Comparative Spectroscopic Investigation of Tm3+:Tellurite Glasses for 2-μm Lasing Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure and Analysis
2.1. Experiment
2.2. Judd–Ofelt Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Absorption Spectroscopy
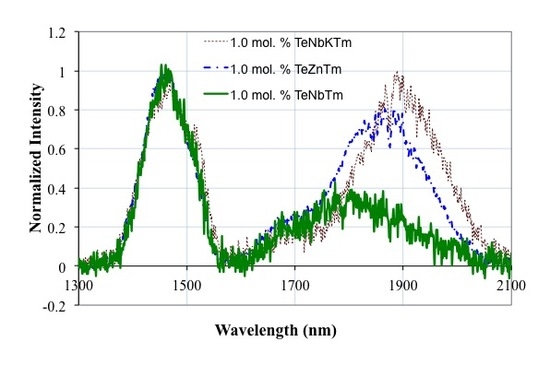
3.2. Emission Spectroscopy and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carrig, T.J.; Hankla, A.K.; Wagner, G.J.; Rawle, C.B.; Kinnie, I.T.M. Tunable Infrared Laser Sources for Dial. In Proceedings of the SPIE Laser Radar Technology and Applications VII, AEROSENSE 2002, Orlando, FL, USA, 1–5 April 2002; pp. 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Bilici, T.; Tabakoglu, H.O.; Topaloglu, N.; Kalaycioglu, H.; Kurt, A.; Sennaroglu, A.; Gulsoy, M. Modulated and continuous-wave operations of low-power thulium (Tm:YAP) laser in tissue welding. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 038001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.S.; Snitzer, E.; Vogel, E.M.; Sigel, J.G.H. 1.47, 1.88, and 2.8 μm emission of Tm3+ and Tm3+-Ho3+-codoped tellurite glasses. J. Lumin. 1994, 60, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAleavey, F.J.; O’Gorman, J.; Donegan, J.F.; MacCraith, B.D.; Hegarty, J.; Maze, G. Narrow linewidth, tunable Tm—Doped fluoride fiber laser for optical-based hydrocarbon gas sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 1997, 3, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanga, Y.H.; Colemana, D.J.; King, T.A. High power 1.9 μm Tm3+-silica fibre laser pumped at 1.09 μm by a Yb3+-silica fibre laser. Opt. Commun. 2004, 231, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.F.; Yao, Z.D.; Zong, J.; Jiang, S.B. Highly efficient high-power thulium-doped germanate glass fiber laser. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.S.; Vogel, E.M.; Snitzer, E. Tellurite glass: A new candidate for fiber devices. Opt.Mater. 1994, 3, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, M.; Asahara, Y. Glasses for Photonics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kalaycioglu, H.; Cankaya, H.; Cizmeciyan, M.N.; Sennaroglu, A.; Ozen, G. Spectroscopic investigation of Tm3+:TeO2-WO3 glass. J. Lumin. 2008, 128, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.L.; Toratani, H. Spectroscopic properties and energy transfers in Tm3+ singly- and Tm3+/Ho3+ doubly-doped glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 1996, 195, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azkargorta, J.; Iparraguirre, I.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J. On the origin of bichromatic laser emission in Nd3+-doped fluoride glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2008, 16, 11894–11906. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, N.; Xu, B.; Jiang, Z.H. Ti:Sapphire laser pumped nd:Tellurite glass laser. Opt. Commun. 1996, 127, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.; Sakamoto, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Shikano, K.; Oikawa, K.; Hoshino, K.; Kanamori, T.; Ohishi, Y.; Shimizu, M. 1.58 um broad-band erbium-doped tellurite fiber amplifier. J. Lightwave Technol. 2002, 20, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Machewirth, D.P.; Wu, F.; Snitzer, E.; Vogel, E.M. Neodymium-doped tellurite single-mode fiber laser. Opt. Lett. 1994, 19, 1448–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaycioglu, H.; Cankaya, H.; Ozen, G.; Ovecoglu, L.; Sennaroglu, A. Lasing at 1065 nm in bulk Nd3+-doped telluride-tungstate glass. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 6056–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cankaya, H.; Sennaroglu, A. Bulk Nd3+-doped tellurite glass laser at 1.37 μm. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2010, 99, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, G.; Hu, L. Watt-level 2 μm laser output in Tm3+-doped tungsten tellurite glass double-cladding fiber. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 4136–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, B.; Tsang, Y.; Binks, D.; Lousteau, J.; Jha, A. 2 μm Tm3+/Yb3+-Doped Tellurite Fibre Laser. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Optical, Optoelectronic and Photonic Materials and Applications, London, UK, 29 July–3 August 2007; pp. 317–320. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, Y.; Richards, B.; Binks, D.; Lousteau, J.; Jha, A. Tm3+/Ho3+ codoped tellurite fiber laser. Opt. Lett. 2008, 32, 1282–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, B.; Shen, S.; Jha, A.; Tsang, Y.; Binks, D. Infrared emission and energy transfer in Tm3+, Tm3+-Ho3+ and Tm3+-Yb3+-doped tellurite fibre. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 6546–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, R.; Bose, S. A comprehensive phononic sof phonon assisted energy transfer in the Yb3+ aided upconversion luminescence of Tm3+ and Ho3+ in solids. J. Lumin. 2015, 161, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, F.; Hu, L. Increased radiative lifetime of Tm3+:3F4 3H6 transition in oxyfluoride tellurite glass. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 64, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, L.X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.D.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, Q.Y. Spectroscopic and structural characterization of barium tellurite glass fibers for mid-infrared ultra-broad tunable fiber lasers. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 2095–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Cai, M.; Lu, Y.; Wang, N.; Huang, F.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J. Preparation and investigation of Tm3+/Ho3+ co-doped germanate-tellurite glass as promising materials for ultrashort pulse laser. Opt. Mater. 2017, 67, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Bai, X.; Zhou, H. Preparation of Ho3+/Tm3+ co-doped lanthanum tungsten germanium tellurite glass fiber and its laser performance for 2.0 μm. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusari, F.; Vetter, S.; Lagatsky, A.A.; Richards, B.; Calvez, S.; Jha, A.; Dawson, M.D.; Sibbett, W.; Brown, C.T.A. Tunable laser operation of a Tm3+-doped tellurite glass laser near 2 μm pumped by a 1211 nm semiconductor disk laser. Opt. Mater. 2010, 32, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusari, F.; Lagatsky, A.A.; Richards, B.; Jha, A.; Sibbett, W.; Brown, C.T.A. Spectroscopic and lasing performance of Tm3+- doped bulk tzn and tzng tellurite glasses operating around 1.9 µm. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 19146–19151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusari, F.; Lagatsky, A.A.; Jose, G.; Calvez, S.; Jha, A.; Dawson, M.D.; Gupta, J.A.; Sibbett, W.; Brown, C.T.A. Femtosecond mode-locked Tm3+ and Tm3+-Ho3+ doped 2 μm glass lasers. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 22090–22098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolga Gorgulu, A.; Cankaya, H.; Kurt, A.; Speghini, A.; Bettinelli, M.; Sennaroglu, A. Spectroscopic characterization of Tm3+:TEO2-K2O-Nb2O5 glasses for 2-μm lasing applications. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, B.R. Optical absorption intensities of rare-earth ions. Phys. Rev. 1962, 127, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofelt, G.S. Intensities of crystal spectra of rare-earth ions. J. Chem. Phys. 1962, 37, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminskii, A.A. Laser Crystals; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gebavi, H.; Milanese, D.; Balda, R.; Chaussedent, S.; Ferrari, M.; Fernandez, J.; Ferraris, M. Spectroscopy and optical characterization of thulium doped TZN glasses. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sennaroglu, A.; Kabalci, I.; Kurt, A.; Demirbas, U.; Ozen, G. Spectroscopic properties of Tm3+:TeO2-PbF2 glasses. J. Lumin. 2006, 116, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, P.F. Spectroscopic and laser characteristics of ti-Al2O3. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B Opt. Phys. 1986, 3, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudesh, V.; Goldys, E.M. Spectroscopic properties of thulium-doped crystalline materials including a novel host, La2Be2O5: A comparative study. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B Opt. Phys. 2000, 17, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCumber, D.E. Einstein relations connecting broadband emission and absorption spectra. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, A954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digonnet, M.J.F.; Murphy-Chutorian, E.; Falquier, D.G. Fundamental limitations of the mccumber relation applied to er-doped silica and other amorphous-host lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron 2002, 38, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennaroglu, A.; Kurt, A.; Özen, G. Effect of cross relaxation on the 1470 and 1800 nm emissions in Tm3+:TeO2-CdCl2 glass. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 16, 2471–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| J-O Parameters | Ω2 | Ω4 | Ω6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (10−20 cm2) | (10−20 cm2) | (10−20 cm2) | |
| TeNbKTm | 4.51 ± 0.79 | 0.76 ± 0.46 | 1.13 ± 0.67 |
| TeZnTm | 4.02 ± 0.56 | 0.93 ± 0.33 | 1.12 ± 0.47 |
| TeNbTm | 4.09 ± 0.03 | 0.69 ± 0.01 | 1.11 ± 0.01 |
| Fluorescence and Radiative Lifetimes and Quantum Yields | τF (μs) | η (%) | τRaveraged (ms) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3H4 | 3F4 | 3H4 | 3F4 | τR (1860 nm) | τR (1460 nm) | |
| TeNbKTm [29] | 1860 nm | 1460 nm | 1860 nm | 1460 nm | (ms) | (ms) |
| 0.125 mol % | 814 | 258 | 32 | 74 | 2.57 | 0.35 |
| 0.25 mol % | 572 | 199 | 22 | 57 | - | - |
| 0.5 mol % | 545 | 148 | 21 | 43 | - | - |
| 1.0 mol % | 439 | 47 | 17 | 14 | - | - |
| TeZnTm | τR (1860 nm) | τR (1460 nm) | ||||
| 0.125 mol % | 806 | 327 | 32 | 89 | 2.55 | 0.37 |
| 0.25 mol % | 722 | 250 | 28 | 68 | - | - |
| 0.5 mol % | 511 | 171 | 20 | 47 | - | - |
| 1.0 mol.% | 145 | 35 | 6 | 10 | - | - |
| TeNbTm | τR (1860 nm) | τR (1460 nm) | ||||
| 0.25 mol % | 893 | 284 | 32 | 76 | 2.76 | 0.37 |
| 1.0 mol % | 382 | 76 | 14 | 20 | - | - |
| Δλ (FWHM, nm) | σem (10−21 cm2) | σa (10−21 cm2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1460 nm | 1860 nm | 1460 nm | 1860 nm | 1860 nm | 794 nm | |
| TeNbKTm [29] | Fucht.-Laden. | McCumber | ||||
| 1.0 mol % | 122 | 170 | 2.67 ± 0.53 | 5.61 ± 0.42 | 6.21 | 9.07 |
| 0.5 mol % | 116 | 231 | 2.74 ± 0.54 | 6.12 ± 0.45 | 6.04 | 8.33 |
| 0.25 mol % | 133 | 319 | 2.40 ± 0.48 | 5.46 ± 0.40 | 5.79 | 8.26 |
| 0.125 mol % | 128 | 240 | 3.00 ± 0.59 | 6.85 ± 0.51 | 6.10 | 7.07 |
| Average | 2.70 ± 0.54 | 6.01 ± 0.45 | 6.04 ± 0.18 | 8.18 | ||
| TeZnTm | ||||||
| 1.0 mol % | 106 | 192 | 2.74 ± 0.40 | 5.48 ± 0.30 | 6.00 | 8.08 |
| 0.5 mol % | 119 | 200 | 2.52 ± 0.37 | 5.65 ± 0.31 | 5.00 | 7.79 |
| 0.25 mol % | 111 | 172 | 2.91 ± 0.37 | 6.85 ± 0.33 | 4.98 | 7.65 |
| 0.125 mol % | 106 | 200 | 2.95 ± 0.43 | 7.36 ± 0.40 | 5,60 | 7.89 |
| Average | 2.78 ± 0.39 | 6.33 ± 0.34 | 5.40 ± 0.5 | 7.85 | ||
| TeNbTm | ||||||
| 1.0 mol % | 105 | 237 | 2.65 ± 0.02 | 4.99 ± 0.02 | 5.00 | 7.68 |
| 0.25 mol % | 100 | 103 | 2.60 ± 0.02 | 6.28 ± 0.02 | 6.20 | 6.90 |
| Average | 2.62 ± 0.02 | 5.63 ± 0.02 | 5.60 ± 0.85 | 7.29 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cankaya, H.; Gorgulu, A.T.; Kurt, A.; Speghini, A.; Bettinelli, M.; Sennaroglu, A. Comparative Spectroscopic Investigation of Tm3+:Tellurite Glasses for 2-μm Lasing Applications. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8030333
Cankaya H, Gorgulu AT, Kurt A, Speghini A, Bettinelli M, Sennaroglu A. Comparative Spectroscopic Investigation of Tm3+:Tellurite Glasses for 2-μm Lasing Applications. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(3):333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8030333
Chicago/Turabian StyleCankaya, Huseyin, Adil Tolga Gorgulu, Adnan Kurt, Adolfo Speghini, Marco Bettinelli, and Alphan Sennaroglu. 2018. "Comparative Spectroscopic Investigation of Tm3+:Tellurite Glasses for 2-μm Lasing Applications" Applied Sciences 8, no. 3: 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8030333
APA StyleCankaya, H., Gorgulu, A. T., Kurt, A., Speghini, A., Bettinelli, M., & Sennaroglu, A. (2018). Comparative Spectroscopic Investigation of Tm3+:Tellurite Glasses for 2-μm Lasing Applications. Applied Sciences, 8(3), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8030333