Hypnotizability and Disordered Personality Styles in Cluster A Personality Disorders
Abstract
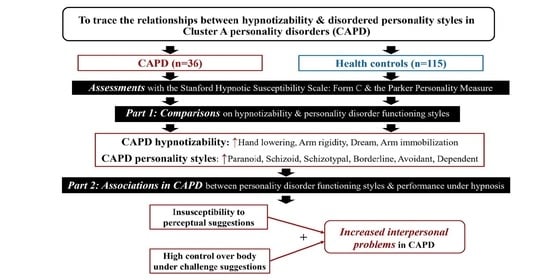
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. The Stanford Hypnotic Susceptibility Scale: Form C
2.2.2. The Parker Personality Measure (PERM)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, R.K. Assessment and management of personality disorders. Am. Fam. Physician 2004, 70, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dixon-Gordon, K.L.; Turner, B.J.; Chapman, A.L. Psychotherapy for personality disorders. Int. Rev. Psychiatry. 2011, 23, 282–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, J.; Modesitt, T.; Palmer, M.; Ward, S.; Martin, B.; Wyatt, R.; Thomas, C. Review of pharmacologic treatment in cluster A personality disorders. Ment. Health Clin. 2016, 6, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendler, K.S.; Aggen, S.H.; Neale, M.C.; Knudsen, G.P.; Krueger, R.F.; Tambs, K.; Czajkowski, N.; Ystrom, E.; Ørstavik, R.E.; Reichborn-Kjennerud, T. A longitudinal twin study of cluster A personality disorders. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otani, K.; Suzuki, A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shibuya, N.; Sadahiro, R.; Enokido, M. Correlations of interpersonal sensitivity with negative working models of the self and other: Evidence for link with attachment insecurity. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2014, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otani, K.; Suzuki, A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shirata, T. Close relation of interpersonal sensitivity with negative core beliefs about the self, the central construct of cognitive vulnerability to depression. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 263, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopwood, C.J.; Ansell, E.B.; Pincus, A.L.; Wright, A.G.; Lukowitsky, M.R.; Roche, M.J. The circumplex structure of interpersonal sensitivities. J. Pers. 2011, 79, 707–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilt, J.L.; van Lier, P.A.; Leflot, G.; Onghena, P.; Colpin, H. Children’s social self-concept and internalizing problems: The influence of peers and teachers. Child Dev. 2014, 85, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, K.; Suzuki, A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shirata, T. Link of negative core beliefs about the self with perceived dysfunctional parenting. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 270, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, E.E.; Pujji, S.D.; Dinzeo, T.J. Cognitive Failures and the Role of Emotion in Dimensional Schizotypy: A Replication and Extension. Psychopathology 2021, 54, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, G.R.; Barabasz, A.F.; Council, J.R.; Spiegel, D. Advancing research and practice: The revised APA division 30 definition of hypnosis. Am. J. Clin. Hypn. 2015, 57, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccione, C.; Hilgard, E.R.; Zimbardo, P.G. On the degree of stability of measured hypnotizability over a 25-year period. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1989, 56, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell, P.F. Is high hypnotizability a necessary diathesis for pathological dissociation? J. Trauma Dissociation 2017, 18, 58–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, R.S.; Bryce, C.P.; Fischer, L.; First, M.B.; Fitzmaurice, G.M.; Costa, P.T.; Galler, J.R. Childhood malnutrition and maltreatment are linked with personality disorder symptoms in adulthood: Results from a Barbados lifespan cohort. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 269, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, L. Schizotypal personality disorder and suicide: Problems and perspectives. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2021, 33, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, V.; Oakley, D.A.; Halligan, P.W.; Deeley, Q. Dissociation in hysteria and hypnosis: Evidence from cognitive neuroscience. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cleveland, J.M.; Reuther, B.T.; Gold, S.N. The varied relationship between hypnosis and dissociative phenomena: Implications for traumatology. Am. J. Clin. Hypn. 2020, 63, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSouza, D.D.; Stimpson, K.H.; Baltusis, L.; Sacchet, M.D.; Gu, M.; Hurd, R.; Wu, H.; Yeomans, D.C.; Willliams, N.; Spiegel, D. Association between anterior cingulate neurochemical concentration and individual differences in hypnotizability. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 3644–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; White, M.P.; Greicius, M.D.; Waelde, L.C.; Spiegel, D. Brain Activity and Functional Connectivity Associated with Hypnosis. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 4083–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terhune, D.B.; Hedman, L.R.A. Metacognition of agency is reduced in high hypnotic suggestibility. Cognition 2017, 168, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.B.; Huang, J.; Cheung, E.F.; Gong, Q.Y.; Chan, R.C. Event-related potential correlates of suspicious thoughts in individuals with schizotypal personality features. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 6, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozhuharova, P.; Diaconescu, A.O.; Allen, P. Reduced cortical GABA and glutamate in high schizotypy. Psychopharmacology 2021, 238, 2459–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Via, E.; Orfila, C.; Pedreño, C.; Rovira, A.; Menchón, J.M.; Cardoner, N.; Palao, D.J.; Soriano-Mas, C.; Obiols, J.E. Structural alterations of the pyramidal pathway in schizoid and schizotypal cluster A personality disorders. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2016, 110, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Thomas, Z.; Pisipati, S.; Jarvis, S.P.; Boutros, N.N. Inhibitory deficits in prepulse inhibition, sensory gating, and antisaccade eye movement in schizotypy. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2017, 114, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fan, H.; Gao, Q.; Mao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, W. Reporting meaningful Chinese words while listening to the Deutsch word illusions in Chinese patients with cluster A personality disorders. J. Psychiatry 2015, 18, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarska, A.D.; Mielimąka, M.; Rutkowski, K. Hypnotizability and psychopathology of patients with personality disorders. Am. J. Clin. Hypn. 2022, 6, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, E.B.; Baker, E.L.; Daitch, C.; Diamond, M.J.; Phillips, M. Hypnosis and the therapeutic relationship: Relational factors of hypnosis in psychotherapy. Am. J. Clin. Hypn. 2020, 62, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhue, J.W.; Lynn, S.J. Fantasy proneness, hypnotizability, and absorption—Are-examination: A brief communication. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Hypn. 1989, 37, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordenstrom, B.; Council, J.R.; Meier, B.P. Hypnotizability and the “Big Five”. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Hypn. 2002, 50, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, C.; Ye, Y.; Shen, S.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, W. Relationship between hypnosis and personality trait in participants with high or low hypnotic susceptibility. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardeña, E.; Terhune, D.B. Hypnotizability, Personality Traits, and the Propensity to Experience Alterations of Consciousness. Psychol. Conscious. 2014, 1, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, W.; Huang, J.; Xu, P.; He, W.; Chai, H.; Zhu, J.; Yu, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, W. Preliminary study of relationships between hypnotic susceptibility and personality disorder functioning styles in healthy volunteers and personality disorder patients. BMC Psychiatry 2011, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weitzenhoffer, A.M.; Hilgard, E.R. Stanford Hypnotic Susceptibility Scale, Form C; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, G.; Hadzi-Pavlovic, D. A question of style: Refining the dimensions of personality disorder style. J. Pers. Disord. 2001, 5, 300–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, S.J. Enhancing Suggestibility: The Effects of Compliance vs. Imagery. Am. J. Clin. Hypn. 2004, 47, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekecs, Z.; Roberts, L.; Na, H.; Yek, M.H.; Slonena, E.E.; Racelis, E.; Voor, T.A.; Johansson, R.; Rizzo, P.; Csikos, E.; et al. Test-Retest reliability of the Stanford Hypnotic Susceptibility Scale, Form C and the Elkins Hypnotizability Scale. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Hypn. 2021, 69, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgard, E.R. The Stanford hypnotic susceptibility scales as related to other measures of hypnotic responsiveness. Am. J. Clin. Hyp. 1978, 21, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roark, J.B.; Barabasz, A.F.; Barabasz, M.; Lin-Roark, I.H. An investigation of Taiwanese norms for the Stanford hypnotic susceptibility scale: Form C (Mandarin Chinese translation). Int. J. Clin. Exp. Hypn. 2012, 60, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, L.; Mu, L.; Chen, D.; Song, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, W.; Hou, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Functioning styles of personality disorders and five-factor normal personality traits: A correlation study in Chinese students. BMC Psychiatry 2003, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, M.C. Suggestibility of chronic schizophrenic and normal males matched for age. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Hypn. 1973, 21, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyun, Y.D. The effective use of hypnosis in schizophrenia: Structure and strategy. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Hypn. 2013, 61, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienes, Z.; Hutton, S. Understanding hypnosis meta-cognitively: rTMS applied to left DLPFC increases hypnotic suggestibility. Cortex 2013, 49, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihlstrom, J.F. Neuro-hypnotism: Prospects for hypnosis and neuroscience. Cortex 2013, 49, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skokou, M.; Gourzis, P. Demographic features and premorbid personality disorder traits in relation to age of onset and sex in paranoid schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 215, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, D. Tranceformations: Hypnosis in brain and body. Depress. Anxiety 2013, 30, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojserkis, R.; McKay, D.; Kim, S.K. Obsessive-compulsive symptom profiles in individuals exposed to interpersonal versus noninterpersonal trauma. Bull. Menninger Clin. 2020, 84, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbin, T. Contributions to role-taking theory: I. Hypnotic behavior. Psychol. Rev. 1950, 57, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheinbaum, T.; Bifulco, A.; Ballespí, S.; Mitjavila, M.; Kwapil, T.R.; Barrantes-Vidal, N. Interview Investigation of Insecure Attachment Styles as Mediators between Poor Childhood Care and Schizophrenia-Spectrum Phenomenology. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Facco, E. Hypnosis and Hypnotic ability between old beliefs and new evidences: An epistemological reflection. Am. J. Clin. Hypn. 2021, 64, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Controls | CAPD | U | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Passing Rate | n | Passing Rate | |||
| Low hypnotizability (passed 0–3 items) | 23 | 20.0% | 11 | 30.6% | - | - |
| Medium (4–8) | 73 | 63.5% | 20 | 55.6% | - | - |
| High (9–12) | 19 | 16.5% | 5 | 13.9% | - | - |
| 01 Hand lowering | 77 | 67.0% | 31 | 86.1% | 1673.50 | 0.027 |
| 02 Moving hands apart | 79 | 68.7% | 28 | 77.8% | 1882.00 | 0.297 |
| 03 Mosquito hallucination | 69 | 60.0% | 19 | 52.8% | 1920.50 | 0.445 |
| 04 Taste hallucination | 73 | 63.5% | 21 | 58.3% | 1963.50 | 0.580 |
| 05 Arm rigidity | 65 | 56.5% | 28 | 77.8% | 1630.00 | 0.023 |
| 06 Dream | 36 | 31.3% | 21 | 58.3% | 1510.50 | 0.004 |
| 07 Age regression | 88 | 76.5% | 27 | 75.0% | 2038.50 | 0.852 |
| 08 Arm immobilization | 54 | 47.0% | 24 | 66.7% | 1662.00 | 0.040 |
| 09 Anosmia to ammonia | 29 | 25.2% | 10 | 27.8% | 2017.00 | 0.760 |
| 10 Hallucinated voice | 10 | 8.7% | 4 | 11.1% | 2020.00 | 0.664 |
| 11 Negative visual hallucination | 41 | 35.7% | 15 | 41.7% | 1945.50 | 0.516 |
| 12 Posthypnotic amnesia | 17 | 14.8% | 10 | 27.8% | 1801.00 | 0.077 |
| Controls | CAPD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Score | T Score | Raw Score | T Score | |
| Paranoid | 20.88 ± 5.26 | 40.41 ± 6.22 | 25.72 ± 9.05 | 44.78 ± 10.10 * |
| Schizoid | 19.38 ± 2.90 | 45.77 ± 5.80 | 27.78 ± 5.32 | 63.11 ± 10.51 *** |
| Schizotypal | 9.50 ± 2.88 | 42.25 ± 5.46 | 14.86 ± 4.00 | 51.61 ± 7.63 *** |
| Antisocial | 19.50 ± 4.12 | 43.17 ± 5.03 | 23.03 ± 5.80 | 45.58 ± 7.00 |
| Borderline | 19.42 ± 5.17 | 36.57 ± 6.00 | 25.28 ± 6.70 | 42.72 ± 8.14 ** |
| Histrionic | 12.70 ± 2.77 | 42.58 ± 6.49 | 12.56 ± 3.64 | 41.47 ± 8.96 |
| Narcissistic | 17.10 ± 3.76 | 42.93 ± 5.45 | 16.94 ± 4.95 | 42.17 ± 7.35 |
| Avoidant | 24.03 ± 5.25 | 40.04 ± 6.46 | 28.78 ± 6.16 | 45.89 ± 7.23 *** |
| Dependent | 22.01 ± 4.67 | 41.50 ± 5.98 | 23.61 ± 6.26 | 43.97 ± 7.72 * |
| Obsessive-Compulsive | 16.32 ± 3.58 | 43.64 ± 7.16 | 15.67 ± 4.13 | 42.86 ± 8.14 |
| Passive-Aggressive | 20.06 ± 4.16 | 40.41 ± 6.22 | 21.28 ± 5.05 | 44.78 ± 10.10 |
| Controls | CAPD | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schizoid | Histrionic | Obsessive-Compulsive | Schizoid | Schizotypal | Histrionic | Avoidant | |
| Mosquito hallucination | - | - | - | - | - | 0.35 * | - |
| Taste hallucination | - | - | - | - | - | 0.35 * | - |
| Dream | - | - | - | −0.34 * | - | - | - |
| Age regression | 0.23 * | 0.23 * | 0.21 * | −0.27 | - | - | - |
| Arm immobilization | - | 0.24 ** | - | - | - | - | −0.41 * |
| Anosmia to ammonia | - | −0.23 * | - | - | - | - | −0.36 * |
| Hallucinated voice | - | - | - | - | −0.45 ** | - | - |
| Negative visual hallucination | - | - | - | - | −0.35 * | - | - |
| Score on challenge suggestions | - | - | - | - | - | - | −0.38 * |
| a-R2 | Controls Beta (B, SE), Predictor | a-R2 | CAPD Beta (B, SE), Predictor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paranoid | - | - | - | - |
| Schizoid | 0.04 | 0.23 (3.13, 1.25), Age regression | 0.09 | −0.34 (−7.12, 3.39), Dream |
| Schizotypal | - | - | 0.18 | −0.45 (−10.81, 3.66), Hallucinated voice |
| Antisocial | 0.03 | 0.19 (2.71, 1.34), Education level | - | - |
| Borderline | 0.08 | 0.27 (3.28, 1.09), gender (female) | - | - |
| Histrionic | 0.16 | 0.27 (3.45, 1.13), Arm immobilization −0.27 (−4.07, 1.29), Anosmia to ammonia 0.22 (3.35, 1.32), Age regression | 0.10 | 0.35 (6.25, 2.84), Mosquito hallucination |
| Narcissistic | 0.03 | 0.19 (2.97, 1.45), Education level | - | - |
| Avoidant | - | - | 0.37 | 0.49 (7.05, 1.94), gender (female) −0.033 (−4.99, 2.06), Arm immobilization |
| Dependent | 0.03 | 0.19 (2.22, 1.11), Gender (female) | 0.28 | −0.47 (−2.89, 0.93), Age 0.39 (6.01, 2.36), Mosquito hallucination 0.30 (4.64, 2.25), Gender (female) |
| Obsessive-Compulsive | 0.04 | 0.21 (3.55, 1.55), Age regression | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Pan, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Lajunen, T.J.; Wang, W. Hypnotizability and Disordered Personality Styles in Cluster A Personality Disorders. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020182
Zhang B, Pan B, Chen J, Wang J, Zhu Z, Lajunen TJ, Wang W. Hypnotizability and Disordered Personality Styles in Cluster A Personality Disorders. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(2):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020182
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bingren, Bing Pan, Jueying Chen, Junjie Wang, Zhenyu Zhu, Timo Juhani Lajunen, and Wei Wang. 2023. "Hypnotizability and Disordered Personality Styles in Cluster A Personality Disorders" Brain Sciences 13, no. 2: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020182
APA StyleZhang, B., Pan, B., Chen, J., Wang, J., Zhu, Z., Lajunen, T. J., & Wang, W. (2023). Hypnotizability and Disordered Personality Styles in Cluster A Personality Disorders. Brain Sciences, 13(2), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020182