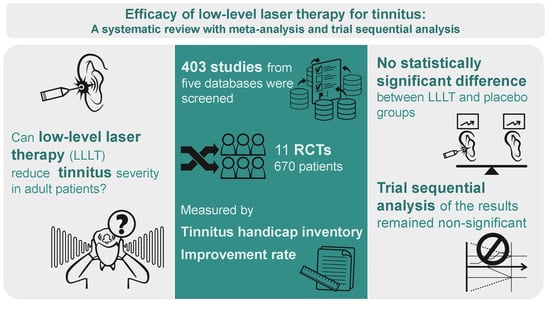
Efficacy of Low-Level Laser Therapy for Tinnitus: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Identification and Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics and Risk of Bias Assessment
3.3. Outcomes
3.3.1. THI Scores after LLLT
3.3.2. Improvement Rate According to Rating Scale Scores
3.3.3. Subgroup Analysis in Patients with SNHL or Idiopathic Tinnitus
3.3.4. Subgroup Analysis According to the Number of Irradiation Sessions
3.3.5. Subgroup Analysis According to Wavelength Setting
3.4. Influence Analysis
3.5. Trial Sequential Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.E.; Lee, M.Y.; Chung, P.S.; Jung, J.Y. A preliminary study on the efficacy and safety of low level light therapy in the management of cochlear tinnitus: A single blind randomized clinical trial. Int. Tinnitus J. 2019, 23, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarenoe, R.; Ledin, T. A cohort study of patients with tinnitus and sensorineural hearing loss in a Swedish population. Auris Nasus Larynx 2013, 40, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaver, A.M.; Renier, L.; Chevillet, M.A.; Morgan, S.; Kim, H.J.; Rauschecker, J.P. Dysregulation of Limbic and Auditory Networks in Tinnitus. Neuron 2011, 69, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Møller, A.R. Pathophysiology of tinnitus. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 36, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, H.F.; Hoare, D.J.; Costa, R.F.P.; Potgieter, I.; Kikidis, D.; Lapira, A.; Nikitas, C.; Caria, H.; Cunha, N.T.; Paço, J.C. Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment of Somatosensory Tinnitus: A Scoping Review. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passarella, S.; Casamassima, E.; Molinari, S.; Pastore, D.; Quagliariello, E.; Catalano, I.M.; Cingolani, A. Increase of proton electrochemical potential and ATP synthesis in rat liver mitochondria irradiated in vitro by helium-neon laser. FEBS Lett. 1984, 175, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Breugel, H.H.; Bär, P.R. Power density and exposure time of He-Ne laser irradiation are more important than total energy dose in photo-biomodulation of human fibroblasts in vitro. Lasers Surg. Med. 1992, 12, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, M.; Bonel, H.; Sroka, R.; Schaffer, P.M.; Busch, M.; Reiser, M.; Dühmke, E. Effects of 780 nm diode laser irradiation on blood microcirculation: Preliminary findings on time-dependent T1-weighted contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2000, 54, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, T.-H.; Lee, M.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Ahn, J.-C.; Chang, S.-Y.; Chung, P.-S.; Rhee, C.-K.; Kim, Y.-H.; Suh, M.-W. Safety assessment of trans-tympanic photobiomodulation. Lasers Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosseau, L.; Robinson, V.; Wells, G.; Debie, R.; Gam, A.; Harman, K.; Morin, M.; Shea, B.; Tugwell, P. Low level laser therapy (Classes I, II and III) for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, 4, CD002049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stausholm, M.B.; Naterstad, I.F.; Joensen, J.; Lopes-Martins RÁ, B.; Sæbø, H.; Lund, H.; Fersum, K.V.; Bjordal, J.M. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy on pain and disability in knee osteoarthritis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo-controlled trials. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e031142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Ma, J.; Chen, J.; Shen, B.; Pei, F.; Kraus, V.B. The effectiveness of low-level laser therapy for nonspecific chronic low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chow, R.T.; Johnson, M.I.; Lopes-Martins, R.A.; Bjordal, J.M. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy in the management of neck pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo or active-treatment controlled trials. Lancet 2009, 374, 1897–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjordal, J.M.; Lopes-Martins, R.A.; Joensen, J.; Couppe, C.; Ljunggren, A.E.; Stergioulas, A.; Johnson, M.I. A systematic review with procedural assessments and meta-analysis of low level laser therapy in lateral elbow tendinopathy (tennis elbow). BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauber, S.; Baumgartner, R.; Schorn, K.; Beyer, W. Lightdosimetric quantitative analysis of the human petrous bone: Experimental study for laser irradiation of the cochlea. Lasers Surg. Med. 2001, 28, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, S.; Jung, J.Y.; Lee, M.Y. Applications of photobiomodulation in hearing research: From bench to clinic. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2019, 9, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, L.; Richardson, C.; Cramond, T. Factors affecting low level laser therapy. Aust. J. Physiother. 1993, 39, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wetterslev, J.; Jakobsen, J.C.; Gluud, C. Trial Sequential Analysis in systematic reviews with meta-analysis. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2017, 17, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Trial Sequential Analysis Software; Copenhagen Trial Unit, Centre for Clinical Intervention Research, Rigshospitalet: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016; Available online: http://www.ctu.dk/tsa (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Gungor, A.; Dogru, S.; Cincik, H.; Erkul, E.; Poyrazoglu, E. Effectiveness of transmeatal low power laser irradiation for chronic tinnitus. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2008, 122, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Ueda, H.; Misawa, H.; Suzuki, T.; Tominaga, M.; Ito, A.; Numata, S.; Kasai, S.; Asahi, K.; Vernon, J.A.; et al. Transmeatal low-power laser irradiation for tinnitus. Otol. Neurotol. 2002, 23, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, M.A.; Einolghozati, S.; Ghasemi, S.M.; Abolbashari, S.; Meshkat, M.; Behzad, H. Effect of low-level laser therapy in the treatment of cochlear tinnitus: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Ear Nose Throat J. 2015, 94, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mirvakili, A.; Mehrparvar, A.; Mostaghaci, M.; Mollasadeghi, A.; Mirvakili, M.; Baradaranfar, M. Low level laser effect in treatment of patients with intractable tinnitus due to sensorineural hearing loss. J. Lasers Med. Sci. 2014, 5, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ngao, C.F.; Tan, T.S.; Narayanan, P.; Raman, R. The effectiveness of transmeatal low-power laser stimulation in treating tinnitus. Eur. Arch. Oto Rhino Laryngol. 2014, 271, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teggi, R.; Bellini, C.; Piccioni, L.O.; Palonta, F.; Bussi, M. Transmeatal low-level laser therapy for chronic tinnitus with cochlear dysfunction. Audiol. Neuro Otol. 2009, 14, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuda, D.; De Caria, A. Effectiveness of combined counseling and low-level laser stimulation in the treatment of disturbing chronic tinnitus. Int. Tinnitus J. 2008, 14, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, C.K.; Lim, E.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Chung, Y.W.; Jung, J.Y.; Chung, P.S. Effect of low level laser (LLL) on cochlear and vestibular inner ear including tinnitus. In Proceedings of the SPIE Photonics West conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 21–26 January 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirz, F.; Zachariae, R.; Andersen, S.E.; Nielsen, A.G.; Johansen, L.V.; Bjerring, P.; Pedersen, C.B. The low-power laser in the treatment of tinnitus. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1999, 24, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollasadeghi, A.; Mirmohammadi, S.J.; Mehrparvar, A.H.; Davari, M.H.; Shokouh, P.; Mostaghaci, M.; Baradaranfar, M.H.; Bahaloo, M. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy in the management of tinnitus due to noise-induced hearing loss: A double-blind randomized clinical trial. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.S.; Kumar, K.; Bhavan, D.; Anandaraj, A. Variations in the External Auditory Canal of 185 Adult Individuals: A Clinico-Morphological Study. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2013, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gerken, G.M.; Saunders, S.S.; Paul, R.E. Hypersensitivity to electrical stimulation of auditory nuclei follows hearing loss in cats. Hear. Res. 1984, 13, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltenbach, J.A.; Afman, C.E. Hyperactivity in the dorsal cochlear nucleus after intense sound exposure and its resemblance to tone-evoked activity: A physiological model for tinnitus. Hear. Res. 2000, 140, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, A.H.; Salvi, R.; Coad, M.; Towsley, M.; Wack, D.; Murphy, B. The functional neuroanatomy of tinnitus: Evidence for limbic system links and neural plasticity. Neurology 1998, 50, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, A.R.; Møller, M.B.; Yokota, M. Some forms of tinnitus may involve the extralemniscal auditory pathway. Laryngoscope 1992, 102, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, A.R. Similarities between Severe. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2000, 11, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shore, S.E.; Roberts, L.E.; Langguth, B. Maladaptive plasticity in tinnitus—Triggers, mechanisms and treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marks, K.L.; Martel, D.T.; Wu, C.; Basura, G.J.; Roberts, L.E.; Schvartz-Leyzac, K.C.; Shore, S.E. Auditory-somatosensory bimodal stimulation desynchronizes brain circuitry to reduce tinnitus in guinea pigs and humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zenner, H.-P.; Delb, W.; Kröner-Herwig, B.; Jäger, B.; Peroz, I.; Hesse, G.; Mazurek, B.; Goebel, G.; Gerloff, C.; Trollmann, R. A multidisciplinary systematic review of the treatment for chronic idiopathic tinnitus. Eur. Arch. Oto Rhino Laryngol. 2017, 274, 2079–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.N.; Straatman, L.V.; Lea, J.; Westerberg, B. Current insights in noise-induced hearing loss: A literature review of the underlying mechanism, pathophysiology, asymmetry, and management options. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 46, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hirose, K.; Liberman, M.C. Dynamics of noise-induced cellular injury and repair in the mouse cochlea. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2002, 3, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demirkol, N.; Usumez, A.; Demirkol, M.; Sari, F.; Akcaboy, C. Efficacy of Low-Level Laser Therapy in Subjective Tinnitus Patients with Temporomandibular Disorders. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2017, 35, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madani, A.S.; Ahrari, F.; Nasiri, F.; Abtahi, M.; Tunér, J. Low-level laser therapy for management of TMJ osteoarthritis. Cranio® 2014, 32, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omidvar, S.; Jafari, Z. Association Between Tinnitus and Temporomandibular Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2019, 128, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, K.W. Temporomandibular Disorder and New Aural Symptoms. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 134, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuttila, S.; Kuttila, M.; Le Bell, Y.; Alanen, P.; Jouko, S. Aural Symptoms and Signs of Temporomandibular Disorder in Association With Treatment Need and Visits to a Physician. Laryngoscope 1999, 109, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowaczewska, M.; Wiciński, M.; Straburzyński, M.; Kaźmierczak, W. The Prevalence of Different Types of Headache in Patients with Subjective Tinnitus and Its Influence on Tinnitus Parameters: A Prospective Clinical Study. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Xirasagar, S.; Yang, T.H.; Wu, C.S.; Kao, Y.W.; Shia, B.C.; Lin, H.C. Increased risk of tinnitus following a trigeminal neuralgia diagnosis: A one-year follow-up study. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Xirasagar, S.; Yang, T.H.; Wu, C.S.; Kuo, N.W.; Lin, H.C. A population-based case-control study of the association between cervical spondylosis and tinnitus. Int J. Audiol. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Study | Location | Laser Modality | Sample Size | Mean Age in Treatment Group | Mean Age in Control Group | Comorbidity | Tinnitus Duration (Month) | Control | Irradiation Session | Treatment Laterality | Post-Intervention Measurement | Reported Adverse Events | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale | Timing | ||||||||||||
| Choi et al., 2019 [1] | Korea | 100 mW; 830 nm; 20 min/day for 10 sessions | 38 | 53.3 | 58.4 | SNHL | >3 M | Sham laser | Fewer irradiation sessions | Unilateral | THI-total | Immediately | No AEs observed |
| Dehkordi et al., 2015 [25] | Iran | 5 mV; 650 nm; 20 min/day for 20 sessions | 66 | 52.5 | 46.8 | Idiopathic | Treatment group: 48 M Control group: 34 M | Sham laser | More irradiation sessions | Unilateral | NRS-loudness | Immediately | NR |
| Mirvakili et al., 2014 [26] | Iran | 5 mW; 650 nm; 20 min/day for 20 sessions | 120 | 41.08 | 39.43 | SNHL | >12 M | Sham laser | More irradiation sessions | NR | VAS-loudness | Immediately | NR |
| Nago et al., 2014 [27] | Malaysia | 5 mW; 650 nm; 20 min/day for 70 sessions | 43 | 56.5 | 58.7 | Idiopathic | >6 M | Sham laser | More irradiation sessions | NR | VAS-loudness | Immediately | NR |
| Mollasadeghi et al., 2013 [32] | Iran | 5 mW; 650 nm; 20 min/day for 20 sessions | 82 | 41.17 | SNHL (NIHL) | 22 M (average) | Sham laser | More irradiation sessions | NR | VAS-loudness | Immediately | NR | |
| Teggi et al., 2009 [28] | Italy | 5 mW; 650 nm; 20 min/day for 90 sessions | 54 | 51.6 | 53.1 | SNHL | Treatment group: 26 M Control group: 26 M | Sham laser | More irradiation sessions | Unilateral | THI-total | Immediately | NR |
| Cuda et al., 2008 [29] | Italy | 5 mW; 650 nm; 20 min/day for 90 sessions | 46 | 50.3 | 64.4 | Mixed (84.8% HL; 15.2% idiopathic) | >36 M | Sham laser | More irradiation sessions | NR | THI-total | Immediately | NR |
| Gungor et al., 2008 [23] | Turkey | 5 mW; 650 nm; 15 min/day for 7 sessions | 66 * | 55.8 | Mixed (54% HL; 45% idiopathic) | 96 M (average) | Sham laser | Fewer irradiation sessions | Unilateral | VRS-loudness | 2 weeks after treatment | No AEs observed | |
| Rhee et al., 2006 [30] | Korea | 67 mW; 830 nm; 20 min/day for 12 sessions | 50 | 49.2 | 52.3 | Idiopathic | Treatment group: 17 M Control group: 20 M | NR | Fewer irradiation sessions | NR | THI-total | 1 week after treatment | No AEs observed |
| Nakashima et al., 2002 [24] | Japan | 60 mW; 810 nm; 6 min per week for 4 sessions | 64 * | 52.4 | 55.2 | SNHL | NR | Sham laser | Fewer irradiation sessions | NR | VRS-loudness | 1 week after treatment | Sudden deafness and dizziness |
| Mirz et al., 1999 [31] | Denmark | 50 mW; 830 nm; 15 min/time for 15 sessions | 41 | 48.6 | 48.7 | Idiopathic | Treatment group: 70 M Control group: 62 M | Sham laser | Fewer irradiation sessions | Unilateral | THI-total | Immediately | NR |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-F. Efficacy of Low-Level Laser Therapy for Tinnitus: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120931
Chen C-H, Huang C-Y, Chang C-Y, Cheng Y-F. Efficacy of Low-Level Laser Therapy for Tinnitus: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(12):931. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120931
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chih-Hao, Chii-Yuan Huang, Chun-Yu Chang, and Yen-Fu Cheng. 2020. "Efficacy of Low-Level Laser Therapy for Tinnitus: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis" Brain Sciences 10, no. 12: 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120931
APA StyleChen, C. -H., Huang, C. -Y., Chang, C. -Y., & Cheng, Y. -F. (2020). Efficacy of Low-Level Laser Therapy for Tinnitus: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Brain Sciences, 10(12), 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120931