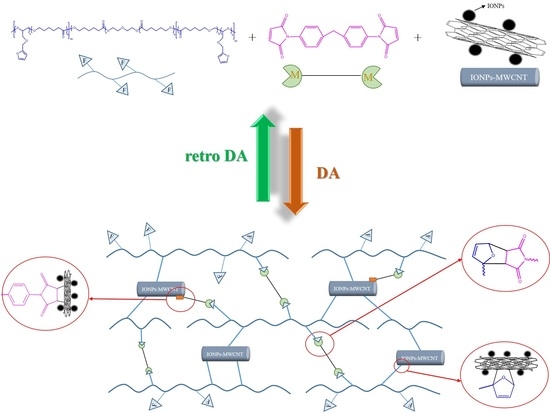
Fabrication of Self-Healable Magnetic Nanocomposites via Diels−Alder Click Chemistry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Synthesis of Polycaprolactone-poly(furfuryl glycidyl ether) Copolymers (PCLF)
2.2.2. Synthesis of IONPs-MWCNTs Hybrid
2.2.3. Preparation of Crosslinked PCLF/BMI/IONPs-MWCNTs Hybrid Material
2.2.4. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toohey, K.S.; Sottos, N.R.; Lewis, J.A.; Moore, J.S.; White, S.R. Self-healing materials with microvascular networks. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toohey, K.S.; Hansen, C.J.; Lewis, J.A.; White, S.R.; Sottos, N.R. Delivery of two-part self-healing chemistry via microvascular networks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.R.; Sottos, N.R.; Geubelle, P.H.; Moore, J.S.; Kessler, M.R.; Sriram, S.R.; Brown, E.N.; Viswanatha, S. Autonomic healing of polymer composites. Nature 2001, 409, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rule, J.D.; Brown, E.N.; Sottos, N.R.; White, S.R.; Moore, J.S. Wax-protected catalyst microspheres for efficient self-healing materials. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzara, G.; Yoon, Y.; Liu, H.; Peng, S.; Lee, W.I. Carbon nanotube reservoirs for self-healing materials. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 335704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchukin, D.G.; Möhwald, H. Self-repairing coatings containing active nanoreservoirs. Small 2007, 3, 926–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.Y.; Meure, S.; Solomon, D. Self-healing polymeric materials: A review of recent developments. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 479–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syrett, J.A.; Becer, C.R.; Haddleton, D.M. Self-healing and self-mendable polymers. Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekas, D.G.; Tsirka, K.; Baltzis, D.; Paipetis, A.S. Self-healing materials: A review of advances in materials, evaluation, characterization and monitoring techniques. Compos. Part B 2016, 87, 92–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-M.; Roh, Y.-S.; Cho, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-G. Crack healing in polymeric materials via photochemical [2+2] cycloaddition. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 3982–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.F.; Schneider, A.D.; Cook, W.D.; Bowman, C.N. Photoinduced plasticity in cross-linked polymers. Science 2005, 308, 1615–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruendling, T.; Kaupp, M.; Blinco, J.P.; Barner-Kowollik, C. Photoinduced conjugation of dithioester- and trithiocarbonate-functional RAFT polymers with Alkenes. Macromolecules 2010, 44, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holten-Andersen, N.; Harrington, M.J.; Birkedal, H.; Lee, B.P.; Messersmith, P.B.; Lee, K.Y.C.; Waite, J.H. pH-induced metal-ligand cross-links inspired by mussel yield self-healing polymer networks with near-covalent elastic moduli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2651–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, B.; Urban, M.W. Self-Repairing Oxetane-substituted chitosan polyurethane Networks. Science 2009, 323, 1458–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuta, T.; Takashima, Y.; Nakahata, M.; Otsubo, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Harada, A. Preorganized hydrogel: Self-healing properties of supramolecular hydrogels formed by polymerization of host-guest monomers that contain cyclodextrins and hydrophobic guest groups. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2849–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahata, M.; Takashima, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Harada, A. Redox-responsive self-healing materials formed from host-guest polymers. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Chuo, T.-W. Self-healing polymers based on thermally reversible Diels–Alder chemistry. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 2194–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diels, O.; Alder, K. Synthesen in der hydroaromatischen Reihe. Justus Liebigs Annalender Chemie 1928, 460, 98–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripoll, J.L.; Rouessac, A.; Rouessac, F. Applications recentes de la reaction de retro-diels-alder en synthese organique. Tetrahedron 1978, 34, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalai, M.L.; McGrath, D.V.; Wheeler, D.R.; Zifer, T.; McElhanon, J.R. Dendrimers Based on Thermally Reversible Furan-Maleimide Diels-Alder Adducts. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.; Philp, D.; Spencer, N. Recognition-induced control of Diels-Alder cycloaddition. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 11365–11384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElhanon, J.R.; Wheeler, D.R. Thermally responsive dendrons and dendrimers based on reversible furan-maleimide Diels-Alder adducts. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 2681–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chujo, Y.; Sada, K.; Saegusa, T. Reversible gelation of polyoxazoline by means of Diels-Alder reaction. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 2636–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallek, H.; Jegat, C.; Mignard, N.; Abid, M.; Abid, S.; Taha, M. Reversibly crosslinked self-healing PCL-based networks. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defize, T.; Thomassin, J.-M.; Alexandre, M.; Gilbert, B.; Riva, R.; Jérôme, C. Comprehensive study of the thermo-reversibility of Diels-Alder based PCL polymer networks. Polymer 2016, 84, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.K.; Kessler, M.R. Self-healing polymer nanocomposite materials: A review. Polymer 2015, 69, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arslan, M.; Tasdelen, M.A. Polymer nanocomposites via click chemistry reactions. Polymers 2017, 9, 499–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, P.K.; Mondal, P.; Singha, N.K. Self-healable and ultrahydrophobic polyurethane-POSS hybrids by Diels-Alder “click” reaction: A new class of coating material. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 4770–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Yao, Y.; Li, G.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.-P. Ultrafastly self-healing nanocomposites via infrared laser and its application in flexible electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3040–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, A.V.; Madras, G.; Bose, S. Ultrafast self-healable interfaces in polyurethane nanocomposites designed using Diels-Alder “Click” as an efficient microwave absorber. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, S.; Kickelbick, G. Diels-Alder reactions on surface-modified magnetite/maghemite nanoparticles: Application in self-healing nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 2640–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, S.; Kickelbick, G. Double reversible networks: Improvement of self-healing in hybrid materials via combination of Diels-Alder cross-linking and hydrogen bonds. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 6099–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.H.; Zakhidov, A.A.; Heer, W.A. Carbon nanotubes—The route toward applications. Science 2002, 297, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Volder, M.F.L.; Tawfick, S.H.; Baughman, R.H.; Hart, A.J. Carbon nanotubes: Present and futurecommercial applications. Science 2013, 339, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsumi, S.; Urita, K.; Kanoh, H.; Yudasaka, M.; Suenaga, K.; Iijima, S.; Kaneko, K. Preparing a magnetically responsive single-wall carbon nanohorn colloid by anchoring magnetite nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7165–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, D. Carbon nanotube-inorganic hybrids. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1348–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Wang, J.; Kong, J.; Yang, P.; Chen, G. Magnetic loading of carbon nanotube/nano-Fe3O4 composite for electrochemical sensing. Talanta 2007, 71, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Huang, L.; Cai, J.-S.; Zheng, X.-M.; Sun, S.-G. Structure and electrochemical performance of nanostructured Fe3O4/carbon nanotube composites as anodes for lithium ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta 2010, 55, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.P.; Marathe, D.A.; Pattabhi, K.; Bose, S. Electromagnetic interference shielding through MWNT grafted Fe3O4 nanoparticles in PC/SAN blends. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Huang, Z.-H.; Lu, M.-M.; Cao, W.-Q.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, D.-Q.; Cao, M.-S. 3D Fe3O4 nanocrystals decorating carbon nanotubes to tune electromagnetic properties and enhance microwave absorption capacity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 12621–12625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Liu, P.; Tang, Z.; Wu, X.; Qiu, J. Facile approach for superparamagnetic CNT-Fe3O4/polystyrene tricomponent nanocomposite via synergetic dispersion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 12017–12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yang, X.; Ye, Y.; Wang, D. Efficient removal of atrazine in water with a Fe3O4/ MWCNTs nanocomposite as a heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 46059–46066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmatara, H.; Seifi, M.; Forooraghi, K. Microwave absorption property of aligned MWCNT/Fe3O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 346, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, N.B.; Singha, N.K. Direct functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) via grafting of poly(furfuryl methacrylate) using Diels–Alder “click chemistry” and its thermoreversibility. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 94321–94327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-M.; Liu, Y.-L. Functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with furan and maleimide compounds through Diels–Alder cycloaddition. Carbon 2009, 47, 3041–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Zuo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T. Mechanically strong polyimide/carbon nanotube composite aerogels with controllable porous structure. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 156, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Sample | Mn (g/mol) | Mw (g/mol) | PDI | FGE/CL Ratio 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCL diol | 2600 | 5300 | 2.04 | -- |
| PCLF | 5700 | 10,900 | 1.91 | 0.15 |
| Sample 1 | FGE/BMI Ratio | IONPs-MWCNTs Amount 2 |
|---|---|---|
| PCLF-DA-0 | 1:1 | 0 wt% |
| PCLF-DA-2 | 1:1 | 2 wt% |
| PCLF-DA-5 | 1:1 | 5 wt% |
| PCLF-DA-10 | 1:1 | 10 wt% |
| Sample 1 | 5 wt% Loss Temperature (°C) 2 | Char Yield at 600 °C (%) 3 | Retro-DA Onset Temperature (°C) 4 | Retro-DA Heat Flow (J/g) 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCLF-DA-0 | 362 | 16.6 | 82 | 20.5 |
| PCLF-DA-2 | 334 | 21.9 | 81 | 26.5 |
| PCLF-DA-5 | 333 | 23.6 | 83 | 28.3 |
| PCLF-DA-10 | 326 | 27.1 | 82 | 32.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-H.; Zhuang, Y.-N.; Wang, H.-T.; Wei, M.-F.; Ko, W.-C.; Chang, W.-J.; Way, T.-F.; Rwei, S.-P. Fabrication of Self-Healable Magnetic Nanocomposites via Diels−Alder Click Chemistry. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030506
Lee Y-H, Zhuang Y-N, Wang H-T, Wei M-F, Ko W-C, Chang W-J, Way T-F, Rwei S-P. Fabrication of Self-Healable Magnetic Nanocomposites via Diels−Alder Click Chemistry. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(3):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030506
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yi-Huan, Yan-Nian Zhuang, Hsin-Ta Wang, Ming-Feng Wei, Wen-Chi Ko, Wei-Jen Chang, Tun-Fun Way, and Syang-Peng Rwei. 2019. "Fabrication of Self-Healable Magnetic Nanocomposites via Diels−Alder Click Chemistry" Applied Sciences 9, no. 3: 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030506
APA StyleLee, Y. -H., Zhuang, Y. -N., Wang, H. -T., Wei, M. -F., Ko, W. -C., Chang, W. -J., Way, T. -F., & Rwei, S. -P. (2019). Fabrication of Self-Healable Magnetic Nanocomposites via Diels−Alder Click Chemistry. Applied Sciences, 9(3), 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030506