Insula Connectivity Abnormalities Predict Impulsivity in Chronic Heroin Use Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Resting-State fMRI Study
Abstract
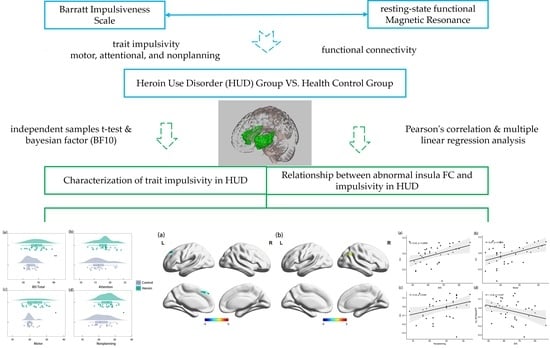
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Research Tools
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Data Acquisition
2.5. RS-fMRI Preprocessing
2.6. Seed-Based Analysis of Whole-Brain FC
2.7. Behavioral Data Analysis
2.7.1. T Test
2.7.2. ROI-Based Correlation Analysis of FC and Behavioral Data
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Results
3.2. Resting-State FC Results
3.3. Association between Insula FC and Trait Impulsivity
4. Discussion
4.1. Characterization of Trait Impulsivity in HUD
4.2. Relationship between Abnormal Insula Functional Connectivity and Impulsivity in HUD
4.3. Limitations and Research Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Fang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Hao, W.; Liao, Y. Neurobiological Mechanisms and Related Clinical Treatment of Addiction: A Review. Psychoradiology 2022, 2, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolomeo, S.; Steele, J.D.; Ekhtiari, H.; Baldacchino, A. Chronic Heroin Use Disorder and the Brain: Current Evidence and Future Implications. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 111, 110148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldacchino, A.; Balfour, D.J.K.; Matthews, K. Impulsivity and Opioid Drugs: Differential Effects of Heroin, Methadone and Prescribed Analgesic Medication. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalley, J.W.; Ersche, K.D. Neural Circuitry and Mechanisms of Waiting Impulsivity: Relevance to Addiction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Salmeron, B.J.; Gu, H.; Stein, E.A.; Yang, Y. Impaired Functional Connectivity within and between Frontostriatal Circuits and Its Association with Compulsive Drug Use and Trait Impulsivity in Cocaine Addiction. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B.J.; Robbins, T.W. Drug Addiction: Updating Actions to Habits to Compulsions Ten Years On. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2016, 67, 23–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.C.; Kaneva, R.; Vasilev, G.; Moeller, F.G.; Vassileva, J. Neurocognitive and Psychiatric Markers for Addiction: Common vs. Specific Endophenotypes for Heroin and Amphetamine Dependence. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdejo-García, A.J.; Perales, J.C.; Pérez-García, M. Cognitive Impulsivity in Cocaine and Heroin Polysubstance Abusers. Addict. Behav. 2007, 32, 950–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belin, D.; Mar, A.C.; Dalley, J.W.; Robbins, T.W.; Everitt, B.J. High Impulsivity Predicts the Switch to Compulsive Cocaine-Taking. Science 2008, 320, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cservenka, A.; Ray, L.A. Self-Reported Attentional and Motor Impulsivity Are Related to Age at First Methamphetamine Use. Addict. Behav. 2017, 65, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochat, L.; Billieux, J.; Gagnon, J.; Van der Linden, M. A Multifactorial and Integrative Approach to Impulsivity in Neuropsychology: Insights from the UPPS Model of Impulsivity. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2018, 40, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattij, T.; De Vries, T.J. The Role of Impulsivity in Relapse Vulnerability. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.-S.; Li, Y.-H.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, N.; Bechara, A.; Sui, N. Working Memory and Affective Decision-Making in Addiction: A Neurocognitive Comparison between Heroin Addicts, Pathological Gamblers and Healthy Controls. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 134, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassileva, J.; Conrod, P.J. Impulsivities and Addictions: A Multidimensional Integrative Framework Informing Assessment and Interventions for Substance Use Disorders. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audrain-McGovern, J.; Rodriguez, D.; Epstein, L.H.; Cuevas, J.; Rodgers, K.; Wileyto, E.P. Does Delay Discounting Play an Etiological Role in Smoking or Is It a Consequence of Smoking? Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009, 103, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slutske, W.S.; Moffitt, T.E.; Poulton, R.; Caspi, A. Undercontrolled Temperament at Age 3 Predicts Disordered Gambling at Age 32: A Longitudinal Study of a Complete Birth Cohort. Psychol. Sci. 2012, 23, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersche, K.D.; Turton, A.J.; Pradhan, S.; Bullmore, E.T.; Robbins, T.W. Drug Addiction Endophenotypes: Impulsive versus Sensation-Seeking Personality Traits. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersche, K.D.; Jones, P.S.; Williams, G.B.; Turton, A.J.; Robbins, T.W.; Bullmore, E.T. Abnormal Brain Structure Implicated in Stimulant Drug Addiction. Science 2012, 335, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, M.S.; Mathias, C.W.; Dougherty, D.M.; Lake, S.L.; Anderson, N.E.; Patton, J.H. Fifty Years of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale: An Update and Review. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2009, 47, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo-Garcia, A.; Albein-Urios, N. Impulsivity Traits and Neurocognitive Mechanisms Conferring Vulnerability to Substance Use Disorders. Neuropharmacology 2021, 183, 108402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rømer Thomsen, K.; Callesen, M.B.; Hesse, M.; Kvamme, T.L.; Pedersen, M.M.; Pedersen, M.U.; Voon, V. Impulsivity Traits and Addiction-Related Behaviors in Youth. J. Behav. Addict. 2018, 7, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, J.H.; Stanford, M.S.; Barratt, E.S. Factor Structure of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale. J. Clin. Psychol. 1995, 51, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; Du, J.; Su, H.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Bao, J.; Zhao, M. Virtual Digital Psychotherapist App-Based Treatment in Patients with Methamphetamine Use Disorder (Echo-APP): Single-Arm Pilot Feasibility and Efficacy Study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2023, 11, e40373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nery, F.G.; Hatch, J.P.; Monkul, E.S.; Matsuo, K.; Zunta-Soares, G.B.; Bowden, C.L.; Soares, J.C. Trait impulsivity is increased in bipolar disorder patients with comorbid alcohol use disorders. Psychopathology 2013, 46, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersche, K.D.; Jones, P.S.; Williams, G.B.; Smith, D.G.; Bullmore, E.T.; Robbins, T.W. Distinctive personality traits and neural correlates associated with stimulant drug use versus familial risk of stimulant dependence. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deserno, L.; Wilbertz, T.; Reiter, A.; Horstmann, A.; Neumann, J.; Villringer, A.; Heinze, H.J.; Schlagenhauf, F. Lateral prefrontal model-based signatures are reduced in healthy individuals with high trait impulsivity. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, W.; Rünger, D. Psychology of Habit. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2016, 67, 289–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadet, J.L. Animal models of addiction: Compulsive drug taking and cognition. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 106, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, K.; Widmer, M. What can the monetary incentive delay task tell us about the neural processing of reward and punishment? Neurosci. Neuroecon. 2015, 3, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, N.H.; Rudrauf, D.; Damasio, H.; Bechara, A. Damage to the Insula Disrupts Addiction to Cigarette Smoking. Science 2007, 315, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Han, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Meng, S.; Lu, L.; Xue, Y.; Shi, J. An Orbitofrontal Cortex-Anterior Insular Cortex Circuit Gates Compulsive Cocaine Use. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Huang, P.; Shen, Z.; Qian, W.; Luo, X.; Li, K.; Zeng, Q.; Gu, Q.; Yu, H.; et al. Abnormal White Matter Tracts of Insula in Smokers. Brain Imaging Behav. 2021, 15, 1955–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Xiao, X.; Yang, T.; Ritola, K.; Hantman, A.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z.J.; Li, B. A genetically defined insula-brainstem circuit selectively controls motivational vigor. Cell 2021, 184, 6344–6360.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, L.Q.; Nomi, J.S.; Hébert-Seropian, B.; Ghaziri, J.; Boucher, O. Structure and Function of the Human Insula. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. Publ. Am. Electroencephalogr. Soc. 2017, 34, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoguchi, H.; Katahira, K.; Inutsuka, A.; Fukumoto, K.; Nakamura, A.; Wang, T.; Nagai, T.; Sato, J.; Sawada, M.; Ohira, H.; et al. Insular Neural System Controls Decision-Making in Healthy and Methamphetamine-Treated Rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3930–E3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhan, Q.; Dong, J.; Peng, H.; Zhai, J.; Zhao, J.; She, S.; Wu, C. Covariation between spontaneous neural activity in the insula and affective temperaments is related to sleep disturbance in individuals with major depressive disorder. Psychol. Med. 2021, 51, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Yan, X.; Ye, J.; et al. Disrupted Default Mode Network and Basal Craving in Male Heroin-Dependent Individuals: A Resting-State fMRI Study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2016, 77, e1211–e1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, L.; Kohl, K.; Morgan, T.A.; Clark, L.A. “Impulsivity”: Relations between Self-Report and Behavior. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2013, 104, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Nieto-Castanon, A. Conn: A functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connect. 2012, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Sheng, W.; Chen, Y.; Pang, Y.; Lu, F.; Tang, Q.; Han, S.; Shen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xie, A.; et al. Dynamic Changes of Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuations in Patients with Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Josephs, O.; Zarahn, E.; Holmes, A.P.; Rouquette, S.; Poline, J.-B. To Smooth or Not to Smooth?: Bias and Efficiency in fMRI Time-Series Analysis. NeuroImage 2000, 12, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.G.; Craddock, R.C.; Zuo, X.N.; Zang, Y.F.; Milham, M.P. Standardizing the intrinsic brain: Towards robust measurement of inter-individual variation in 1000 functional connectomes. NeuroImage 2013, 80, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirer, W.R.; Jiang, H.; Price, C.M.; Ng, B.; Greicius, M.D. Optimization of rs-fMRI Pre-processing for Enhanced Signal-Noise Separation, Test-Retest Reliability, and Group Discrimination. NeuroImage 2015, 117, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordes, D.; Haughton, V.M.; Arfanakis, K.; Carew, J.D.; Turski, P.A.; Moritz, C.H.; Quigley, M.A.; Meyerand, M.E. Frequencies Contributing to Functional Connectivity in the Cerebral Cortex in “Resting-State” Data. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Friston, K.J.; Frith, C.D.; Liddle, P.F.; Frackowiak, R.S. Functional connectivity: The principal-component analysis of large (PET) data sets. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1993, 13, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, K.; Fox, M.D. Towards a consensus regarding global signal regression for resting state functional connectivity MRI. NeuroImage 2017, 154, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenmakers, E.J.; Marsman, M.; Jamil, T.; Ly, A.; Verhagen, J.; Love, J.; Selker, R.; Gronau, Q.F.; Šmíra, M.; Epskamp, S.; et al. Bayesian inference for psychology. Part I: Theoretical advantages and practical ramifications. Psychon. Bull Rev. 2018, 25, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetzels, R.; Matzke, D.; Lee, M.D.; Rouder, J.N.; Iverson, G.J.; Wagenmakers, E.J. Statistical Evidence in Experimental Psychology: An Empirical Comparison Using 855 t Tests. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2011, 6, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, V.; Romaniuk, L.; Cardinal, R.N.; Pope, M.; Nicol, K.; Hall, J. Impulsivity in Borderline Personality Disorder. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakowski, M.I.; Czobor, P. Distinctive Profiles of Traits Predisposing to Violence in Schizophrenia and in the General Population. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 202, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, F.; Wagner, A.; Müller, A.; Eggert, F. Subscales of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale Differentially Relate to the Big Five Factors of Personality. Scand. J. Psychol. 2017, 58, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubczyk, A.; Klimkiewicz, A.; Topolewska-Wochowska, A.; Serafin, P.; Sadowska-Mazuryk, J.; Pupek-Pyzioł, J.; Brower, K.J.; Wojnar, M. Relationships of Impulsiveness and Depressive Symptoms in Alcohol Dependence. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 136, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, C.; Liu, N.; Wang, C.; Zhang, N. Childhood Emotional Abuse and Motor Impulsiveness among Male Violent Inmates with Antisocial Personality Disorder. Personal. Ment. Health 2022, 16, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannelli, F.; Giganti, F.; Righi, S.; Peru, A.; Borgheresi, A.; Zaccara, G.; Viggiano, M.P.; Cincotta, M. Audio-Visual Integration Effect in Lateral Occipital Cortex during an Object Recognition Task: An Interference Pilot Study. Brain Stimulat. 2016, 9, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, N.; Lin, L.-Z.; Wang, X.; Shi, L.; Xu, X.-Y.; Jin, Y.-Y.; Tan, S.; Song, X.-J.; Jing, J.; Li, X.-H. Brain Structure Underlying the Empathizing-Systemizing Difference in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. World J. Pediatr. 2023, 19, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, G.F.; Lambon Ralph, M.A.; Simons, J.S. A Unifying Account of Angular Gyrus Contributions to Episodic and Semantic Cognition. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.A.; Poeppel, D.; Murphy, G.L. Contrasting Semantic versus Inhibitory Processing in the Angular Gyrus: An fMRI Study. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 2470–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, C.; Cai, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Zhu, J.; Yu, Y. Functional Hierarchy of the Angular Gyrus and Its Underlying Genetic Architecture. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2023, 44, 2815–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcq, E.; Kieffer, B.L. Opioid Receptors: Drivers to Addiction? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Xiao, L.; Huo, X.; Ding, J.; Sun, T. Is the Insula Linked to Sleep? A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C. Dynamic Brain Functional Network Based on EEG Microstate during Sensory Gating in Schizophrenia. J. Neural Eng. 2022, 19, 026007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Boisgueheneuc, F.; Levy, R.; Volle, E.; Seassau, M.; Duffau, H.; Kinkingnehun, S.; Samson, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dubois, B. Functions of the Left Superior Frontal Gyrus in Humans: A Lesion Study. Brain J. Neurol. 2006, 129, 3315–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, P.; Heil, M.; Bender, S.; Dippel, G.; Korb, F.M.; Smolka, M.N.; Marxen, M. Modulating Functional Connectivity between Medial Frontopolar Cortex and Amygdala by Inhibitory and Excitatory Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 4301–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.-W.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Du, Y. Trait Impulsivity and Impaired Prefrontal Impulse Inhibition Function in Adolescents with Internet Gaming Addiction Revealed by a Go/No-Go fMRI Study. Behav. Brain Funct. BBF 2014, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha-Bang, S.; Stenbæk, D.S.; Holst, K.; Licht, C.L.; Jensen, P.S.; Frokjaer, V.G.; Mortensen, E.L.; Knudsen, G.M. Trait aggression and trait impulsivity are not related to frontal cortex 5-HT2A receptor binding in healthy individuals. Psychiatry Res. 2013, 212, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.N.; Nguyen, N.P.K.; Nguyen, L.T.H.; Shin, H.M.; Yang, I.J. Screening for Neuroprotective and Rapid Antidepressant-like Effects of 20 Essential Oils. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Simmler, L.D.; Van Zessen, R.; Flakowski, J.; Wan, J.X.; Deng, F.; Li, Y.L.; Nau-tiyal, K.M.; Pascoli, V.; Lüscher, C. Synaptic mechanism underlying serotonin modulation of transition to cocaine addiction. Science 2021, 373, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitcher, D. Visual Motion: Asymmetrical Processing Differences between the Cerebral Hemispheres. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, R957–R960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.D.B. How Do You Feel--Now? The Anterior Insula and Human Awareness. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, N.J.; Johnson, D.C.; Flagan, T.; Simmons, A.N.; Kotturi, S.A.; Van Orden, K.F.; Potterat, E.G.; Swain, J.L.; Paulus, M.P. Detecting Emotion in Others: Increased Insula and Decreased Medial Prefrontal Cortex Activation during Emotion Processing in Elite Adventure Racers. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2014, 9, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Miller, L.A.; McGrillen, K. The Lateralization of Gustatory Function and the Flow of Information from Tongue to Cortex. Neuropsychologia 2013, 51, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, S.; Kullmann, S.; Veit, R. Food Related Processes in the Insular Cortex. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, R.; Feng, T.; Turel, O.; He, Q. Gender-specific resting-state rDMPFC-centric functional connectivity underpinnings of intertemporal choice. Cereb. Cortex 2023, 33, 10066–10075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| ROI | Brain Regions | Volume-Based ROI | Peak t-Scores | Voxel Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X(voxel) | Y(voxel) | Z(voxel) | ||||
| Right insula | sLOC r | 20 | 19 | 38 | 4.61 | 88 |
| AG r | 14 | 26 | 36 | 3.50 | 45 | |
| Left insula | SFG l | 72 | 161 | 114 | −3.72 | 48 |
| FP l | 39 | 61 | 28 | −3.57 | 27 | |
| SFG r | 112 | 157 | 116 | −4.06 | 17 | |
| Predictor Variable | Outcome Variable: Trait Impulsivity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | t | p | R2 | F | |
| FC ICr | 0.436 | 2.162 | 0.043 | 0.217 | 2.770 |
| FC ICl | −0.269 | −1.476 | 0.198 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Shao, Y.; Gong, J. Insula Connectivity Abnormalities Predict Impulsivity in Chronic Heroin Use Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Resting-State fMRI Study. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13111508
Zhang Y, Zhong X, Shao Y, Gong J. Insula Connectivity Abnormalities Predict Impulsivity in Chronic Heroin Use Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Resting-State fMRI Study. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(11):1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13111508
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yan, Xiao Zhong, Yongcong Shao, and Jingjing Gong. 2023. "Insula Connectivity Abnormalities Predict Impulsivity in Chronic Heroin Use Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Resting-State fMRI Study" Brain Sciences 13, no. 11: 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13111508
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhong, X., Shao, Y., & Gong, J. (2023). Insula Connectivity Abnormalities Predict Impulsivity in Chronic Heroin Use Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Resting-State fMRI Study. Brain Sciences, 13(11), 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13111508