Does Empagliflozin Modulate Leukocyte–Endothelium Interactions, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Sample Collection
2.2. Anthropometric and Biochemical Analysis
2.3. Leukocyte Isolation
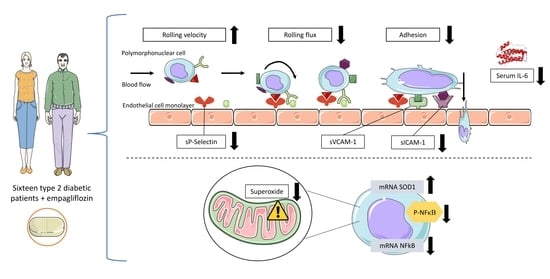
2.4. Leukocyte–Endothelium Interactions, Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines, and Cellular Adhesion Molecule Evaluation
2.5. Evaluation of Mitochondrial ROS Production in Leukocytes
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Gene Expression Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anthropometric and Biochemical Analysis
3.2. Leukocyte–Endothelium Interactions and Adhesion Molecule Expression
3.3. Mitochondrial Superoxide Production
3.4. Inflammatory Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Study’s Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strain, W.D.; Paldanius, P.M. Diabetes, cardiovascular disease and the microcirculation. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bevilacqua, M.P.; Stengelin, S.; Gimbrone, M.A., Jr.; Seed, B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: An inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science 1989, 243, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jay, D.; Hitomi, H.; Griendling, K.K. Oxidative stress and diabetic cardiovascular complications. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 40, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 2001, 414, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frampton, J.E. Empagliflozin: A Review in Type 2 Diabetes. Drugs 2018, 78, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schernthaner, G.; Schernthaner-Reiter, M.H.; Schernthaner, G.H. EMPA-REG and Other Cardiovascular Outcome Trials of Glucose-lowering Agents: Implications for Future Treatment Strategies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banuls, C.; de Maranon, A.M.; Veses, S.; Castro-Vega, I.; Lopez-Domenech, S.; Salom-Vendrell, C.; Orden, S.; Alvarez, A.; Rocha, M.; Victor, V.M.; et al. Malnutrition impairs mitochondrial function and leukocyte activation. Nutr. J. 2019, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Maranon, A.M.; Canet, F.; Abad-Jimenez, Z.; Jover, A.; Morillas, C.; Rocha, M.; Victor, V.M. Does Metformin Modulate Mitochondrial Dynamics and Function in Type 2 Diabetic Patients? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyani, C.N.; Plastira, I.; Sourij, H.; Hallstrom, S.; Schmidt, A.; Rainer, P.P.; Bugger, H.; Frank, S.; Malle, E.; von Lewinski, D. Empagliflozin protects heart from inflammation and energy depletion via AMPK activation. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A. Update on developments with SGLT2 inhibitors in the management of type 2 diabetes. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 8, 1335–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haring, H.U.; Merker, L.; Seewaldt-Becker, E.; Weimer, M.; Meinicke, T.; Broedl, U.C.; Woerle, H.J.; Investigators, E.-R.M.T. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pieber, T.R.; Famulla, S.; Eilbracht, J.; Cescutti, J.; Soleymanlou, N.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Kaspers, S. Empagliflozin as adjunct to insulin in patients with type 1 diabetes: A 4-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (EASE-1). Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, S.; Zeller, C.; Iliev, H.; Kaspers, S. Safety and Tolerability of Empagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Pooled Analysis of Phase I-III Clinical Trials. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 1707–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stroes, E. Statins and LDL-cholesterol lowering: An overview. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2005, 21 (Suppl. S6), S9–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannantuoni, F.; de Marañon, A.M.; Diaz-Morales, N.; Falcon, R.; Banuls, C.; Abad-Jimenez, Z.; Victor, V.M.; Hernandez-Mijares, A.; Rovira-Llopis, S. The SGLT2 Inhibitor Empagliflozin Ameliorates the Inflammatory Profile in Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Promotes an Antioxidant Response in Leukocytes. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Gene Name | Primer Name | Primer Sequence | Sequence Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superoxide dismutase 1 | SOD1 Forward | GGTGTGGCCGATGTGTCTAT | NM_000454 |
| SOD1 Reverse | TTCCACCTTTGCCCAAGTCA | ||
| Glutathione peroxidase 1 | GPX1 Forward | TTGAGAAGTTCCTGGTGGGC | NM_000581.4 |
| GPX1 Reverse | CGATGTCAGGCTCGATGTCA | ||
| RELA proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit | NFkB p65 Forward | ATCCCATCTTTGACAATCGTGC | NM_021975 |
| NFkB p65 Reverse | CTGGTCCCGTGAAATACACCTC | ||
| Actin beta | Actin B Forward | CCTCGCCTTTGCCGATCC | NM_001101 |
| Actin B Reverse | CGCGGCGATATCATCATCC |
| Patient | Lipid-Lowering Medication | Antihypertensive Medication | Antithrombotic Medication | Diuretic Medication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | Atorvastatin | - | - | - |
| 3 | Excluded from the study | |||
| 4 | Atorvastatin | - | ASA | - |
| 5 | Atorvastatin | Enalapril + bimatoprost + timolol | - | HCTZ |
| 6 | Simvastatin | Valsartan + Amlodipine | - | HCTZ |
| 7 | - | - | - | - |
| 8 | Atorvastatin | Ramipril | ASA | - |
| 9 | Atorvastatin | Nebivolol + Valsartan | Clopidogrel + ASA | - |
| 10 | Pravastatin + Fenofibrate | - | - | - |
| 11 | Atorvastatin | - | ASA | - |
| 12 | - | - | - | - |
| 13 | Simvastatin | Manidipine + Olmesartan | - | HCTZ |
| 14 | Atorvastatin | Amlodipine + Irbesartan | - | HCTZ |
| 15 | Atorvastatin | Eprosartan | HCTZ | |
| 16 | Simvastatin | Telmisartan | ASA | HCTZ |
| 17 | Atorvastatin | - | - | - |
| 18 | Excluded from the study | |||
| Baseline | 12-Week Empagliflozin | 24-Week Empagliflozin | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| Age (years) | 59.7 ± 10.8 | - | - |
| Sex (female) | 5 | ||
| Weight (kg) | 85.7 ± 20.1 | 82.9 ± 20.3 ** | 81.6 ± 20.3 ** # |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 102.7 ± 12.3 | 99.8 ± 13.5 | 97.1 ± 13.7 ** # |
| BMI | 31.4 ± 5.3 | 30.3 ± 5.4 * | 29.9 ± 5.6 ** |
| SBP (mmHg) | 139.5 ± 26.9 | 139.6 ± 24.6 | 133.9 ± 21.7 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 76.4 ± 14.1 | 81.0 ± 16.3 | 73.9 ± 12.7 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 149.1 ± 35.9 | 134.1 ± 32.6 | 125.2 ± 19.9 * |
| HbA1C (%) | 7.6 ± 1.3 | 7.2 ± 1.3 * | 6.8 ± 0.9 * |
| Insulin (μUI/mL) | 9.6 ± 5.4 | 9.6 ± 5.5 | 9.5 ± 5.9 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.88 ± 2.16 | 3.32 ± 1.54 | 3.10 ± 2.10 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 141.0 ± 25.4 | 154.7 ± 27.6 * | 149.5 ± 27.1 * |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 82.3 ± 16.9 | 87.2 ± 16.6 | 89.1 ± 19.8 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 46.1 ± 6.1 | 43.2 ± 7.1 | 47.5 ± 3.7 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 92 (83–131) | 113 (100–168) | 104 (82–122) |
| hs-RCP | 2.42 (1.2–11.5) | 4.28 (1.5–7.8) | 1.9 (1.3–5.8) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Canet, F.; Iannantuoni, F.; Marañon, A.M.d.; Díaz-Pozo, P.; López-Domènech, S.; Vezza, T.; Navarro, B.; Solá, E.; Falcón, R.; Bañuls, C.; et al. Does Empagliflozin Modulate Leukocyte–Endothelium Interactions, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes? Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081228
Canet F, Iannantuoni F, Marañon AMd, Díaz-Pozo P, López-Domènech S, Vezza T, Navarro B, Solá E, Falcón R, Bañuls C, et al. Does Empagliflozin Modulate Leukocyte–Endothelium Interactions, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes? Antioxidants. 2021; 10(8):1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081228
Chicago/Turabian StyleCanet, Francisco, Francesca Iannantuoni, Aránzazu Martínez de Marañon, Pedro Díaz-Pozo, Sandra López-Domènech, Teresa Vezza, Blanca Navarro, Eva Solá, Rosa Falcón, Celia Bañuls, and et al. 2021. "Does Empagliflozin Modulate Leukocyte–Endothelium Interactions, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes?" Antioxidants 10, no. 8: 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081228
APA StyleCanet, F., Iannantuoni, F., Marañon, A. M. d., Díaz-Pozo, P., López-Domènech, S., Vezza, T., Navarro, B., Solá, E., Falcón, R., Bañuls, C., Morillas, C., Rocha, M., & Víctor, V. M. (2021). Does Empagliflozin Modulate Leukocyte–Endothelium Interactions, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes? Antioxidants, 10(8), 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081228