TIR-MS: Thermal Infrared Mean-Shift for Robust Pedestrian Head Tracking in Dynamic Target and Background Variations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Pedestrian Tracking for Thermal Infrared Image
2.2. Pedestrian Tracking Based Mean-Shift Using Brightness
2.3. Limitation of Brightness
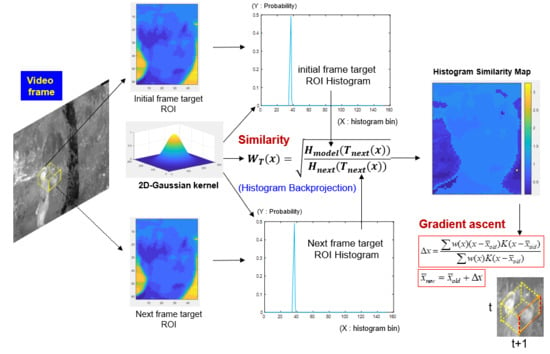
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Temperature Extraction
3.2. 8-Bit Brightness Extraction
3.2.1. Blackbody-Based Radiometric Calibration
3.2.2. Comparison Brightness Histogram and Temperature Histogram
3.3. Proposed Temperature-Based Mean-Shift Tracking
3.3.1. Temperature-Based Histogram Backprojection
3.3.2. Temperature-Based Gradient Ascent
4. Experimental Result
4.1. YU TIR Pedestrian Tracking Dataset
4.2. Qualitative Performance Evaluation
4.2.1. Limitation of the Brightness Histogram in IR Pedestrian Tracking
4.2.2. Quantitative Comparison
4.2.3. Limitations of the Proposed Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Comaniciu, D.; Ramesh, V.; Meer, P. Real-time tracking of non-rigid objects using mean shift. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2000, 2, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Hou, Q.; Hao, L. Improved infrared target-tracking algorithm based on mean shift. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 5051–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Ju, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, G.; Qian, S.; Li, Y. MeanShift tracking algorithm with adaptive block color histogram. In Proceedings of the 2012 2nd International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Communications and Networks (CECNet), Piscataway, NJ, USA, 21–23 April 2012; pp. 2692–2695. [Google Scholar]
- An, X.; Kim, J.; Han, Y. Optimal colour-based mean shift algorithm for tracking objects. IET Comput. Vis. 8.3 2014, 8, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Wu, X.J.; Xu, T. Object tracking with kernel correlation filters based on mean shift. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Wuxi, China, 14–17 September 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Wu, C. Robust mean-shift tracking with corrected background-weighted histogram. IET Comput. Vis. 6.1 2012, 6, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ning, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Wu, C. Scale and orientation adaptive mean shift tracking. IET Comput. Vis. 6.1 2012, 6, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H. Extended social force model-based mean shift for pedestrian tracking under obstacle avoidance. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Asia (ICCE-Asia), Seoul, Korea, 26–28 October 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sahi, A.; Jammoussi, A.Y. Object tracking system using Camshift, Meanshift and Kalman filter. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 6, 674–679. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Jalil, A.; Ahmed, J.; Iftikhar, M.A.; Hussain, M. Robust Correlation, Kalman filter and adaptive fast mean shift based heuristic approach for robust visual tracking. Signal Image Video Process. 2015, 9, 1567–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Yoon, T.S.; Park, J.B. Mean shift tracker combined with online learning-based detector and Kalman filtering for real-time tracking. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 79, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, X.; Fujimura, K. Pedestrian detection and tracking with night vision. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2005, 6, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kim, S. Pedestrian detection at night time in FIR domain: Comprehensive study about temperature and brightness and new benchmark. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 79, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, R.; Moeslund, T.B. Thermal cameras and applications: a survey. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2014, 25, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, W. Detection and tracking of moving targets for thermal infrared video sequences. Sensors 2018, 18, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, X.; Yu, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y. Pedestrian detection and tracking from low-resolution unmanned aerial vehicle thermal imagery. Sensors 2016, 16, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, A.; Buongiorno, D.; Trotta, G.F.; Bevilacqua, V. Computer vision and deep learning techniques for pedestrian detection and tracking: A survey. Neurocomputing 2018, 300, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Lu, H.; Yang, M.H. Visual tracking via adaptive structural local sparse appearance model. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 1822–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Felsberg, M. Enhanced distribution field tracking using channel representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, W.; Lu, H.; Yang, M.H. Robust object tracking via sparsity-based collaborative model. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 1838–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Häger, G.; Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Nottingham, UK, 1–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, A.; Ahlberg, J.; Felsberg, M. A thermal object tracking benchmark. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Karlsruhe, Germany, 25–28 August 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Felsberg, M.; Berg, A.; Hager, G.; Ahlberg, J.; Kristan, M.; Matas, J.; Nebehay, G. The thermal infrared visual object tracking VOT-TIR2015 challenge results. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 76–88. [Google Scholar]
- Prioletti, A.; Møgelmose, A.; Grisleri, P.; Trivedi, M.M.; Broggi, A.; Moeslund, T.B. Part-based pedestrian detection and feature-based tracking for driver assistance: Real-time, robust algorithms, and evaluation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2013, 14, 1346–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, T.; Trivedi, M.M. Pedestrian protection systems: Issues, survey, and challenges. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2007, 8, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comaniciu, D.; Ramesh, V.; Meer, P. Kernel-based object tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, D. Mean-Shift Tracking for Surveillance: Evaluations and Enhancements. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Dublin, Dublin, Ireland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gorry, B.; Chen, Z.; Hammond, K.; Wallace, A.; Michaelson, G. Using mean-shift tracking algorithms for real-time tracking of moving images on an autonomous vehicle testbed platform. Proceedings of World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology. 2007. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/4eed/a6bcee928e4ed1e1b497a6420127748424d0.pdf (accessed on 26 July 2019).
- Milian, A.; Rezatofighi, S.H.; Dick, A.R.; Reid, I.D.; Schindler, K. Online Multi-Target Tracking Using Recurrent Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1604.03635. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, S.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Pedestrian behavior understanding and prediction with deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; pp. 263–279. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Xu, W.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Y. Human tracking using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2010, 21, 1610–1623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, P.A. Society of Photo-optical Instrumentation Engineers. In Thermal infrared Characterization of Ground Targets and Backgrounds; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Held, D.; Thrun, S.; Savarese, S. Learning to track at 100 fps with deep regression networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 749–765. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, D.; Farhadi, A.; Fox, D. Re 3: Re al-Time Recurrent Regression Networks for Visual Tracking of Generic Objects. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Choi, J.; Yoo, Y.; Yun, K.; Young Choi, J. Action-decision networks for visual tracking with deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2711–2720. [Google Scholar]















| FEATURES | FLIR T620 |
|---|---|
| Spectral range | 7.5–14 um |
| Temperature range | to |
| Thermal sensitivity (N.E.T.D) | < at |
| Frame rate | 30FPS |
| Resolution | pixels (14-bit) |
| Field of view (FOV) | Horizontal |
| Date | Season | Total Frame | Time | Temperature | ROI Size | Scenario | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 18.08.14 | Summer | 723 | 17 s | / | Image contrast | |
| S2 | 19.01.21 | Winter | 390 | 11 s | / | Image contrast, Background clutter | |
| S3 | 19.02.02 | Winter | 417 | 13 s | / | Image contrast, Object variation | |
| S4 | 19.02.26 | Winter | 520 | 17 s | / | Image contrast, Object variation | |
| S5 | 19.02.26 | Winter | 568 | 18 s | / | Image contrast, Size variation | |
| S6 | 19.03.06 | Spring | 400 | 12 s | / | Image contrast, Background clutter | |
| S7 | 19.03.08 | Spring | 601 | 19 s | / | Image contrast, Background clutter | |
| S8 | 19.03.15 | Spring | 650 | 24 s | / | Image contrast |
| Algorithm | Baseline (8-bit) | Baseline (14-bit) | Proposed (TIR-MS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | |||
| S2 | |||
| S3 | |||
| S4 | |||
| S5 | |||
| S6 | |||
| S7 | |||
| S8 | |||
| Mean | |||
| STDEV |
| Algorithm | Baseline (8-bit) | Baseline (14-bit) | Proposed (TIR-MS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 138 | 33 | 29 |
| S2 | 21 | 7 | 8 |
| S3 | 40 | 96 | 21 |
| S4 | 17 | 15 | 11 |
| S5 | 137 | 18 | 13 |
| S6 | 11 | 47 | 9 |
| S7 | 23 | 16 | 10 |
| S8 | 43 | 22 | 16 |
| Mean | |||
| STDEV |
| Algorithm | Baseline (8-bit) | Baseline (14-bit) | Proposed (TIR-MS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | |||
| S2 | |||
| S3 | |||
| S4 | |||
| S5 | |||
| S6 | |||
| S7 | |||
| S8 | |||
| Mean | |||
| STDEV |
| Algorithm | Baseline (8-bit) | Baseline (14-bit) | Proposed (TIR-MS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | |||
| S2 | |||
| S3 | |||
| S4 | |||
| S5 | |||
| S6 | |||
| S7 | |||
| S8 | |||
| Mean | |||
| STDEV |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, S.; Kim, S. TIR-MS: Thermal Infrared Mean-Shift for Robust Pedestrian Head Tracking in Dynamic Target and Background Variations. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153015
Yun S, Kim S. TIR-MS: Thermal Infrared Mean-Shift for Robust Pedestrian Head Tracking in Dynamic Target and Background Variations. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(15):3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153015
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Sungmin, and Sungho Kim. 2019. "TIR-MS: Thermal Infrared Mean-Shift for Robust Pedestrian Head Tracking in Dynamic Target and Background Variations" Applied Sciences 9, no. 15: 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153015
APA StyleYun, S., & Kim, S. (2019). TIR-MS: Thermal Infrared Mean-Shift for Robust Pedestrian Head Tracking in Dynamic Target and Background Variations. Applied Sciences, 9(15), 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153015