The Effect of Interfacial Ge and RF-Bias on the Microstructure and Stress Evolution upon Annealing of Ag/AlN Multilayers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
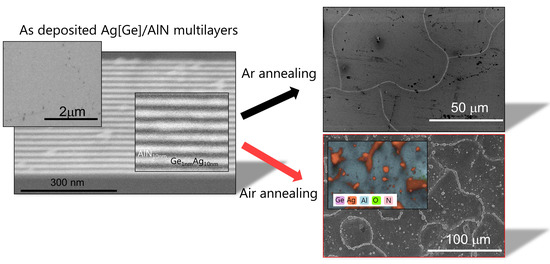
2.1. Microstructure of the as-Deposited Ag[Ge]/AlN NMLs
2.2. Microstructure of the Annealed Ag[Ge]/AlN NMLs
2.2.1. Structural Evolution by XRD
2.2.2. Annealed Microstructure by SEM
3. Discussion
The Effect of the Initial Stress State and Interfacial Ge on the Mechanism of Stress Relaxation during Annealing
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
- RF-bias application created disorder and roughness in the as deposited samples (both in planar and cross-sectional morphology) as well as a compressive state in Ag. The presence of Ge was found to smooth the Ag/AlN interface which appeared flatter and more regular in comparison with the Ag/AlN system.
- Wrinkling and cracking were observed at temperatures ≥400 C in air and Ar depending on the initial stress state of the system: compressive for bias samples leading to wrinkling and tensile for non-bias samples leading to cracking. The presence of Ge was determined to change the internal stress state in the Ag layers from compressive to tensile in non-bias samples in the as-deposited state.
- The Ag surface migration is observed prominently in air at 700 C for both, bias and non-bias samples, mostly through the previously formed cracks (at 400 C) due to stress relaxation. However, the Ag amount on the surface was found to be considerably lower in comparison with Ag/AlN systems annealed at 400 C.
- The presence of Ge was proved to hinder the Ag mobility and diffusion at high temperatures in air. Ge accumulation was measured close to Ag particle on the surface.
- Minimal Ag surface migration is observed for all the samples annealed in Ar at any temperatures. In particular, for non-bias samples, the high temperature treatment in Ar atmosphere is found to create a network of cracks extending all over the sample surface . These samples preserve the multilayer periodic ordered structure and keep a high internal tensile stress state up to 700 C.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lloyd, S.J.; Molina-Aldareguia, J.M. Multilayered materials: A palette for the materials artist. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 2003, 361, 2931–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janczak-Rusch, J.; Kaptay, G.; Jeurgens, L.P.H. Interfacial Design for Joining Technologies: An Historical Perspective. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, G. Metallic Multilayers and Their Applications: Theory, Experiments, and Applications Related to Thin Metallic Multilayers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Stueber, M.; Holleck, H.; Leiste, H.; Seemann, K.; Ulrich, S.; Ziebert, C. Concepts for the Design of Advanced Nanoscale PVD Multilayer Protective Thin Films. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 483, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, J.; Larché, F. A simple model for coherent equilibrium. Acta Metall. 1984, 32, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moszner, F.; Cancellieri, C.; Chiodi, M.; Yoon, S.; Ariosa, D.; Janczak-Rusch, J.; Jeurgens, L. Thermal Stability of Cu/W Nano-multilayers. Acta Mater. 2016, 107, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamleh, S.; Rezaei, G.; Jalilian, J. Stress and strain effects on the electronic structure and optical properties of ScN monolayer. Phys. Lett. A 2018, 382, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodi, M.; Cancellieri, C.; Moszner, F.; Andrzejczuk, M.; Janczak-Rusch, J.; Jeurgens, L.P. Massive Ag migration through Metal/Ceramic Nano-multilayers: An interplay between Temperature, Stress-Relaxation and Oxygen-Enhanced Mass Transport. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 4927–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigozzi, G.; Antušek, A.; Janczak-Rusch, J.; Parlinska-Wojtan, M.; Passerone, D.; Antonio Pignedoli, C.; Bissig, V.; Patscheider, J.; Jeurgens, L.P. Phase Constitution and Interface Structure of Nano-sized Ag-Cu/AlN Multilayers: Experiment and ab initio Modeling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 181602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Herman, H. Liquid-quenched Ag-Ge Alloys; Formation and Evolution of Metastable phases. J. Mater. Sci. 1977, 12, 2021–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jeurgens, L.P.H.; Sigle, W.; Mittemeijer, E.J. Observation and Origin of Extraordinary Atomic Mobility at Metal-Semiconductor Interfaces at Low Temperatures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 016102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flötotto, D.; Wang, Z.M.; Jeurgens, L.P.H.; Bischoff, E.; Mittemeijer, E.J. Effect of adatom surface diffusivity on microstructure and intrinsic stress evolutions during Ag film growth. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 043503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniuk, T.; Olivier, N.; Belardini, A.; McPolin, C.; Sibilia, C.; Wronkowska, A.A.; Wronkowski, A.; Szoplik, T.; Zayats, A.V. Self-Assembled Silver–Germanium Nanolayer Metamaterial with the Enhanced Nonlinear Response. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1700753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, P.; Stefaniuk, T.; Trzcinski, M.; Wronkowska, A.A.; Wronkowski, A.; Szoplik, T. Ge Wetting Layer Increases Ohmic Plasmon Losses in Ag Film due to Segregation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8999–9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariosa, D.; Cancellieri, C.; Araullo-Peters, V.; Chiodi, M.; Klyatskina, E.; Janczak-Rusch, J.; Jeurgens, L.P.H. Modeling of Interface and Internal Disorder Applied to XRD Analysis of Ag-Based Nano-Multilayers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 20938–20949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furgeaud, C.; Simonot, L.; Michel, A.; Mastail, C.; Abadias, G. Impact of Ge alloying on the early growth stages, microstructure and stress evolution of sputter-deposited Cu-Ge thin films. Acta Mater. 2018, 159, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Tien, S.K.; Kuo, Y.C. The effects of substrate bias, substrate temperature, and pulse frequency on the microstructures of chromium nitride coatings deposited by pulsed direct current reactive magnetron sputtering. J. Electron. Mater. 2005, 34, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovac, H.S.; Zoch, H. Influence of Substrate Bias Voltage on the Properties of Sputtered Aluminum-Scandium Thin Sheets. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 2012, 2, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Maekawa, T.; Okano, S.; Bandow, T. Effects of rf-Bias on Properties of Sputtered Silicon Films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 20, L485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Gong, C. Effects of Pulsed Bias Duty Ratio on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiN/TiAlN Multilayer Coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7881–7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryhalski, J.; Fontana, L.C.A.; Odorczyk, M.F.; Scholtz, J.S.; Sagas, J.C.A.; Recco, A.A. Pulsed bias effect on crystallinity and nano-roughness of Ti6Al4V-N films deposited by grid assisted magnetron sputtering system. Mater. Res. 2014, 17, 1545–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clemens, B.M.; Gay, J.G. Effect of layer-thickness fluctuations on superlattice diffraction. Phys. Rev. B 1987, 35, 9337–9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupeau, C. Atomic force microscopy study of the morphological shape of thin film buckling. Thin Solid Films 2002, 406, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logeeswaran, V.; Kobayashi, N.P.; Islam, M.S.; Wu, W.; Chaturvedi, P.; Fang, N.X.; Wang, S.Y.; Williams, R.S. Ultrasmooth Silver Thin Films Deposited with a Germanium Nucleation Layer. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chason, E.; Sheldon, B.W.; Freund, L.B.; Floro, J.A.; Hearne, S.J. Origin of Compressive Residual Stress in Polycrystalline Thin Films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 156103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, W.M.; Paff, R.J. Thermal expansion of AlN, sapphire, and silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 1974, 45, 1456–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, V.; Schwartzman, A.; Freund, L. Crack patterns in brittle thin films. Int. J. Fract. 2001, 109, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, V. Residual stress and cracking in thin PVD coatings. Vacuum 2002, 64, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracht, H.; Stolwijk, N.A. Diffusion in Si, Ge, and their alloys—Introduction. In Diffusion in Semiconductors; Beke, D.L., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Welzel, U.; Ligot, J.; Lamparter, P.; Vermeulen, A.C.; Mittemeijer, E.J. Stress analysis of polycrystalline thin films and surface regions by X-ray diffraction. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2005, 38, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clemens, B.; Bain, J. Stress Determination in Textured Thin Films Using X-ray Diffraction. MRS Bull. 1992, 17, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cancellieri, C.; Klyatskina, E.; Chiodi, M.; Janczak-Rusch, J.; Jeurgens, L.P.H. The Effect of Interfacial Ge and RF-Bias on the Microstructure and Stress Evolution upon Annealing of Ag/AlN Multilayers. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122403
Cancellieri C, Klyatskina E, Chiodi M, Janczak-Rusch J, Jeurgens LPH. The Effect of Interfacial Ge and RF-Bias on the Microstructure and Stress Evolution upon Annealing of Ag/AlN Multilayers. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(12):2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122403
Chicago/Turabian StyleCancellieri, Claudia, Elizaveta Klyatskina, Mirco Chiodi, Jolanta Janczak-Rusch, and Lars P. H. Jeurgens. 2018. "The Effect of Interfacial Ge and RF-Bias on the Microstructure and Stress Evolution upon Annealing of Ag/AlN Multilayers" Applied Sciences 8, no. 12: 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122403
APA StyleCancellieri, C., Klyatskina, E., Chiodi, M., Janczak-Rusch, J., & Jeurgens, L. P. H. (2018). The Effect of Interfacial Ge and RF-Bias on the Microstructure and Stress Evolution upon Annealing of Ag/AlN Multilayers. Applied Sciences, 8(12), 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122403