Chronodisruption and Loss of Melatonin Rhythm, Associated with Alterations in Daily Motor Activity and Mitochondrial Dynamics in Parkinsonian Zebrafish, Are Corrected by Melatonin Treatment
Abstract
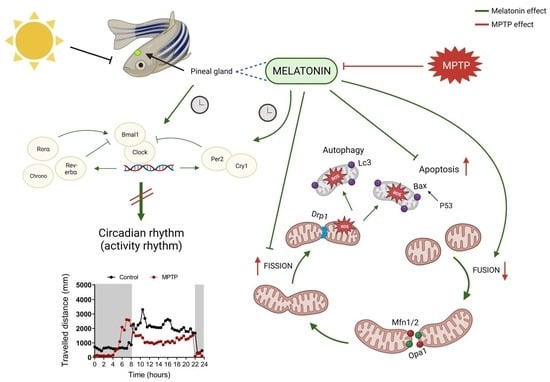
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Maintenance
2.2. Treatments
2.3. Activity Rhythm
2.4. Determination of Melatonin Concentration
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. Circadian Rhythm Analysis of the Clock Genes Expression
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MPTP Blunts the Day/Night Melatonin Rhythm, and It Is Restored by Melatonin Treatment
3.2. Melatonin Restores the Motor Activity Rhythm Disrupted by MPTP
3.3. MPTP Changes in Circadian Rhythms of Clock Genes Are Normalized after Melatonin Treatment
3.4. Changes in the Acrophase of Clock Genes Rhythms in Zebrafish Embryos Due to MPTP and/or aMT Treatments
3.5. Changes in the Mesor of Clock Genes Rhythm in Zebrafish Embryos due to MPTP and/or aMT Treatments
3.6. Changes in the Amplitude of Clock Genes Rhythm in Zebrafish Embryos Due to MPTP and/or aMT Treatments
3.7. Parkinsonian Zebrafish Had Impaired Mitochondrial Dynamics
3.8. MPTP Administration Altered Apoptosis and Autophagy Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mantovani, S.; Smith, S.S.; Gordon, R.; O’sullivan, J.D. An Overview of Sleep and Circadian Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Sleep Res. 2018, 27, e12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.G.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Caselli, R.J.; Parish, J.M.; Wingerchuk, D.M. “Idiopathic” Rapid-Eye-Movement (REM) Sleep Behavior Disorder Is Associated with Future Development of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neurologist 2007, 13, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowers, J.R.; Vlachakis, N. Circadian Variation in Plasma Dopamine Levels in Man. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 1984, 7, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordet, R.; Devos, D.; Brique, S.; Touitou, Y.; Guieu, J.D.; Libersa, C.; Destée, A. Study of Circadian Melatonin Secretion Pattern at Different Stages of Parkinson’s Disease. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2003, 26, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonuccelli, U.; Del Dotto, P.; Lucetti, C.; Petrozzi, L.; Bernardini, S.; Gambaccini, G.; Rossi, G.; Piccini, P. Diurnal Motor Variations to Repeated Doses of Levodopa in Parkinson’s Disease. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2000, 23, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacksteder, R.E.; Kimmey, J.M. Immunity, Infection, and the Zebrafish Clock. Infect. Immun. 2022, 90, e0058821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, G.M. Clock Mechanisms in Zebrafish. Cell Tissue Res. 2002, 309, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goriki, A.; Hatanaka, F.; Kim, M.J.; Yoritaka, J.K. A Novel Protein, CHRONO, Functions as a Core Component of the Mammalian Circadian Clock. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, 1001839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anafi, R.C.; Lee, Y.; Sato, T.K.; Venkataraman, A.; Ramanathan, C. Machine Learning Helps Identify CHRONO as a Circadian Clock Component. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, 1001840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, M.H.; Maywood, E.S.; Brancaccio, M. Generation of Circadian Rhythms in the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Cabello, E.; Díaz-Casado, M.E.; Guerrero, J.A.; Otalora, B.B.; Escames, G.; Lõpez, L.C.; Reiter, R.J.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. A Review of the Melatonin Functions in Zebrafish Physiology. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda-martínez, P.; Fernández-martínez, J.; Ramírez-casas, Y.; Guerra-librero, A.; Rodríguez-santana, C.; Escames, G.; Acuña-castroviejo, D. The Zebrafish, an Outstanding Model for Biomedical Research in the Field of Melatonin and Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Feng, D.; Feng, X. Melatonin Mitigated Circadian Disruption and Cardiovascular Toxicity Caused by 6-Benzylaminopurine Exposure in Zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genario, R.; Giacomini, A.C.V.V.; Demin, K.A.; dos Santos, B.E.; Marchiori, N.I.; Volgin, A.D.; Bashirzade, A.; Amstislavskaya, T.G.; de Abreu, M.S.; Kalueff, A.V. The Evolutionarily Conserved Role of Melatonin in CNS Disorders and Behavioral Regulation: Translational Lessons from Zebrafish. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 99, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Escames, G.; Leon, L.; Carazo, A.; Khaldy, H. Mitochondrial regulation by melatonin and its metabolites. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2003, 527, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Casado, M.E.; Lima, E.; García, J.A.; Doerrier, C.; Aranda, P.; Sayed, R.K.A.; Guerra-Librero, A.; Escames, G.; López, L.C.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin Rescues Zebrafish Embryos from the Parkinsonian Phenotype Restoring the Parkin/PINK1/DJ-1/MUL1 Network. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Casado, M.E.; Rusanova, I.; Aranda, P.; Fernández-Ortiz, M.; Sayed, R.K.A.; Fernández-Gil, B.I.; Hidalgo-Gutiérrez, A.; Escames, G.; López, L.C.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. In Vivo Determination of Mitochondrial Respiration in 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine-Treated Zebrafish Reveals the Efficacy of Melatonin in Restoring Mitochondrial Normalcy. Zebrafish 2018, 15, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. In A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio); University Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Videnovic, A.; Golombek, D. Circadian Dysregulation in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol. Sleep Circadian Rhythm. 2017, 2, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, A.A.; Chakravarthy, S.; Phillips, J.R.; Gupta, A.; Keri, S.; Polner, B.; Frank, M.J.; Jahanshahi, M. Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease: A Unified Framework. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 68, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipson, O.T. Alpha-Synuclein, Epigenetics, Mitochondria, Metabolism, Calcium Traffic, & Circadian Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. An Integrated Strategy for Management. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 40, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrima, R.; Cela, O.; Merla, G.; Augello, B.; Rubino, R.; Quarato, G.; Fugetto, S.; Menga, M.; Fuhr, L.; Relógio, A.; et al. Clock-Genes and Mitochondrial Respiratory Activity: Evidence of a Reciprocal Interplay. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2016, 1857, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Abraham, N.; Gao, G.; Yang, Q. Dysregulation of Autophagy and Mitochondrial Function in Parkinson’s Disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2016, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Moshe Livne, Z.; Alon, S.; Vallone, D.; Bayleyen, Y.; Tovin, A.; Shainer, I.; Nisembaum, L.G.; Aviram, I.; Smadja-Storz, S.; Fuentes, M.; et al. Genetically Blocking the Zebrafish Pineal Clock Affects Circadian Behavior. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basti, A.; Fior, R.; Yalçin, M.; Póvoa, V.; Astaburuaga, R.; Li, Y.; Naderi, J.; Godinho Ferreira, M.; Relógio, A. The Core-Clock Gene NR1D1 Impacts Cell Motility In Vitro and Invasiveness in A Zebrafish Xenograft Colon Cancer Model. Cancers 2020, 12, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, D.; Tian, C.; Hu, B. Circadian Genes Period1b and Period2 Differentially Regulate Inflammatory Responses in Zebrafish. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 77, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alifu, Y.; Kofuji, S.; Sunaga, S.; Kusaba, M.; Hirayama, J.; Nishina, H. The Light-Inducible Genes Per2, Cry1a, and Cry2a Regulate Oxidative Status in Zebrafish. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, F.; Ye, Q.; Wang, H. The Circadian Clock Regulates Autophagy Directly through the Nuclear Hormone Receptor Nr1d1/Rev-Erbα and Indirectly via Cebpb/(C/Ebpβ) in Zebrafish. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1292–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, P.; Hajny, S.; Mekis, R.; Orel, L.; Dinhopl, N.; Tessmar-Raible, K.; Nowikovsky, K. The Cation Exchanger Letm1, Circadian Rhythms, and NAD(H) Levels Interconnect in Diurnal Zebrafish. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, e202101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaldy, H.; Escames, G.; León, J.; Bikjdaouene, L.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Synergistic Effects of Melatonin and Deprenyl against MPTP-Induced Mitochondrial Damage and DA Depletion. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaldy, H.; León, J.; Escames, G.; Bikjdaouene, L.; García, J.J.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Circadian Rhythms of Dopamine and Dihydroxyphenyl Acetic Acid in the Mouse Striatum: Effects of Pinealectomy and of Melatonin Treatment. Neuroendocrinology 2002, 75, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, A.C.V.V.; Teixeira, K.H.; Marcon, L.; Scolari, N.; Bueno, B.W.; Genario, R.; de Abreu, N.S.; Demin, K.A.; Galstyan, D.S.; Kalueff, A.; et al. Melatonin Treatment Reverses Cognitive and Endocrine Deficits Evoked by a 24-h Light Exposure in Adult Zebrafish. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 733, 135073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HURD, M.; DEBRUYNE, J.; STRAUME, M.; CAHILL, G. Circadian Rhythms of Locomotor Activity in Zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 1998, 65, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, K.; Mohd Nasir, M.H.; Othman, N.; Doolaanea, A.A.; Kumar, J.; Nabeel Ibrahim, W.; Mohamed, W.M.Y. Characterization of Neurobehavioral Pattern in a Zebrafish 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-Induced Model: A 96-Hour Behavioral Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Rahim, I.; Acuña-Fernández, C.; Fernández-Ortiz, M.; Solera-Marín, J.; Sayed, R.K.; Díaz-Casado, M.E.; Rusanova, I.; López, L.C.; Escames, G. Melatonin, Clock Genes and Mitochondria in Sepsis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3965–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanova, I.V.; Wang, S.Y.; Leclair, O.U.; Danilova, N.P. Melatonin Promotes Sleep-like State in Zebrafish. Brain Res. 2001, 903, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Ruan, Y.; Yan, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xue, N.; Yan, Y.; Tian, J.; Yin, X.; Pu, J.; Zhang, B. Melatonin Attenuates Neuroinflammation by Down-Regulating NLRP3 Inflammasome via a SIRT1-Dependent Pathway in MPTP-Induced Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, F.B.; Ozsoy, O.; Tanriover, G.; Kaya, Y.; Ogut, E.; Gemici, B.; Dilmac, S.; Ozkan, A.; Agar, A.; Aslan, M. Mechanism of the Beneficial Effect of Melatonin in Experimental Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 79, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavithra, S.; Selvakumar, K.; Sundareswaran, L.; Arunakaran, J. Neuroprotective Effect of Melatonin Against PCBs Induced Behavioural, Molecular and Histological Changes in Cerebral Cortex of Adult Male Wistar Rats. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongjie, S.; Rajendran, R.S.; Xia, Q.; She, G.; Tu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, K. Neuroprotective Effects of Tongtian Oral Liquid, a Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Parkinson’s Disease-Induced Zebrafish Model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Yin, S.; Wan, F.; Hu, J.; Kou, L.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, J.; et al. Targeting Microglial α-Synuclein/TLRs/NF-KappaB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Axis in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 719807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyn, M.; Ekker, M. Cerebroventricular Microinjections of MPTP on Adult Zebrafish Induces Dopaminergic Neuronal Death, Mitochondrial Fragmentation, and Sensorimotor Impairments. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 718244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Lin, J.; Liu, Y.; Hua, B.; Cheng, Q.; Lin, C.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, N.; Qian, R.; et al. CLOCK Regulates Drp1 MRNA Stability and Mitochondrial Homeostasis by Interacting with PUF60. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, K.; Grimm, A.; Dallmann, R.; Oettinghaus, B.; Restelli, L.M.; Witzig, M.; Ishihara, N.; Mihara, K.; Ripperger, J.A.; Albrecht, U.; et al. Circadian Control of DRP1 Activity Regulates Mitochondrial Dynamics and Bioenergetics. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 657–666.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, L.; Chi, X.; Sun, Y.; Han, C.; Wan, F.; Hu, J.; Yin, S.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. The Circadian Clock Protein Rev-Erbα Provides Neuroprotection and Attenuates Neuroinflammation against Parkinson’s Disease via the Microglial NLRP3 Inflammasome. J. Neuroinflammation 2022, 19, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jang, S.; Choi, M.; Chung, S.; Choe, Y.; Choe, H.K.; Son, G.H.; Rhee, K.; Kim, K. Abrogation of the Circadian Nuclear Receptor REV-ERBα Exacerbates 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Gene | Accession Number | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| bmal1 | NM_131577 | AGGGCAGCACCACTGAATAC | TCCCTTCCCAGTGTCTTGTC |
| clock | NM_130957 | GCAAACATCCAGAGACAGCA | ACTCGGCTGCAGAAACATCT |
| per2 | NM_182857 | AGGCTTTGGGGAAAGTCAAT | GCAGAATATGGCGTCTGGAT |
| cry1 | NM_001077297 | CACGCTCTACGATCTGGACA | GGAAGCGCTTATACGTGAGC |
| rorα | NM_001110167 | TCGACCCTCAGAACAACACA | CCCAAACTCGAAGACAGAGC |
| rev-erbα | NM_200647 | CCTCCCAAACACCTGAAAAA | CGCTGTTCATCTCTTGTCCA |
| chrono | NM_001327898 | CGGTTGTGGAGGTAGCATTT | GTGCTACAATGGCCGACTTT |
| mfn1 | NM_200647 | AACGAAGTGTGCTCTGCTCA | GGATTCAGAGTTCGCCACCA |
| mfn2 | NM_001128254 | ACACATTTGCCACCTCTTCC | AGGCACGTGAGAGCCTAAAA |
| opa1 | NM_001007298 | AGACTGGAAGCAGAGGTGGA | GGAAGTGACGTCGAAAGAGC |
| drp1 | NM_200922 | AACATCCAGGACAGCGTACC | TCACCACAAGTGCGTCTCTC |
| dyn2 | NM_200099 | CGCAGATAGCAGTTGTCGGA | TCTGCTTCAATCTCCTGCCG |
| bax | NM_131562 | AACTGGGGAAGAGTTGTGGC | GGGTGCCAAAATAACTGCGG |
| bcl-2 | NM_001030253 | CGAGTTTGGTGGGACCATGT | CGTACATCTCCACGAAGGCA |
| p53 | NM_001271820 | GAATCCCCAAAACTCCACGC | GGATGGCTGAGGCTGTTCTT |
| lc3 | NM_199604 | GGAGAGAAGCAACTGCCGAT | CCTGATTGGATGGGGAAGGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aranda-Martínez, P.; Fernández-Martínez, J.; Ramírez-Casas, Y.; Rodríguez-Santana, C.; Rusanova, I.; Escames, G.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Chronodisruption and Loss of Melatonin Rhythm, Associated with Alterations in Daily Motor Activity and Mitochondrial Dynamics in Parkinsonian Zebrafish, Are Corrected by Melatonin Treatment. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040954
Aranda-Martínez P, Fernández-Martínez J, Ramírez-Casas Y, Rodríguez-Santana C, Rusanova I, Escames G, Acuña-Castroviejo D. Chronodisruption and Loss of Melatonin Rhythm, Associated with Alterations in Daily Motor Activity and Mitochondrial Dynamics in Parkinsonian Zebrafish, Are Corrected by Melatonin Treatment. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(4):954. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040954
Chicago/Turabian StyleAranda-Martínez, Paula, José Fernández-Martínez, Yolanda Ramírez-Casas, César Rodríguez-Santana, Iryna Rusanova, Germaine Escames, and Darío Acuña-Castroviejo. 2023. "Chronodisruption and Loss of Melatonin Rhythm, Associated with Alterations in Daily Motor Activity and Mitochondrial Dynamics in Parkinsonian Zebrafish, Are Corrected by Melatonin Treatment" Antioxidants 12, no. 4: 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040954
APA StyleAranda-Martínez, P., Fernández-Martínez, J., Ramírez-Casas, Y., Rodríguez-Santana, C., Rusanova, I., Escames, G., & Acuña-Castroviejo, D. (2023). Chronodisruption and Loss of Melatonin Rhythm, Associated with Alterations in Daily Motor Activity and Mitochondrial Dynamics in Parkinsonian Zebrafish, Are Corrected by Melatonin Treatment. Antioxidants, 12(4), 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040954