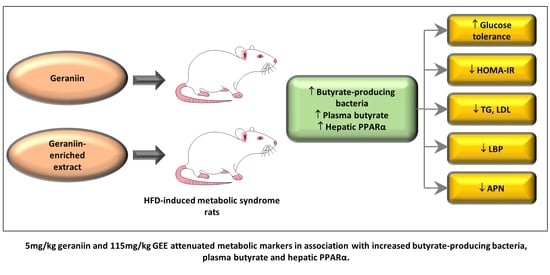
The Prebiotic Potential of Geraniin and Geraniin-Enriched Extract against High-Fat-Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Sprague Dawley Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Geraniin Enriched Extract (GEE) and Geraniin
2.2. Animal Study
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Lipid Profile
2.5. Glucose Homeostasis
2.6. Plasma Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein
2.7. Gene Expression
2.8. Plasma Adipocytokines
2.9. SCFAs Quantification in Plasma
2.10. DNA Extraction and 16 s rRNA Sequencing
2.11. Bioinformatics
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Geraniin and GEE Characterisation
3.2. Impact of Geraniin and GEE on Lipid Profile, Body Weight, Adiposity, and Energy Intake
3.3. Impact of Geraniin and GEE on Glucose Homeostasis
3.4. Influence of Geraniin and GEE on Metabolic Endotoxemia, Gene Expression, and Plasma Cytokines
3.5. Influence of Geraniin and GEE on Plasma Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production
3.6. Effect of Geraniin and GEE on Gut Microbiota Composition
3.7. Correlation between Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Parameters and Biomarkers
4. Discussion
Study limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NIH. Metabolic Syndrome. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/metabolic-syndrome (accessed on 16 January 2021).
- Mazloomzadeh, S.; Karami Zarandi, F.; Shoghli, A.; Dinmohammadi, H. Metabolic syndrome, its components and mortality: A population-based study. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran. 2019, 33, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiva-Blanch, G.; Badimon, L. Effects of Polyphenol Intake on Metabolic Syndrome: Current Evidences from Human Trials. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 5812401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Francisqueti, F.V.; Chiaverini, L.C.; Santos, K.C.; Minatel, I.O.; Ronchi, C.B.; Ferron, A.J.; Ferreira, A.L.; Correa, C.R. The role of oxidative stress on the pathophysiology of metabolic syndrome. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2017, 63, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boden, G.; Homko, C.; Barrero, C.A.; Stein, T.P.; Chen, X.; Cheung, P.; Fecchio, C.; Koller, S.; Merali, S. Excessive caloric intake acutely causes oxidative stress, GLUT4 carbonylation, and insulin resistance in healthy men. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 304re7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zatterale, F.; Longo, M.; Naderi, J.; Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Chronic Adipose Tissue Inflammation Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2020, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. Metabolic syndrome—A new world-wide definition. A consensus statement from the international diabetes federation. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pataky, Z.; Carrard, I.; Gay, V.; Thomas, A.; Carpentier, A.; Bobbioni-Harsch, E.; Golay, A. Effects of a Weight Loss Program on Metabolic Syndrome, Eating Disorders and Psychological Outcomes: Mediation by Endocannabinoids? Obes. Facts 2018, 11, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallappa, R.H.; Rokana, N.; Duary, R.K.; Panwar, H.; Batish, V.K.; Grover, S. Management of metabolic syndrome through probiotic and prebiotic interventions. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belizário, J.E.; Faintuch, J. Microbiome and gut dysbiosis. In Metabolic Interaction in Infection; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 459–476. [Google Scholar]
- Boulange, C.L.; Neves, A.L.; Chilloux, J.; Nicholson, J.K.; Dumas, M.E. Impact of the gut microbiota on inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, R.; Long, X.; Yang, J.; Du, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Hou, C. Pomegranate peel polyphenols reduce chronic low-grade inflammatory responses by modulating gut microbiota and decreasing colonic tissue damage in rats fed a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 8273–8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Ding, Z.; Ma, H.; Seeram, N.P.; Mu, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, L. Jamun (Eugenia jambolana Lam.) Fruit Extract Prevents Obesity by Modulating the Gut Microbiome in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1801370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthy, M.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Jacob, S.A.; Palanisamy, U.D. Prebiotic potential of polyphenols, its effect on gut microbiota and anthropometric/clinical markers: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J. 2-Polyphenols: Absorption, bioavailability, and metabolomics. In Polyphenols: Properties, Recovery, and Applications; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Swaston, UK, 2018; pp. 45–67. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.S.; Ton, S.H.; Abdul Kadir, K. Ellagitannin geraniin: A review of the natural sources, biosynthesis, pharmacokinetics and biological effects. Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 159–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitilertdecha, N.; Teerawutgulrag, A.; Kilburn, J.D.; Rakariyatham, N. Identification of major phenolic compounds from Nephelium lappaceum L. and their antioxidant activities. Molecules 2010, 15, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palanisamy, U.D.; Ling, L.T.; Manaharan, T.; Appleton, D. Rapid isolation of geraniin from Nephelium lappaceum rind waste and its anti-hyperglycemic activity. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.P.Y.S.; Ton, S.H.; Gurtu, S.; Palanisamy, U.D. Ellagitannin geraniin supplementation ameliorates metabolic risks in high-fat diet-induced obese Sprague Dawley rats. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 9, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phang, S.C.W.; Palanisamy, U.D.; Kadir, K.A. Effects of geraniin (rambutan rind extract) on blood pressure and metabolic parameters in rats fed high-fat diet. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 17, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.S.; Goh, B.H.; Phang, S.C.W.; Amanullah, M.M.; Ton, S.H.; Palanisamy, U.D.; Kadir, K.A.; Tan, J.B.L. Pleiotrosepic ameliorative effects of ellagitannin geraniin against metabolic syndrome induced by high-fat diet in rats. Nutrition 2020, 79–80, 110973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumita, E. Physicochemical Properties, Permeability and Bioavailability of Geraniin and Geraniin-Phospholipid Complex. Ph.D. Thesis, Monash University, Subang Jaya, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Palanisamy, U.; Cheng, H.M.; Masilamani, T.; Subramaniam, T.; Ling, L.T.; Radhakrishnan, A.K. Rind of the rambutan, Nephelium lappaceum, a potential source of natural antioxidants. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.; Khoo, J.J.; Palanisamy, U.D. Acute oral toxicity of the ellagitannin geraniin and a geraniin-enriched extract from Nephelium lappaceum L rind in Sprague Dawley rats. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Baere, S.; Eeckhaut, V.; Steppe, M.; De Maesschalck, C.; De Backer, P.; Van Immerseel, F.; Croubels, S. Development of a HPLC–UV method for the quantitative determination of four short-chain fatty acids and lactic acid produced by intestinal bacteria during in vitro fermentation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 80, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.2-0. 2014. Available online: http://cran.rproject.org/package=vegan (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- Fernandes, A.D.; Reid, J.N.; Macklaim, J.M.; McMurrough, T.A.; Edgell, D.R.; Gloor, G.B. Unifying the analysis of high-throughput sequencing datasets: Characterizing RNA-seq, 16S rRNA gene sequencing and selective growth experiments by compositional data analysis. Microbiome 2014, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, K.E.; Tucker, L.A.; Bailey, B.W.; LeCheminant, J.D. Expanded Normal Weight Obesity and Insulin Resistance in US Adults of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 9502643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaigne, D.; Butruille, L.; Staels, B. PPAR control of metabolism and cardiovascular functions. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Cousins, R.S.; Liu, S.; Phelps, B.M.; Promes, J.A. Connecting pancreatic islet lipid metabolism with insulin secretion and the development of type 2 diabetes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1461, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, L.V.; Aksenov, I.V.; Nikitin, N.S.; Guseva, G.V.; Avrenyeva, L.I.; Trusov, N.V.; Balakina, A.S.; Tutelyan, V.A. Lipoic Acid Exacerbates Oxidative Stress and Lipid Accumulation in the Liver of Wistar Rats Fed a Hypercaloric Choline-Deficient Diet. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Palanivel, R.; Rai, E.; Park, M.; Gabor, T.V.; Scheid, M.P.; Xu, A.; Sweeney, G. Adiponectin stimulates autophagy and reduces oxidative stress to enhance insulin sensitivity during high-fat diet feeding in mice. Diabetes 2015, 64, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perera, A.; Ton, S.H.; Moorthy, M.; Palanisamy, U.D. The insulin-sensitising properties of the ellagitannin geraniin and its metabolites from Nephelium lappaceum rind in 3T3-L1 cells. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 940–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, E.W.; Oliveira, D.C.; Hastreiter, A.; Silva, G.B.; Beltran, J.S.d.O.; Rogero, M.M.; Fock, R.A.; Borelli, P. Short-term high-fat diet affects macrophages inflammatory response, early signs of a long-term problem. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 55, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.M.; Campbell, F.M.; Drew, J.E.; Koch, C.; Hoggard, N.; Rees, W.D.; Kamolrat, T.; Thi Ngo, H.; Steffensen, I.-L.; Gray, S.R.; et al. The Development of Diet-Induced Obesity and Glucose Intolerance in C57Bl/6 Mice on a High-Fat Diet Consists of Distinct Phases. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muralidhar, M.; Prasad, S.; Kiran Kumar, B.; Giridharan, N.; Rajender Rao, K. Differential response of rat strains to obesogenic diets underlines the importance of genetic makeup of an individual towards obesity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porras, D.; Nistal, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Pisonero-Vaquero, S.; Olcoz, J.L.; Jover, R.; González-Gallego, J.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Protective effect of quercetin on high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice is mediated by modulating intestinal microbiota imbalance and related gut-liver axis activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 102, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.O.; Kuerban, A.; Alshehri, Z.A.; Abdulaal, W.H.; Khan, J.A.; Khan, M.I. Urolithins Attenuate Multiple Symptoms of Obesity in Rats Fed on a High-Fat Diet. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 3337–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polce, S.A.; Burke, C.; França, L.M.; Kramer, B.; Paes, A.M.D.A.; Carrillo-Sepulveda, M.A. Ellagic Acid Alleviates Hepatic Oxidative Stress and Insulin Resistance in Diabetic Female Rats. Nutrients 2018, 10, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosele, J.I.; Gosalbes, M.J.; Macia, A.; Rubio, L.; Vazquez-Castellanos, J.F.; Jimenez Hernandez, N.; Moya, A.; Latorre, A.; Motilva, M.J. Effect of daily intake of pomegranate juice on fecal microbiota and feces metabolites from healthy volunteers. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, S.; Avagliano, C.; Calignano, A.; Berni Canani, R. The protective role of butyrate against obesity and obesity-related diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, A.C.; Sweet, D.H.; Walle, T. Site-specific accumulation of the cancer preventive dietary polyphenol ellagic acid in epithelial cells of the aerodigestive tract. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Groups | Genus | Metabolic Marker/Gene | Correlation, r | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFD vs. HFD + 5 GE | Clostridium sensu stricto 13 | HOMA IR | −0.76 | 4.10 × 10−3 |
| FI | −0.743 | 5.70 × 10−3 | ||
| IL 6 gene (rWAT) | 0.583 | 0.046 | ||
| Candidatus Saccharimonas | IL 6 gene (rWAT) | −0.633 | 0.027 | |
| HFD vs. HFD + 50 GE | Christensenellaceae R 7 group | PPARα gene (L) | −0.651 | 0.022 |
| FI | 0.581 | 0.047 | ||
| IL 6 gene (rWAT) | −0.639 | 0.025 | ||
| NK4A214 group | PPARα gene (L) | −0.613 | 0.034 | |
| FI | 0.62 | 0.032 | ||
| IL 6 gene (rWAT) | −0.674 | 0.016 | ||
| HFD vs. HFD + GEE | Clostridia UCG 014 | Leptin | 0.636 | 0.026 |
| TG | 0.727 | 7.40 × 10−3 | ||
| Ruminococcus | FI | 0.685 | 0.014 | |
| Leptin | 0.594 | 0.042 | ||
| TG | 0.615 | 0.033 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moorthy, M.; Wie, C.C.; Mariño, E.; Palanisamy, U.D. The Prebiotic Potential of Geraniin and Geraniin-Enriched Extract against High-Fat-Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Sprague Dawley Rats. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040632
Moorthy M, Wie CC, Mariño E, Palanisamy UD. The Prebiotic Potential of Geraniin and Geraniin-Enriched Extract against High-Fat-Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Sprague Dawley Rats. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(4):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040632
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoorthy, Mohanambal, Chong Chun Wie, Eliana Mariño, and Uma D. Palanisamy. 2022. "The Prebiotic Potential of Geraniin and Geraniin-Enriched Extract against High-Fat-Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Sprague Dawley Rats" Antioxidants 11, no. 4: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040632
APA StyleMoorthy, M., Wie, C. C., Mariño, E., & Palanisamy, U. D. (2022). The Prebiotic Potential of Geraniin and Geraniin-Enriched Extract against High-Fat-Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Sprague Dawley Rats. Antioxidants, 11(4), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040632