Hyperplanar Morphological Clustering of a Hippocampus by Using Volumetric Computerized Tomography in Early Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Imaging Protocol
2.3. SSA Software
2.4. Supervised Model Clustering
2.5. Benchmarking with Conventional Metric Analysis
2.6. Validation and Performance Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hippocampal Morphology Variability
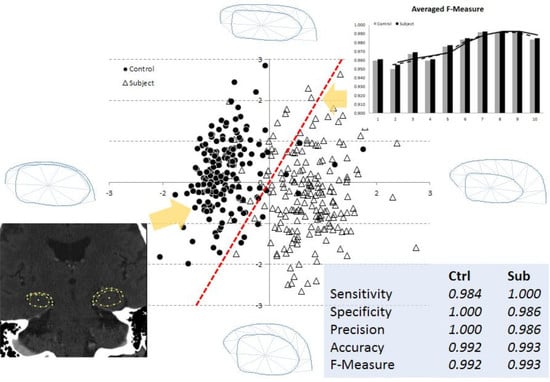
3.2. Multi-Dimensional SVM Classification
3.3. Optimal Number of Model Parameters
- (1)
- Both seen and unseen samples can be described by a linear combination of only 10 bases (compactness and generalization abilities of the model).
- (2)
- Any linear combination generated by randomized (with a Gaussian distribution) model parameters can synthesize a sample that is closely resemble to those previously seen (specificity) [31].
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Killin, L.O.J.; Starr, J.M.; Shiue, I.J.; Russ, T.C. Environmental risk factors for dementia: A systematic review. BMC Geriatr. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povova, J.; Ambroz, P.; Bar, M.; Pavukova, V.; Sery, O.; Tomaskova, H.; Janout, V. Epidemiological of and risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease: A review. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2012, 156, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordberg, A. Dementia in 2014: Towards early diagnosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroutunian, V.; Purohit, D.P.; Perl, D.P. Neurofibrillary tangles in nondemented elder subjects and mild Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R.A.; Karlawish, J.; Johnson, K.A. Preclinical Alzheimer’s disease-the challenges ahead. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopman, D.S.; Boeve, B.F.; Petersen, R.C. Essentials of the proper diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and major subtypes of dementia. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2003, 78, 1290–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 332–384. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Jacova, C.; DeKosky, S.T. Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, P.; Karnieli-Miller, O.; Eidelman, C. Current knowledge and future directions about the disclosure of dementia: A systematic review of the first decade of the 21st Century. Alzheimers Dement. 2013, 9, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang-Wai, D. A quick guide for neuroimaging of commons dementias seen in clinical practice. CGS J. CME 2012, 2, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Vernooij, M.W.; Smits, M. Structural neuroimaging in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2012, 22, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisoni, G.B. Structural imaging in the clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Problems and tools. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 70, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shear, P.K.; Sullivan, E.V.; Mathalon, D.H.; Lim, K.O.; Davis, L.F.; Yesavage, J.A. Longitudinal volumetric computed tomographic analysis of regional brain changes in normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Neurol. 1995, 52, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csernansky, J.G.; Wang, L.; Swank, J.; Miller, J.P.; Gado, M.; McKeel, D.; Miller, M.I.; Morris, J.C. Preclinical detection of Alzheimer’s disease: Hippocampal shape and volume predict onset in the elderly. Neuroimage 2005, 25, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimiya, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Arai, H.; Ikeda, K.; Kosaka, K. A computed tomography study of Alzheimer’s disease by reginal volumetric and parenchymal density measurements. J. Neurol. 1986, 233, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cootes, T.F.; Edwards, G.J.; Taylor, C.J. Active appearance models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Recognit. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, C. Procrustes methods in the statistical analysis of shape. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1991, 53, 285–339. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, A.; Lorenz, C. Statistical shape model based segmentation of medical images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 1998, 22, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshia, S.H.; Narra, K.L.; Philipsa, O.R.; Nuechterlein, K.H.; Asarnow, R.F.; Toga, A.W.; Woods, R.P. Statistical shape analysis of the corpus callosum in Schizophrenia. Neuroimage 2013, 64, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrzilkova, J.; Zach, P.; Bartos, A.; Bartoš, A.; Tintěra, J.; Řípová, D. Volumetric analysis of the pons, cerebellum and hippocampi in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2012, 34, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Swank, J.S.; Glick, I.E.; Gado, M.H.; Miller, M.I.; Morris, J.C.; Csernansky, J.G. Changes in hippocampal volume and shape across time distinguish dementia of the Alzheimer type from healthy aging. Neuroimage 2003, 20, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, A.I.; Xu, Y.; Korf, E.S.C.; White, L.R.; Scheltens, P.; Toga, A.W.; Thompson, P.M.; Hartley, S.W.; Witter, M.P.; Valentino, D.J.; et al. Hippocampal shape analysis in Alzheimer’s disease: A population-based study. Neuroimage 2007, 36, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association, Task Force on DSM-IV. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM-IV-TR, 4th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 78–94. [Google Scholar]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging and the Alzheimer’s Association workgroup. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Kearney, J.; Kendall, A. Arc-Length Parameterized Spline Curves for Real-Time Simulation; Curve and Surface Design: Saint-Malo, France, 2002; pp. 387–396. [Google Scholar]
- Gower, J.C.; Dijksterhuis, G.B. Procrustes Problems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004; p. 248. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V. Statistical Learning Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. Libsvm: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Sys. Technol. 2011, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.K.; Fripp, J.; Mériaudeau, F.; Salvado, O. Detecting global and local hippocampal shape changes in Alzheimer’s disease using statistical shape models. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 2155–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horkaew, P.; Yang, G.Z. Construction of 3D Dynamic Statistical Deformable Models for Complex Topological Shapes. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Saint-Malo, France, 26–29 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn, W.M. The Myth of Occam’s razor. Mind 1918, 27, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyakin, V.V.; Lucas, J.; Dyakina-Fagnano, N.V.; Posner, E.V.; Vadasz, C. Chain of Chirality Transfer as Determinant of Brain Functional Laterality. Breaking the Chirality Silence: Search for New Generation of Biomarkers. Relevance to Neurodegenerative Diseases, Cognitive Psychology and Nutrition Science. Neurol. Neurosci. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves-Pereira, P.M.; Oliveira, E.; Insausti, R. Quantitative volumetric analysis of the hippocampus, amygdala and entorhinal cortex: Normative database for the adult Portuguese population. Rev. Neurol. 2006, 42, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woolard, A.A.; Heckers, S. Anatomical and functional correlates of human hippocampal volume asymmetry. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 201, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Subject N = 33 | Control N = 30 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (40–90 Year) | 68.51 ± 5.5 | 67.93 ± 5 | 0.076 |
| Female | 25 (75.8%) | 15 (50%) | 0.065 |
| Highest level of education | Less than Level 6 (90.9%) | Less than Level 6 (60%) | 0.034 |
| Occupation | Retired (75.8%) | Retired (50%) | 0.066 |
| Family history of dementia | None | None | - |
| Average blood pressure (mmHg) | 135.1/75.5 ± 14.2/7.3 | 139.2/81.4 ± 14.4/8 | 0.064 |
| TMSE* score (point) | 18.3 ± 1.6 | 27.5 ± 1.6 | 0.027 |
| Attributes | Left | % | Right | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correctly Classified Instances | 60 | 95.2381 | 62 | 98.4127 |
| Incorrectly Classified Instance | 3 | 4.7619 | 1 | 1.5873 |
| Kappa Statistics | 0.9047 | 0.9682 | ||
| Mean Absolute Error | 0.0476 | 0.0159 | ||
| Root Mean Squared Error | 0.2182 | 0.1260 | ||
| Relative Absolute Error | 9.5395% | 3.1798% | ||
| Root Relative Squared Error | 43.6690% | 25.2123% |
| Left | Correctly Classified (Samples) | Incorrectly Classified (Samples) | ||||||
| Modes | TP–C | TP–S | TN–C | TN–S | FP–C | FP–S | FN–C | FN–S |
| 1 | 29 | 30 | 29 | 30 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 28 | 31 | 28 | 31 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 29 | 31 | 29 | 31 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 29 | 30 | 29 | 30 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 5 | 29 | 31 | 29 | 31 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 6 | 29 | 32 | 29 | 32 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 29 | 33 | 29 | 33 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 8 | 29 | 33 | 29 | 33 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 9 | 29 | 33 | 29 | 33 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 10 | 29 | 33 | 29 | 33 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Right | Correctly Classified (Samples) | Incorrectly Classified (Samples) | ||||||
| Modes | TP-C | TP-S | TN-C | TN-S | FP-C | FP-S | FN-C | FN-S |
| 1 | 30 | 32 | 30 | 32 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 29 | 32 | 29 | 32 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 30 | 32 | 30 | 32 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 30 | 32 | 30 | 32 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | 30 | 33 | 30 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 30 | 33 | 30 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 30 | 33 | 30 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 30 | 33 | 30 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 30 | 33 | 30 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 30 | 32 | 30 | 32 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| L | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | Accuracy | F-Measure | |||||
| M | C | S | C | S | C | S | C | S | C | S |
| 1 | 0.967 | 0.909 | 0.906 | 0.968 | 0.906 | 0.968 | 0.935 | 0.938 | 0.935 | 0.938 |
| 2 | 0.933 | 0.939 | 0.933 | 0.939 | 0.933 | 0.939 | 0.933 | 0.939 | 0.933 | 0.939 |
| 3 | 0.967 | 0.939 | 0.935 | 0.969 | 0.935 | 0.969 | 0.951 | 0.954 | 0.951 | 0.954 |
| 4 | 0.967 | 0.909 | 0.906 | 0.968 | 0.906 | 0.968 | 0.935 | 0.938 | 0.935 | 0.938 |
| 5 | 0.967 | 0.939 | 0.935 | 0.969 | 0.935 | 0.969 | 0.951 | 0.954 | 0.951 | 0.954 |
| 6 | 0.967 | 0.970 | 0.967 | 0.970 | 0.967 | 0.970 | 0.967 | 0.970 | 0.967 | 0.970 |
| 7 | 0.967 | 1 | 1 | 0.971 | 1 | 0.971 | 0.983 | 0.985 | 0.983 | 0.985 |
| 8 | 0.967 | 1 | 1 | 0.971 | 1 | 0.971 | 0.983 | 0.985 | 0.983 | 0.985 |
| 9 | 0.967 | 1 | 1 | 0.971 | 1 | 0.971 | 0.983 | 0.985 | 0.983 | 0.985 |
| 10 | 0.967 | 1 | 1 | 0.971 | 1 | 0.971 | 0.983 | 0.985 | 0.983 | 0.985 |
| R | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | Accuracy | F-Measure | |||||
| M | C | S | C | S | C | S | C | S | C | S |
| 1 | 1 | 0.970 | 0.968 | 1 | 0.968 | 1 | 0.984 | 0.985 | 0.984 | 0.985 |
| 2 | 0.967 | 0.970 | 0.967 | 0.970 | 0.967 | 0.970 | 0.967 | 0.970 | 0.967 | 0.970 |
| 3 | 1 | 0.970 | 0.968 | 1 | 0.968 | 1 | 0.984 | 0.985 | 0.984 | 0.985 |
| 4 | 1 | 0.970 | 0.968 | 1 | 0.968 | 1 | 0.984 | 0.985 | 0.984 | 0.985 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 10 | 1 | 0.970 | 0.968 | 1 | 0.968 | 1 | 0.984 | 0.985 | 0.984 | 0.985 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suksuphew, S.; Horkaew, P. Hyperplanar Morphological Clustering of a Hippocampus by Using Volumetric Computerized Tomography in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7110155
Suksuphew S, Horkaew P. Hyperplanar Morphological Clustering of a Hippocampus by Using Volumetric Computerized Tomography in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sciences. 2017; 7(11):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7110155
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuksuphew, Sarawut, and Paramate Horkaew. 2017. "Hyperplanar Morphological Clustering of a Hippocampus by Using Volumetric Computerized Tomography in Early Alzheimer’s Disease" Brain Sciences 7, no. 11: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7110155
APA StyleSuksuphew, S., & Horkaew, P. (2017). Hyperplanar Morphological Clustering of a Hippocampus by Using Volumetric Computerized Tomography in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sciences, 7(11), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7110155