Intraparenchymal and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Stereotactic Electroencephalography Caused by Indirect Adjacent Arterial Injury: Illustrative Case
Abstract
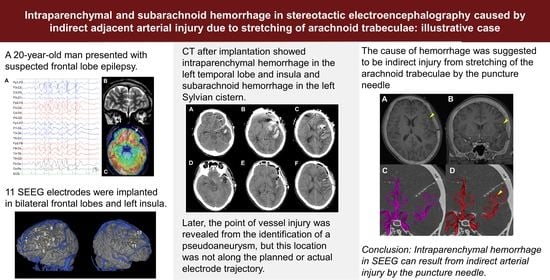
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serletis, D.; Bulacio, J.; Bingaman, W.; Najm, I.; González-Martínez, J. The stereotactic approach for mapping epileptic networks: A prospective study of 200 patients. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinale, F.; Casaceli, G.; Raneri, F.; Miller, J.; Lo Russo, G. Implantation of Stereoelectroencephalography Electrodes: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 33, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reif, P.S.; Strzelczyk, A.; Rosenow, F. The history of invasive EEG evaluation in epilepsy patients. Seizure 2016, 41, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isnard, J.; Taussig, D.; Bartolomei, F.; Bourdillon, P.; Catenoix, H.; Chassoux, F.; Chipaux, M.; Clémenceau, S.; Colnat-Coulbois, S.; Denuelle, M.; et al. French guidelines on stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG). Neurophysiol. Clin. 2018, 48, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, H.M.; Hall, J.A.; Dubeau, F.; Tani, N.; Oshino, S.; Fujita, Y.; Gotman, J.; Kishima, H. Technical Aspects of SEEG and Its Interpretation in the Delineation of the Epileptogenic Zone. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2020, 60, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGovern, R.A.; Ruggieri, P.; Bulacio, J.; Najm, I.; Bingaman, W.E.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.A. Risk analysis of hemorrhage in stereo-electroencephalography procedures. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullin, J.P.; Shriver, M.; Alomar, S.; Najm, I.; Bulacio, J.; Chauvel, P.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J. Is SEEG safe? A systematic review and meta-analysis of stereo-electroencephalography-related complications. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kojima, Y.; Uda, T.; Kawashima, T.; Koh, S.; Hattori, M.; Mito, Y.; Kunihiro, N.; Ikeda, S.; Umaba, R.; Goto, T. Primary Experiences with Robot-assisted Navigation-based Frameless Stereo-electroencephalography: Higher Accuracy than Neuronavigation-guided Manual Adjustment. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2022, 62, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomar, S.; Mullin, J.P.; Smithason, S.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J. Indications, technique, and safety profile of insular stereoelectroencephalography electrode implantation in medically intractable epilepsy. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, B.C.; Katz, J.; Lepard, J.; Blount, J.P. Variation in pediatric stereoelectroencephalography practice among pediatric neurosurgeons in the United States: Survey results. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2021, 28, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afif, A.; Chabardes, S.; Minotti, L.; Kahane, P.; Hoffmann, D. Safety and usefulness of insular depth electrodes implanted via an oblique approach in patients with epilepsy. Neurosurgery 2008, 62 (Suppl. 2), ONS471–ONS479; discussion 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machetanz, K.; Grimm, F.; Wuttke, T.V.; Kegele, J.; Lerche, H.; Tatagiba, M.; Rona, S.; Gharabaghi, A.; Honegger, J.; Naros, G. Frame-based and robot-assisted insular stereo-electroencephalography via an anterior or posterior oblique approach. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 135, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Electrode # | Side | Entry | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Left | SFG | anterior Orb |
| 2 | Left | IFG | posterior Orb |
| 3 | Left | MFG | anterior Cing |
| 4 | Left | IFG | anterior Cing |
| 5 | Left | FEF | middle Cing |
| 6 | Left | IFG | middle Cing |
| 7 | Left | anterior SFG | SMA |
| 8 | Left | posterior SFG | SMA |
| 9 | Left | PreCG | insula |
| 10 | Right | SFG | SMA |
| 11 | Right | MFG | middle Cing |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawashima, T.; Uda, T.; Koh, S.; Yindeedej, V.; Ishino, N.; Ichinose, T.; Arima, H.; Sakuma, S.; Goto, T. Intraparenchymal and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Stereotactic Electroencephalography Caused by Indirect Adjacent Arterial Injury: Illustrative Case. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030440
Kawashima T, Uda T, Koh S, Yindeedej V, Ishino N, Ichinose T, Arima H, Sakuma S, Goto T. Intraparenchymal and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Stereotactic Electroencephalography Caused by Indirect Adjacent Arterial Injury: Illustrative Case. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(3):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030440
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawashima, Toshiyuki, Takehiro Uda, Saya Koh, Vich Yindeedej, Noboru Ishino, Tsutomu Ichinose, Hironori Arima, Satoru Sakuma, and Takeo Goto. 2023. "Intraparenchymal and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Stereotactic Electroencephalography Caused by Indirect Adjacent Arterial Injury: Illustrative Case" Brain Sciences 13, no. 3: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030440
APA StyleKawashima, T., Uda, T., Koh, S., Yindeedej, V., Ishino, N., Ichinose, T., Arima, H., Sakuma, S., & Goto, T. (2023). Intraparenchymal and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Stereotactic Electroencephalography Caused by Indirect Adjacent Arterial Injury: Illustrative Case. Brain Sciences, 13(3), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030440