Domestic Cat Sound Classification Using Learned Features from Deep Neural Nets
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cat Sound Dataset
3. Method for Classification
3.1. Data Augmentation and Pre-Processing
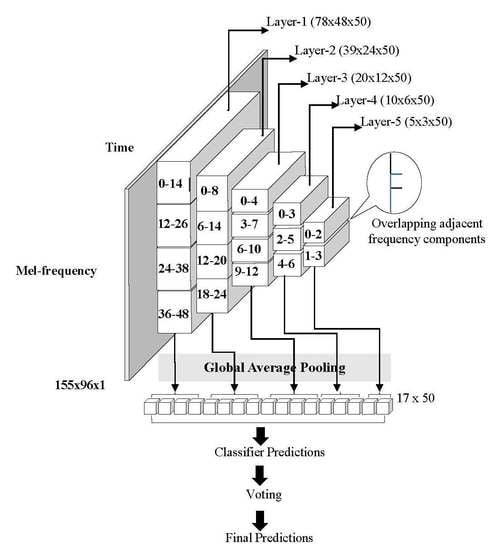
3.2. Frequency Division Average Pooling
3.3. Transfer Learning of CNN
3.4. CDBN Feature Extraction
3.5. Cat Sound Classification
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitrovic, D.; Zeppelzauer, M.; Breiteneder, C. Discrimination and retrieval of animal sounds. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Multi-Media Modelling Conference, Beijing, China, 4–6 January 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gunasekaran, S.; Revathy, K. Content-based classification and retrieval of wild animal sounds using feature selection algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing, Bangalore, India, 9–11 February 2010; pp. 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, N.; Mathini, S.; Lakshrni, T.; Preethi, P.; Chandrasekar, M. Identifying the population of animals through pitch, formant, short time energy-A sound analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computing, Electronics and Electrical Technologies (ICCEET), Kumaracoil, India, 21–22 March 2012; pp. 704–709. [Google Scholar]
- Zaugg, S.; Schaar, M.; Houégnigan, L.; Gervaise, C.; André, M. Real-time acoustic classification of sperm whale clicks and shipping impulses from deep-sea observatories. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Hernandez, F.R.; Sanchez-Fernandez, L.P.; Suarez-Guerra, S.; Sanchez-Perez, L.A. Marine mammal sound classification based on a parallel recognition model and octave analysis. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 119, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeli, R.; Wolff, D.; Kurth, F.; Koch, M.; Tauchert, K.-H.; Frommolt, K.-H. Detecting bird sounds in a complex acoustic environment and applicationto bioacoustic monitoring. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 1524–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Adaptive energy detection for bird sound detection in complex environments. Neurocomputing 2015, 155, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassak, S.; Nachamai, M.; Murthy, A.K. Survey study on the methods of bird vocalization classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Current Trends in Advanced Computing (ICCTAC), Bangalore, India, 10–11 March 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowell, D.; Benetos, E.; Gill, L.F. On-bird sound recordings: Automatic acoustic recognition of activities and contexts. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2017, 25, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Bellisario, K.; Dai, N.; Omrani, H.; Pijanowski, B.C. Automated bird acoustic event detection and robust species classification. Ecol. Inform. 2017, 39, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, J.; Bello, J.P.; Farnsworth, A.; Kelling, S. Fusing shallow and deep learning for bioacoustic bird species classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowell, D.; Wood, M.; Stylianou, Y.; Glotin, H. Bird detection in audio: A survey and a chanllange. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing, Vietri sul Mare, Italy, 13–16 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, J.J.; Travieso, C.M.; Rodríguez, D.S.; Dutta, M.K.; Singh, A. Using bioacoustic signals and support vector machine for automatic classification of insects. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 11–12 February 2016; pp. 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, W.; Aibinu, A.M.; Salami, M.J.E.; Akmelawati, R.; Muthalif, A.G.A. Animal sound activity detection using multi-class support vector machines. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics (ICOM), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–19 May 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntalampiras, S. Bird species identification via transfer learning from music genres. Ecol. Inform. 2018, 44, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, C. House Cat: How to Keep Your Indoor Cat Sane and Sound; Howell Book House: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, D.C. The Domestic Cat: The Biology of Its Behaviour, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ntalampiras, S. A Novel Holistic Modeling Approach for Generalized Sound Recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2013, 20, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandeya, Y.R.; Lee, J. Domestic cat sound classification using transfer learning. Int. J. Fuzzy Log. Intell. Syst. 2018, 18, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, J.; Bello, J.P. Deep convolutional neural networks and data augmentation for environmental sound classification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cat Communication. 2018. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cat_communication (accessed on 1 March 2017).
- Moss, L. Cat Sounds and What They Mean. 2013. Available online: https://www.mnn.com/family/pets/stories/cat-sounds-and-what-they-mean (accessed on 1 April 2013).
- Choi, K.; Fazekas, G.; Cho, K. A tutorial on deep learning for music information retrieval. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1709.04396. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.; Joo, D.; Kim, J. Kapre: On-GPU audio preprocessing layers for a quick implementation of deep neural network models with keras. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1706.05781. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.L.Q.; Yan, S. Network in network. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1312.4400v3. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, R.; Serra, X. Towards an efficient deep learning model for musical onset detection. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1806.06773v2. [Google Scholar]
- Oquab, M.; Bottou, L.; Laptev, I.; Sivic, J. Learning and transferring mid-level image representations using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1717–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Z.; Pan, S.J.; Xue, G.R.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Q. Heterogeneous transfer learning for image classification. In Proceedings of the Association of Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–11 August 2011; pp. 1304–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Mun, S.; Shon, S.; Kim, W.; Han, D.K.; Ko, H. Deep neural network based learning and transferring mid-level audio features for acoustic scene classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 796–800. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, P.; Umbach, R.H. A study on transfer learning for acoustic event detection in a real life scenario. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP), Luton, UK, 16–18 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zheng, T.F. Transfer learning for speech and language processing. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA), Hong Kong, China, 16–19 December 2015; pp. 1225–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Dieleman, S.; Schrauwen, B. Transfer learning by supervised rre-training for audio-based music classification. In Proceedings of the International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), Jeju, Korea, 13–16 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.; Fazekas, G.; Sandler, M.; Cho, K. Transfer learning for music classification and regression task. In Proceedings of the International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference, Suzhou, China, 23–27 October 2017; pp. 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Mahieux, T.B.; Ellis, D.P.W.; Whitman, B.; Lamere, P. The Million Song Dataset. In Proceedings of the International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), Miami, FL, USA, 24–28 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle, E.L. An Investigation of the Relationship between Human Music and Animal Songs. Ph.D. Thesis, Pinceton University, Princeton, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brumm, H. Biomusic and Popular Culture: The Use of Animal Sounds in the Music of the Beatles. J. Pop. Music Stud. 2012, 24, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird in Music. 2018. Available online: https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Birds_in_music (accessed on 16 July 2018).
- Rohrmeier, M.; Zuidema, W.; Wiggins, G.A.; Scharff, C. Principles of structure building in music, language and animal song. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Grosse, R.; Ranganath, R.; Ng, A.Y. Convolutional deep belief networks for scalable unsupervised learning of hierarchical representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–18 June 2009; pp. 609–616. [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins, G.; Bengio, Y. Empirical Evaluation of Convolutional RBMs for Vision; Technical Report; Université de Montréal: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.-W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzi, M.; Ranjbar, M.; Mori, G. Stacks of convolutional restricted boltzmann machines for shift-invariant feature learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Largman, Y.; Pham, P.; Ng, A.Y. Unsupervised feature learning for audio classification using convolutional deep belief networks. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–10 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Bias, Variance, and Arching Classifiers; University of California: Oakland, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Laaksonen, J.; Oja, E. Classification with Learning k-Nearest Neighbors. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Washington, DC, USA, 3–6 June 1996; pp. 1480–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurts, P.; Ernst, D.; Wehenkel, L. Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 2006, 63, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linear Discriminant Analysis. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_discriminant_analysis (accessed on 1 August 2018).
- Fisher, R.A. The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Ann. Eugen. 1936, 7, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahuleyan, H. Music genre classification using machine learning techniques. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1804.01149. [Google Scholar]
- Dietterich, T.G. Ensemble methods in machine learning. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Multiple Classifier Systems, Cagliari, Italy, 21–23 June 2000; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, Y. The Truth of the F-Measure; University of Manchester: Manchester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijsbergen, C.J.V. Information Retrieval, 2nd ed.; Butterworths: London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Kohavi, R. A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–25 August 1995; pp. 1137–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Jin, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Cichocki, A. Multi-kernel extreme learning machine for EEG classification in brain-computer interfaces. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 96, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Class | Input | Layer_1 (Channel_0) | Layer_2 (Channel_0) | Layer_3 (Channel_0) | Layer_4 (Channel_0) | Layer_5 (Channel_0) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angry |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Defence |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Fighting |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Happy |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Hunting Mind |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Mating |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Mother Call |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Paining |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Resting |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Warning |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Classifiers | Accuracy (%) | F1-Score | AUC Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN (±SD) | CDBN (±SD) | CNN | CDBN | CNN | CDBN | |
| RF | 84.64 (0.02) | 86.32 (0.03) | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.988 | 0.988 |
| KNN | 81.60 (0.02) | 80.32 (0.02) | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.898 | 0.890 |
| Extra Trees | 83.80 (0.03) | 84.29 (0.03) | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.987 | 0.985 |
| LDA | 78.48 (0.02) | 81.84 (0.03) | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.975 | 0.979 |
| SVM | 87.43 (0.03) | 90.88 (0.04) | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.992 | 0.994 |
| Ensemble | 90.80 | 91.13 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.994 | 0.995 |
| Cat Sound Dataset | Accuracy (%) | F1-Score | AUC Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | CDBN | CNN | CDBN | CNN | CDBN | |
| Original_GAP * | 70.71 | 76.09 | 0.690 | 0.760 | 0.958 | 0.963 |
| Original_FDAP # | 79.12 | 82.15 | 0.780 | 0.820 | 0.974 | 0.982 |
| 1x_Aug_GAP | 80.61 | 76.39 | 0.810 | 0.760 | 0.977 | 0.970 |
| 1x_Aug_FDAP | 86.51 | 87.52 | 0.860 | 0.880 | 0.989 | 0.989 |
| 2x_Aug_GAP | 81.89 | 76.60 | 0.820 | 0.760 | 0.982 | 0.969 |
| 2x_Aug_FDAP | 89.31 | 87.96 | 0.890 | 0.880 | 0.993 | 0.991 |
| 3x_Aug_GAP | 83.04 | 79.49 | 0.830 | 0.790 | 0.985 | 0.977 |
| 3x_Aug_FDAP | 90.80 | 91.13 | 0.910 | 0.910 | 0.994 | 0.995 |
| Angry | Defense | Fighting | Happy | Hunting Mind | Mating | Mother Call | Paining | Resting | Warning | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angry | 83 */94 # | 2/– | 2/– | –/– | –/– | 2/1 | 1/– | 4/1 | –/– | 7/4 |
| Defense | 1/– | 92/97 | –/– | –/– | 4/1 | 1/3 | 1/– | –/– | –/– | 1/– |
| Fighting | 1/1 | 2/– | 84/90 | 1/– | 7/5 | 1/1 | –/2 | 3/1 | –/– | 1/1 |
| Happy | 4/2 | 4/2 | 3/– | 74/90 | 5/1 | 1/– | 1/1 | 1/1 | –/– | –/– |
| HuntingMind | 1/– | 4/– | 4/1 | –/– | 78/96 | 6/1 | –/– | –/– | 2/– | 6/2 |
| Mating | 2/2 | –/– | 2/1 | –/2 | 7/3 | 76/85 | 1/– | 2/2 | 2/– | 8/5 |
| MotherCall | 1/– | –/– | 2/– | 4/2 | 4/2 | 3/1 | 78/94 | 4/– | 5/2 | –/– |
| Paining | 7/5 | 1/– | 3/1 | 8/4 | 1/2 | 1/– | 4/3 | 75/85 | –/– | –/– |
| Resting | –/– | 3/3 | 1/– | –/– | 6/3 | 4/– | 1/– | –/– | 78/92 | 7/1 |
| Warning | 5/2 | 5/2 | 2/– | 1/2 | 4/2 | 5/2 | –/– | 1/1 | 2/1 | 76/89 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pandeya, Y.R.; Kim, D.; Lee, J. Domestic Cat Sound Classification Using Learned Features from Deep Neural Nets. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101949
Pandeya YR, Kim D, Lee J. Domestic Cat Sound Classification Using Learned Features from Deep Neural Nets. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(10):1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101949
Chicago/Turabian StylePandeya, Yagya Raj, Dongwhoon Kim, and Joonwhoan Lee. 2018. "Domestic Cat Sound Classification Using Learned Features from Deep Neural Nets" Applied Sciences 8, no. 10: 1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101949
APA StylePandeya, Y. R., Kim, D., & Lee, J. (2018). Domestic Cat Sound Classification Using Learned Features from Deep Neural Nets. Applied Sciences, 8(10), 1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101949