Orthotopic Transplantation of Human Paediatric High-Grade Glioma in Zebrafish Larvae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
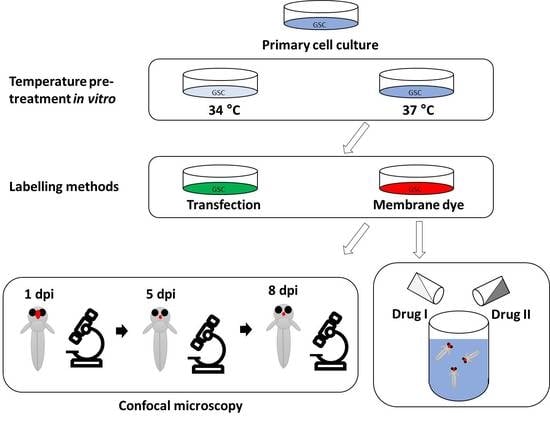
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Animals
2.3. Cerebral Injection of Larvae
2.4. Live Imaging of Larvae
2.5. Imaging Analysis
2.6. Immunocytochemistry
2.7. Immunohistochemistry
2.8. Drug Treatments
3. Results
3.1. Temperature Acclimatisation of GSCs Prior to Injection Causes Morphological Differences and Reduced Survival In Vitro and In Vivo
3.2. Evaluation of Labelling Methods of GSC Lines
3.3. Evaluating Take-Rate, Cell Survival, Growth and Morphology of a Panel of Primary Paediatric GSC Lines In Vivo
3.4. GSCs Respond to Drug Treatments In Vitro
3.5. Xenotransplanted GSCs Respond to Drug Treatments of the Larvae
4. Discussion
4.1. Site of Cell Injections
4.2. Temperatures for Implanted Fish and Human Cells
4.3. GSC Labelling Methods
4.4. Length of Observation
4.5. The Role of Immune System
4.6. Pharmacological Treatment Effects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Farah, P.; Ondracek, A.; Chen, Y.; Wolinsky, Y.; Stroup, N.E.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2006–2010. Neuro-oncology 2013, 15 (Suppl. 2), ii1–ii56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sturm, D.; Bender, S.; Jones, D.T.; Lichter, P.; Grill, J.; Becher, O.; Hawkins, C.; Majewski, J.; Jones, C.; Costello, J.F.; et al. Paediatric and adult glioblastoma: Multiform (epi)genomic culprits emerge. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gestrich, C.K.; Jajosky, A.N.; Elliott, R.; Stearns, D.; Sadri, N.; Cohen, M.L.; Couce, M.E. Molecular Profiling of Pediatric and Adult Glioblastoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 155, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, R. Pediatric and adult gliomas: How different are they? Neuro-oncology 2010, 12, 1203–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, A.L.; Joseph, R.W.; Copland, J.A. Patient-derived tumor xenograft models for melanoma drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, N.; Fernández, V.; Pereira, R.C.; Rancati, S.; Pelizzoli, R.; De Pietri Tonelli, D. A Xenotransplant Model of Human Brain Tumors in Wild-Type Mice. iScience 2020, 23, 100813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, S.; Vaeteewoottacharn, K.; Kariya, R. Application of Highly Immunocompromised Mice for the Establishment of Patient-Derived Xenograft (PDX) Models. Cells 2019, 8, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zarzosa, P.; Navarro, N.; Giralt, I.; Molist, C.; Almazán-Moga, A.; Vidal, I.; Soriano, A.; Segura, M.F.; Hladun, R.; Villanueva, A.; et al. Patient-derived xenografts for childhood solid tumors: A valuable tool to test new drugs and personalize treatments. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 19, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, K.M.; Kim, J.; Jin, J.; Kim, M.; Seol, H.J.; Muradov, J.; Yang, H.; Choi, Y.L.; Park, W.Y.; Kong, D.S.; et al. Patient-specific orthotopic glioblastoma xenograft models recapitulate the histopathology and biology of human glioblastomas in situ. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsson, S.; Wenger, A.; Dósa, S.; Sabel, M.; Kling, T.; Carén, H. Cell line-based xenograft mouse model of paediatric glioma stem cells mirrors the clinical course of the patient. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, S.H.; Chua, H.L.; Gong, Z.; Lam, T.J.; Sin, Y.M. Development and maturation of the immune system in zebrafish, Danio rerio: A gene expression profiling, in situ hybridization and immunological study. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, M.; Ablain, J.; Chuan, Y.; Langenau, D.M.; Zon, L.I. Zebrafish patient avatars in cancer biology and precision cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimunde, P.; Pensado-López, A.; Carreira Crende, M.; Lombao Iglesias, V.; Sánchez, L.; Torrecilla-Parra, M.; Ramírez, C.M.; Anfray, C.; Torres Andón, F. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Glioblastoma and Zebrafish Models for the Discovery of New Treatments. Cancers 2021, 13, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, M.J.; Stewart, R.A. Pediatric Cancer Models in Zebrafish. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eden, C.J.; Ju, B.; Murugesan, M.; Phoenix, T.N.; Nimmervoll, B.; Tong, Y.; Ellison, D.W.; Finkelstein, D.; Wright, K.; Boulos, N.; et al. Orthotopic models of pediatric brain tumors in zebrafish. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geiger, G.A.; Fu, W.; Kao, G.D. Temozolomide-mediated radiosensitization of human glioma cells in a zebrafish embryonic system. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3396–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamin, D.C.; Hynes, R.O. Intravital imaging of metastasis in adult Zebrafish. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, A.; Ye, T.; Cao, D.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xie, Y.; Yao, S.; Zhao, C. Identify a Blood-Brain Barrier Penetrating Drug-TNB using Zebrafish Orthotopic Glioblastoma Xenograft Model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabezas-Sáinz, P.; Pensado-López, A.; Sáinz, B., Jr.; Sánchez, L. Modeling Cancer Using Zebrafish Xenografts: Drawbacks for Mimicking the Human Microenvironment. Cells 2020, 9, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittori, M.; Motaln, H.; Turnšek, T.L. The study of glioma by xenotransplantation in zebrafish early life stages. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 2015, 63, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, L.; Astell, K.R.; Velikova, G.; Sieger, D. A Zebrafish Live Imaging Model Reveals Differential Responses of Microglia Toward Glioblastoma Cells In Vivo. Zebrafish 2016, 13, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Targen, S.; Kaya, T.; Avci, M.E.; Gunes, D.; Keskus, A.G.; Konu, O. ZenoFishDb v1.1: A Database for Xenotransplantation Studies in Zebrafish. Zebrafish 2020, 17, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vittori, M.; Breznik, B.; Gredar, T.; Hrovat, K.; Bizjak Mali, L.; Lah, T.T. Imaging of human glioblastoma cells and their interactions with mesenchymal stem cells in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryonic brain. Radiol. Oncol. 2016, 50, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umans, R.A.; Ten Kate, M.; Pollock, C.; Sontheimer, H. Fishing for Contact: Modeling Perivascular Glioma Invasion in the Zebrafish Brain. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, A.M.; Jaros, B.D.; Puduvalli, V.K.; Imitola, J.; Kaur, B.; Beattie, C.E. Standardized orthotopic xenografts in zebrafish reveal glioma cell-line-specific characteristics and tumor cell heterogeneity. Dis. Models Mech. 2016, 9, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almstedt, E.; Rosén, E.; Gloger, M.; Stockgard, R.; Hekmati, N.; Koltowska, K.; Krona, C.; Nelander, S. Real-time evaluation of glioblastoma growth in patient-specific zebrafish xenografts. Neuro-oncology 2021, 24, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, H.S.; Kerby, T.; Calvert, H. Temozolomide and treatment of malignant glioma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2585–2597. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.H.; Chang, Y.J.; Ku, M.S.; Chung, K.T.; Yang, J.T. Enhancement of temozolomide-induced apoptosis by valproic acid in human glioma cell lines through redox regulation. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shervington, A.; Patel, R. Silencing DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) enhances glioma chemosensitivity. Oligonucleotides 2008, 18, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duenas-Gonzalez, A.; Candelaria, M.; Perez-Plascencia, C.; Perez-Cardenas, E.; de la Cruz-Hernandez, E.; Herrera, L.A. Valproic acid as epigenetic cancer drug: Preclinical, clinical and transcriptional effects on solid tumors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2008, 34, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Llamas Luceño, N.; Sander, B.; Golas, M.M. Synergistic anti-cancer effects of epigenetic drugs on medulloblastoma cells. Cell. Oncol. 2017, 40, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, A.; Larsson, S.; Danielsson, A.; Elbæk, K.J.; Kettunen, P.; Tisell, M.; Sabel, M.; Lannering, B.; Nordborg, C.; Schepke, E.; et al. Stem cell cultures derived from pediatric brain tumors accurately model the originating tumors. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 18626–18639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribas, L.; Vanezis, K.; Imués, M.A.; Piferrer, F. Treatment with a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor feminizes zebrafish and induces long-term expression changes in the gonads. Epigenetics Chromatin 2017, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farooq, M.; El-Faham, A.; Khattab, S.N.; Elkayal, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Taha, N.A.; Baabbad, A.; Wadaan, M.A.; Hamed, E.A. Biological screening of novel derivatives of valproic acid for anticancer and antiangiogenic properties. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2014, 15, 7785–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bliss, C.I. The toxicity of poisons applied jointly. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1939, 26, 585–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabezas-Sainz, P.; Guerra-Varela, J.; Carreira, M.J.; Mariscal, J.; Roel, M.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Sciara, A.A.; Abal, M.; Botana, L.M.; López, R.; et al. Improving zebrafish embryo xenotransplantation conditions by increasing incubation temperature and establishing a proliferation index with ZFtool. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pype, C.; Verbueken, E.; Saad, M.A.; Casteleyn, C.R.; Van Ginneken, C.J.; Knapen, D.; Van Cruchten, S.J. Incubation at 32.5 °C and above causes malformations in the zebrafish embryo. Reprod. Toxicol. 2015, 56, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Sainz, P.; Coppel, C.; Pensado-López, A.; Fernandez, P.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; López-López, R.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Sánchez, L. Morphological Abnormalities and Gene Expression Changes Caused by High Incubation Temperatures in Zebrafish Xenografts with Human Cancer Cells. Genes 2021, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lally, B.E.; Geiger, G.A.; Kridel, S.; Arcury-Quandt, A.E.; Robbins, M.E.; Kock, N.D.; Wheeler, K.; Peddi, P.; Georgakilas, A.; Kao, G.D.; et al. Identification and biological evaluation of a novel and potent small molecule radiation sensitizer via an unbiased screen of a chemical library. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8791–8799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pudelko, L.; Edwards, S.; Balan, M.; Nyqvist, D.; Al-Saadi, J.; Dittmer, J.; Almlöf, I.; Helleday, T.; Bräutigam, L. An orthotopic glioblastoma animal model suitable for high-throughput screenings. Neuro-oncology 2018, 20, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Patron, L.A.; Agudelo-Dueñas, N.; Madrid-Wolff, J.; Venegas, J.A.; González, J.M.; Forero-Shelton, M.; Akle, V. Xenotransplantation of Human glioblastoma in Zebrafish larvae: In vivo imaging and proliferation assessment. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio043257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, D.W.; Oh, E.S.; Park, S.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Kim, C.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Williams, D.R. A novel zebrafish human tumor xenograft model validated for anti-cancer drug screening. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 1930–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Xie, X.; Walker, S.; White, D.T.; Mumm, J.S.; Cowell, J.K. Evaluating human cancer cell metastasis in zebrafish. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Ent, W.; Burrello, C.; Teunisse, A.F.; Ksander, B.R.; van der Velden, P.A.; Jager, M.J.; Jochemsen, A.G.; Snaar-Jagalska, B.E. Modeling of human uveal melanoma in zebrafish xenograft embryos. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 6612–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Cui, W.; Gu, A.; Xu, C.; Yu, S.C.; Li, T.T.; Cui, Y.H.; Zhang, X.; Bian, X.W. A novel zebrafish xenotransplantation model for study of glioma stem cell invasion. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pudelko, L.; Rouhi, P.; Sanjiv, K.; Gad, H.; Kalderén, C.; Höglund, A.; Squatrito, M.; Schuhmacher, A.J.; Edwards, S.; Hägerstrand, D.; et al. Glioblastoma and glioblastoma stem cells are dependent on functional MTH1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 84671–84684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almstedt, E.; Elgendy, R.; Hekmati, N.; Rosén, E.; Wärn, C.; Olsen, T.K.; Dyberg, C.; Doroszko, M.; Larsson, I.; Sundström, A.; et al. Integrative discovery of treatments for high-risk neuroblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Brunson, D.C.; Tang, Q.; Do, D.; Iftimia, N.A.; Moore, J.C.; Hayes, M.N.; Welker, A.M.; Garcia, E.G.; Dubash, T.D.; et al. Visualizing Engrafted Human Cancer and Therapy Responses in Immunodeficient Zebrafish. Cell 2019, 177, 1903–1914.e1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcan, S.; Fabius, A.W.; Borodovsky, A.; Pedraza, A.; Brennan, C.; Huse, J.; Viale, A.; Riggins, G.J.; Chan, T.A. Efficient induction of differentiation and growth inhibition in IDH1 mutant glioma cells by the DNMT Inhibitor Decitabine. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Naz, A.; Thompson, D.H.; Irudayaraj, J. Decitabine nanoconjugate sensitizes human glioblastoma cells to temozolomide. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Öz, S.; Raddatz, G.; Rius, M.; Blagitko-Dorfs, N.; Lübbert, M.; Maercker, C.; Lyko, F. Quantitative determination of decitabine incorporation into DNA and its effect on mutation rates in human cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catalano, M.G.; Fortunati, N.; Pugliese, M.; Costantino, L.; Poli, R.; Bosco, O.; Boccuzzi, G. Valproic acid induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in poorly differentiated thyroid cancer cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riva, G.; Baronchelli, S.; Paoletta, L.; Butta, V.; Biunno, I.; Lavitrano, M.; Dalprà, L.; Bentivegna, A. In vitro anticancer drug test: A new method emerges from the model of glioma stem cells. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welker, A.M.; Jaros, B.D.; An, M.; Beattie, C.E. Changes in tumor cell heterogeneity after chemotherapy treatment in a xenograft model of glioblastoma. Neuroscience 2017, 356, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canella, A.; Welker, A.M.; Yoo, J.Y.; Xu, J.; Abas, F.S.; Kesanakurti, D.; Nagarajan, P.; Beattie, C.E.; Sulman, E.P.; Liu, J.; et al. Efficacy of Onalespib, a Long-Acting Second-Generation HSP90 Inhibitor, as a Single Agent and in Combination with Temozolomide against Malignant Gliomas. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6215–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffin, M.; Khan, R.; Basu, S.; Smith, S. Ion Channels as Therapeutic Targets in High Grade Gliomas. Cancers 2020, 12, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Larsson, S.; Kettunen, P.; Carén, H. Orthotopic Transplantation of Human Paediatric High-Grade Glioma in Zebrafish Larvae. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12050625
Larsson S, Kettunen P, Carén H. Orthotopic Transplantation of Human Paediatric High-Grade Glioma in Zebrafish Larvae. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(5):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12050625
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarsson, Susanna, Petronella Kettunen, and Helena Carén. 2022. "Orthotopic Transplantation of Human Paediatric High-Grade Glioma in Zebrafish Larvae" Brain Sciences 12, no. 5: 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12050625
APA StyleLarsson, S., Kettunen, P., & Carén, H. (2022). Orthotopic Transplantation of Human Paediatric High-Grade Glioma in Zebrafish Larvae. Brain Sciences, 12(5), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12050625