Somatosensory Gating Responses Are Associated with Prognosis in Patients with Migraine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. MEG Recordings
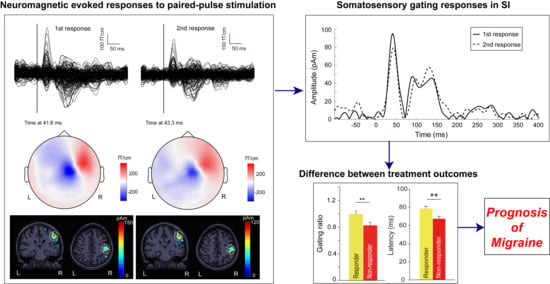
2.4. MEG Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics and Clinical Profiles
3.2. Cortical Responses to Paired-Pulse Stimuli in Patients with EM and CM
3.3. Between-Subgroup Differences in Treatment Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Probyn, K.; Bowers, H.; Caldwell, F.; Mistry, D.; Underwood, M.; Matharu, M.; Pincus, T.; CHESS Team. Prognostic factors for chronic headache: A systematic review. Neurology 2017, 89, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, T.H.; Chou, K.H.; Fuh, J.L.; Lee, P.L.; Kung, Y.C.; Lin, C.P.; Wang, S.J. Gray matter changes related to medication overuse in patients with chronic migraine. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Chou, K.H.; Lee, P.L.; Fuh, J.L.; Niddam, D.M.; Lai, K.L.; Hsiao, F.J.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chen, W.T.; Wang, S.J.; et al. Hippocampus and amygdala volume in relation to migraine frequency and prognosis. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Lee, P.L.; Chou, K.H.; Lai, K.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Chen, S.P.; Chen, W.T.; Wang, S.J. The cerebellum is associated with 2-year prognosis in patients with high-frequency migraine. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burstein, R. Deconstructing migraine headache into peripheral and central sensitization. Pain 2001, 89, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, G.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Schoenen, J.; Pierelli, F. Habituation and sensitization in primary headaches. J. Headache Pain 2013, 14, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Tommaso, M.; Ambrosini, A.; Brighina, F.; Coppola, G.; Perrotta, A.; Pierelli, F.; Sandrini, G.; Valeriani, M.; Marinazzo, D.; Stramaglia, S.; et al. Altered processing of sensory stimuli in patients with migraine. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.T.; Hsiao, F.J.; Ko, Y.C.; Liu, H.Y.; Wang, P.N.; Fuh, J.L.; Lin, Y.Y.; Wang, S.J. Comparison of somatosensory cortex excitability between migraine and “strict-criteria” tension-type headache: A magnetoencephalographic study. Pain 2018, 159, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, F.J.; Wang, S.J.; Lin, Y.Y.; Fuh, J.L.; Ko, Y.C.; Wang, P.N.; Chen, W.T. Somatosensory gating is altered and associated with migraine chronification: A magnetoencephalographic study. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Clemente, L.; Puledda, F.; Biasiotta, A.; Vigano, A.; Vicenzini, E.; Truini, A.; Cruccu, G.; Di Piero, V. Topiramate modulates habituation in migraine: Evidences from nociceptive responses elicited by laser evoked potentials. J. Headache Pain 2013, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Tommaso, M.; Delussi, M.; Ricci, K.; Montemurno, A.; Carbone, I.; Vecchio, E. Effects of OnabotulintoxinA on Habituation of Laser Evoked Responses in Chronic Migraine. Toxins 2016, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.T.; Wang, S.J.; Fuh, J.L.; Ko, Y.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Hamalainen, M.S.; Lin, Y.Y. Visual cortex excitability and plasticity associated with remission from chronic to episodic migraine. Cephalalgia 2012, 32, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamalainen, M.S.; Ilmoniemi, R.J. Interpreting magnetic fields of the brain: Minimum norm estimates. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1994, 32, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.H.; Fuh, J.L.; Wang, S.J. Validity, reliability and application of the taiwan version of the migraine disability assessment questionnaire. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2006, 105, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, S.J.; Tsai, J.C.; Chen, H.C. Epidemiology, impact and preventive care of chronic kidney disease in Taiwan. Nephrology (Carlton) 2010, 15 (Suppl. 2), 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Chou, K.H.; Lee, P.L.; Hsiao, F.J.; Niddam, D.M.; Lai, K.L.; Fuh, J.L.; Lin, C.P.; Wang, S.J. Comparison of gray matter volume between migraine and “strict-criteria” tension-type headache. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.T.; Lin, Y.Y.; Fuh, J.L.; Hamalainen, M.S.; Ko, Y.C.; Wang, S.J. Sustained visual cortex hyperexcitability in migraine with persistent visual aura. Brain 2011, 134, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.T.; Wang, S.J.; Fuh, J.L.; Lin, C.P.; Ko, Y.C.; Lin, Y.Y. Peri-ictal normalization of visual cortex excitability in migraine: An MEG study. Cephalalgia 2009, 29, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.T.; Wang, S.J.; Fuh, J.L.; Lin, C.P.; Ko, Y.C.; Lin, Y.Y. Persistent ictal-like visual cortical excitability in chronic migraine. Pain 2011, 152, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, K.L.; Niddam, D.M.; Fuh, J.L.; Chen, S.P.; Wang, Y.F.; Chen, W.T.; Wu, J.C.; Wang, S.J. Flunarizine versus topiramate for chronic migraine prophylaxis: A randomized trial. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2017, 135, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, F.J.; Cheng, C.H.; Chen, W.T.; Lin, Y.Y. Neural correlates of somatosensory paired-pulse suppression: A MEG study using distributed source modeling and dynamic spectral power analysis. NeuroImage 2013, 72, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadel, F.; Baillet, S.; Mosher, J.C.; Pantazis, D.; Leahy, R.M. Brainstorm: A user-friendly application for MEG/EEG analysis. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 879716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, N.; Glenthoj, B.Y.; Rostrup, E.; Larsson, H.B.; Oranje, B. Source localization of sensory gating: A combined EEG and fMRI study in healthy volunteers. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 2711–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, D.W.; Mason, R.; Marsden, C.A. Sensory gating, cannabinoids and schizophrenia. Neuropharmacology 2013, 67, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restuccia, D.; Vollono, C.; del Piero, I.; Martucci, L.; Zanini, S. Different levels of cortical excitability reflect clinical fluctuations in migraine. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, T.; Viana, M.; Tassorelli, C. Current Prophylactic Medications for Migraine and Their Potential Mechanisms of Action. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Dong, Z.; Ma, L.; Yu, S. Altered functional connectivity of amygdala underlying the neuromechanism of migraine pathogenesis. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jassar, H.; Nascimento, T.D.; Kaciroti, N.; DosSantos, M.F.; Danciu, T.; Koeppe, R.A.; Smith, Y.R.; Bigal, M.E.; Porreca, F.; Casey, K.L.; et al. Impact of chronic migraine attacks and their severity on the endogenous mu-opioid neurotransmission in the limbic system. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 23, 101905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Yu, S. Grey matter alterations in migraine: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 14, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sand, T.; Zhitniy, N.; White, L.R.; Stovner, L.J. Visual evoked potential latency, amplitude and habituation in migraine: A longitudinal study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, N.M.; Legg, N.J.; Anderson, D.J. Long term decline of P100 amplitude in migraine with aura. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 69, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamed, S.A. A migraine variant with abdominal colic and Alice in Wonderland syndrome: A case report and review. BMC Neurol. 2010, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, B.; Coppola, G.; Shoaran, M. Migraine classification using somatosensory evoked potentials. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, E.; Kaltenhauser, M.; Neundorfer, B.; Seidler, S. Hyperexcitability of the primary somatosensory cortex in migraine—A magnetoencephalographic study. Brain 2004, 127, 2459–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| CM (n = 37) | EM (n = 30) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 36.4 ± 10.7 | 37.0 ± 10.0 | 0.83 |
| Sex | 34 F/3 M | 24 F/6 M | 0.28 |
| HADS_A | 9.1 ± 4.1 | 7.4 ± 4.2 | 0.099 |
| HADS_D | 7.3 ± 3.8 | 5.3 ± 3.1 | 0.026 |
| Migraine profile | |||
| Headache days (/month) | 23.4 ± 6.7 | 7.5 ± 3.5 | <0.001 |
| Duration (month) | 229.7 ± 149.0 | 192.0 ± 125.4 | 0.289 |
| Days with painkiller (/month) | 6.8 ± 8.4 | 3.4 ± 6.0 | 0.07 |
| MIDAS | 43.1 ± 58.2 | 32.3 ± 28.2 | 0.362 |
| Good (n = 19) | Poor (n = 11) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 38.5 ± 10.3 | 34.6 ± 9.6 | 0.34 |
| Sex | 15 F/4 M | 9 F/2 M | >0.9 |
| HADS_A | 7.7 ± 4.3 | 6.9 ± 4.2 | 0.61 |
| HADS_D | 5.5 ± 3.1 | 4.9 ± 3.3 | 0.61 |
| Migraine profile | |||
| Headache days (/month) | 8.4 ± 3.1 | 6.1 ± 3.9 | 0.09 |
| Duration (month) | 188.0 ± 135.3 | 199.2 ± 111.9 | 0.83 |
| Days with painkiller (/month) | 4.0 ± 7.2 | 2.4 ± 3.3 | 0.49 |
| MIDAS | 34.4 ± 29.7 | 28.7 ± 26.5 | 0.61 |
| Good (n = 19) | Poor (n = 18) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 35.4 ± 12.1 | 37.4 ± 9.5 | 0.593 |
| Sex | 18 F/1 M | 16 F/2 M | >0.9 |
| HADS_A | 9.0 ± 2.9 | 9.3 ± 4.9 | 0.85 |
| HADS_D | 7.1 ± 3.6 | 7.4 ± 4.1 | 0.81 |
| Migraine profile | |||
| Headache days (/month) | 24.3 ± 7.5 | 22.7 ± 6.1 | 0.52 |
| Duration (month) | 253.3 ± 169.8 | 204.7 ± 123.5 | 0.34 |
| Days with painkiller (/month) | 7.4 ± 9.2 | 6.3 ± 7.7 | 0.7 |
| MIDAS | 50.1 ± 74.7 | 36.5 ± 37.5 | 0.49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsiao, F.-J.; Chen, W.-T.; Wang, Y.-F.; Chen, S.-P.; Lai, K.-L.; Liu, H.-Y.; Pan, L.-L.H.; Wang, S.-J. Somatosensory Gating Responses Are Associated with Prognosis in Patients with Migraine. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020166
Hsiao F-J, Chen W-T, Wang Y-F, Chen S-P, Lai K-L, Liu H-Y, Pan L-LH, Wang S-J. Somatosensory Gating Responses Are Associated with Prognosis in Patients with Migraine. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(2):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020166
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsiao, Fu-Jung, Wei-Ta Chen, Yen-Feng Wang, Shih-Pin Chen, Kuan-Lin Lai, Hung-Yu Liu, Li-Ling Hope Pan, and Shuu-Jiun Wang. 2021. "Somatosensory Gating Responses Are Associated with Prognosis in Patients with Migraine" Brain Sciences 11, no. 2: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020166
APA StyleHsiao, F.-J., Chen, W.-T., Wang, Y.-F., Chen, S.-P., Lai, K.-L., Liu, H.-Y., Pan, L.-L. H., & Wang, S.-J. (2021). Somatosensory Gating Responses Are Associated with Prognosis in Patients with Migraine. Brain Sciences, 11(2), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020166