Ethanol-Induced Neurodegeneration and Glial Activation in the Developing Brain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Neurodegeneration Is Tightly Associated with Glial Activation
3. Excessive Ethanol Intake May Induce Neurodegeneration and Glial Activation/Neuroinflammation
4. Glial Activation Is Associated with Neurodegeneration in Animal Models of FASD
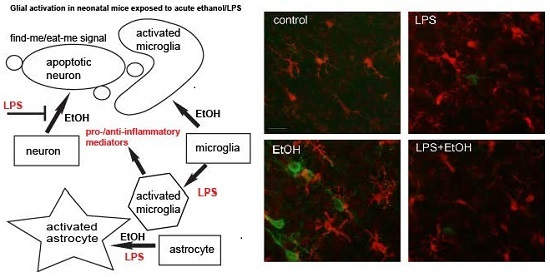
5. Comparison between the Effects of LPS and Ethanol on Neurodegeneration and Glial Activation in the Neonatal Brain
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riley, E.P.; McGee, C.L. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: An overview with emphasis on changes in brain and behavior. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2005, 230, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- May, P.A.; Gossage, J.P.; Kalberg, W.O.; Robinson, L.K.; Buckley, D.; Manning, M.; Hoyme, H.E. Prevalence and epidemiologic characteristics of FASD from various research methods with an emphasis on recent in-school studies. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2009, 15, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, P.A.; Baete, A.; Russo, J.; Elliot, A.J.; Blankenship, J.; Kalberg, W.O.; Buckley, D.; Brooks, M.; Hasken, J.; Abdul-Rahman, O.; et al. Prevalence and characteristics of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Pediatrics 2014, 134, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astley, S.J.; Aylward, E.H.; Olson, H.C.; Kerns, K.; Brooks, A.; Coggins, T.E.; Davies, J.; Dorn, S.; Gendler, B.; Jirikowic, T.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging outcomes from a comprehensive magnetic resonance study of children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1671–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, A.L.; Crocker, N.; Mattson, S.N.; Riley, E.P. Neuroimaging and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2009, 15, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, E.P.; Infante, M.A.; Warren, K.R. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: An overview. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2011, 21, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonthius, D.J.; Bonthius, N.E.; Napper, R.M.; West, J.R. Early postnatal alcohol exposure acutely and permanently reduces the number of granule cells and mitral cells in the rat olfactory bulb: A stereological study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1992, 324, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonthius, D.J.; West, J.R. Alcohol-induced neuronal loss in developing rats: Increased brain damage with binge exposure. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1990, 14, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerri, C.; Bazinet, A.; Riley, E.P. Foetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders and alterations in brain and behaviour. Alcohol. Alcohol. 2009, 44, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonomidou, C.; Bittigau, P.; Ishimaru, M.J.; Wozniak, D.F.; Koch, C.; Genz, K.; Price, M.T.; Stefovska, V.; Horster, F.; Tenkova, T.; et al. Ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration and fetal alcohol syndrom. Science 2000, 287, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olney, J.W.; Tenkova, T.; Dikranian, K.; Qin, Y.Q.; Labruyere, J.; Ikonomidou, C. Ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing C57BL/6 mouse brai. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 2002, 133, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olney, J.W. New insights and new issues in developmental neurotoxicology. Neurotoxicology 2002, 23, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlers, K.E.; Karacay, B.; Fuller, L.; Bonthius, D.J.; Dailey, M.E. Transient activation of microglia following acute alcohol exposure in developing mouse neocortex is primarily driven by BAX-dependent neurodegeneration. Glia 2015, 63, 1694–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodlett, C.R.; Leo, J.T.; O’Callaghan, J.P.; Mahoney, J.C.; West, J.R. Transient cortical astrogliosis induced by alcohol exposure during the neonatal brain growth spurt in rats. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 1993, 72, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, C.J.; Phelan, K.D.; Drew, P.D. Neuroimmune mechanisms in fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, C.J.; Phelan, K.D.; Han, L.; Smith, R.R.; Xie, J.; Douglas, J.C.; Drew, P.D. Protection of neurons and microglia against ethanol in a mouse model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, S137–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Chakraborty, G.; Mao, R.F.; Paik, S.M.; Vadasz, C.; Saito, M. Tau phosphorylation and cleavage in ethanol-induced neurodegeneration in the developing mouse brain. Neurochem. Res. 2010, 35, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Chakraborty, G.; Shah, R.; Mao, R.F.; Kumar, A.; Yang, D.S.; Dobrenis, K.; Saito, M. Elevation of GM2 ganglioside during ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing mouse brain. J. Neurochem. 2012, 121, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Wu, G.; Hui, M.; Masiello, K.; Dobrenis, K.; Ledeen, R.W.; Saito, M. Ganglioside accumulation in activated glia in the developing brain: Comparison between WT and GalNAcT KO mice. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1434–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, P.D.; Johnson, J.W.; Douglas, J.C.; Phelan, K.D.; Kane, C.J. Pioglitazone blocks ethanol induction of microglial activation and immune responses in the hippocampus, cerebellum, and cerebral cortex in a mouse model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, J.; Qi, Y.; Dai, L.; Zhang, M.; Frank, J.A.; Handshoe, J.W.; Cui, J.; Xu, W.; Chen, G. Deficient PKR in RAX/PKR Association Ameliorates Ethanol-Induced Neurotoxicity in the Developing Cerebellum. Cerebellum 2015, 14, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, V.; Chopra, K. Resveratrol prevents alcohol-induced cognitive deficits and brain damage by blocking inflammatory signaling and cell death cascade in neonatal rat brain. J. Neurochem. 2011, 117, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topper, L.A.; Baculis, B.C.; Valenzuela, C.F. Exposure of neonatal rats to alcohol has differential effects on neuroinflammation and neuronal survival in the cerebellum and hippocampus. J. Neuroinflammation 2015, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonthius, D.J.; West, J.R. Permanent neuronal deficits in rats exposed to alcohol during the brain growth spurt. Teratology 1991, 44, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, L.G., Jr.; Oguz, I.; Lee, J.; Styner, M.; Crews, F.T. Postnatal day 7 ethanol treatment causes persistent reductions in adult mouse brain volume and cortical neurons with sex specific effects on neurogenesi. Alcohol 2012, 46, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ieraci, A.; Herrera, D.G. Nicotinamide protects against ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing mouse brain. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadrian, B.; Lopez-Guzman, M.; Wilson, D.A.; Saito, M. Distinct neurobehavioral dysfunction based on the timing of developmental binge-like alcohol exposure. Neuroscience 2014, 280, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadrian, B.; Subbanna, S.; Wilson, D.A.; Basavarajappa, B.S.; Saito, M. Lithium prevents long-term neural and behavioral pathology induced by early alcohol exposure. Neuroscience 2012, 206, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smiley, J.F.; Saito, M.; Bleiwas, C.; Masiello, K.; Ardekani, B.; Guilfoyle, D.N.; Gerum, S.; Wilson, D.A.; Vadasz, C. Selective reduction of cerebral cortex GABA neurons in a late gestation model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Alcohol 2015, 49, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.A.; Masiello, K.; Lewin, M.P.; Hui, M.; Smiley, J.F.; Saito, M. Developmental ethanol exposure-induced sleep fragmentation predicts adult cognitive impairment. Neuroscience 2016, 322, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.A.; Peterson, J.; Basavaraj, B.S.; Saito, M. Local and regional network function in behaviorally relevant cortical circuits of adult mice following postnatal alcohol exposure. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1974–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, D.F.; Hartman, R.E.; Boyle, M.P.; Vogt, S.K.; Brooks, A.R.; Tenkova, T.; Young, C.; Olney, J.W.; Muglia, L.J. Apoptotic neurodegeneration induced by ethanol in neonatal mice is associated with profound learning/memory deficits in juveniles followed by progressive functional recovery in adults. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 17, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank-Cannon, T.C.; Alto, L.T.; McAlpine, F.E.; Tansey, M.G. Does neuroinflammation fan the flame in neurodegenerative diseases? Mol. Neurodegener. 2009, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, J.D.; Olschowka, J.A.; O’Banion, M.K. Neuroinflammation and M2 microglia: The good, the bad, and the inflamed. J. Neuroinflammation 2014, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, C.J.; Phelan, K.D.; Douglas, J.C.; Wagoner, G.; Johnson, J.W.; Xu, J.; Phelan, P.S.; Drew, P.D. Effects of ethanol on immune response in the brain: Region-specific changes in adolescent versus adult mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso-Loeches, S.; Pascual-Lucas, M.; Blanco, A.M.; Sanchez-Vera, I.; Guerri, C. Pivotal role of TLR4 receptors in alcohol-induced neuroinflammation and brain damage. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 8285–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, F.T.; Bechara, R.; Brown, L.A.; Guidot, D.M.; Mandrekar, P.; Oak, S.; Qin, L.; Szabo, G.; Wheeler, M.; Zou, J. Cytokines and alcohol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, F.T.; Nixon, K. Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and regeneration in alcoholism. Alcohol. Alcohol. 2009, 44, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Crews, F.T. NADPH oxidase and reactive oxygen species contribute to alcohol-induced microglial activation and neurodegeneration. J. Neuroinflammation 2012, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, F.T.; Vetreno, R.P. Mechanisms of neuroimmune gene induction in alcoholism. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2016, 233, 1543–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.J.; Zakhari, S.; Jung, M.K. Alcohol, inflammation, and gut-liver-brain interactions in tissue damage and disease development. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, F.T.; Qin, L.; Sheedy, D.; Vetreno, R.P.; Zou, J. High mobility group box 1/Toll-like receptor danger signaling increases brain neuroimmune activation in alcohol dependence. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Leak, R.K.; Shi, Y.; Suenaga, J.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, P.; Chen, J. Microglial and macrophage polarization-new prospects for brain repair. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, M.K.; Lee, W.H.; Suk, K. Functional polarization of neuroglia: Implications in neuroinflammation and neurological disorders. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 103, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orihuela, R.; McPherson, C.A.; Harry, G.J. Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivest, S. Regulation of innate immune responses in the brain. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, R.A. Polarizing question: Do M1 and M2 microglia exist? Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadani, S.P.; Walsh, J.T.; Lukens, J.R.; Kipnis, J. Dealing with Danger in the CNS: The Response of the Immune System to Injury. Neuron 2015, 87, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karve, I.P.; Taylor, J.M.; Crack, P.J. The contribution of astrocytes and microglia to traumatic brain injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnardt, S. Innate immunity and neuroinflammation in the CNS: The role of microglia in Toll-like receptor-mediated neuronal injury. Glia 2010, 58, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnardt, S.; Lachance, C.; Patrizi, S.; Lefebvre, S.; Follett, P.L.; Jensen, F.E.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Volpe, J.J.; Vartanian, T. The toll-like receptor TLR4 is necessary for lipopolysaccharide-induced oligodendrocyte injury in the CNS. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 2478–2486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lehnardt, S.; Massillon, L.; Follett, P.; Jensen, F.E.; Ratan, R.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Volpe, J.J.; Vartanian, T. Activation of innate immunity in the CNS triggers neurodegeneration through a Toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8514–8519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausler, K.G.; Prinz, M.; Nolte, C.; Weber, J.R.; Schumann, R.R.; Kettenmann, H.; Hanisch, U.K. Interferon-gamma differentially modulates the release of cytokines and chemokines in lipopolysaccharide- and pneumococcal cell wall-stimulated mouse microglia and macrophages. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 16, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A.; Robinson, S.M. Minimal penetration of lipopolysaccharide across the murine blood-brain barrier. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.K.; Jou, I.; Joe, E.H. Systemic LPS administration induces brain inflammation but not dopaminergic neuronal death in the substantia nigra. Exp. Mol. Med. 2010, 42, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Block, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Breese, G.R.; Hong, J.S.; Knapp, D.J.; Crews, F.T. Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia 2007, 55, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Trapp, B.D. Microglia and neuroprotection. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, A.; Encinas, J.M.; Deudero, J.J.; Chancey, J.H.; Enikolopov, G.; Overstreet-Wadiche, L.S.; Tsirka, S.E.; Maletic-Savatic, M. Microglia shape adult hippocampal neurogenesis through apoptosis-coupled phagocytosis. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolowski, J.D.; Mandell, J.W. Phagocytic clearance in neurodegeneration. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolzing, A.; Grune, T. Neuronal apoptotic bodies: Phagocytosis and degradation by primary microglial cells. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 743–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, C.B.; Ravichandran, K.S. Do not let death do us part: ‘Find-me’ signals in communication between dying cells and the phagocytes. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Liou, A.K.; Leak, R.K.; Xu, M.; An, C.; Suenaga, J.; Shi, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, P.; Chen, J. Neurobiology of microglial action in CNS injuries: Receptor-mediated signaling mechanisms and functional roles. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 119–120, 60–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabiec, A.M.; Hussell, T. The role of airway macrophages in apoptotic cell clearance following acute and chronic lung inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.R.; Oguin, T.H.; Martinez, J. The clearance of dying cells: Table for two. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffo, A.; Rolando, C.; Ceruti, S. Astrocytes in the damaged brain: Molecular and cellular insights into their reactive response and healing potential. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loov, C.; Hillered, L.; Ebendal, T.; Erlandsson, A. Engulfing astrocytes protect neurons from contact-induced apoptosis following injury. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.M.; MacLean, A.G. New advances on glial activation in health and disease. World J. Virol. 2015, 4, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.A.; Burda, J.E.; Ren, Y.; Ao, Y.; O’Shea, T.M.; Kawaguchi, R.; Coppola, G.; Khakh, B.S.; Deming, T.J.; Sofroniew, M.V. Astrocyte scar formation aids central nervous system axon regeneration. Nature 2016, 532, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, M.K.; Tansey, M.G. TNF signaling inhibition in the CNS: Implications for normal brain function and neurodegenerative disease. J. Neuroinflammation 2008, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simi, A.; Tsakiri, N.; Wang, P.; Rothwell, N.J. Interleukin-1 and inflammatory neurodegeneration. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saijo, K.; Winner, B.; Carson, C.T.; Collier, J.G.; Boyer, L.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Gage, F.H.; Glass, C.K. A Nurr1/CoREST pathway in microglia and astrocytes protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-induced death. Cell 2009, 137, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, S.M.; Rothwell, N.J.; Gibson, R.M. The role of inflammation in CNS injury and disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, S232–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, M.V.; McGavern, D.B. Immune Surveillance of the CNS following Infection and Injury. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelso, M.L.; Liput, D.J.; Eaves, D.W.; Nixon, K. Upregulated vimentin suggests new areas of neurodegeneration in a model of an alcohol use disorder. Neuroscience 2011, 197, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Xue, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, X.X.; Dong, Y.X.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y.N.; Yao, X.C.; Cui, W.; Wu, C.F. Role of microglia in ethanol-induced neurodegenerative disease: Pathological and behavioral dysfunction at different developmental stages. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, C. The neuropathology of alcohol-related brain damage. Alcohol. Alcohol. 2009, 44, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, F.T.; Sarkar, D.K.; Qin, L.; Zou, J.; Boyadjieva, N.; Vetreno, R.P. Neuroimmune Function and the Consequences of Alcohol Exposure. Alcohol. Res. 2015, 37, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crews, F.T.; Collins, M.A.; Dlugos, C.; Littleton, J.; Wilkins, L.; Neafsey, E.J.; Pentney, R.; Snell, L.D.; Tabakoff, B.; Zou, J.; et al. Alcohol-induced neurodegeneration: When, where and why? Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2004, 28, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbloom, M.J.; Pfefferbaum, A. Magnetic resonance imaging of the living brain: Evidence for brain degeneration among alcoholics and recovery with abstinence. Alcohol. Res. Health 2008, 31, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vetreno, R.P.; Qin, L.; Crews, F.T. Increased receptor for advanced glycation end product expression in the human alcoholic prefrontal cortex is linked to adolescent drinking. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 59, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okvist, A.; Johansson, S.; Kuzmin, A.; Bazov, I.; Merino-Martinez, R.; Ponomarev, I.; Mayfield, R.D.; Harris, R.A.; Sheedy, D.; Garrick, T.; et al. Neuroadaptations in human chronic alcoholics: Dysregulation of the NF-kappaB system. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Vetreno, R.P.; Crews, F.T. ATP-P2X7 receptor signaling controls basal and TNFalpha-stimulated glial cell proliferation. Glia 2012, 60, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Crews, F.T. Increased MCP-1 and microglia in various regions of the human alcoholic brain. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 210, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majchrowicz, E. Induction of physical dependence upon ethanol and the associated behavioral changes in rats. Psychopharmacologia 1975, 43, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.A.; Corso, T.D.; Neafsey, E.J. Neuronal degeneration in rat cerebrocortical and olfactory regions during subchronic “binge” intoxication with ethanol: Possible explanation for olfactory deficits in alcoholics. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1996, 20, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obernier, J.A.; Bouldin, T.W.; Crews, F.T. Binge ethanol exposure in adult rats causes necrotic cell death. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 26, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajuddin, N.; Moon, K.H.; Marshall, S.A.; Nixon, K.; Neafsey, E.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Collins, M.A. Neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in adult rat brain from binge ethanol exposure: Abrogation by docosahexaenoic acid. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101223. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, S.A.; McClain, J.A.; Kelso, M.L.; Hopkins, D.M.; Pauly, J.R.; Nixon, K. Microglial activation is not equivalent to neuroinflammation in alcohol-induced neurodegeneration: The importance of microglia phenotype. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 54, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahr, N.M.; Luong, R.; Sullivan, E.V.; Pfefferbaum, A. Measurement of serum, liver, and brain cytokine induction, thiamine levels, and hepatophthology in rats exposed to a 4-day alcohol binge protocol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 1858–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, S.A.; Geil, C.R.; Nixon, K. Prior binge ethanol exposure potentiates the microglial response in a model of alcohol-induced neurodegeneration. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; He, J.; Hanes, R.N.; Pluzarev, O.; Hong, J.S.; Crews, F.T. Increased systemic and brain cytokine production and neuroinflammation by endotoxin following ethanol treatment. J. Neuroinflammation 2008, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles, S.L.; Blanco, A.M.; Pascual, M.; Guerri, C. Chronic ethanol treatment enhances inflammatory mediators and cell death in the brain and in astrocytes. Brain Pathol. 2004, 14, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, D.M.; Deeny, M.A.; Shaner, C.A.; Nixon, K. Determining the threshold for alcohol-induced brain damage: New evidence with gliosis markers. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G.; Lippai, D. Converging actions of alcohol on liver and brain immune signaling. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2014, 118, 359–380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pruett, S.B.; Zheng, Q.; Fan, R.; Matthews, K.; Schwab, C. Acute exposure to ethanol affects Toll-like receptor signaling and subsequent responses: An overview of recent studies. Alcohol 2004, 33, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.Y.; Crews, F.T. Release of neuronal HMGB1 by ethanol through decreased HDAC activity activates brain neuroimmune signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.J.; Colivicchi, M.A.; Allen, R.; Schol, F.; Lallemand, F.; de Witte, P.; Ballini, C.; Corte, L.D.; Dexter, D. Neuro-inflammation induced in the hippocampus of ‘binge drinking’ rats may be mediated by elevated extracellular glutamate content. J. Neurochem. 2009, 111, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Lucas, M.; Fernandez-Lizarbe, S.; Montesinos, J.; Guerri, C. LPS or ethanol triggers clathrin- and rafts/caveolae-dependent endocytosis of TLR4 in cortical astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2014, 129, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyadjieva, N.I.; Sarkar, D.K. Microglia play a role in ethanol-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in developing hypothalamic neurons. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Lizarbe, S.; Pascual, M.; Guerri, C. Critical role of TLR4 response in the activation of microglia induced by ethanol. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4733–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archibald, S.L.; Fennema-Notestine, C.; Gamst, A.; Riley, E.P.; Mattson, S.N.; Jernigan, T.L. Brain dysmorphology in individuals with severe prenatal alcohol exposure. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2001, 43, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, M.A.; Moore, E.M.; Bischoff-Grethe, A.; Migliorini, R.; Mattson, S.N.; Riley, E.P. Atypical cortical gyrification in adolescents with histories of heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Brain Res. 2015, 1624, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliorini, R.; Moore, E.M.; Glass, L.; Infante, M.A.; Tapert, S.F.; Jones, K.L.; Mattson, S.N.; Riley, E.P. Anterior cingulate cortex surface area relates to behavioral inhibition in adolescents with and without heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 292, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, P.D.; Kane, C.J. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders and neuroimmune changes. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2014, 118, 41–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kane, C.J.; Drew, P.D. Inflammatory responses to alcohol in the CNS: Nuclear receptors as potential therapeurics for alcohol-induced neuropathologies. J. Leukoc Biol. 2016, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigland, L.; Ford, M.M.; Lerch, J.P.; Kroenke, C.D. The influence of fetal ethanol exposure on subsequent development of the cerebral cortex as revealed by magnetic resonance imaging. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.W.; Potempa, G. Numbers of neurons and glia in mature rat somatosensory cortex: Effects of prenatal exposure to ethanol. J. Comp. Neurol. 1990, 293, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonthius, D.J.; McKim, R.A.; Koele, L.; Harb, H.; Kehrberg, A.H.; Mahoney, J.; Karacay, B.; Pantazis, N.J. Severe alcohol-induced neuronal deficits in the hippocampus and neocortex of neonatal mice genetically deficient for neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS). J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 499, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Mohapel, J.; Boehme, F.; Kainer, L.; Christie, B.R. Hippocampal cell loss and neurogenesis after fetal alcohol exposure: Insights from different rodent models. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 64, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaton, M.B.; Paiva, M.; Madorsky, I.; Siler-Marsiglio, K.; Shaw, G. Effect of bax deletion on ethanol sensitivity in the neonatal rat cerebellum. J. Neurobiol. 2006, 66, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, J.R.; Goodlett, C.R.; Bonthius, D.J.; Hamre, K.M.; Marcussen, B.L. Cell population depletion associated with fetal alcohol brain damage: Mechanisms of BAC-dependent cell loss. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1990, 14, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschen, K.E.; Ruggiero, M.J.; Klintsova, A.Y. Neonatal binge alcohol exposure increases microglial activation in the developing rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 2016, 324, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topper, L.A.; Valenzuela, C.F. Effect of repeated alcohol exposure during the third trimester-equivalent on messenger RNA levels for interleukin-1beta, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2, and interleukin 10 in the developing rat brain after injection of lipopolysaccharide. Alcohol 2014, 48, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Mao, R.F.; Wang, R.; Vadasz, C.; Saito, M. Effects of gangliosides on ethanol-induced neurodegeneration in the developing mouse brain. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.M.; Field, R.H.; Perry, V.H.; Murray, C.L.; Cunningham, C. Microglia in the degenerating brain are capable of phagocytosis of beads and of apoptotic cells, but do not efficiently remove PrPSc, even upon LPS stimulation. Glia 2010, 58, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles, S.; Pitarch, J.; Renau-Piqueras, J.; Guerri, C. Ethanol exposure affects glial fibrillary acidic protein gene expression and transcription during rat brain development. J. Neurochem. 1997, 69, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, T.L.; Shain, W. Ethanol-induced changes in astrocyte gene expression during rat central nervous system development. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1993, 17, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.W.; Kaizaki, A.; Tien, L.T.; Pang, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Numazawa, S.; Bhatt, A.J.; Cai, Z. Celecoxib attenuates systemic lipopolysaccharide-induced brain inflammation and white matter injury in the neonatal rats. Neuroscience 2013, 240, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, S.; Herkenham, M. Toll-like receptor 4 on nonhematopoietic cells sustains CNS inflammation during endotoxemia, independent of systemic cytokines. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Pang, Y.; Lin, S.; Rhodes, P.G. Differential roles of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta in lipopolysaccharide-induced brain injury in the neonatal rat. Brain Res. 2003, 975, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.; Fan, L.W.; Kaizaki, A.; Pang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Tien, L.T. Neonatal lipopolysaccharide exposure induces long-lasting learning impairment, less anxiety-like response and hippocampal injury in adult rats. Neuroscience 2013, 234, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.W.; Pang, Y.; Lin, S.; Rhodes, P.G.; Cai, Z. Minocycline attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced white matter injury in the neonatal rat brain. Neuroscience 2005, 133, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.W.; Tien, L.T.; Zheng, B.; Pang, Y.; Lin, R.C.; Simpson, K.L.; Ma, T.; Rhodes, P.G.; Cai, Z. Dopaminergic neuronal injury in the adult rat brain following neonatal exposure to lipopolysaccharide and the silent neurotoxicity. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarlestedt, K.; Naylor, A.S.; Dean, J.; Hagberg, H.; Mallard, C. Decreased survival of newborn neurons in the dorsal hippocampus after neonatal LPS exposure in mice. Neuroscience 2013, 253, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, F.L.; Herz, J.; Fernandes, A.; Rocha, J.; Sepodes, B.; Brito, M.A.; McGavern, D.B.; Brites, D. Systemic inflammation in early neonatal mice induces transient and lasting neurodegenerative effects. J. Neuroinflammation 2015, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardon, M.C. Lipopolysaccharide hyporesponsiveness: Protective or damaging response to the brain? Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2015, 56, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Wang, J.; Saad, Y.; Warble, L.; Becerra, E.; Kolattukudy, P.E. Participation of MCP-induced protein 1 in lipopolysaccharide preconditioning-induced ischemic stroke tolerance by regulating the expression of proinflammatory cytokines. J. Neuroinflammation 2011, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shpargel, K.B.; Jalabi, W.; Jin, Y.; Dadabayev, A.; Penn, M.S.; Trapp, B.D. Preconditioning paradigms and pathways in the brain. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2008, 75, S77–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasaki, K.; Ruetzler, C.A.; Ohtsuki, T.; Martin, D.; Nawashiro, H.; Hallenbeck, J.M. Lipopolysaccharide pre-treatment induces resistance against subsequent focal cerebral ischemic damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res. 1997, 748, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariko, K.; Weissman, D.; Welsh, F.A. Inhibition of toll-like receptor and cytokine signaling—A unifying theme in ischemic tolerance. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2004, 24, 1288–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, B.; Stevens, S.L.; Packard, A.E.; Gopalan, B.; Hunter, B.; Leung, P.Y.; Harrington, C.A.; Stenzel-Poore, M.P. Systemic lipopolysaccharide protects the brain from ischemic injury by reprogramming the response of the brain to stroke: A critical role for IRF3. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9839–9849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, K.F. Lipopolysaccharide preconditioning reduces neuroinflammation against hypoxic ischemia and provides long-term outcome of neuroprotection in neonatal rat. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 66, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, G.; Saito, M.; Mao, R.F.; Wang, R.; Vadasz, C.; Saito, M. Lithium blocks ethanol-induced modulation of protein kinases in the developing brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creeley, C.E.; Dikranian, K.T.; Johnson, S.A.; Farber, N.B.; Olney, J.W. Alcohol-induced apoptosis of oligodendrocytes in the fetal macaque brain. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2013, 1, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basta-Kaim, A.; Fijal, K.; Slusarczyk, J.; Trojan, E.; Glombik, K.; Budziszewska, B.; Leskiewicz, M.; Regulska, M.; Kubera, M.; Lason, W.; et al. Prenatal administration of lipopolysaccharide induces sex-dependent changes in glutamic acid decarboxylase and parvalbumin in the adult rat brain. Neuroscience 2015, 287, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, T.A.; Harte, M.K.; Stenson, G.; Reynolds, G.P. Neonatal lipopolysaccharide induces pathological changes in parvalbumin immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wischhof, L.; Irrsack, E.; Osorio, C.; Koch, M. Prenatal LPS-exposure—A neurodevelopmental rat model of schizophrenia—Differentially affects cognitive functions, myelination and parvalbumin expression in male and female offspring. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 57, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.D.; Aksenov, M.Y.; Kelly, S.J. Vitamin E protects against alcohol-induced cell loss and oxidative stress in the neonatal rat hippocampus. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2004, 22, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.D.; Kelly, S.J. Critical periods for ethanol-induced cell loss in the hippocampal formation. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2003, 25, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saito, M.; Chakraborty, G.; Hui, M.; Masiello, K.; Saito, M. Ethanol-Induced Neurodegeneration and Glial Activation in the Developing Brain. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci6030031
Saito M, Chakraborty G, Hui M, Masiello K, Saito M. Ethanol-Induced Neurodegeneration and Glial Activation in the Developing Brain. Brain Sciences. 2016; 6(3):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci6030031
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaito, Mariko, Goutam Chakraborty, Maria Hui, Kurt Masiello, and Mitsuo Saito. 2016. "Ethanol-Induced Neurodegeneration and Glial Activation in the Developing Brain" Brain Sciences 6, no. 3: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci6030031
APA StyleSaito, M., Chakraborty, G., Hui, M., Masiello, K., & Saito, M. (2016). Ethanol-Induced Neurodegeneration and Glial Activation in the Developing Brain. Brain Sciences, 6(3), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci6030031