fiber membrane contactor. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4861–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprott, G.D.; Patel, G.B. Ammonia toxicity in pure cultures of methanogenic bacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1986, 7, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.R.; Hawkes, F.R. The anaerobic digestion of poultry manure: Variation of gas yield with influent concentration and ammonium-nitrogen levels. Agric. Wastes 1985, 14, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, T.V.; Keesman, K.J.; Zeeman, G.; van Lier, J.B. Effect of ammonia on the anaerobic hydrolysis of cellulose and tributyrin. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 47, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Xue, L.; Chen, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, R. Effects of Ammonia on Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: Process Performance and Microbial Community. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 5749–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelenien, F.; Fujiwara, W.; Namba, Y.; Kosseva, M.; Nishio, N.; Nakashimada, Y. Improved methane fermentation of chicken manure via ammonia removal by biogas recycle. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6368–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahav, O.; Schwartz, Y.; Nativ, P.; Gendel, Y. Sustainable removal of ammonia from anaerobic-lagoon swine waste effluents using an electrochemically-regenerated ion exchange process. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jin, H.-F.; Lim, B.-R.; Park, K.-Y.; Lee, K. Ammonia removal from anaerobic digestion effluent of livestock waste using green alga Scenedesmus sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8649–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Jahng, D. Enhanced anaerobic digestion of piggery wastewater by ammonia stripping: Effects of alkali types. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.-H. Sustainable nitrogen elimination biotechnologies: A review. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guštin, S.; Marinšek-Logar, R. Effect of pH, temperature and air flow rate on the continuous ammonia stripping of the anaerobic digestion effluent. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2011, 89, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yuan, S.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Lu, X. Removal of ammonia nitrogen in wastewater by microwave radiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabumon, P.C. Anaerobic ammonia removal in presence of organic matter: A novel route. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uludag-Demirer, S.; Demirer, G.N.; Chen, S. Ammonia removal from anaerobically digested dairy manure by struvite precipitation. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 3667–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatsi, J.; Affes, R.; Fernandez, B.; Pereira, M.A.; Alves, M.M.; Flotats, X. Influence of adsorption and anaerobic granular sludge characteristics on long chain fatty acids inhibition process. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5268–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zonta, Ž.; Alves, M.M.; Flotats, X.; Palatsi, J. Modelling inhibitory effects of long chain fatty acids in the anaerobic digestion process. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, S.T.; Martin, A.D. Long chain fatty acids degradation in anaerobic digester: Thermodynamic equilibrium consideration. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Gómez, X.; Otero, M.; Morán, A. Anaerobic digestion of solid slaughterhouse waste (SHW) at laboratory scale: Influence of co-digestion with the organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW). Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 40, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.; Oliveira, R.; Alves, M.M. Anaerobic co-digestion of coffee waste and sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sánchez, M.; Gomez, X.; Barriocanal, G.; Cuetos, M.J.; Morán, A. Assessment of the stability of livestock farm wastes treated by anaerobic digestion. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2008, 62, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, L.; Massé, D.I.; Kennedy, K.J.; Chou, S.P. Neutral fat hydrolysis and long-chain fatty acid oxidation during anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse wastewater. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002, 79, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palatsi, J.; Laureni, M.; Andrés, M.V.; Flotats, X.; Nielsen, H.B.; Angelidaki, I. Strategies for recovering inhibition caused by long chain fatty acids on anaerobic thermophilic biogas reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4588–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalman, J.; Bagley, D.M. Effects of C18 long chain fatty acids on glucose, butyrate and hydrogen degradation. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3307–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaleiro, A.J.; Pereira, M.A.; Alves, M. Enhancement of methane production from long chain fatty acid based effluents. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4086–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Facchin, V.; Cavinato, C.; Fatone, F.; Pavan, P.; Cecchi, F.; Bolzonella, D. Effect of trace element supplementation on the mesophilic anaerobic digestion of foodwaste in batch trials: The influence of inoculum origin. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 70, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schattauer, A.; Abdoun, E.; Weiland, P.; Plöchl, M.; Heiermann, M. Abundance of trace elements in demonstration biogas plants. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 108, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climenhaga, M.A.; Banks, C.J. Anaerobic digestion of catering wastes: Effect of micronutrients and retention time. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Duan, N.; Dong, B.; Dai, L. High-solids anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and food waste in comparison with mono digestions: Stability and performance. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson-Moss, C.A.; Duncan, J.R.; Cooper, D.R. The effect of calcium on anaerobic digestion. Biotechnol. Lett. 1989, 11, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pinder, K.L. Effects of calcium on development of anaerobic acidogenic biofilms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1995, 45, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugelman, I.J.; Mccarty, P.L. Cation Toxicity and Stimulation in Anaerobic Waste Treatment. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1965, 37, 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- Buswell, A.M.; Mueller, H.F. Mechanism of Methane Fermentation. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1952, 44, 550–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, W.C. Energy recovery from sanitary landfills—A review. In Microbial Energy Conversion; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 119–138. ISBN 978-0-08-021791-8. [Google Scholar]
- Standard, V.D.I. VDI 4630 Fermentation of Organic Materials—Characterisation of the Substrate, Sampling, Collection of Material Data, Fermentation Tests; The Association of German Engineers (VDI): Düsseldorf, Germany, 2006; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, R.; Takeuchi, H.; Hasegawa, T. Methane production from lignocellulosic agricultural crop wastes: A review in context to second generation of biofuel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1462–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.O.; Lins, P.; Malin, C.; Reitschuler, C.; Illmer, P. Impact of protein-, lipid- and cellulose-containing complex substrates on biogas production and microbial communities in batch experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Xu, F.; Ge, X.; Li, Y. Challenges and strategies for solid-state anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; Li, D.; Yan, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Y. Anaerobic Mesophilic Codigestion of Rice Straw and Chicken Manure: Effects of Organic Loading Rate on Process Stability and Performance. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 179, 846–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kallistova, A.Y.; Goel, G.; Nozhevnikova, A.N. Microbial diversity of methanogenic communities in the systems for anaerobic treatment of organic waste. Microbiology 2014, 83, 462–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnürer, A.; Nordberg, Å. Ammonia, a selective agent for methane production by syntrophic acetate oxidation at mesophilic temperature. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelidaki, I.; Ahring, B.K. Effects of free long-chain fatty acids on thermophilic anaerobic digestion. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.L.; Chan, Y.J.; Chong, M.F. A new energy source from the anaerobic co-digestion (acd) treatment of oleo chemical effluent with glycerin pitch: Co-digestion of Oleo Chemical Effluent with Glycerin Pitch. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Sánchez, A.; Font, X. Anaerobic co-digestion of a simulated organic fraction of municipal solid wastes and fats of animal and vegetable origin. Biochem. Eng. J. 2005, 26, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesteur, M.; Bellon-Maurel, V.; Gonzalez, C.; Latrille, E.; Roger, J.M.; Junqua, G.; Steyer, J.P. Alternative methods for determining anaerobic biodegradability: A review. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Alves, M.; Bolzonella, D.; Borzacconi, L.; Campos, J.L.; Guwy, A.J.; Kalyuzhnyi, S.; Jenicek, P.; van Lier, J.B. Defining the biomethane potential (BMP) of solid organic wastes and energy crops: A proposed protocol for batch assays. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Owens, J.M.; Chynoweth, D.P. Biochemical Methane Potential of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Components. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, H.B.; Sommer, S.G.; Ahring, B.K. Methane productivity of manure, straw and solid fractions of manure. Biomass Bioenergy 2004, 26, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triolo, J.M.; Sommer, S.G.; Møller, H.B.; Weisbjerg, M.R.; Jiang, X.Y. A new algorithm to characterize biodegradability of biomass during anaerobic digestion: Influence of lignin concentration on methane production potential. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9395–9402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, D.A.; Flores, R.A.; Shanklin, C.W.; Whitworth, M.K. Proximate Analysis of Food Service Wastes. Appl. Eng. Agric. 1995, 11, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Cour Jansen, J.; Gruvberger, C.; Hanner, N.; Aspegren, H.; Svärd, A. Digestion of sludge and organic waste in the sustainability concept for Malmö, Sweden. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redondas, V.; Gómez, X.; García, S.; Pevida, C.; Rubiera, F.; Morán, A.; Pis, J.J. Hydrogen production from food wastes and gas post-treatment by CO2 adsorption. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.-L.; Zhang, S.-C.; Shi, H.-Z.; Cai, W.-M. The Influence of pH on Hydrolysis and Acidogenesis of Kitchen Wastes in Two-phase Anaerobic Digestion. Environ. Technol. 2005, 26, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosnowski, P.; Klepacz-Smolka, A.; Kaczorek, K.; Ledakowicz, S. Kinetic investigations of methane co-fermentation of sewage sludge and organic fraction of municipal solid wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5731–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y. A bench scale study of fermentative hydrogen and methane production from food waste in integrated two-stage process. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, C.J.; Chesshire, M.; Heaven, S.; Arnold, R. Anaerobic digestion of source-segregated domestic food waste: Performance assessment by mass and energy balance. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-W.; Han, S.-K.; Shin, H.-S. The optimisation of food waste addition as a co-substrate in anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. Res. 2003, 21, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Chen, S.; Li, X. Anaerobic Co-digestion of Kitchen Waste and Cattle Manure for Methane Production. Energy Sour. Part Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2009, 31, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Gómez, X.; Otero, M.; Morán, A. Anaerobic digestion and co-digestion of slaughterhouse waste (SHW): Influence of heat and pressure pre-treatment in biogas yield. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, N.H.; Park, S.C.; Kang, H. Effects of Mixture Ratio and Hydraulic Retention Time on Single-Stage Anaerobic Co-digestion of Food Waste and Waste Activated Sludge. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2004, 39, 1739–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, F.J.; Wase, D.A.J.; Thayanithy, K.; Forster, C.F. Continuous co-digestion of cattle slurry with fruit and vegetable wastes and chicken manure. Biomass Bioenergy 2002, 22, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mashad, H.M.; Zhang, R. Biogas production from co-digestion of dairy manure and food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4021–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, R.; Szolar, O.; Braun, R. Feedstocks for Anaerobic Digestion; University of Agricultural Science: Vienna, India, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, L.; Oliveira, R.; Alves, M.M. Co-digestion of cow manure, food waste and intermittent input of fat. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neves, L.; Oliveira, R.; Alves, M.M. Fate of LCFA in the co-digestion of cow manure, food waste and discontinuous addition of oil. Water Res. 2009, 43, 5142–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavinato, C.; Fatone, F.; Bolzonella, D.; Pavan, P. Thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of cattle manure with agro-wastes and energy crops: Comparison of pilot and full scale experiences. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, F.A.; Mahmood, Q.; Rashid, N.; Pervez, A.; Raja, I.A.; Shah, M.M. Co-digestion, pretreatment and digester design for enhanced methanogenesis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astals, S.; Batstone, D.J.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Jensen, P.D. Identification of synergistic impacts during anaerobic co-digestion of organic wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Astals, S.; Ariso, M.; Galí, A.; Mata-Alvarez, J. Co-digestion of pig manure and glycerine: Experimental and modelling study. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Al Seadi, T.; Oleskowicz-Popiel, P. The future of anaerobic digestion and biogas utilization. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5478–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagadabhi, P.S.; Lehtomäki, A.; Rintala, J. Co-Digestion of grass silage and cow manure in a cstr by re-circulation of alkali treated solids of the digestate. Environ. Technol. 2008, 29, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata-Alvarez, J.; Dosta, J.; Romero-Güiza, M.S.; Fonoll, X.; Peces, M.; Astals, S. A critical review on anaerobic co-digestion achievements between 2010 and 2013. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 36, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Alvarez, J.; Dosta, J.; Macé, S.; Astals, S. Codigestion of solid wastes: A review of its uses and perspectives including modeling. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2011, 31, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata-Alvarez, J.; Macé, S.; Llabrés, P. Anaerobic digestion of organic solid wastes. An overview of research achievements and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 74, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabbai, V.; Ballico, M.; Aneggi, E.; Goi, D. BMP tests of source selected OFMSW to evaluate anaerobic codigestion with sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astals, S.; Nolla-Ardèvol, V.; Mata-Alvarez, J. Anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and crude glycerol at mesophilic conditions: Biogas and digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolzonella, D.; Battistoni, P.; Susini, C.; Cecchi, F. Anaerobic codigestion of waste activated sludge and OFMSW: The experiences of Viareggio and Treviso plants (Italy). Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, M.R.; Zeshan; Yousaf, S.; Malik, R.N.; Visvanathan, C. Effect of mixing ratio of food waste and rice husk co-digestion and substrate to inoculum ratio on biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 190, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tan, T. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and straw for biogas production. Renew. Energy 2015, 78, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Romano, R.T.; Zhang, R. Anaerobic digestion of food wastes for biogas production. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2010, 3, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bouallagui, H.; Rachdi, B.; Gannoun, H.; Hamdi, M. Mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of abattoir wastewater and fruit and vegetable waste in anaerobic sequencing batch reactors. Biodegradation 2009, 20, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, J.; Perez, M.; Romero, L. Effect of substrate concentration on dry mesophilic anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW). Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6075–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; Pérez, M.; Romero, L.I. Kinetics of mesophilic anaerobic digestion of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste: Influence of initial total solid concentration. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6322–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottet, A.; François, E.; Latrille, E.; Steyer, J.P.; Déléris, S.; Vedrenne, F.; Carrère, H. Estimating anaerobic biodegradability indicators for waste activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, H.; Angelidaki, I.; Ahring, B.K. Co-digestion of the organic fraction of municipal waste with other waste types. In Biomethanization of the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Wastes; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, N.H.; Park, S.C.; Lee, J.S.; Kang, H.; Park, D.H. Single-Stage Anaerobic Codigestion for Mixture Wastes of Simulated Korean Food Waste and Waste Activated Sludge. In Biotechnology for Fuels and Chemicals; Davison, B.H., Lee, J.W., Finkelstein, M., McMillan, J.D., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 567–579. ISBN 978-1-4612-6592-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sosnowski, P.; Wieczorek, A.; Ledakowicz, S. Anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and organic fraction of municipal solid wastes. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 7, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhanian, M.; Hardy, S. The impact of four design parameters on the performance of a high-solids anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste for fuel gas production. Environ. Technol. 1994, 15, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulvoulis, N. Water and sanitation provision in a low carbon society: The need for a systems approach. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2012, 4, 041403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murto, M.; Björnsson, L.; Mattiasson, B. Impact of food industrial waste on anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and pig manure. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 70, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroot, P. Anaerobic codigestion of municipal solid waste and biosolids under various mixing conditions—I. digester performance. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzonella, D.; Innocenti, L.; Pavan, P.; Traverso, P.; Cecchi, F. Semi-dry thermophilic anaerobic digestion of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste: Focusing on the start-up phase. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 86, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, B.; Stentiford, E.I. Co-digestion—Enhancing recovery of organic waste. Orbit Artic. 2006, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dohányos, M.; Zábranská, J.; Kutil, J.; Jeníek, P. Improvement of anaerobic digestion of sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaiz, C.; Gutierrez, J.C.; Lebrato, J. Biomass stabilization in the anaerobic digestion of wastewater sludges. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougrier, C.; Carrère, H.; Delgenès, J.P. Solubilisation of waste-activated sludge by ultrasonic treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 106, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafitte-Trouqué, S.; Forster, C. The use of ultrasound and γ-irradiation as pre-treatments for the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge at mesophilic and thermophilic temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 84, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W. Ultrasonic treatment of biological sludge: Floc disintegration, cell lysis and inactivation. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskicioglu, C.; Prorot, A.; Marin, J.; Droste, R.L.; Kennedy, K.J. Synergetic pretreatment of sewage sludge by microwave irradiation in presence of H2O2 for enhanced anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4674–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, A.; Arshad, M.; Anjum, M.; Mahmood, T.; Dawson, L. The anaerobic digestion of solid organic waste. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sialve, B.; Bernet, N.; Bernard, O. Anaerobic digestion of microalgae as a necessary step to make microalgal biodiesel sustainable. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Guo, R.; Xu, X.; Fan, X.; Luo, S. Hydrogen and methane production from lipid-extracted microalgal biomass residues. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 3465–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Duong, T.H.; Smits, M.; Verstraete, W.; Carballa, M. Enhanced biomethanation of kitchen waste by different pre-treatments. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbeshbishy, E.; Nakhla, G. Comparative study of the effect of ultrasonication on the anaerobic biodegradability of food waste in single and two-stage systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6449–6457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesaro, A.; Naddeo, V.; Amodio, V.; Belgiorno, V. Enhanced biogas production from anaerobic codigestion of solid waste by sonolysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Liang, Y.; Wei, L. Pilot-scale operation of enhanced anaerobic digestion of nutrient-deficient municipal sludge by ultrasonic pretreatment and co-digestion of kitchen garbage. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Torres, M.; Espinosa Lloréns, M. del C. Effect of alkaline pretreatment on anaerobic digestion of solid wastes. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jin, Y. Effects of thermal pretreatment on acidification phase during two-phase batch anaerobic digestion of kitchen waste. Renew. Energy 2015, 77, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariunbaatar, J.; Panico, A.; Esposito, G.; Pirozzi, F.; Lens, P.N.L. Pretreatment methods to enhance anaerobic digestion of organic solid waste. Appl. Energy 2014, 123, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, H.; Warith, M.; Hamoda, M.; Kennedy, K. Evaluation of single vs. staged mesophilic anaerobic digestion of kitchen waste with and without microwave pretreatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 125, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, H.B.; Takyu, K.; Sakashita, H.; Nakano, Y.; Nishijima, W.; Okada, M. Biological solubilization and mineralization as novel approach for the pretreatment of food waste. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fdez.-Güelfo, L.A.; Álvarez-Gallego, C.; Sales Márquez, D.; Romero García, L.I. The effect of different pretreatments on biomethanation kinetics of industrial Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Wastes (OFMSW). Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.W.; Wang, J.-Y. Enhanced hydrolysis and methane yield by applying microaeration pretreatment to the anaerobic co-digestion of brown water and food waste. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Liu, D.; Zeng, R.J.; Angelidaki, I. Hydrogen and methane production from household solid waste in the two-stage fermentation process. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2230–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Borghi, A.; Converti, A.; Palazzi, E.; Del Borghi, M. Hydrolysis and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge and organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Bioprocess Eng. 1999, 20, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavouraki, A.I.; Angelis, E.M.; Kornaros, M. Optimization of thermo-chemical hydrolysis of kitchen wastes. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Bao, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Su, H. The anaerobic digestion of biologically and physicochemically pretreated oily wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 151, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, A.; Mahmood, T. Pretreatment technologies for advancing anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper biotreatment residues. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4273–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patinvoh, R.J.; Osadolor, O.A.; Chandolias, K.; Sárvári Horváth, I.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Innovative pretreatment strategies for biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.K.; Elander, R.T. Pretreatments for Enhanced Digestibility of Feedstocks. In Biomass Recalcitrance; Himmel, M.E., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 436–453. ISBN 978-1-4443-0541-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Kwak, M.-S.; Lee, S.-B.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, J.-W. Effects of Pretreatments on Thermophilic Aerobic Digestion. J. Environ. Eng. 2002, 128, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, L.; Baeyens, J.; Degrève, J.; Dewil, R. Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 755–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ai, P.; Yu, L.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, Y. Comparing the hydrolysis and biogas production performance of alkali and acid pretreatments of rice straw using two-stage anaerobic fermentation. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 132, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wei, S.J.; Wen, Q.M.; Zhang, X.J. Comparison of Pretreatments for Lignocellulosic Biomass. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1008–1009, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskicioglu, C.; Kennedy, K.J.; Droste, R.L. Characterization of soluble organic matter of waste activated sludge before and after thermal pretreatment. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3725–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prorot, A.; Julien, L.; Christophe, D.; Patrick, L. Sludge disintegration during heat treatment at low temperature: A better understanding of involved mechanisms with a multiparametric approach. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 54, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariunbaatar, J.; Panico, A.; Frunzo, L.; Esposito, G.; Lens, P.N.L.; Pirozzi, F. Enhanced anaerobic digestion of food waste by thermal and ozonation pretreatment methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, L.F.; Bochman, G. Pretreatment of Feedstock for Enhanced Biogas Production; IEA Bioenergy: Paris, France, 2014; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, M.; Lagerkvist, A.; Morgan-Sagastume, F. The effects of substrate pre-treatment on anaerobic digestion systems: A review. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1634–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deublein, D.; Steinhauser, A. Biogas from Waste and Renewable Resources: An introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraro, A.; Dottorini, G.; Massini, G.; Mazzurco Miritana, V.; Signorini, A.; Lembo, G.; Fabbricino, M. Combined bioaugmentation with anaerobic ruminal fungi and fermentative bacteria to enhance biogas production from wheat straw and mushroom spent straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.; Matthews, H.S.; Morawski, C. Review and meta-analysis of 82 studies on end-of-life management methods for source separated organics. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasco-Correa, J.; Khanal, S.; Manandhar, A.; Shah, A. Anaerobic digestion for bioenergy production: Global status, environmental and techno-economic implications, and government policies. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caine, M. Biogas Flares: State of the Art and Market Review, Topic report of the IEA Bioenergy Agreement Task 24-. Biological Conversion of Municipal Solid Waste; AEA Technology Environment: Oxfordshire, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, H.; Gable, J.J.; Park, J.K. Evaluation of organic waste diversion alternatives for greenhouse gas reduction. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börjesson, P.; Berglund, M. Environmental systems analysis of biogas systems—Part II: The environmental impact of replacing various reference systems. Biomass Bioenergy 2007, 31, 326–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkeby, J.T.; Birgisdottir, H.; Hansen, T.L.; Christensen, T.H.; Bhander, G.S.; Hauschild, M. Evaluation of environmental impacts from municipal solid waste management in the municipality of Aarhus, Denmark (EASEWASTE). Waste Manag. Res. 2006, 24, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woon, K.S.; Lo, I.M.C.; Chiu, S.L.H.; Yan, D.Y.S. Environmental assessment of food waste valorization in producing biogas for various types of energy use based on LCA approach. Waste Manag. 2016, 50, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelisti, S.; Lettieri, P.; Borello, D.; Clift, R. Life cycle assessment of energy from waste via anaerobic digestion: A UK case study. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güereca, L.P.; Gassó, S.; Baldasano, J.M.; Jiménez-Guerrero, P. Life cycle assessment of two biowaste management systems for Barcelona, Spain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2006, 49, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, S.; Oliviero, L.; Pedrini, M.; Buscaroli, A.; Della Casa, C. Life Cycle Assessment of management systems for sewage sludge and food waste: Centralized and decentralized approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 44, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Aramaki, T.; Hwang, Y.; Hanaki, K. Environmental Impact of Solid Waste Treatment Methods in Korea. J. Environ. Eng. 2004, 130, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M.; Strid, I.; Hansson, P.-A. Carbon footprint of food waste management options in the waste hierarchy—A Swedish case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 93, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Food Waste Composition | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FW Type and Origin | TS [%] | VS [%] | Proteins [%] | Lipids [%] | Carbohydrates [%] | VFA [%] | C [%] | N [%] | C/N Ratio | Reference | |||||
| Household individual sorted materials | [36] | ||||||||||||||
| Meat and bone | 70–75 | 23–30 | 1 | [37] | |||||||||||
| Fish and fishbone | 75.6 | 20.2 | [38] | ||||||||||||
| Egg and shell | 35 | 32 | 2 | [39] | |||||||||||
| Dairy products | 25–35 | 20–45 | 53 | [39] | |||||||||||
| Fruit | 4 | 2 | 83 | [40] | |||||||||||
| Vegetable | 27 | 1.4 | 27 | [41] | |||||||||||
| Individual fractions from OFMSC | [42] | ||||||||||||||
| Animal kitchen waste | 33.3 | 54.4 | 35.7 | 9.9 | |||||||||||
| Vegetable kitchen waste | 13.4 | 21.6 | 19.4 | 57.6 | |||||||||||
| Raw animal waste | 38.6 | 59.8 | 27.2 | 13 | |||||||||||
| Raw vegetable waste | 10.8 | 19.4 | 11.1 | 69.4 | |||||||||||
| OFMSC in Sweden | 90.8 | 18.2 | 20 | 29.4 | 0.35 | 50 | 2.8 | 17.85 | [43] | ||||||
| Fractions of OFMSC in Denmark | [44] | ||||||||||||||
| Animal food waste | 41 | 84 | 12 | 25 | 52 a | ||||||||||
| Vegetable food waste | 24 | 93 | 5 | 14 | 53 a | ||||||||||
| Food waste | 29.3 | 26.6 | 35 | 32.5 | 48.4 | 3.8 | 12.7 | [45] | |||||||
| Food waste | 18.1 | 17.1 | 23.3 | 61.9 | [46] | ||||||||||
| Food waste | 23.1 | 21.0 | 56.1 | 2.3 | 24.5 | [47] | |||||||||
| Food waste for AD | 30.9 | 26.35 | 46.8 | 3.54 | 13.2 | [48] | |||||||||
| Kitchen waste | 24 | 23.2 | 15 | 23.9 | 55.2 | 54 | 2.4 | 22.5 | [49] | ||||||
| Food waste | 23.2 | 21.7 | 2.9 | 6.5 | 13.7 | [50] | |||||||||
| OFMSC from municipal biowaste | 20 | 18 | 30 | 4.4 | 10.7 | 17 | [51] | ||||||||
| Food waste | 16.7 | 15.3 | 2.4 | 1.4 | 11.5 | [52] | |||||||||
| Notes a: Only easily-degradable carbohydrates | |||||||||||||||
| Metal Elements in FW [g/kg-TS] | |||||||||||||||
| S | Ca | Mg | K | Na | Fe | Zn | Cu | Mn | Mo | Reference | |||||
| Food waste | 3.4 | 1.7 | 0.7 | 9.6 | 10.1 | 0.041 | 0.032 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.00003 | [45] | ||||
| C [%weight] | H [%weight] | N [%weight] | O [%weight] | S [%weight] | Ref. | Theoretical Biogas Yield [Nl/kg-TS] | Theoretical Biogas Composition [%CH4 vol.] [%CO2 vol.] | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 | 12 | - | 12 | - | 1390 | 72 | 28 | ||
| 46 | 5 | 18.5 | 30 | 0.5 | [37] | 800 | 60 | 40 | [149] |
| 40 | 7 | - | 53 | - | 750 | 50 | 50 | ||
| Mono-Digestion Experiences | ||||||||
| Substrate | Operational Conditions | CH4 Yield [mlCH4/gVSdeg] | Reference | |||||
| Food Waste | 234 | [36,186] | ||||||
| Food Waste | 234 | [183] | ||||||
| Food Waste | Two stage | 546 | [187] | |||||
| Food Waste | Full scale | 399 | [188] | |||||
| Food Waste | Batch | 410 | [24] | |||||
| Animal FW | Batch | 500 | [42] | |||||
| Vegetable FW | 400 | |||||||
| Animal FW | Batch | 500 | [44] | |||||
| Vegetable FW | 400 | |||||||
| Co-Digestion Experiences | ||||||||
| Sub 1 | Sub 2 | Ratio | Operational Conditions | CH4 Yield [mlCH4/gVSdeg] | Improvements | Reference | ||
| (a) | (b) [%] | (c) [%] | ||||||
| SS | FW | 50:50 | Lab Scale | 215 | Increased OLR Increased buffering capacity from ammonia | +24.27 | +85.3 | [189] |
| SS | FW | 20:80 | 157 | +54.60 | +35.3 | |||
| SS | FW | 75:25 | - | 439 | +47.81 | [186] | ||
| SS | FW | 80:20 | Continuous pilot scale | 326 | Increased buffering capacity from ammonia | +10.80 | +21 | [183] |
| CM | FW | 67:33 | Continuous lab scale | 388 | High buffering capacity and trace element supplement | +41.1 | [24] | |
| CM | FW | 50:50 | Batch | 298 | High buffering capacity of ammonia | +44 | [190] | |
| FW | ShW | 83:17 | Lab scale | 300 | Trace element supplement. Ammonia accumulation | −61.9 | [191] | |
| WAS | FW | 90:10 | - | 186 | Nutrient balance. Increased buffering capacity from ammonia | CH4 yield increases while addition of FW increases. | [192] | |
| WAS | FW | 50:50 | - | 321 | ||||
| WAS | FW | 10:90 | - | 346 | ||||
| frW | CM | 20:80 | Batch | 380 | Nutrient and C/N ratio balance. High buffer capacity | CH4 yield increases while addition of FW increases. | [193] | |
| frW | CM | 30:70 | 340 | |||||
| frW | CM | 40:60 | 380 | |||||
| frW | CM | 50:50 | 450 | |||||
| FW | PWw | 93:7 | Continuous Lab scale | 358 | Trace elements supplements. | [46] | ||
| FW | PWw | 83:17 | 388 | |||||
| Notes: | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Abbreviations: | ||||||||
| SS (Sewage Sludge) CM (Cattle Manure) ShW (Slaughterhouse Waste) WAS (Waste Activated Sludge) frW (Fruit Waste) PWw (Piggery Waste Water) | ||||||||
| Pre-Treatment | Substrate | Factors Affected | Results and Improvements | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical and Physical Pre-Treatments | ||||
| Screw press and screening | OFMSW |
|
| [4] |
| Grinding | FW |
|
| [45] |
| Milling | FW |
|
| [95] |
| Comminution | FW + SS |
|
| [92] |
| Pressure (10 bar) + Depressure (1 bar) | FW |
|
| [235] |
| Sonication | FW |
|
| [236] |
| [237] | |||
| Ultrasonication (US) | SS |
|
| [238] |
| Chemical Pre-Treatments | ||||
| Alkaline pre-treatment | OFMSW |
|
| [239] |
| Acid pre-treatment (HCl until pH = 2) | FW |
|
| [235] |
| H2SO4 pre-treatment | Lignocellulosic waste |
|
| [46] |
| Thermal Pre-Treatments | ||||
| Heat (90–120 °C) | FW |
|
| [240] |
| Heat (80 °C) |
| [241] | ||
| Heating (120 °C–30 min) |
|
| [235] | |
| Microwave (145 °C) | FW |
|
| [242] |
| Freezing + thawing (−80–55 °C) | FW |
|
| [113] |
| [235] | |||
| Biological Pre-Treatments | ||||
| Biological solubilization | FW + Waste Water |
|
| [243] |
| Composting | OFMSW |
|
| [244] |
| Microaireation | FW |
|
| [245] |
| Two stages | OFMSW |
|
| [246] |
| Combination of Pre-Treatments | ||||
| Bacterial hydrolysis and alkaline addition | FW + SS |
|
| [247] |
| Thermo-acid (HCl + 120 °C) | FW |
|
| [235] |
| Thermo-acid (HCl at 100 °C) | OFMSW |
|
| [248] |
| Bio-Physico-Chemical (Bacillusat + US + Acid) | Oil + Waste Water |
|
| [249] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales-Polo, C.; Cledera-Castro, M.D.M.; Moratilla Soria, B.Y. Reviewing the Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: From Waste Generation and Anaerobic Process to Its Perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101804
Morales-Polo C, Cledera-Castro MDM, Moratilla Soria BY. Reviewing the Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: From Waste Generation and Anaerobic Process to Its Perspectives. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(10):1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101804
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales-Polo, Carlos, María Del Mar Cledera-Castro, and B. Yolanda Moratilla Soria. 2018. "Reviewing the Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: From Waste Generation and Anaerobic Process to Its Perspectives" Applied Sciences 8, no. 10: 1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101804
APA StyleMorales-Polo, C., Cledera-Castro, M. D. M., & Moratilla Soria, B. Y. (2018). Reviewing the Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: From Waste Generation and Anaerobic Process to Its Perspectives. Applied Sciences, 8(10), 1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101804