Estimation of High-Resolution Daily Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentration in Beijing 2013–2017 Using 1 km MAIAC AOT Data
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Ground-Level PM2.5 Data Sets
2.3. AOT Data Sets
2.4. Data Preprocessing
2.5. LMEM Model Fitting and Validation
3. Results
3.1. Data Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Results of Model Fitting and Validation
3.3. Comparing between Estimated and Measured PM2.5 Concentrations
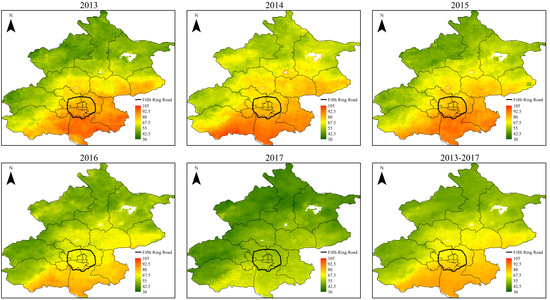
3.4. Spatiotemporal Trends of PM2.5 Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health Effects of Fine Particulate Air Pollution: Lines that Connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Xu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Dong, S.; Guo, C.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, X. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the adverse health effects of ambient PM2.5 and PM10 pollution in the Chinese population. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xiang, X.; Wu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Song, J.; Sun, K.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y. Fine Particulate Air Pollution and First Hospital Admissions for Ischemic Stroke in Beijing, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, J.S.; Messier, K.P.; Gani, S.; Brauer, M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Lunden, M.M.; Marshall, J.D.; Portier, C.J.; Rch, V.; Hamburg, S.P. High-Resolution Air Pollution Mapping with Google Street View Cars: Exploiting Big Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel-Cox, J.A.; Hoff, R.M.; Haymet, A.D.J. Recommendations on the Use of Satellite Remote-Sensing Data for Urban Air Quality. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 1360–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Christopher, S.A. Intercomparison between satellite-derived aerosol optical thickness and PM2. 5 mass: Implications for air quality studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel-Cox, J.A.; Holloman, C.H.; Coutant, B.W.; Hoff, R.M. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of MODIS satellite sensor data for regional and urban scale air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2495–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A. Particulate matter air quality assessment using integrated surface, satellite, and meteorological products: Multiple regression approach. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Waller, L.A.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Crosson, W.L.; Estes, M.G., Jr.; Estes, S.M.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Sarnat, J.A.; Liu, Y. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in the southeastern U.S. using geographically weighted regression. Environ. Res. 2013, 121, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tang, Q.; Gong, D.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing using a satellite-based geographically and temporally weighted regression model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Hsu, N.C.; Kahn, R.A.; Levy, R.C.; Lyapustin, A.; Sayer, A.M.; Winker, D.M. Global Estimates of Fine Particulate Matter using a Combined Geophysical-Statistical Method with Information from Satellites, Models, and Monitors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3762–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Park, R.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Li, Q.; Kilaru, V.; Sarnat, J.A. Mapping annual mean ground-level PM2.5 concentrations using Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol optical thickness over the contiguous United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D22206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Liu, Y.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P. A novel calibration approach of MODIS AOD data to predict PM2.5 concentrations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 7991–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Waller, L.A.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Crosson, W.L.; Estes, M.G.; Estes, S.M.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Puttaswamy, S.J.; et al. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in the Southeastern United States using MAIAC AOD retrievals and a two-stage model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Waller, L.A.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. 10-year spatial and temporal trends of PM2.5 concentrations in the southeastern US estimated using high-resolution satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6301–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Waller, L.A.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Improving satellite-driven PM2.5 models with Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer fire counts in the southeastern U.S. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Chatfield, R.B.; Strawa, A.W. Enhancing the Applicability of Satellite Remote Sensing for PM2.5 Estimation Using MODIS Deep Blue AOD and Land Use Regression in California, United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6546–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Sayer, A.M.; Levy, R.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, Y.; Tong, S.; Bi, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Satellite-Based Spatiotemporal Trends in PM2.5 Concentrations: China, 2004–2013. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Bi, J. Satellite-derived high resolution PM2.5 concentrations in Yangtze River Delta Region of China using improved linear mixed effects model. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 133, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliep, E.M.; Gelfand, A.E.; Holland, D.M. Autoregressive spatially varying coefficients model for predicting daily PM2.5 using VIIRS satellite AOT. Adv. Stat. Climatol. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2015, 1, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Jia, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. A satellite-based geographically weighted regression model for regional PM2. 5 estimation over the Pearl River Delta region in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, H. Improving Satellite-Driven PM2.5 Models with VIIRS Nighttime Light Data in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Geng, G.; He, K. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over three megalopolises in China using satellite-derived aerosol optical depth measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R. Estimating Ground-Level PM2.5 Using Fine-Resolution Satellite Data in the Megacity of Beijing, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Dong, W.; Lv, B.; Bai, Y. Daily Estimation of Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentrations over Beijing Using 3 km Resolution MODIS AOD. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12280–12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Kahn, R.; Korkin, S.; Remer, L.; Levy, R.; Reid, J.S. Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 2. Aerosol algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyapustin, A.; Martonchik, J.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Korkin, S. Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 1. Radiative transfer basis and look-up tables. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.C.; Munchak, L.A. MODIS 3 km aerosol product: Algorithm and global perspective. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, M.; Huang, B. Spatio-temporal variation and impact factors analysis of satellite-based aerosol optical depth over China from 2002 to 2015. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. Estimating Ground-Level PM2.5 in China Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7436–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, W.; Zang, Z.; Pan, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D. Estimating PM2.5 in Xi’an, China using aerosol optical depth: A comparison between the MODIS and MISR retrieval models. Sci Total Environ 2015, 505, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Lau, A.K.H.; Li, C.; Fung, J.C.H. Using satellite remote sensing data to estimate the high-resolution distribution of ground-level PM2.5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudnovsky, A.A.; Koutrakis, P.; Kloog, I.; Melly, S.; Nordio, F.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Schwartz, J. Fine particulate matter predictions using high resolution Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) retrievals. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.H.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y. Calibrating MODIS aerosol optical depth for predicting daily PM2.5 concentrations via statistical downscaling. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudnovsky, A.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Tang, C.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P. High resolution aerosol data from MODIS satellite for urban air quality studies. Open Geosci. 2014, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sarnat, J.A.; Kilaru, V.; Jacob, D.J.; Koutrakis, P. Estimating Ground-Level PM2.5 in the Eastern United States Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3269–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Ma, P.; Tao, J.; Jia, S. A study of urban pollution and haze clouds over northern China during the dusty season based on satellite and surface observations. Atmos. Environ. 82, 183–192. [CrossRef]
- Plan of Action for Preventing and Controlling of Atmospheric Pollution. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2013-09/12/content_2486773.htm?tdsourcetag=s_pcqq_aiomsg (accessed on 22 November 2018).
- Beijing Clean Air Action Plan 2013–2017. Available online: http://zfxxgk.beijing.gov.cn/110001/szfwj/2013-09/12/content_cae7ba16b4bb46d68d78a11e928aebcd.shtml (accessed on 22 November 2018).














| Year | N 1 | Model | Model Fitting | Cross Validation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSPE (root-mean-squared prediction error) (μg/m3) | MPE (mean prediction error) (μg/m3) | R2 | RMSPE (μg/m3) | MPE (μg/m3) | |||
| 2013 | 6290 | I 2 | 0.93 | 20.64 | 12.67 | 0.91 | 22.42 | 13.70 |
| II 3 | 0.91 | 23.72 | 13.52 | 0.89 | 26.15 | 14.75 | ||
| 2014 | 6750 | I | 0.91 | 22.08 | 12.90 | 0.89 | 24.34 | 14.05 |
| II | 0.91 | 22.99 | 12.93 | 0.89 | 25.90 | 14.18 | ||
| 2015 | 6768 | I | 0.93 | 19.46 | 11.23 | 0.91 | 21.95 | 12.32 |
| II | 0.92 | 21.10 | 11.57 | 0.89 | 25.20 | 12.85 | ||
| 2016 | 6970 | I | 0.90 | 19.72 | 11.36 | 0.87 | 22.73 | 12.56 |
| II | 0.92 | 18.68 | 10.55 | 0.90 | 21.21 | 11.71 | ||
| 2017 | 6950 | I | 0.94 | 14.26 | 8.11 | 0.93 | 16.19 | 8.94 |
| II | 0.93 | 16.01 | 8.77 | 0.92 | 18.20 | 9.69 | ||
| All | 33728 | I | 0.90 | 16.98 | 11.22 | 0.90 | 21.67 | 12.28 |
| II | 0.92 | 20.61 | 11.42 | 0.90 | 23.46 | 12.58 | ||
| Year | N 1 | Model | Model Fitting | Cross Validation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSPE (μg/m3) | MPE (μg/m3) | R2 | RMSPE (μg/m3) | MPE (μg/m3) | |||
| 2014 | 3163 | I 2 | 0.84 | 16.95 | 10.79 | 0.80 | 19.02 | 11.87 |
| II 3 | 0.83 | 20.54 | 12.25 | 0.79 | 22.67 | 13.44 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, W.; Tong, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Yan, B.; Liu, X. Estimation of High-Resolution Daily Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentration in Beijing 2013–2017 Using 1 km MAIAC AOT Data. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122624
Han W, Tong L, Chen Y, Li R, Yan B, Liu X. Estimation of High-Resolution Daily Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentration in Beijing 2013–2017 Using 1 km MAIAC AOT Data. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(12):2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122624
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Weihong, Ling Tong, Yunping Chen, Runkui Li, Beizhan Yan, and Xue Liu. 2018. "Estimation of High-Resolution Daily Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentration in Beijing 2013–2017 Using 1 km MAIAC AOT Data" Applied Sciences 8, no. 12: 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122624
APA StyleHan, W., Tong, L., Chen, Y., Li, R., Yan, B., & Liu, X. (2018). Estimation of High-Resolution Daily Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentration in Beijing 2013–2017 Using 1 km MAIAC AOT Data. Applied Sciences, 8(12), 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122624