Whey- and Soy Protein Isolates Added to a Carrot-Tomato Juice Alter Carotenoid Bioavailability in Healthy Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Carotenoid Standards and Food Matrices
2.2. Participants
2.3. Study Procedure
2.3.1. Recruitment
2.3.2. Information Session
2.3.3. Screening Visit
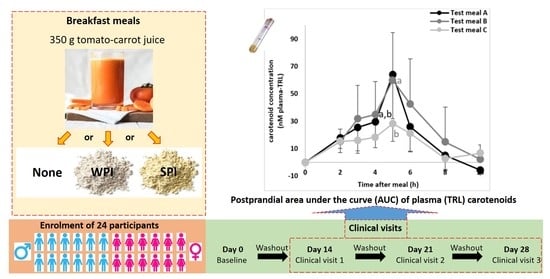
2.3.4. Experimental Design
2.3.5. Clinical Visit and Postprandial Experiments
2.4. Sample Processing
2.5. Extraction of Carotenoids
2.6. Carotenoid Analysis
2.7. AUC, Cmax, Tmax
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Description of Subjects
3.2. Breakfast Meal and Carotenoid Composition
3.3. Plasma Levels and Effect of Washout
3.4. Effect of Proteins on Carotenoid AUC of Plasma-TRL Fraction over Time
3.4.1. Total Population (n = 24)
3.4.2. Males (n = 12)
3.4.3. Females (n =12)
3.5. Effect of Proteins on Maximum Plasma TRL-Carotenoid Concentration (Cmax)
3.5.1. Total Population (n = 24)
3.5.2. Males (n = 12)
3.5.3. Females (n = 12)
3.6. Influence of Proteins on the Time to Peak Plasma TRL-Carotenoid Concentration (Tmax)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elliott, R. Mechanisms of genomic and non-genomic actions of carotenoids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1740, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sluijs, I.; Cadier, E.; Beulens, J.W.J.; Spijkerman, A.M.W.; van der Schouw, Y.T. Dietary intake of carotenoids and risk of type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharoni, Y.; Linnewiel-Hermoni, K.; Khanin, M.; Salman, H.; Veprik, A.; Danilenko, M.; Levy, J. Carotenoids and apocarotenoids in cellular signaling related to cancer: A review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunkumar, R.; Calvo, C.M.; Conrady, C.D.; Bernstein, P.S. What do we know about the macular pigment in AMD: The past, the present, and the future. Eye 2018, 32, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohn, T. Carotenoids and Markers of Oxidative Stress in Human Observational Studies and Intervention Trials: Implications for Chronic Diseases. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiedor, J.; Burda, K. Potential role of carotenoids as antioxidants in human health and disease. Nutrients 2014, 6, 466–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krinsky, N.I.; Johnson, E.J. Carotenoid actions and their relation to health and disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2005, 26, 459–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaulmann, A.; Bohn, T. Carotenoids, inflammation, and oxidative stress—Implications of cellular signaling pathways and relation to chronic disease prevention. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 907–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.; Grune, T. The contribution of β-carotene to vitamin A supply of humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, M.; Laubscher, R. Seasonal availability and dietary intake of beta-carotene-rich vegetables and fruit of 2-year-old to 5-year-old children in a rural South African setting growing these crops at household level. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 59, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeum, K.J.; Russell, R.M. Carotenoid bioavailability and bioconversion. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 483–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, T. Bioavailability of Non-Provitamin A Carotenoids. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2008, 4, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, P.; Grolier, P.; Armand, M.; Partier, A.; Lafont, H.; Lairon, D.; Azais-Braesco, V. Carotenoids in biological emulsions: Solubility, surface-to-core distribution, and release from lipid droplets. J. Lipid Res. 1996, 37, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iddir, M.; Porras Yaruro, J.F.; Cocco, E.; Hardy, E.M.; Appenzeller, B.M.R.; Guignard, C.; Larondelle, Y.; Bohn, T. Impact of Protein-Enriched Plant Food Items on the Bioaccessibility and Cellular Uptake of Carotenoids. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, T.; Desmarchelier, C.; Dragsted, L.O.; Nielsen, C.S.; Stahl, W.; Rühl, R.; Keijer, J.; Borel, P. Host-related factors explaining interindividual variability of carotenoid bioavailability and tissue concentrations in humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmarchelier, C.; Borel, P. Overview of carotenoid bioavailability determinants: From dietary factors to host genetic variations. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huo, T.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Schwartz, S.J.; Failla, M.L. Impact of fatty acyl composition and quantity of triglycerides on bioaccessibility of dietary carotenoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8950–8957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unlu, N.Z.; Bohn, T.; Clinton, S.K.; Schwartz, S.J. Carotenoid absorption from salad and salsa by humans is enhanced by the addition of avocado or avocado oil. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, O.; Ryan, L.; O’Sullivan, L.; Aherne-Bruce, S.A.; O’Brien, N.M. Carotenoid micellarization varies greatly between individual and mixed vegetables with or without the addition of fat or fiber. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2008, 78, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palafox-Carlos, H.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; González-Aguilar, G.A. The role of dietary fiber in the bioaccessibility and bioavailability of fruit and vegetable antioxidants. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, R6–R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClements, D.J.; Li, Y. Review of in vitro digestion models for rapid screening of emulsion-based systems. Food Funct. 2010, 1, 32–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, R.J.; Kellerby, S.S.; Decker, E.A. Antioxidant activity of proteins and peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iddir, M.; Dingeo, G.; Porras Yaruro, J.F.; Hammaz, F.; Borel, P.; Schleeh, T.; Desmarchelier, C.; Larondelle, Y.; Bohn, T. Influence of soy and whey protein, gelatin and sodium caseinate on carotenoid bioaccessibility. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5446–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Peanut Oil (Survey (FNDDS), 343874). Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/343874/nutrients (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Bohn, T.; Blackwood, M.; Francis, D.; Tian, Q.; Schwartz, S.J.; Clinton, S.K. Bioavailability of phytochemical constituents from a novel soy fortified lycopene rich tomato juice developed for targeted cancer prevention trials. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unlu, N.Z.; Bohn, T.; Francis, D.; Clinton, S.K.; Schwartz, S.J. Carotenoid absorption in humans consuming tomato sauces obtained from tangerine or high-beta-carotene varieties of tomatoes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iddir, M.; Porras Yaruro, J.F.; Larondelle, Y.; Bohn, T. Gastric lipase can significantly increase lipolysis and carotenoid bioaccessibility from plant food matrices in the harmonized INFOGEST static in vitro digestion model. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 9043–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, G.; Liaaen-Jensen, S.; Pfander, H. Carotenoids Handbook; Mercadante, A.Z., Egeland, E.S., Eds.; Birkhauser Verlag: Basle, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 38, p. 885. [Google Scholar]
- Corte-Real, J.; Bertucci, M.; Soukoulis, C.; Desmarchelier, C.; Borel, P.; Richling, E.; Hoffmann, L.; Bohn, T. Negative effects of divalent mineral cations on the bioaccessibility of carotenoids from plant food matrices and related physical properties of gastro-intestinal fluids. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapelli-Brahm, P.; Corte-Real, J.; Melendez-Martinez, A.J.; Bohn, T. Bioaccessibility of phytoene and phytofluene is superior to other carotenoids from selected fruit and vegetable juices. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte-Real, J.; Guignard, C.; Gantenbein, M.; Weber, B.; Burgard, K.; Hoffmann, L.; Richling, E.; Bohn, T. No influence of supplemental dietary calcium intake on the bioavailability of spinach carotenoids in humans. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iddir, M.; Degerli, C.; Dingeo, G.; Desmarchelier, C.; Schleeh, T.; Borel, P.; Larondelle, Y.; Bohn, T. Whey protein isolate modulates beta-carotene bioaccessibility depending on gastro-intestinal digestion conditions. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mashurabad, P.C.; Palika, R.; Jyrwa, Y.W.; Bhaskarachary, K.; Pullakhandam, R. Dietary fat composition, food matrix and relative polarity modulate the micellarization and intestinal uptake of carotenoids from vegetables and fruits. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goupy, P.; Genot, C.; Hammaz, F.; Halimi, C.; Caris-Veyrat, C.; Borel, P. Mechanisms Governing the Transfer of Pure and Plant Matrix Carotenoids toward Emulsified Triglycerides. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e1900911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensi, A.; Choiset, Y.; Rabesona, H.; Haertle, T.; Borel, P.; Chobert, J.M. Interactions of beta-lactoglobulin variants A and B with Vitamin A. Competitive binding of retinoids and carotenoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4114–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Kelly, A.L.; Miao, S. Bioaccessibility and Cellular Uptake of β-Carotene Encapsulated in Model O/W Emulsions: Influence of Initial Droplet Size and Emulsifiers. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mapelli-Brahm, P.; Desmarchelier, C.; Margier, M.; Reboul, E.; Meléndez Martínez, A.J.; Borel, P. Phytoene and Phytofluene Isolated from a Tomato Extract are Readily Incorporated in Mixed Micelles and Absorbed by Caco-2 Cells, as Compared to Lycopene, and SR-BI is Involved in their Cellular Uptake. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1800703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, N.E.; Novotny, J.A.; Cichon, M.J.; Riedl, K.M.; Rogers, R.B.; Grainger, E.M.; Schwartz, S.J.; Erdman, J.W., Jr.; Clinton, S.K. Absorption and distribution kinetics of the 13C-labeled tomato carotenoid phytoene in healthy adults. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meléndez-Martínez, A.J.; Paulino, M.; Stinco, C.M.; Mapelli-Brahm, P.; Wang, X.-D. Study of the Time-Course of cis/trans (Z/E) Isomerization of Lycopene, Phytoene, and Phytofluene from Tomato. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12399–12406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapelli-Brahm, P.; Margier, M.; Desmarchelier, C.; Halimi, C.; Nowicki, M.; Borel, P.; Meléndez-Martínez, A.J.; Reboul, E. Comparison of the bioavailability and intestinal absorption sites of phytoene, phytofluene, lycopene and β-carotene. Food Chem. 2019, 300, 125232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, D.G.; Kruger, F.A.; Robinson, H.B. Studies on the absorption of beta-carotene and the distribution of total carotenoid in human serum lipoproteins after oral administration*. J. Lipid Res. 1962, 3, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goltz, S.R.; Campbell, W.W.; Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; Failla, M.L.; Ferruzzi, M.G. Meal triacylglycerol profile modulates postprandial absorption of carotenoids in humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, P.; Desmarchelier, C.; Dumont, U.; Halimi, C.; Lairon, D.; Page, D.; Sebedio, J.L.; Buisson, C.; Buffiere, C.; Remond, D. Dietary calcium impairs tomato lycopene bioavailability in healthy humans. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widjaja-Adhi, M.A.K.; Lobo, G.P.; Golczak, M.; Von Lintig, J. A genetic dissection of intestinal fat-soluble vitamin and carotenoid absorption. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 3206–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Delaimy, W.K.; van Kappel, A.L.; Ferrari, P.; Slimani, N.; Steghens, J.-P.; Bingham, S.; Johansson, I.; Wallström, P.; Overvad, K.; Tjønneland, A.; et al. Plasma levels of six carotenoids in nine European countries: Report from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodside, J.V.; Young, I.S.; Gilchrist, S.E.C.M.; Vioque, J.; Chakravarthy, U.; de Jong, P.T.V.M.; Rahu, M.; Seland, J.; Soubrane, G.; Tomazzoli, L.; et al. Factors associated with serum/plasma concentrations of vitamins A, C, E and carotenoids in older people throughout Europe: The EUREYE study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.S. Absorption, metabolism, and transport of carotenoids. Faseb. J. 1996, 10, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.M.; Thompson, F.E.; Midthune, D.; Subar, A.F.; Berrigan, D.; Schatzkin, A.; Potischman, N. Strength of the relationships between three self-reported dietary intake instruments and serum carotenoids: The Observing Energy and Protein Nutrition (OPEN) Study. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, R.; Nolan, J.M.; Stack, J.; O’Halloran, A.M.; Feeney, J.; Akuffo, K.O.; Kenny, R.A.; Beatty, S. Non-dietary correlates and determinants of plasma lutein and zeaxanthin concentrations in the Irish population. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, W.E.; Mares-Perlman, J.A.; Bowen, P.; Stacewicz-Sapuntzakis, M. Human serum carotenoid concentrations are related to physiologic and lifestyle factors. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burke, J.D.; Curran-Celentano, J.; Wenzel, A.J. Diet and serum carotenoid concentrations affect macular pigment optical density in adults 45 years and older. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allore, T.; Lemieux, S.; Vohl, M.-C.; Couture, P.; Lamarche, B.; Couillard, C. Correlates of the difference in plasma carotenoid concentrations between men and women. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 121, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.J.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Nguyen, M.L.; Cooper, D.A.; Eldridge, A.L.; Schwartz, S.J.; White, W.S. Carotenoid bioavailability is higher from salads ingested with full-fat than with fat-reduced salad dressings as measured with electrochemical detection. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meléndez-Martínez, A.J.; Böhm, V.; Borge, G.I.A.; Cano, M.P.; Fikselová, M.; Gruskiene, R.; Lavelli, V.; Loizzo, M.R.; Mandić, A.I.; Brahm, P.M.; et al. Carotenoids: Considerations for Their Use in Functional Foods, Nutraceuticals, Nutricosmetics, Supplements, Botanicals, and Novel Foods in the Context of Sustainability, Circular Economy, and Climate Change. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 433–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, I.E.I.; Danielsen, M.; Dalsgaard, T.K.; Rejnmark, L.; Bollen, P.; Bertram, H.C. Milk protein complexation enhances post prandial vitamin D3 absorption in rats. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4953–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Male (n = 12) | Female (n = 12) | All Participants (n = 24) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Max | Min | Mean (SD) | Max | Min | Mean (SD) | Max | Min | |
| Anthropometric measures 1 | |||||||||
| Age (years) | 30.9 (6.4) | 46.0 | 22.0 | 29.7 (6.3) | 42.0 | 22.0 | 30.3 (6.3) | 46.0 | 22.0 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.1 (2.3) | 28.7 | 19.7 | 22.8 (1.8) | 25.7 | 18.9 | 23.9 (2.4) | 28.7 | 18.9 |
| Body fat (%) | 18.4 (5.7) | 27.5 | 8.9 | 31.5 (5.0) | 38.4 | 22.9 | 24.9 (8.5) | 38.4 | 8.9 |
| Waist/hip ratio | 0.9 (0.1) | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.8 (0.1) | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.9 (0.1) | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| Blood biochemistry profile 2 | |||||||||
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 96.6 (8.0) | 108.0 | 82.0 | 87.9 (7.3) | 106.0 | 79.0 | 92.3 (8.7) | 108.0 | 79.0 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 152.3 (31.2) | 193.0 | 94.0 | 176.4 (36.3) | 230.0 | 99.0 | 164.3 (35.3) | 230.0 | 94.0 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 48.5 (15.4) | 88.0 | 32.0 | 67.3 (14.9) | 95.0 | 48.0 | 57.9 (17.7) | 95.0 | 32.0 |
| Non-HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 103.6 (33.7) | 161.0 | 43.0 | 109.1 (31.6) | 152.0 | 37.0 | 106.3 (32.1) | 161.0 | 37.0 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) 3 | 95.1 (29.3) | 144.0 | 43.0 | 106.5 (29.7) | 143.0 | 32.0 | 100.8 (29.4) | 144.0 | 32.0 |
| TAG (mg/dL) | 88.7 (44.7) | 192.0 | 44.0 | 75.4 (29.9) | 129.0 | 39.0 | 82.0 (37.8) | 192.0 | 39.0 |
| Amounts | Ingredients | Nutritional Values Per Serving | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breakfast meal (mornings) | |||
| Mixture carrot juice/ tomato juice (1:1, v/v) | 350 mL | 99% carrot juice, 1% concentrate from lemon 99.5% tomato juice, 0.5% salt | Energy: 282 kJ/67 kcal/Fat: 0.9 g, of which saturated 0.2 g/Carbohydrates: 13.5 g, of which sugars 13.5 g/Fibers: 1.6 g/Proteins: 2.5 g/Salt: 1.6 g |
| Peanut oil 1 | 5 mL | Refined peanut oil 100% | Energy: 185 kJ/45 kcal/Fat: 45 g, of which saturated: 0.85 g, mono-unsaturated: 3.3 g, polyunsaturated: 0.85 g |
| Proteins 1 | |||
| Control (A) | 0 g | n.a. 3 | n.a. 3 |
| WPI (B) | 30 g | Whey protein isolate, emulsifier (soy lecithin) | Energy: 503 kJ/119 kcal/Fat: 0.3 g, of which saturated 0.2 g/Carbohydrates: 0.5 g, of which sugars 0.5 g/ Fibers: 1 g/Proteins: 28.0 g/Salt: 0.2 g |
| SPI (C) | 30 g | Soy protein isolate, emulsifier (E322-sunflower) | Energy: 472 kJ/113 kcal/Fat: 0.3 g, of which saturated 0.06 g/Carbohydrates: 0.3 g, of which sugars 0.03 g/Fibers: 0.3 g/Proteins: 27.2 g/Salt: 0.09 g |
| Toasted bread | 40 g | Wheat flour (65%), water, sugar, colza oil, salt, vinegar, yeast, bean flour, wheat gluten, aroma (contains alcohol), acerola extract | Energy: 457 kJ/108 kcal/Fat: 1.6 g, of which saturated 0.2 g/Carbohydrates: 19.6 g, of which sugars 3.0 g/Fibers: 1.6 g/Proteins: 3.0 g/Salt: 0.4 g |
| Butter 2 | 12.5 g | Fat 82% | Energy: 385 kJ/94 kcal/Fat: 10.3 g, of which saturated 7.1 g/Carbohydrates: 0.1 g, of which sugars 0.1 g/Proteins: 0.1 g/Salt: <0.1 g |
| Cream cheese 2 | 19 g | Rehydrated skimmed milk, cheese, butter, milk mineral concentrate. | Energy: 172 kJ/41 kcal/Fat: 3.3 g, of which saturated 2.2 g/Carbohydrates: 0.9 g, of which sugars 0.9 g/Proteins: 2.0 g/Salt: 0.32 g |
| Water | 300 mL | Analysis (mg/L): Ca:5; Mg:2; Na:3; K:0.5; Cl:5; SO4:4; NO3:1.5; HCO3:17; SiO2:7 | n.a. 3 |
| Total energy Control meal WPI meal SPI meal | 1281 kJ/355 kcal 1759 kJ/467 kcal 1753 kJ/468 kcal | ||
| Lunch (4 h after breakfast meal) | |||
| Toasted bread | 60 g | Energy: 686 kJ/163 kcal/Fat: 2.5 g, of which saturated 0.3 g/Carbohydrates: 29.3 g, of which sugars 4.6 g/Fibers: 2.3 g/Proteins: 4.6 g/ Salt: 0.7 g | |
| Butter 2 | 12.5 g | Fat 82% | Energy: 385 kJ/94 kcal/Fat: 10.3 g, of which saturated 7.1 g/Carbohydrates: 0.1 g, of which sugars 0.1 g/Proteins: 0.1 g/Salt: <0.1 g |
| Turkey 2 | 60 g | Turkey fillet 90%, salt, dextrose, spices, acidity regulator (sodium lactate), stabilizers (sodium citrate, carrageenans), flavor, antioxidant (sodium ascorbate), preservative (sodium nitrite) | Energy: 247 kJ/58 kcal/Fat: 0.9 g, of which saturated 0.3 g/Carbohydrates: 0.5 g, of which sugars 0.4 g/Proteins: 12.0 g/Salt: 1.2 g |
| Greek yogurt | 150 g | Pasteurized cow milk, milk cream, milk protein, yogurt culture | Energy: 804 kJ/194 kcal/Fat: 15 g, of which saturated 11.3 g/Carbohydrates: 5.3 g, of which sugars 5.3 g/Fibers: <0.5 g/Proteins: 8.3 g/ Salt: 0.2 g |
| Apple | 150 g | n.a. 3 | Energy: 321 kJ/77 kcal/Fat: >0.5 g, of which saturated >0.1g/Carbohydrates: 16.5 g, of which sugars 15.0 g /Fibers: 3.8 g/Proteins: <0.5 g/Salt: <0.01 g. |
| Water | 300 mL | Analysis (mg/L): Ca:5; Mg:2; Na:3; K:0.5; Cl:5; SO4:4; NO3:1.5; HCO3:17; SiO2:7 | n.a. 3 |
| Total energy | 2443 kJ/586 kcal | ||
| Breakfast Meal | Lut+Zea | Ptf | Pte | α-Car | β-Car | Lyc | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomato juice | 0.04 | 1.15 | 1.63 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 7.79 | 10.9 |
| Carrot juice | 0.09 | 0.88 | 0.49 | 1.70 | 4.40 | 0.04 | 7.6 |
| Juice mix 100 g | 0.06 | 1.01 | 1.06 | 0.86 | 2.32 | 3.91 | 9.25 |
| Juice mix 350 g | 0.2 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 3.0 | 8.1 | 13.7 | 32.4 |
| Gender | Carotenoids/Visits | Lut+Zea | β-Car | α-Car | Lyc | Pte | Ptf | β-Cry | Total carot. † |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female (n = 12) | D0 | 282.4 (±237.6) a | 85.3 (±76.0) a | 12.9 (±8.3) a | 53.3 (±39.5) a | 31.7 (±14.2) a | 60.0 (±46.1) a | 56.0 (±35.9) a | 581.3 (±361.8) a |
| V1 | 214.4 (±202.8) b | 55.4 (±61.6) b | 10.0 (±5.6) a | 42.4 (±52.0) b | 22.6 (±35.6) b | 44.9 (±45.5) b | 39.5 (±23.1) b | 429.3 (±386.1) b | |
| V2 | 173.6 (±134.9) b | 55.2 (±50.7) b | 10.8 (±4.8) a | 40.2 (±46.1) b | 17.8 (±11.9) b | 44.4 (±39.8) b | 34.8 (±20.7) b | 376.9 (±271.6) b | |
| V3 | 175.0 (±120.4) b | 58.0 (±57.7) b | 11.2 (±5.0) a | 35.3 (±35.3) b | 15.8 (±9.0) b | 46.5 (±46.8) b | 35.4 (±22.8) b | 377.3 (±262.1) b | |
| Male (n = 12) | D0 | 100.9 (±59.8) a | 63.5 (±59.6) a | 22.5 (±24.3) a | 40.8 (±26.9) a | 38.7 (±30.4) a | 29.4 (±21.0) a | 32.9 (±16.7) a | 328.8 (±139.3) a |
| V1 | 61.6 (±37.9) a | 38.0 (±34.0) b | 13.5 (±13.9) b | 23.1 (±15.4) b | 11.6 (±6.0) b | 14.2 (±7.4) b | 19.6 (±10.0) a | 181.6 (±74.0) b | |
| V2 | 79.8 (±61.3) a | 37.0 (±30.1) b | 13.0 (±11.9) b | 19.3 (±11.8) b | 10.8 (±6.7) b | 13.8 (±7.0) b | 19.9 (±9.5) a | 193.7 (±71.4) b | |
| V3 | 79.0 (±62.8) a | 35.5 (±29.2) b | 13.2 (±11.7) b | 18.0 (±10.9) b | 12.2 (±6.5) b | 14.5 (±9.7) b | 21.1 (±13.3) a | 193.7 (±76.9) b | |
| TotalParticipants (n = 24) | D0 | 191.7 (±193.1) a | 74.4 (±67.7) a | 17.7 (±18.4) a | 47.0 (±33.6) a | 35.2 (±23.5) a | 44.5 (±38.3) a | 44.7 (±29.8) a | 455.0 (±297.5) a |
| V1 | 138.0 (±162.6) b | 46.7 (±49.5) b | 11.7 (±10.5) b | 32.7 (±38.8) b | 17.1 (±25.6) b | 29.5 (±35.5) b | 29.6 (±20.2) b | 305.4 (±299.9) b | |
| V2 | 126.7 (±113.1) b | 46.1 (±41.9) b | 11.9 (±8.9) b | 29.8 (±34.6) b | 14.3 (±10.1) b | 29.1 (±32.0) b | 27.4 (±17.5) b | 285.3 (±215.6) b | |
| V3 | 127.0 (±105.9) b | 46.8 (±46.2) b | 12.2 (±8.9) b | 26.7 (±30.3) b | 14.0 (±8.0) b | 30.5 (±36.9) b | 28.3 (±28.3) b | 285.5 (±210.9) b |
| Carotenoids † /TAGs | Breakfast Meal | Female | Male | Total Participants |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lut + Zea | Control | −16.4 ± 4.5 a | 15.0 ± 2.4 a | −0.6 ± 1.8 a |
| WPI | −7.1 ± 4.5 a | 17.5 ± 2.4 a | 5.2 ± 1.8 a | |
| SPI | 0.2 ± 4.5 a | 28.7 ± 2.4 a | 14.4 ± 1.8 a | |
| β-Car | Control | 1.7 ± 3.1 a | 24.9 ± 3.2 a,b | 13.3 ± 1.4 a,b |
| WPI | 1.7 ± 3.1 a | 43.4 ± 3.2 b | 22.6 ± 1.4 b | |
| SPI | −0.2 ± 3.1 a | 6.6 ± 3.2 a | 3.2 ± 1.4 a | |
| α-Car | Control | 4.2 ± 0.4 a,b | 10.7 ± 1.6 a,b | 7.4 ± 0.6 a,b |
| WPI | 5.9 ± 0.4 b | 22.2 ± 1.6 b | 14.1 ± 0.6 b | |
| SPI | 2.0 ± 0.4 a | 4.2 ± 1.6 a | 3.1 ± 0.6 a | |
| Lyc | Control | −8.8 ± 1.7 a | 1.7 ± 1.2 a | −3.6 ± 0.7 a |
| WPI | −13.5 ± 1.7 a | 6.4 ± 1.2 a | −3.6 ± 0.7 a | |
| SPI | −8.3 ± 1.7 a | 4.2 ± 1.2 a | −2.0 ± 0.7 a | |
| Pte | Control | 94.5 ± 2.3 b | 176.9 ± 9.1 a,b | 135.7 ± 3.3 b |
| WPI | 112.1 ± 2.3 b | 207.6 ± 9.1 b | 159.9 ± 3.3 b | |
| SPI | 63.3 ± 2.3 a | 100.5 ± 9.1 a | 81.9 ± 3.3 a | |
| Ptf | Control | 28.9 ± 1.7 a | 49.2 ± 2.1 a | 39.0 ± 0.9 a |
| WPI | 40.1 ± 1.7 a | 69.2 ± 2.1 b | 54.7 ± 0.9 b | |
| SPI | 26.3 ± 1.7 a | 36.2 ± 2.1 a | 31.2 ± 0.9 a | |
| β-Cry | Control | −10.2 ± 0.7 a | 0.7 ± 0.8 a | −4.7 ±0.7 a |
| WPI | −6.2 ± 0.7 a | −1.5 ± 0.8 a | −3.8 ± 0.3 a | |
| SPI | −6.5 ± 0.7 a | 2.0 ± 0.8 a | −2.3 ± 0.7 a | |
| Totalcarot. ‡ | Control | 93.8 ± 9.7 a | 279.2 ± 17.4 a,b | 186.5 ± 7.0 a,b |
| WPI | 133.1 ± 9.7 a | 364.5 ± 17.4 b | 248.8 ± 7.0 b | |
| SPI | 76.8 ± 9.7 a | 171.5 ± 17.4 a | 124.1 ± 7.0 a | |
| TAGs | Control | 165.3 ± 6.3 a | 232.1 ± 25.8 a | 196.3 ± 9.6 a |
| WPI | 238.2 ± 6.3 b | 426.7 ± 25.8 a | 332.4 ± 9.3 b | |
| SPI | 191.5 ± 6.3 a,b | 360.8 ± 25.8 a | 276.2 ± 9.3 a,b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iddir, M.; Pittois, D.; Guignard, C.; Weber, B.; Gantenbein, M.; Larondelle, Y.; Bohn, T. Whey- and Soy Protein Isolates Added to a Carrot-Tomato Juice Alter Carotenoid Bioavailability in Healthy Adults. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111748
Iddir M, Pittois D, Guignard C, Weber B, Gantenbein M, Larondelle Y, Bohn T. Whey- and Soy Protein Isolates Added to a Carrot-Tomato Juice Alter Carotenoid Bioavailability in Healthy Adults. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(11):1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111748
Chicago/Turabian StyleIddir, Mohammed, Denis Pittois, Cédric Guignard, Bernard Weber, Manon Gantenbein, Yvan Larondelle, and Torsten Bohn. 2021. "Whey- and Soy Protein Isolates Added to a Carrot-Tomato Juice Alter Carotenoid Bioavailability in Healthy Adults" Antioxidants 10, no. 11: 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111748
APA StyleIddir, M., Pittois, D., Guignard, C., Weber, B., Gantenbein, M., Larondelle, Y., & Bohn, T. (2021). Whey- and Soy Protein Isolates Added to a Carrot-Tomato Juice Alter Carotenoid Bioavailability in Healthy Adults. Antioxidants, 10(11), 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111748