Effect of Mental Fatigue on Postural Sway in Healthy Older Adults and Stroke Populations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
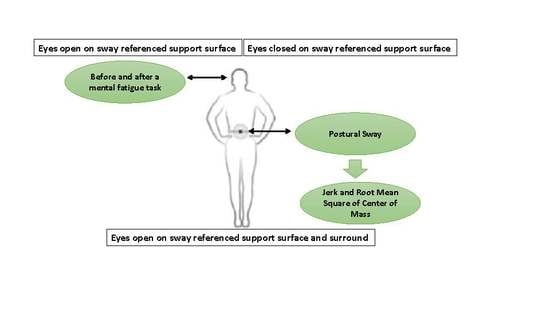
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.3. Cognitive Fatigue and Control Intervention Tasks
2.4. Postural Sway Assessment
2.5. Dual-Task Protocol
2.6. Psychophysiological Workload
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Psychophysiological Workload and Subjective Fatigue
3.2. Balance Assessments
3.2.1. Jerk of COM during Single-Task Assessments
3.2.2. Jerk of COM during Dual-Task Assessments
3.2.3. Root Mean Square during Single-Task Assessments
3.2.4. Root Mean Square during Dual-Task Assessments
3.3. Performance during Cognitive Fatigue Intervention
3.4. Performance during Dual-Task Protocol
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Mental Fatigue on Psychophysiological Workload and Subjective Fatigue
4.2. Effect of Group and Sensory Conditions on Postural Sway
4.3. Effect of Mental Fatigue on Postural Sway
4.4. Effect of Mental Fatigue on Dual-Task Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ishii, A.; Tanaka, M.; Watanabe, Y. Neural mechanisms of mental fatigue. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 25, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldadah, B.A. Fatigue and fatigability in older adults. PM R 2010, 2, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumming, T.B.; Packer, M.; Kramer, S.F.; English, C. The prevalence of fatigue after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Stroke 2016, 11, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staub, F.; Bogousslavsky, J. Fatigue after stroke: A major but neglected issue. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2001, 12, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, G.; Christensen, D.; Kirkevold, M.; Johnsen, S.P. Post-stroke fatigue and return to work: A 2-year follow-up. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2012, 125, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boksem, M.A.; Tops, M. Mental fatigue: Costs and benefits. Brain Res. Rev. 2008, 59, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, R.S.; Schneider, J.A.; Boyle, P.A.; Arnold, S.E.; Tang, Y.; Bennett, D.A. Chronic distress and incidence of mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2007, 68, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubost, V.; Kressig, R.W.; Gonthier, R.; Herrmann, F.R.; Aminian, K.; Najafi, B.; Beauchet, O. Relationship between dual-task related changes in stride velocity and stride time variability in healthy older adults. Hum. Mov. 2006, 25, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lersel, M.B.; Ribbers, H.; Munneke, M.; Borm, G.F.; Rikkert, M.G. The effect of cognitive dual tasks on balance during walking in physically fit elderly people. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, H.; Taghizadeh, G.; Ghomashchi, H.; Parnianpour, M.; Khalaf, K.; Salehi, R.; Esteki, A.; Ebrahimi, I.; Sangelaji, B. The effects of a short-term memory task on postural control of stroke patients. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2015, 22, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Endo, H.; Kizuka, T. Mental fatigue and impaired response processes: Event-related brain potentials in a Go/NoGo task. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2009, 72, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner, R.; Steinborn, M.B.; Chatterjee, A.; Sturm, W.; Willmes, K. Mental Fatigue and Temporal Preparation in Simple Reaction-Time Performance. Acta Psychol. (AMSF) 2010, 133, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.; Conforto, S.; Lopez, L.; D’Alessio, T. Cognitive load affects postural control in children. Exp. Brain Res. 2007, 179, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, B.E.; McIlroy, W.E. Postural control in the older adult. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 1996, 12, 635–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verghese, J.; Buschke, H.; Viola, L.; Katz, M.; Hall, C.; Kuslansky, G.; Lipton, R. Validity of divided attention tasks in predicting falls in older individuals: A preliminary study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 1572–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camicioli, R.; Wang, Y.; Powell, C.; Mitnitski, A.; Rockwood, K. Gait and posture impairment, parkinsonism and cognitive decline in older people. J. Neural. Transm. 2007, 114, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.; Mau-Moeller, A.; Lischke, A.; Katlun, F.; Gube, M.; Zschorlich, V.; Weippert, M. Mental fatigue increases gait variability during dual-task walking in old adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, F.L.; Qu, X. Effects of mental fatigue on biomechanics of slips. Ergonomics 2014, 57, 1927–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, T.; Beauchet, O.; Annweiler, C.; Cornu, C.; Mignardot, J.B. Postural control and cognitive decline in older adults: Position versus velocity implicit motor strategy. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mignardot, J.B.; Beauchet, O.; Annweiler, C.; Cornu, C.; Deschamps, T. Postural sway, falls, and cognitive status: A cross-sectional study among older adults. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 41, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garde, A.H.; Laursen, B.; Jorgensen, A.H.; Jensen, B.R. Effects of mental and physical demands on heart rate variability during computer work. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 87, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbruggen, F.; Logan, G.D. Response inhibition in the stop-signal paradigm. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2008, 12, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Logan, G.D.; Cowan, W.B.; Davis, K.A. On the ability to inhibit simple and choice reaction time responses: A model and a method. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1984, 10, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford-Smith, C.D.; Wyman, J.F.; Elswick, R.K., Jr.; Fernandez, T.; Newton, R.A. Test–retest reliability of the sensory organization test in noninstitutionalized older adults. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1995, 76, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Horak, F.B.; Zampieri, C.; Carlson-Kuhta, P.; Nutt, J.G.; Chiari, L. Trunk accelerometry reveals postural instability in untreated Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flash, T.; Hogan, N. The coordination of arm movements: An experimentally confirmed mathematical model. J Neurosci. 1985, 5, 1688–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granacher, U.; Wolf, I.; Wehrle, A.; Bridenbaugh, S.; Kressig, R.W. Effects of muscle fatigue on gait characteristics under single- and dual-task conditions in young and older adults. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2010, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thayer, J.F.; Ahs, F.; Fredrikson, M.; Sollers, J.J., 3rd; Wager, T.D. A meta-analysis of heart rate variability and neuroimaging studies: Implications for heart rate variability as a marker of stress and health. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarvainen, M.P.; Niskanen, J.P.; Lipponen, J.A.; Ranta-Aho, P.O.; Karjalainen, P.A. Kubios HRV—Heart rate variability analysis software. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 113, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Heart rate variability: Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Circulation 1996, 93, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pageaux, B.; Marcora, S.M.; Lepers, R. Prolonged mental exertion does not alter neuromuscular function of the knee extensors. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 2254–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hjortskov, N.; Rissén, D.; Blangsted, A.K.; Fallentin, N.; Lundberg, U.; Søgaard, K. The effect of mental stress on heart rate variability and blood pressure during computer work. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 92, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzer, R.; Shuman, M.; Mahoney, J.R.; Lipton, R.; Verghese, J. Cognitive fatigue defined in the context of attention networks. Neuropsychol. Dev. Cogn. B Aging Neuropsychol. Cogn. 2011, 18, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marigold, D.S.; Eng, J.J. The relationship of asymmetric weight-bearing with postural sway and visual reliance in stroke. Gait Posture 2006, 23, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roerdink, M.; De Haart, M.; Daffertshofer, A.; Donker, S.F.; Geurts, A.C.; Beek, P.J. Dynamical structure of center-of-pressure trajectories in patients recovering from stroke. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 174, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, E.V.; Rose, J.; Rohlfing, T.; Pfefferbaum, A. Postural sway reduction in aging men and women: Relation to brain structure, cognitive status, and stabilizing factors. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancini, M.; Horak, F.B. The relevance of clinical balance assessment tools to differentiate balance deficits. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 46, 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Marigold, D.S.; Eng, J.J.; Tokuno, C.D.; Donnelly, C.A. Contribution of muscle strength and integration of afferent input to postural instability in persons with stroke. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2004, 18, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansfield, A.; Mochizuki, G.; Inness, E.L.; McIlroy, W.E. Clinical correlates of between-limb synchronization of standing balance control and falls during inpatient stroke rehabilitation. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2012, 26, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lajoie, Y.; Teasdale, N.; Bard, C.; Fleury, M. Attentional demands for static and dynamic equilibrium. Exp. Brain Res. 1993, 97, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palluel, E.; Nougier, V.; Oliver, L. Postural control and attentional demand during adolescence. Brain Res. 2010, 1358, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, C.; Feys, P.; Moumdjian, L.; D’Amico, E.; Zappia, M.; Patti, F. Cognitive-motor dual-task interference: A systematic review of neural correlates. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 75, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yogev-Seligmann, G.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Giladi, N. The role of executive function and attention in gait. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plummer, P.; Eskes, G.; Wallace, S.; Giuffrida, C.; Fraas, M.; Campbell, G.; Skidmore, E.R. Cognitive-motor interference during functional mobility after stroke: State of the science and implications for future research. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 2565–2574.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Variables | Older Adult Group | Stroke Group | Control Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 66.1 ± 6.02 | 62.6 ± 5.2 | 65.6 ± 6.2 |
| Weight (kg) | 77.4 ± 12.06 | 75.6 ± 5.2 | 78.9 ± 4.4 |
| Hight (cm) | 173.67 ± 6 | 175.1 ± 4.7 | 178.3 ± 8.1 |
| MOCA test Impairment level | 27.4 ± 2.2 | 27.1 ± 1.8 | 28.1 ± 2.5 |
| CMSA (leg) | - | 5.18 ± 2.01 | - |
| CMSA (foot) | - | 4.6 ± 2.1 | - |
| BBS | 54.2 ± 1 | 47.4 ± 6 * | 54.2 ± 1.3 |
| TUG (s) | 7.3 ± 2.8 | 13.7 ± 5.3 * | 7.1 ± 1.3 |
| FSS | 21.2 | 22.4 | 21.5 |
| Older Adult Group | Stroke Group | Control Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Variables | Baseline | Post-Intervention Task | Baseline | Post-Intervention Task | Baseline | Post-Intervention Task |
| Mean of heart rate (beat/min) | 64.6 ± 1.7 | 63.4 ± 3.5 | 66.3 ± 1.1 | 67.1 ± 3.1 | 62.8 ± 1.8 | 63.6 ± 4.7 |
| Mean of R-R intervals | 0.857 ± 0.03 | 0.840 ± 0.08 | 0.847 ± 0.07 | 0.820 ± 0.03 | 0.817 ± 0.02 | 0.822 ± 0.06 |
| RMSSD (ms) | 28.57 ± 7.3 | 19.51 ± 2.87 * | 27.1 ± 16.98 | 22.22 ± 9.77 * | 23.42 ± 9.38 | 23.62 ± 9.06 |
| HRV HF power (n.u.) | 26.04 ± 8.69 | 21.7 ± 12.8 | 27.49 ± 20.7 | 18.9 ± 16.45 * | 21.38 ± 9.7 | 20.33 ± 6.20 |
| NASA-TLX | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Mental demand | - | 68.4 ± 22.7 | - | 70.9 ± 31.9 | - | 13.4 ± 24.6 |
| Physical demand | - | 19.1 ± 11.5 | - | 27.5 ± 9.3 | - | 3.4 ± 6.7 |
| Temporal demand | - | 46.7 ± 38.1 | - | 55.8 ± 48.2 | - | 5.1 ± 13.6 |
| Performance | - | 59.8 ± 31.1 | - | 67.4 ± 33.8 | - | 91.4 ± 16.4 |
| Effort | - | 77.4 ± 23.6 | - | 81.3 ± 31.3 | - | 17.6 ± 15.5 |
| Frustration level | - | 39.6 ± 37.6 | - | 31.3 ± 35.6 | - | 4.7 ± 4.8 |
| Global score | - | 51.8 ± 22.6 ** | - | 55.7 ± 16.4 ** | - | 22.6 ± 12.8 |
| A | |||||
| Main effects and Interaction | Df (df1,df2) | Jerk of COM F Value | RMS F Value | ||
| Group effect | 2,504 | 132.104 *** | 23.74 *** | ||
| Time effect | 1,504 | 71.175 *** | 37.496 *** | ||
| Cognitive task effect (ST, DT) | 1,504 | 16.021 *** | 13.749 *** | ||
| SOT condition effect | 2,504 | 74.751 *** | 20.782 *** | ||
| Group × time effect | 2,504 | 25.489 *** | 11.811 *** | ||
| Group × cognitive task (ST, DT) | 2,504 | 2.533 | 2.249 | ||
| Group × SOT condition effect | 2,504 | 2.485 * | 1.833 | ||
| Time × cognitive task (ST, DT) | 1,504 | 1.277 | 0.453 | ||
| Time × SOT condition | 2,504 | 0.932 | 3.20 ** | ||
| Cognitive task × SOT condition | 2,504 | 2.644 | 1.045 | ||
| Group × time × cognitive task (ST, DT) | 2,504 | 0.914 | 0.477 | ||
| Group × time × SOT condition | 4,504 | 1.273 | 1.872 | ||
| Group × cognitive task × SOT condition | 4,504 | 0.157 | 0.498 | ||
| Time × cognitive task × SOT condition | 2,504 | 0.801 | 0.966 | ||
| Group × time × cognitive task × SOT condition | 4,504 | 0.305 | 0.129 | ||
| B | |||||
| Df (df1,df2) | Single-Task Condition | Dual-Task Condition | |||
| Jerk of COM F Values | RMS F Values | Jerk of COM F Values | RMS F Values | ||
| Group effect | 2,126 | 40.641 *** | 6.627 ** | 65.021 *** | 14.568 ** |
| Time effect | 1,126 | 37.733 *** | 30.481 *** | 59.493 *** | 15.760 ** |
| SOT condition | 2,126 | 20.618 *** | 7.092 *** | 39.895 *** | 11.168 ** |
| Group × time | 2,126 | 12.348 *** | 10.607 *** | 22.970 *** | 4.511 * |
| Group × SOT condition | 4,126 | 0.724 | 1.442 | 1.343 | 0.714 |
| Time × SOT condition | 2,126 | 2.375 | 4.90 ** | 0.068 | 0.481 |
| Group × time × SOT condition | 4,126 | 1.438 | 0.994 | 0.73 | 1.324 |
| A | |||||||
| Main Effects and Interaction | Single-Task Condition | ||||||
| Df (df1,df2) | Jerk of COM F Values | RMS of COM F Values | |||||
| EOSS | ECSS | EOSSV | EOSS | ECSS | EOSSV | ||
| Group effect | 2,42 | 9.79 *** | 15.11 *** | 15.49 *** | 4.35 * | 1.179 | 3.184 |
| Time effect | 1,42 | 5.51 * | 21.91 *** | 12.255 *** | 4.053 | 12.15 *** | 15.97 *** |
| Group × time | 2,42 | 0.81 | 6.42 ** | 5.56 ** | 4.98 * | 4.61 * | 3.90 * |
| B | |||||||
| Main Effects and Interaction | Dual-Task Condition | ||||||
| Df (df1,df2) | Jerk of COM F Values | RMS of COM F Values | |||||
| Group effect | 2,42 | 11.13 *** | 31.22 *** | 26.91 *** | 9.98 *** | 6.85 ** | 3.44 *** |
| Time effect | 1,42 | 27.41 *** | 11.56 *** | 30.58 *** | 11.77 *** | 6.30 * | 4.34 * |
| Group × time | 2,42 | 4.94 * | 7.05 ** | 13.43 *** | 1.71 | 3.98 * | 2.37 |
| Older Adults Group | Stroke Group | Control | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Post-Intervention Task | Baseline | Post-Intervention Task | Baseline | Post-Intervention Task | |
| CITP | 24.01 ± 7.6 | 14.06 ± 6.4 ** | 21.2 ± 5.6 | 14.4 ± 6.8 ** | 20.6 ± 6.4 | 17.8 ± 5.01 |
| CFTP (%of correct answers) | 60.94 | 59.64 | - | |||
| Block 1 | 65.3 ± 17.3 | 68.5 ± 12.7 | - | |||
| Block 2 | 61.6 ± 27.3 | 61.6 ± 22.5 | - | |||
| Block 3 | 67.1 ± 23.4 | 50.1 ± 43.3 | - | |||
| Block 4 | 51.6 ± 39.9 | 63.7 ± 37.2 | - | |||
| Block 5 | 59.1 ± 28.6 | 54.3 ± 33.9 | - | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varas-Diaz, G.; Kannan, L.; Bhatt, T. Effect of Mental Fatigue on Postural Sway in Healthy Older Adults and Stroke Populations. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060388
Varas-Diaz G, Kannan L, Bhatt T. Effect of Mental Fatigue on Postural Sway in Healthy Older Adults and Stroke Populations. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(6):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060388
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaras-Diaz, Gonzalo, Lakshmi Kannan, and Tanvi Bhatt. 2020. "Effect of Mental Fatigue on Postural Sway in Healthy Older Adults and Stroke Populations" Brain Sciences 10, no. 6: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060388
APA StyleVaras-Diaz, G., Kannan, L., & Bhatt, T. (2020). Effect of Mental Fatigue on Postural Sway in Healthy Older Adults and Stroke Populations. Brain Sciences, 10(6), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060388