Preventive Effects against Retinal Degeneration by Centella asiatica Extract (CA-HE50) and Asiaticoside through Apoptosis Suppression by the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
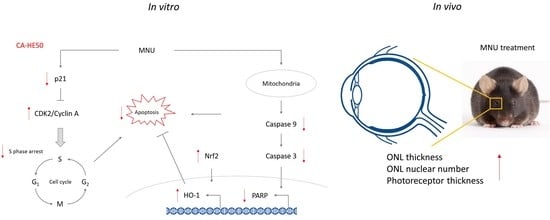
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.2.1. Preparation of C. asiatica Extract (CA-HE50)
2.2.2. HPLC Analysis of Asiaticoside in CA-HE50
2.3. In Vivo Analysis
2.3.1. Animal Care and Experimental Design
2.3.2. Fixation of Eyes and Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.3.3. Western Blot Analysis of Ocular Tissue
2.4. In Vitro Analysis
2.4.1. Cell Culture
2.4.2. MTT Assays
2.4.3. Western Blot Analysis
2.4.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Protective Effect of CA-HE50 against MNU-Induced Retinal Degeneration
3.2. CA-HE50 Inhibits MNU-Induced Apoptosis in ARPE-19 Cells
3.3. CA-HE50 Inhibits Apoptosis through Inhibition of MNU-Mediated S Phase Arrest
3.4. Asiaticoside, a Functional Component of CA-HE50, Inhibits MNU-induced Apoptosis
3.5. A2E Oxidation Inhibition and Cell Protection Effects of CA-HE50 and Asiaticoside
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedman, D.S.; O’Colmain, B.J.; Muñoz, B.; Tomany, S.C.; Mccarty, C.; De Jong, P.T.V.M.; Nemesure, B.; Mitchell, P.; Kempen, J. Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration in the United States. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coleman, H.R.; Chan, C.-C.; Ferris, F.L.; Chew, E.Y. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 2008, 372, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.L.; Su, X.; Li, B.X.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Klein, B.E.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Wong, T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e106–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, J.R. Risk factors for age-related macular degeneration. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2001, 20, 227–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, J.M.; Sharma, S.; Adelman, R.A. Evaluation of the clinical age-related maculopathy staging System. Ophthalmology 2006, 113, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagasingam, Y.; Bhuiyan, A.; Abràmoff, M.D.; Smith, R.T.; Goldschmidt, L.; Wong, T.Y. Progress on retinal image analysis for age related macular degeneration. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2014, 38, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, C.N.; Green, B.D.; Thompson, R.B.; Hollander, A.I.D.; Lengyel, I.; on behalf of the EYE-RISK Consortium Metabolomics and age-related macular degeneration. Metabolomics and Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Metabolites 2019, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellezza, I.; Mierla, A.L.; Minelli, A. Nrf2 and NF-κB and their concerted modulation in cancer pathogenesis and progression. Cancers 2010, 2, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Sternberg, P.; Freeman, M.L.; Grossniklaus, H.E.; Cai, J. Age-related retinopathy in NRF2-deficient mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Talalay, P. Induction of phase 2 genes by sulforaphane protects retinal pigment epithelial cells against photooxidative damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10446–10451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dulull, N.K.; Dias, D.A.; Thrimawithana, T.R.; Kwa, F.A.A. L-Sulforaphane confers protection against oxidative stress in an in vitro model of age-related macular degeneration. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frede, K.; Ebert, F.; Kipp, A.P.; Schwerdtle, T.; Baldermann, S. Lutein activates the transcription factor Nrf2 in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5944–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orhan, C.; Akdemir, F.; Tuzcu, M.; Sahin, N.; Yilmaz, I.; Ali, S.; Deshpande, J.; Juturu, V.; Sahin, K. Mesozeaxanthin protects retina from oxidative stress in a rat model. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 32, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.R.; Lawrenson, J.G. Antioxidant vitamin and mineral supplements for preventing age-related macular degeneration. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 7, CD000253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrenson, J.G.; Evans, J.R. Omega 3 fatty acids for preventing or slowing the progression of age-related macular degeneration. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, CD010015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satia, J.A.; Littman, A.J.; Slatore, C.G.; Galanko, J.A.; White, E. Long-term use of beta-carotene, retinol, lycopene, and lutein supplements and lung cancer risk: Results from the VITamins And Lifestyle (VITAL) study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, S.S.; Nizami, Q.; Salam, M. Centella asiatica (Linn.) Urban—A Review. Nat. Prod. Radiance 2007, 6, 158–170. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/123456789/7855 (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Park, D.W.; Jeon, H.; So, R.; Kang, S.C. Centella asiatica extract prevents visual impairment by promoting the production of rhodopsin in the retina. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2020, 14, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, E.; Tschopp, M.; Tappeiner, C.; Sallin, P.; Jaźwińska, A.; Enzmann, V. Methylnitrosourea (MNU)-induced retinal degeneration and regeneration in the zebrafish: Histological and functional characteristics. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 20, e51909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SanGiovanni, J.P.; Chew, E.Y.; Clemons, T.E.; Rd, F.F.; Gensler, G.; Lindblad, A.S.; Milton, R.C.; Seddon, J.M.; Sperduto, R.D.; Age-Related Eye Disease Study Research Group. The relationship of dietary carotenoid and vitamin A, E, and C intake with age-related macular degeneration in a case-control study: AREDS Report No. 22. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2007, 125, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, C.K.; Tan, L.T.H.; Pusparajah, P.; Htar, T.T.; Chuah, L.-H.; Lee, V.S.; Low, L.E.; Tang, S.Y.; Chan, K.-G.; Goh, B.H. Detrimental Effects of UVB on Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells and Its Role in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1904178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canton, V.M.; Quiroz-Mercado, H.; Velez-Montoya, R.; Lopez-Miranda, M.J.; Moshfeghi, A.A.; Shusterman, E.M.; Kaiser, P.K.; Sanislo, S.R.; Gertner, M.; Moshfeghi, D.M. 16-Gy Low-Voltage X-ray Irradiation with Ranibizumab Therapy for AMD: 6-Month Safety and Functional Outcomes. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retin. 2011, 42, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustin, A. Triple therapy for age-related macular degeneration. Retina 2009, 29, S8–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, S.; Nishimura, T.; Harada, T.; Kurosaka, D. Retinal ganglion cell function after repeated intravitreal injections of ranibizumab in patients with age-related macular degeneration. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2012, 6, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruschi, M.; Bartolucci, M.; Petretto, A.; Calzia, D.; Caicci, F.; Manni, L.; Traverso, C.E.; Candiano, G.; Panfoli, I. Differential expression of the five redox complexes in the retinal mitochondria or rod outer segment disks is consistent with their different functionality. FASEB J. 2020, 2, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzia, D.; Degan, P.; Caicci, F.; Bruschi, M.; Manni, L.; Ramenghi, L.A.; Candiano, G.; Traverso, C.E.; Panfoli, I. Modulation of the rod outer segment aerobic metabolism diminishes the production of radicals due to light absorption. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 117, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunaief, J.L.; Dentchev, T.; Ying, G.-S.; Milam, A.H. The role of apoptosis in age-related macular degeneration. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frenkel, S.; Hendler, K.; Siegal, T.; Shalom, E.; Pe’Er, J. Intravitreal methotrexate for treating vitreoretinal lymphoma: 10 years of experience. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 92, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.; Duker, J.S.; Ishikawa, H.; Ko, T.H.; Schuman, J.S.; Fujimoto, J.G. Quantification of photoreceptor layer thickness in normal eyes using optical coherence tomography. Retina 2006, 26, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igney, F.H.; Krammer, P.H. Death and anti-death: Tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkavan, H.; Green, D.R. MOMP, cell suicide as a BCL-2 family business. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnum, K.J.; O’Connell, M.J. Cell cycle regulation by checkpoints. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1170, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blasiak, J.; Piechota, M.; Pawlowska, E.; Szatkowska, M.; Sikora, E.; Kaarniranta, K. Cellular Senescence in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Can Autophagy and DNA Damage Response Play a Role? Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 5293258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementi, M.E.; Sampaolese, B.; Sciandra, F.; Tringali, G. Punicalagin Protects Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells from Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Oxidative Damage by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway and Reducing Apoptosis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Dong, Y.; Liu, H.; Ren, H.; Cui, Z. Hesperetin protects against H2O2-triggered oxidative damage via upregulation of the Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway in ARPE-19 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, N.F.; Sun, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, D.D. Nrf2 and p21 regulate the fine balance between life and death by controlling ROS levels. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3255–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, D.-W.; Lee, Y.-G.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Jeon, H.; Kang, S.-C. Preventive Effects against Retinal Degeneration by Centella asiatica Extract (CA-HE50) and Asiaticoside through Apoptosis Suppression by the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10040613
Park D-W, Lee Y-G, Jeong Y-J, Jeon H, Kang S-C. Preventive Effects against Retinal Degeneration by Centella asiatica Extract (CA-HE50) and Asiaticoside through Apoptosis Suppression by the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(4):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10040613
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Dae-Won, Yeong-Geun Lee, Yong-Joon Jeong, Hyelin Jeon, and Se-Chan Kang. 2021. "Preventive Effects against Retinal Degeneration by Centella asiatica Extract (CA-HE50) and Asiaticoside through Apoptosis Suppression by the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway" Antioxidants 10, no. 4: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10040613
APA StylePark, D. -W., Lee, Y. -G., Jeong, Y. -J., Jeon, H., & Kang, S. -C. (2021). Preventive Effects against Retinal Degeneration by Centella asiatica Extract (CA-HE50) and Asiaticoside through Apoptosis Suppression by the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants, 10(4), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10040613