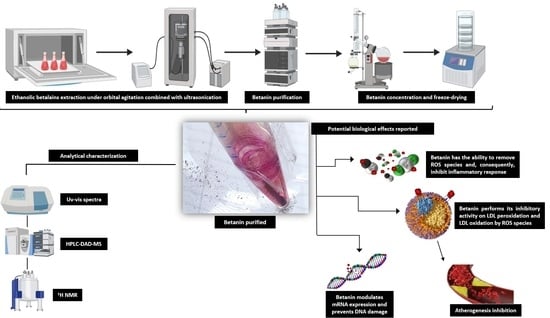
Combining Conventional Organic Solvent Extraction, Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction, and Chromatographic Techniques to Obtain Pure Betanin from Beetroot for Clinical Purposes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Betalains Extraction through Conventional and Ultrasonic Methods
2.2. Betanin Purification by Semi-Preparative Chromatography
2.3. Photometric Quantification and Comparative UV–Vis Spectra of Beet Samples
2.4. RP-HPLC Analysis and Betanin Identification by LC-ESI (+) MS
2.5. NMR Spectroscopy
2.6. Total Antioxidant Potential of Purified and Commercial Betanin
3. Results
3.1. Betalains Content and Efficiency of Conventional and Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Methods
3.2. RP-HPLC-DAD Profile of Beet-Derived Pigments and ESI(+)-MS of Purified Betanin
3.3. NMR Spectroscopy
3.4. Total Antioxidant Potential (TAP) of Purified Betanin and Commercial Betanin
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strack, D.; Vogt, T.; Schliemann, W. Recent advances in betalain research. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanner, J.; Harel, S.; Granit, R. Betalains—A new class of dietary cationized antioxidants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5178–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esatbeyoglu, T.; Wagner, A.E.; Schini-Kerth, V.B.; Rimbach, G. Betanin—A food colorant with biological activity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Code of Federal Regulations. 2009. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=73.260 (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific opinion on the re-evaluation of beetroot red (E 162) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.V.T.; Baião, D.S.; Silva, F.O.; Alves, G.; Perrone, D.; Mere Del Aguila, E.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Betanin, a Natural Food Additive: Stability, Bioavailability, Antioxidant and Preservative Ability Assessments. Molecules 2019, 24, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliszczyńska-Swigło, A.; Szymusiak, H.; Malinowska, P. Betanin, the main pigment of red beet: Molecular origin of its exceptionally high free radical-scavenging activity. Food Addit. Contam. 2006, 23, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska-Przyjemska, M.; Olejnik, A.; Kostrzewa, A.; Łuczak, M.; Jagodziński, P.P.; Baer-Dubowska, W. The beetroot component betanin modulates ROS production, DNA damage and apoptosis in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Paluszczak, J.; Szaefer, H.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Betanin, a beetroot component, induces nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2-mediated expression of detoxifying/antioxidant enzymes in human liver cell lines. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 2138–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.V.T.; Baião, D.D.S.; Ferreira, V.F.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Betanin as a multipath oxidative stress and inflammation modulator: A beetroot pigment with protective effects on cardiovascular disease pathogenesis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 62, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fernando, G.S.N.; Sergeeva, N.N.; Vagkidis, N.; Chechik, V.; Do, T.; Marshall, L.J.; Boesch, C. Uptake and Immunomodulatory Properties of Betanin, Vulgaxanthin I and Indicaxanthin towards Caco-2 Intestinal Cells. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesoriere, L.; Butera, D.; D’Arpa, D.; Di Gaudio, F.; Allegra, M.; Gentile, C.; Livrea, M.A. Increased resistance to oxidation of betalain-enriched human low-density lipoproteins. Free Rad. Res. 2003, 37, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiordelisi, A.; Iaccarino, G.; Morisco, C.; Coscioni, E.; Sorriento, D. NFkappaB is a Key Player in the Crosstalk between Inflammation and Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.V.T.; Pereira, A.D.; Boaventura, G.T.; Ribeiro, R.S.A.; Verícimo, M.A.; Carvalho-Pinto, C.E.; Baião, D.D.S.; Del Aguila, E.M.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Short-Term Betanin Intake Reduces Oxidative Stress in Wistar Rats. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Tan, D. Betanin attenuates paraquat-induced liver toxicity through a mitochondrial pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 70, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Tan, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Tan, D. Betanin reduces the accumulation and cross-links of collagen in high-fructose-fed rat heart through inhibiting non-enzymatic glycation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 227, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Wang, Y.; Bai, B.; Yang, X.; Han, J. Betanin attenuates oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction in kidney of paraquat-treated rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhananjayan, I.; Kathiroli, S.; Subramani, S.; Veerasamy, V. Ameliorating effect of betanin, a natural chromoalkaloid by modulating hepatic carbohydrate metabolic enzyme activities and glycogen content in streptozotocin—Nicotinamide induced experimental rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutariya, B.; Saraf, M. Betanin, isolated from fruits of Opuntia elatior Mill attenuates renal fibrosis in diabetic rats through regulating oxidative stress and TGF-β pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 198, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Chen, S.; Hua, F.; Bian, S.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Wu, X. Betanin Prevents Experimental Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Progression by Modulating the TLR4/NF-κB and Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, T.; Constantinou, C.M.; Keane, K.M.; West, D.J.; Howatson, G.; Stevenson, E.J. The plasma bioavailability of nitrate and betanin from Beta vulgaris rubra in humans. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedimanesh, N.; Asghari, S.; Mohammadnejad, K.; Daneshvar, Z.; Rahmani, S.; Shokoohi, S.; Farzaneh, A.H.; Hosseini, S.H.; Jafari Anarkooli, I.; Noubarani, M.; et al. The anti-diabetic effects of betanin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through modulating AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, H.; Nayeri, Z.; Minuchehr, Z.; Sabouni, F.; Mohammadi, M. Betanin purification from red beetroots and evaluation of its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity on LPS-activated microglial cells. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbach, K.M.; Stintzing, F.; Carle, R. Betalain Stability and Degradation—Structural and Chromatic Aspects. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, R41–R50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I. Stabilization of betalains: A review. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aztatzi-Rugerio, L.; Granados-Balbuena, S.Y.; Zainos-Cuapio, Y.; Ocaranza-Sánchez, E.; Rojas-López, M. Analysis of the degradation of betanin obtained from beetroot using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 3677–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R. Analysis of Betalains. In Food Colorants: Chemical and Functional Properties, 1st ed.; Carmen Socaciu: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; p. 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Ugarte, G.A.; Sosa-Morales, M.E.; Ballard, T.; Liceaga, A.; San Martín-González, M.F. Microwave-assisted extraction of betalains from red beet (Beta vulgaris). LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Shi, J.; Xie, S.Y.; Zhang, T.Y.; Soladoye, O.P.; Aluko, R.E. Red Beetroot Betalains: Perspectives on Extraction, Processing, and Potential Health Benefits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11595–11611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumorkiewicz, A.; Szmyr, N.; Popenda, L.; Pietrzkowski, Z.; Wybraniec, S. Alternative Mechanisms of Betacyanin Oxidation by Complexation and Radical Generation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7455–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, G.S.N.; Wood, K.; Papaioannou, E.H.; Marshall, L.J.; Sergeeva, N.N.; Boesch, C. Application of an Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Method to Recover Betalains and Polyphenols from Red Beetroot Waste. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 8736–8747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusznierewicz, B.; Mróz, M.; Koss-Mikołajczyk, I.; Namieśnik, J. Comparative evaluation of different methods for determining phytochemicals and antioxidant activity in products containing betalains—Verification of beetroot samples. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stintzing, F.C.; Schieber, A.; Carle, R. Evaluation of colour properties and chemical quality parameters of cactus juices. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2003, 216, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatnar, A.; Stampar, F.; Veberic, R.; Jakopic, J. HPLC-MS(n) Identification of Betalain Profile of Different Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L. ssp. vulgaris) Parts and Cultivars. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C1952–C1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.V.; Silva, F.d.O.; Perrone, D.; Pierucci, A.P.; Conte, C.A., Jr.; Alvares, T.d.S.; Aguila, E.M.; Paschoalin, V.M. Physicochemical, nutritional, and sensory analyses of a nitrate-enriched beetroot gel and its effects on plasmatic nitric oxide and blood pressure. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 29909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouairi, M.E.; Freha, M.; Bellil, A. Study by absorption and emission spectrophotometry of the efficiency of the binary mixture (Ethanol-Water) on the extraction of betanin from red beetroot. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 260, 119939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, L.C.P.; Trassi, M.A.S.; Lopes, N.B.; Dorr, F.A.; dos Santos, M.T.; Baader, W.J.; Oliveira, V.X., Jr.; Bastos, E.L. A comparative study of the purification of betanin. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, H.R.P.; da Silva, C.; Bolanho, B.C. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of betalains from red beet (Beta vulgaris L.). J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roriz, C.L.; Barros, L.; Prieto, M.A.; Barreiro, M.F.; Morales, P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Modern extraction techniques optimized to extract betacyanins from Gomphrena globosa L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 105, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeredo, H.M.C. Betalains: Properties, sources, applications, and stability—A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 44, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Giridhar, P. Enhanced chemical stability, chromatic properties and regeneration of betalains in Rivina humilis L. berry juice. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 58, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, P.; Bendiak, B.; Clowers, B.H.; Hill, H.H., Jr. Rapid resolution of carbohydrate isomers by electrospray ionization ambient pressure ion mobility spectrometry-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ESI-APIMS-TOFMS). J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 18, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, Y.; Qayyum, A.; Nisa, S.; Waheed, A.; Chaudhary, M.F. Isolation Studies from Stem Extract of Pistacia Integerrima Stew. Ex Brand. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2016, 61, 2916–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvano, C.D.; Cataldi, T.R.I.; Kögel, J.F. Structural Characterization of Neutral Saccharides by Negative Ion MALDI Mass Spectrometry Using a Superbasic Proton Sponge as Deprotonating Matrix. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 28, 1666–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gass, D.T.; Quintero, A.V.; Hatvany, J.B.; Gallagher, E.S. Metal adduction in mass spectrometric analyses of carbohydrates and glycoconjugates. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2022, e21801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutor-Świeży, K.; Antonik, M.; Proszek, J.; Nemzer, B.; Pietrzkowski, Z.; Popenda, Ł.; Świergosz, T.; Wybraniec, S. Dehydrogenation of Betacyanins in Heated Betalain-Rich Extracts of Red Beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbach, K.M.; Stintzing, F.; Carle, R. Thermal degradation of betacyanins in juices from purple pitaya [Hylocereus polyrhizus (Weber) Britton & Rose] monitored by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectometric analyses. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2004, 219, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wybraniec, S. Formation of decarboxylated betacyanins in heated purified betacyanin fractions from red beet root (Beta vulgaris L.) monitored by LC-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3483–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wybraniec, S.; Mizrahi, Y. Generation of decarboxylated and dehydrogenated betacyanins in thermally treated purified fruit extract from purple pitaya (Hylocereus polyrhizus) monitored by LC-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6704–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska-Bartosz, I.; Bartosz, G. Biological Properties and Applications of Betalains. Molecules 2021, 26, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.D.; Rosser, A.A.; Fellows, C.M.; Guillaneuf, Y.; Clement, J.L.; Gaborieau, M.; Castignolles, P. Understanding and improving direct UV detection of monosaccharides and disaccharides in free solution capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 809, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaijanen, L.; Paakkunainen, M.; Pietarinen, S.; Jernstrom, E.; Reinikainen, S.T. Ultraviolet Detection of Monosaccharides: Multiple Wavelength Strategy to Evaluate Results after Capillary Zone Electrophoretic Separation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 2950–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patyra, E.; Kwiatek, K. Comparison of HPLC–DAD and LC–MS Techniques for the Determination of Tetracyclines in Medicated Feeds Using One Extraction Protocol. Chromatographia 2021, 84, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, G.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Hu, X. Different effects of microwave and ultrasound on the stability of (all-E)-astaxanthin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8346–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzah, C.S.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Ma, H. The effects of ultrasound assisted extraction on yield, antioxidant, anticancer and antimicrobial activity of polyphenol extracts: A review. Food Biosci. 2020, 35, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stintzing, F.C.; Conrad, J.; Klaiber, I.; Beifuss, U.; Carle, R. Structural investigations on betacyanin pigments by LC NMR and 2D NMR spectroscopy. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, L.C.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Pioli, R.M.; Penna, T.C.; Baader, W.J.; Correra, T.C.; Bastos, E.L. Revisiting the Mechanism of Hydrolysis of Betanin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas-Dörr, B.C.; Machado, C.O.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Fernandes, A.B.; Dörr, F.A.; Pinto, E.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Abdellah, M.; Sá, J.; Bastos, E.L. A metal-free blue chromophore derived from plant pigments. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz0421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampaoli, O.; Sciubba, F.; Conta, G.; Capuani, G.; Tomassini, A.; Giorgi, G.; Brasili, E.; Aureli, W.; Miccheli, A. Red Beetroot’s NMR-Based Metabolomics: Phytochemical Profile Related to Development Time and Production Year. Foods 2021, 10, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głód, B.K.; Piszcz, P.; Czajka, K.; Zarzycki, P.K. A New Total Antioxidant Potential Measurements Using RP-HPLC Assay with Fluorescence Detection. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2011, 49, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical Methods Used in Determining Antioxidant Activity: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Red Beet Powder | Betalain Pool | Purified Betanin | Commercial Betanin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Betacyanins (mg/g) | 4.26 ± 0.12 | 3.50 ± 0.09 | 1.74 ± 0.01 * | 1.79 ± 0.20 |
| Betaxanthins (mg/g) | 3.11 ± 0.02 | 2.89 ± 0.01 | - | 0.84 ± 0.12 |
| Betacyanins yield (%) | - | 86% | 41% | - |
| Betaxanthins yield (%) | - | 92.8% | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Da Silva, D.V.T.; Baião, D.d.S.; Magalhães, A.; Almeida, N.F.; Conte, C.A., Jr.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Combining Conventional Organic Solvent Extraction, Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction, and Chromatographic Techniques to Obtain Pure Betanin from Beetroot for Clinical Purposes. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12101823
Da Silva DVT, Baião DdS, Magalhães A, Almeida NF, Conte CA Jr., Paschoalin VMF. Combining Conventional Organic Solvent Extraction, Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction, and Chromatographic Techniques to Obtain Pure Betanin from Beetroot for Clinical Purposes. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(10):1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12101823
Chicago/Turabian StyleDa Silva, Davi Vieira Teixeira, Diego dos Santos Baião, Alviclér Magalhães, Nathan Farias Almeida, Carlos Adam Conte, Jr., and Vania Margaret Flosi Paschoalin. 2023. "Combining Conventional Organic Solvent Extraction, Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction, and Chromatographic Techniques to Obtain Pure Betanin from Beetroot for Clinical Purposes" Antioxidants 12, no. 10: 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12101823
APA StyleDa Silva, D. V. T., Baião, D. d. S., Magalhães, A., Almeida, N. F., Conte, C. A., Jr., & Paschoalin, V. M. F. (2023). Combining Conventional Organic Solvent Extraction, Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction, and Chromatographic Techniques to Obtain Pure Betanin from Beetroot for Clinical Purposes. Antioxidants, 12(10), 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12101823