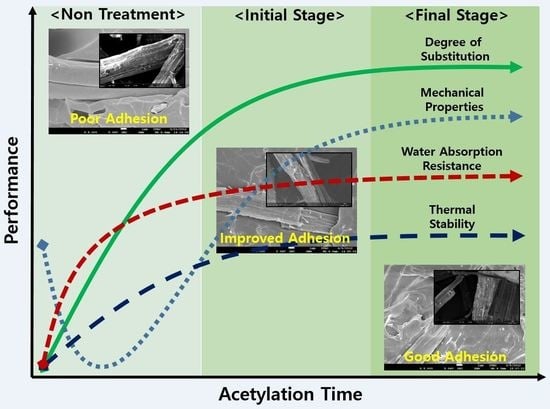
The Improvement of Mechanical Properties, Thermal Stability, and Water Absorption Resistance of an Eco-Friendly PLA/Kenaf Biocomposite Using Acetylation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.2. Acetylation of Kenaf Fibers
2.3. Fabrication of Composites
2.3.1. Compounding of PLA/Kenaf Composites
2.3.2. Preparation of Test Specimens
2.4. Fiber Characterization
2.4.1. Functional Group Analysis
2.4.2. Acetyl Content
2.4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.4. Thermal Stability
2.5. Composite Characterization
2.5.1. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
2.5.2. Mechanical Properties
2.5.3. Viscoelastic Properties
2.5.4. Water Uptake
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avella, M.; Bogoeva-Gaceva, G.; Bužarovska, A.; Errico, M.E.; Gentile, G.; Grozdanov, A. Poly(lactic acid)-based biocomposites reinforced with kenaf fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 3542–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.-J.; Dorgan, J.R. Bio-composites of kenaf fibers in polylactide: Role of improved interfacial adhesion in the carding process. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 2573–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madival, S.; Auras, R.; Singh, S.P.; Narayan, R. Assessment of the environmental profile of PLA, PET and PS clamshell containers using LCA methodology. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, E.T.; Rabago, K.R.; Glassner, D.A.; Gruber, P.R. Applications of life cycle assessment to Natureworks™ polylactide (PLA) production. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 80, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukyai, P.; Sriroth, K.R.; Lee, B.H.; Hyun, J.K. The effect of bacterial cellulose on the mechanical and thermal expansion properties of kenaf/polylactic acid composites. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 117–119, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksman, K.; Skrifvars, M.; Selin, J.-F. Natural fibres as reinforcement in polylactic acid (PLA) composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.; Lee, B.; Lee, H.; Kwon, H.; Jang, W.; Kim, H.; Eom, Y. Performance evaluation of bio-composites composed of acetylated kenaf fibers and poly(lactic acid) (PLA). Elastom. Compos. 2011, 46, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Webber, C.L., III; Bhardwaj, H.L.; Bledsoe, V.K. Kenaf production: Fiber, feed, and seed. In Trends in New Crops and New Uses; ASHS Press: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2002; pp. 327–339. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Drzal, L.T. Natural Fibers, Biopolymers, and Biocomposites; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-S.; Kim, H.-J.; Cho, D. Thermal analysis of hydrolysis and degradation of biodegradable polymer and bio-composites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 96, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Abdullah, A.H.; Bakar, A.A. Influence of acetylation on the tensile properties, water absorption, and thermal stability of (high-density polyethylene)/(soya powder)/(kenaf core) composites. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2011, 17, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yussuf, A.; Massoumi, I.; Hassan, A. Comparison of polylactic acid/kenaf and polylactic acid/rise husk composites: The influence of the natural fibers on the mechanical, thermal and biodegradability properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, T.; Hirao, K.; Kotera, M.; Nakamae, K.; Inagaki, H. Kenaf reinforced biodegradable composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akil, H.; Omar, M.; Mazuki, A.; Safiee, S.; Ishak, Z.M.; Bakar, A.A. Kenaf fiber reinforced composites: A review. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4107–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavudeen, A.; Rajini, N.; Karthikeyan, S.; Thiruchitrambalam, M.; Venkateshwaren, N. Mechanical properties of banana/kenaf fiber-reinforced hybrid polyester composites: Effect of woven fabric and random orientation. Mater. Des. (1980–2015) 2015, 66, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chen, S.; Xu, Q.; Wang, H. Solvent-free acetylation of bacterial cellulose under moderate conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifuku, S.; Morooka, S.; Morimoto, M.; Saimoto, H. Acetylation of chitin nanofibers and their transparent nanocomposite films. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.-J.; Sunthornvarabhas, J.; Park, J.-W.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Piyachomkwan, K.; Sriroth, K.; Cho, D. Tensile properties of kenaf fiber and corn husk flour reinforced poly(lactic acid) hybrid bio-composites: Role of aspect ratio of natural fibers. Compos. B Eng. 2014, 56, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonoobi, M.; Harun, J.; Mathew, A.P.; Hussein, M.Z.B.; Oksman, K. Preparation of cellulose nanofibers with hydrophobic surface characteristics. Cellulose 2010, 17, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.G.; Zong, M.H.; Li, G.J. Lipase-catalyzed modification of konjac glucomannan. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichazo, M.; Albano, C.; Gonzalez, J.; Perera, R.; Candal, M. Polypropylene/wood flour composites: Treatments and properties. Compos. Struct. 2001, 54, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Chemical modification of wood. Wood Fiber Sci. 2007, 26, 270–280. [Google Scholar]
- Hassouna, F.; Raquez, J.-M.; Addiego, F.; Dubois, P.; Toniazzo, V.; Ruch, D. New approach on the development of plasticized polylactide (PLA): Grafting of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) via reactive extrusion. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 2134–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tserki, V.; Matzinos, P.; Panayiotou, C. Novel biodegradable composites based on treated lignocellulosic waste flour as filler. Part II. Development of biodegradable composites using treated and compatibilized waste flour. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Zhou, X.D.; Pei, C.H. Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose/polylactide nanocomposites. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2010, 49, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.F.; Sun, R. Comparative study of acetylation of rice straw fiber with or without catalysts. Wood Fiber Sci. 2007, 34, 306–317. [Google Scholar]
- Vaca-Garcia, C.; Borredon, M.; Gaseta, A. Determination of the degree of substitution (DS) of mixed cellulose esters by elemental analysis. Cellulose 2001, 8, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-S.; Lee, B.-H.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.-J.; Dorgan, J.R. Enhanced interfacial adhesion, mechanical, and thermal properties of natural flour-filled biodegradable polymer bio-composites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 104, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.C.; Pinto, R.J.; Trovatti, E.; Freire, C.S.; Silvestre, A.J.; Neto, C.P.; Gandini, A. Transparent bionanocomposites with improved properties prepared from acetylated bacterial cellulose and poly(lactic acid) through a simple approach. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabir, M.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.; Cardona, F.; Aravinthan, T. Mechanical properties of chemically-treated hemp fibre reinforced sandwich composites. Compos. B Eng. 2012, 43, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Cho, D.; Song, B.K.; Kim, H.-J. Novel jute/polycardanol biocomposites: Effect of fiber surface treatment on their properties. Compos. Interfaces 2009, 16, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingaut, P.; Zimmermann, T.; Lopez-Suevos, F. Synthesis and characterization of bionanocomposites with tunable properties from poly(lactic acid) and acetylated microfibrillated cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2009, 11, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bher, A.; Uysal Unalan, I.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M.; Schvezov, C.E. Toughening of poly(lactic acid) and thermoplastic cassava starch reactive blends using graphene nanoplatelets. Polymers 2018, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahit, M.U.; Hassan, A.; Ibrahim, A.N.; Zawawi, N.A.; Kunasegeran, K. Mechanical, thermal and chemical resistance of epoxidized natural rubber toughened polylactic acid blends. Sains Malays. 2015, 44, 1615–1623. [Google Scholar]










| Weight Loss Point | TD5% (°C) | TD10% (°C) | TD50% (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time of Acetylation (h) | |||
| 0 | 270.2 | 297.4 | 373.3 |
| 0.5 | 300.51 | 325.4 | 375.8 |
| 1 | 315.11 | 334.7 | 378.5 |
| 2 | 322.43 | 338.9 | 379.7 |
| 3 | 323.41 | 339.5 | 379 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, T.-J.; Park, J.-W.; Lee, H.-J.; Kwon, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Tai Yin Tze, W. The Improvement of Mechanical Properties, Thermal Stability, and Water Absorption Resistance of an Eco-Friendly PLA/Kenaf Biocomposite Using Acetylation. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8030376
Chung T-J, Park J-W, Lee H-J, Kwon H-J, Kim H-J, Lee Y-K, Tai Yin Tze W. The Improvement of Mechanical Properties, Thermal Stability, and Water Absorption Resistance of an Eco-Friendly PLA/Kenaf Biocomposite Using Acetylation. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(3):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8030376
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Taek-Jun, Ji-Won Park, Hyun-Ji Lee, Hueck-Jin Kwon, Hyun-Joong Kim, Young-Kyu Lee, and William Tai Yin Tze. 2018. "The Improvement of Mechanical Properties, Thermal Stability, and Water Absorption Resistance of an Eco-Friendly PLA/Kenaf Biocomposite Using Acetylation" Applied Sciences 8, no. 3: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8030376
APA StyleChung, T. -J., Park, J. -W., Lee, H. -J., Kwon, H. -J., Kim, H. -J., Lee, Y. -K., & Tai Yin Tze, W. (2018). The Improvement of Mechanical Properties, Thermal Stability, and Water Absorption Resistance of an Eco-Friendly PLA/Kenaf Biocomposite Using Acetylation. Applied Sciences, 8(3), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8030376