Effects of Percutaneous Electrolysis on Endogenous Pain Modulation: A Randomized Controlled Trial Study Protocol
Abstract
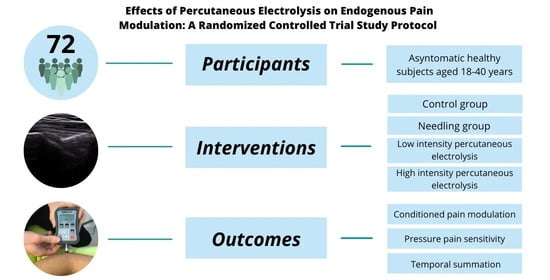
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Participants and Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Interventions
2.4. Outcomes
2.4.1. Primary Outcome
2.4.2. Secondary Outcome
2.5. Sample Size
2.6. Allocation and Randomization
2.7. Blinding
2.8. Statistical Methods
3. Discussion
3.1. Potential Impact and Significance of the Study
3.2. Limitations
3.3. Contributions to Physical Therapy
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Bermejo, P.; De-La-Cruz-Torres, B.; Naranjo-Orellana, J.; Albornoz-Cabello, M. Autonomic Responses to Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Needle Electrolysis: Effect of Needle Puncture or Electrical Current? J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2018, 24, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Cruz Torres, B.; Cabello, M.A.; Bermejo, P.G.; Orellana, J.N. Autonomic responses to ultrasoundguided percutaneous needle electrolysis of the patellar tendon in healthy male footballers. Acupunct. Med. 2016, 34, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera-Garrido, F.; Minaya-Muñoz, F. Fisioterapia Invasiva, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Barcelona, Spain, 2016; ISBN 9788491131618. [Google Scholar]
- Valera-Garrido, F.; Minaya-Muñoz, F.; Medina-Mirapeix, F. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous needle electrolysis in chronic lateral epicondylitis: Short-term and long-term results. Acupunct. Med. 2014, 32, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abat, F.; Diesel, W.-J.; Gelber, P.-E.; Polidori, F.; Monllau, J.C.; Sanchez-Ibanez, J.-M. Effectiveness of the Intratissue Percutaneous Electrolysis (EPI®) technique and isoinertial eccentric exercise in the treatment of patellar tendinopathy at two years follow-up. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014, 4, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera-Garrido, F.; Polidori, F.; Benavent-Canet, J.; Botet, F.S.; Martínez-Ramírez, P.; Calvo, S.; Belsué-Pastora, J.; Minaya-Muñoz, F. Clinical criteria for the application of percutaneous needle electrolysis in tendinopathies: An expert Consensus cocument and cross-sectional study among physical therapists. Rev. Fisioter. Invasiva J. Invasive Tech. Phys. Ther. 2019, 2, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Chiguano, G.F.; Navarro-Santana, M.J.; Cleland, J.A.; Arias-Buría, J.L.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Ortega-Santiago, R.; Plaza-Manzano, G. Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Electrolysis for Musculoskeletal Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abat, F.; Gelber, P.E.; Polidori, F.; Monllau, J.C.; Sanchez-Ibañez, J.M. Clinical results after ultrasound-guided intratissue percutaneous electrolysis (EPI®) and eccentric exercise in the treatment of patellar tendinopathy. Knee Surg. Sport. Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2015, 23, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-Miguel-Valtierra, L.; Salom Moreno, J.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Cleland, J.A.; Arias-Buría, J.L. Ultrasound-Guided Application of Percutaneous Electrolysis as an Adjunct to Exercise and Manual Therapy for Subacromial Pain Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Pain 2018, 19, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Buriá, J.L.; Truyols-Domínguez, S.; Valero-Alcaide, R.; Salom-Moreno, J.; Atín-Arratibel, M.A.; Fernández-De-Las-Penãs, C. Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Electrolysis and Eccentric Exercises for Subacromial Pain Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Evidence-based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Naranjo, J.; Barroso-Rosa, S.; Loro-Ferrer, J.F.; Limiñana-Cañal, J.M.; Suarez-Hernández, E. A novel approach in the treatment of acute whiplash syndrome: Ultrasound-guided needle percutaneous electrolysis. A randomized controlled trial. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2017, 103, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Martos, R.; Gonzalez-Perez, L.M.; Ruiz-Canela-Mendez, P.; Urresti-Lopez, F.J.; Gutierrez-Perez, J.L.; Infante-Cossio, P. Randomized, double-blind study comparing percutaneous electrolysis and dry needling for the management of temporomandibular myofascial pain. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2018, 23, e454–e462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, L.M.; Canivell-Zabaleta, M.; Rodriguez-Posada, F.; Caro-Jimenez, M.J.; Lopez-Martos, R.; Infante-Cossio, P.; Gutierrez-Perez, J.L. Study comparing intratissue percutaneous electrolysis, deep dry needling and botulinum toxin for the management of temporomandibular myofascial pain. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiussi, G.; Moreno, C. Treatment of proximal hamstring tendinopathyrelated sciatic nerve entrapment: Presentation of an ultrasound-guided “Intratissue Percutaneous Electrolysis” application. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2016, 6, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abat, F.; Valles, S.-L.; Gelber, P.-E.; Polidori, F.; Jorda, A.; García-Herreros, S.; Monllau, J.-C.; Sanchez-Ibáñez, J.-M. An experimental study of muscular injury repair in a mouse model of notexin-induced lesion with EPI® technique. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abat, F.; Valles, S.L.; Gelber, P.E.; Polidori, F.; Stitik, T.P.; García-Herreros, S.; Monllau, J.C.; Sanchez-Ibánez, J.M. Mecanismos moleculares de reparación mediante la técnica Electrólisis Percutánea Intratisular en la tendinosis rotuliana. Rev. Esp. Cir. Ortop. Traumatol. 2014, 58, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, J.L.; Calderón-Díez, L.; Herrero-Turrión, J.; Méndez-Sánchez, R.; Arias-Buría, J.L.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C. Changes in Gene Expression Associated with Collagen Regeneration and Remodeling of Extracellular Matrix after Percutaneous Electrolysis on Collagenase-Induced Achilles Tendinopathy in an Experimental Animal Model: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, L.W.; Kao, M.J.; Lin, J.G. Probable mechanisms of needling therapies for myofascial pain control. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnie, B.; Dewitte, V.; Barbe, T.; Timmermans, F.; Delrue, N.; Meeus, M. Physiologic effects of dry needling topical collection on myofascial pain. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2013, 17, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C.; Nijs, J. Trigger point dry needling for the treatment of myofascial pain syndrome: Current perspectives within a pain neuroscience paradigm. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moana-Filho, E.J.; Babiloni, A.H.; Theis-Mahon, N.R. Endogenous pain modulation in chronic orofacial pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 2018, 159, 1441–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staud, R. Abnormal endogenous pain modulation is a shared characteristic of many chronic pain conditions. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2012, 12, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossipov, M.H.; Morimura, K.; Porreca, F. Descending pain modulation and chronification of pain. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2014, 8, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damien, J.; Colloca, L.; Bellei-Rodriguez, C.É.; Marchand, S. Pain Modulation: From Conditioned Pain Modulation to Placebo and Nocebo Effects in Experimental and Clinical Pain. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2018, 139, 255–296. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Hopewell, S.; Schulz, K.F.; Montori, V.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Devereaux, P.J.; Elbourne, D.; Egger, M.; Altman, D.G. CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ 2010, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, A.W.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Altman, D.G.; Laupacis, A.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Krleža-Jerić, K.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Mann, H.; Dickersin, K.; Berlin, J.A.; et al. SPIRIT 2013 statement: Defining standard protocol items for clinical trials. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Huguet, M.; Góngora-Rodríguez, J.; Lomas-Vega, R.; Martín-Valero, R.; Díaz-Fernández, Á.; Obrero-Gaitán, E.; Ibáñez-Vera, A.J.; Rodríguez-Almagro, D. Percutaneous Electrolysis in the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylalgia: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Rodríguez, T.; Fernández-Rolle, Á.; Truyols-Domínguez, S.; Benítez-Martínez, J.C.; Casaña-Granell, J. Prospective Randomized Trial of Electrolysis for Chronic Plantar Heel Pain. Foot Ankle Int. Am. Orthop. Foot Ankle Soc. Swiss Foot Ankle Soc. 2018, 39, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Mattiussi, G.; Núñez, F.J.; Messina, G.; Rejc, E. Intratissue percutaneous electolysis combined with active physical therapy for the treatment of adductor longus enthesopathy-related groin pain: A randomized trial. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2017, 57, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-Country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yarnitsky, D.; Bouhassira, D.; Drewes, A.M.; Fillingim, R.B.; Granot, M.; Hansson, P.; Landau, R.; Marchand, S.; Matre, D.; Nilsen, K.B.; et al. Recommendations on practice of conditioned pain modulation (CPM) testing. Eur. J. Pain 2015, 19, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, A.; Waddington, G.; Cathcart, S. High-Definition Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Enhances Conditioned Pain Modulation in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized Trial. J. Pain 2016, 17, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobbackx, Y.; Meeus, M.; Wauters, L.; De Vilder, P.; Roose, J.; Verhaeghe, T.; Nijs, J. Does acupuncture activate endogenous analgesia in chronic whiplash-associated disorders? A randomized crossover trial. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Andersen, H.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Temporal summation of pain evoked by mechanical stimulation in deep and superficial tissue. J. Pain 2005, 6, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeus, M.; Hermans, L.; Ickmans, K.; Struyf, F.; Van Cauwenbergh, D.; Bronckaerts, L.; De Clerck, L.S.; Moorken, G.; Hans, G.; Grosemans, S.; et al. Endogenous pain modulation in response to exercise in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, patients with chronic fatigue syndrome and comorbid fibromyalgia, and healthy controls: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Pain Pract. 2015, 15, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspinall, S.L.; Jacques, A.; Leboeuf-Yde, C.; Etherington, S.J.; Walker, B.F. No difference in pressure pain threshold and temporal summation after lumbar spinal manipulation compared to sham: A randomised controlled trial in adults with low back pain. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2019, 43, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Muntión, A.; Godefroy, L.; Robert, H.; Muñoz-García, D.; Calvo-Lobo, C.; López-de-Uralde-Villanueva, I. Study of the mechanisms of action of the hypoalgesic effect of pressure under shock waves application: A randomised controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 42, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebano, R.E.; Vance, C.G.; Rakel, B.A.; Lee, J.E.; Cooper, N.A.; Marchand, S.; Walsh, D.M.; Sluka, K.A. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and conditioned pain modulation influence the perception of pain in humans. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtney, C.A.; Steffen, A.D.; Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C.; Kim, J.; Chmell, S.J. Joint mobilization enhances mechanisms of conditioned pain modulation in individuals with osteoarthritis of the knee. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2016, 46, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Carnero, J.; Sierra-Silvestre, E.; Beltran-Alacreu, H.; Gil-Martínez, A.; La-Touche, R. Neural Tension Technique Improves Immediate Conditioned Pain Modulation in Patients with Chronic Neck Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Pain Med. 2019, 20, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhsen, A.; Moss, P.; Gibson, W.; Walker, B.; Angela Jacques, M.B.; Schug, S.; Wright, A. The association between conditioned pain modulation and manipulation-induced analgesia in people with lateral epicondylalgia. Clin. J. Pain 2019, 35, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsouhibani, A.; Vaegter, H.B.; Hoeger Bement, M. Systemic Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia Following Isometric Exercise Reduces Conditioned Pain Modulation. Pain Med. 2019, 20, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellingson, L.D.; Koltyn, K.F.; Kim, J.S.; Cook, D.B. Does exercise induce hypoalgesia through conditioned pain modulation? Psychophysiology 2014, 51, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales Tejera, D.; Fernandez-Carnero, J.; Suso-Martí, L.; Cano-de-la-Cuerda, R.; Lerín-Calvo, A.; Remón-Ramiro, L.; La Touche, R. Comparative study of observed actions, motor imagery and control therapeutic exercise on the conditioned pain modulation in the cervical spine: A randomized controlled trial. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 2020, 37, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Wu, F.; Gan, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, B.; Liu, L. The Involvement of Descending Pain Inhibitory System in Electroacupuncture-Induced Analgesia. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.T.; Shen, L.L.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Ma, C.Y.; Huang, G.F.; Yin, J.; Yu, L.L.; Yu, S.Y.; Ding, M.Q.; et al. Effects of intensity of electroacupuncture on chronic pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varela-Rodríguez, S.; Sánchez-González, J.L.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J.L.; Delicado-Miralles, M.; Velasco, E.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Calderón-Díez, L. Effects of Percutaneous Electrolysis on Endogenous Pain Modulation: A Randomized Controlled Trial Study Protocol. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11060801
Varela-Rodríguez S, Sánchez-González JL, Sánchez-Sánchez JL, Delicado-Miralles M, Velasco E, Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Calderón-Díez L. Effects of Percutaneous Electrolysis on Endogenous Pain Modulation: A Randomized Controlled Trial Study Protocol. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(6):801. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11060801
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarela-Rodríguez, Sergio, Juan Luis Sánchez-González, José Luis Sánchez-Sánchez, Miguel Delicado-Miralles, Enrique Velasco, César Fernández-de-las-Peñas, and Laura Calderón-Díez. 2021. "Effects of Percutaneous Electrolysis on Endogenous Pain Modulation: A Randomized Controlled Trial Study Protocol" Brain Sciences 11, no. 6: 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11060801
APA StyleVarela-Rodríguez, S., Sánchez-González, J. L., Sánchez-Sánchez, J. L., Delicado-Miralles, M., Velasco, E., Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C., & Calderón-Díez, L. (2021). Effects of Percutaneous Electrolysis on Endogenous Pain Modulation: A Randomized Controlled Trial Study Protocol. Brain Sciences, 11(6), 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11060801