Artemisia gmelinii Extract Attenuates Particulate Matter-Induced Neutrophilic Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Lung Injury
Abstract
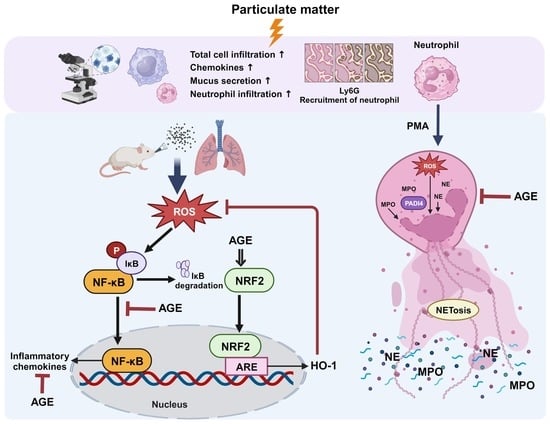
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Preparation of PM
2.1.2. Plant Material and Preparation of Extracts
2.2. Animal Study
2.2.1. PM-Induced Lung Injury Mouse Model and Experimental Design
2.2.2. Analysis of Chemokines in BALF
2.2.3. Analysis of the Infiltration Cell Counts and Diff-Quick Stain in BALF
2.2.4. Histological Analysis and Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining of the Lung Tissues
2.2.5. Western Blot
2.3. HL-60 Cell Experiment
2.3.1. Cell Culture and Differentiation
2.3.2. Cell Viability
2.3.3. NETosis Assay
2.3.4. ROS Production Assay
2.3.5. Visualization of NETs
2.3.6. Visualization of Cytosolic ROS Production
2.3.7. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of AGE in the PM-Induced Lung Injury Mouse Model
3.2. Effect of AGE on the Protein Expression in PM-Stimulated Lung Tissues
3.3. Effect of AGE on Histopathologic Analysis of the PM-Stimulated Lung Tissues
3.4. Effect of AGE on NETs Released from dHL-60 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AG | Artemisia gmelinii Weber ex Stechm |
| AGE | Artemisia gmelinii Weber ex Stechm ethanol extract |
| ALI | Acute lung injury |
| BALF | Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| CS | Cigarette smoke |
| CSE | Cigarette smoke extract |
| CXCL-1 | C-X- motif chemokine ligand 1 |
| CXCR-1 | C-X-C Motif chemokine receptor 1 |
| CXCR-2 | C-X-C Motif chemokine receptor 2 |
| CXCR-4 | C-X-C Motif chemokine receptor 4 |
| CX3CR-1 | C-X3-C Motif chemokine receptor 1 |
| DAB | 3,3′-diaminobenzidine |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidine-2′-phenylindole dihydrochloride |
| dHL-60 | Differentiated HL-60 |
| DHR123 | Dihydrorhodamine 123 |
| HBSS | Hank’s balanced salt solution |
| HMGB1 | High mobility group box 1 |
| HO-1 | Heme Oxygenase-1 |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| ITGAL | Integrin Alpha L |
| KLF6 | Kruppel-like factor 6 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| MIP-1α | Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1α |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| NE | Neutrophil elastase |
| NETs | Neutrophil extracellular traps |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NIST | National Institute of Standard and Technology |
| NRF2 | Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 |
| PADI4 | Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4 |
| PAHs | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| PAS | Periodic acid–Schiff |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PM | Particulate matter |
| PMA | Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate |
| RANTES | Regulated on activation, Normal T cell Expressed and Secreted |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RUNX1 | Run-related transcription factor 1 |
| TARC | Thymus and Activation-Regulated Chemokine |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WST-1 | Water-Soluble Tetrazolium 1 |
References
- World Health Organization. WHO’s global air-quality guidelines. Lancet 2006, 368, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexeeff, S.E.; Liao, N.S.; Liu, X.; Van Den Eeden, S.K.; Sidney, S. Long-Term PM(2.5) Exposure and Risks of Ischemic Heart Disease and Stroke Events: Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, 016890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Sera, F.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Guo, Y.; Tong, S.; Coelho, M.S.Z.S.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Lavigne, E.; Matus, P.; et al. Ambient particulate air pollution and daily mortality in 652 cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.F.; Xu, Y.H.; Shi, M.H.; Lian, Y.X. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Goshua, A.; Akdis, C.A.; Nadeau, K.C. World Health Organization global air quality guideline recommendations: Executive summary. Allergy 2022, 77, 1955–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, A.; Ran, Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Niu, B.; Liu, S.; Li, G. PM2.5 aggravates NQO1-induced mucus hyper-secretion through release of neutrophil extracellular traps in an asthma model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 218, 112272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhong, T.; Zhu, Y.; Ge, D.; Lin, X.; Li, Q. Effects of particulate matter (PM) on childhood asthma exacerbation and control in Xiamen, China. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, J. Role of PM2.5 in the development and progression of COPD and its mechanisms. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, W.; Feng, F.; Qin, L.; Ji, W.; Li, D.; Liang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; et al. Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in fine particulate matter-induced acute lung injury. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, C.; Yan, W.; Luo, A.; Wu, T.; Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; et al. Ovarian dysfunction induced by chronic whole-body PM2.5 exposure. Small 2020, 16, 2000845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V. Pulmonary innate immune response determines the outcome of inflammation during pneumonia and sepsis-associated acute lung injury. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, W.M.T.; Zhang, L.; Schuiki, I.; Curi, R.; Volchuk, A.; Alba-Loureiro, T.C. NADPH oxidase-dependent production of reactive oxygen species induces endoplasmatic reticulum stress in neutrophil-like HL60 cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, A.; Shelver, W.L. Micro- and nanoplastic induced cellular toxicity in mammals: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masucci, M.T.; Minopoli, M.; Del Vecchio, S.; Carriero, M.V. The emerging role of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in tumor progression and metastasis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.-K.; Lee, H.O.; Park, H.-S.; Lee, S.-C.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, T.J.; Sung, S.H.; Yang, T.-J. The complete chloroplast genome sequences of Artemisia gmelinii andArtemisia capillaris (Asteraceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2016, 1, 410–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhigzhitzhapova, S.V.; Namzalov, B.-T.B.; Radnaeva, L.D. Composition of Essential Oil of Artemisia gmelinii Web. ex Stechm. of Priolkhonian Flora (Lake Baikal). Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2021, 14, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Maurya, A.K.; Waza, A.A.; Agnihotri, V.K.; Shah, W.A. Chemical composition, antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of Artemisia gmelinii essential oil growing wild in Kashmir valley. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 3289–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Vetrivel, P.; Kim, H.H.; Ha, S.E.; Venkatarame Gowda Saralamma, V.; Kim, G.S. Artemisia iwayomogi (Dowijigi) inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 macrophages by suppressing the NF κB signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 2161–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, C.-H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Eun, J.-S.; Shin, T.-Y. Anti-allergic effects of artemisia iwayomogi on mast cell-mediated allergy model. Exp. Biol. Med. 2005, 230, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Shin, D.U.; Eom, J.E.; Jung, S.Y.; Song, H.J.; Lim, K.M.; Kim, G.D.; Yun, S.I.; Kim, M.Y.; Shin, H.S.; et al. Artemisia gmelinii attenuates lung inflammation by suppressing the NF-κB/MAPK pathway. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Norris, C.; Cui, X.; Li, Z.; Barkjohn, K.K.; Brehmer, C.; Teng, Y.; Fang, L.; Lin, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Personal exposure to PM2.5 oxidative potential is associated with pulmonary pathophysiological outcomes in children with asthma. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3101–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valderrama, A.; Ortiz-Hernández, P.; Agraz-Cibrián, J.M.; Tabares-Guevara, J.H.; Gómez, D.M.; Zambrano-Zaragoza, J.F.; Taborda, N.A.; Hernandez, J.C. Particulate matter (PM10) induces in vitro activation of human neutrophils, and lung histopathological alterations in a mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenda, A.; Rousseau, S. P38 MAP-Kinases pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1358–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Sig. Transduct Target Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kwon, O.-K.; Kim, J.-H.; Oh, S.-R.; Han, S.-B.; Park, J.-W.; Ahn, K.-S. Purpurin suppresses atopic dermatitis via TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced inflammation in HaCaT cells. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2022, 36, 946320221111135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xing, Q.; Duan, H.; Qin, G.; Sang, N. Suppression of NADPH oxidase 4 inhibits PM2.5-induced cardiac fibrosis through ROS-P38 MAPK pathway. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, C.A.; Baker, K.J.; McCaffrey, A.; AuCoin, D.P.; Dechert, M.A.; Gerthoffer, W.T. p38 MAPK and NF-κB mediate COX-2 expression in human airway myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, L1087–L1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Xia, W.; Li, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, A. COX-2 mediates PM2.5-induced apoptosis and inflammation in vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 3967–3976. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Guo, L.; Ku, T.; Chen, M.; Li, G.; Sang, N. PM2.5 exposure stimulates COX-2-mediated excitatory synaptic transmission via ROS-NF-κB pathway. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Zu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Shou, Q.; Ding, Z. PM2.5 exposure induces inflammatory response in macrophages via the TLR4/COX-2/NF-κB pathway. Inflammation 2020, 43, 1948–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdis, A.; Colucci, R.; Fornai, M.; Blandizzi, C.; Duranti, E.; Pinto, S.; Bernardini, N.; Segnani, C.; Antonioli, L.; Taddei, S.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition improves vascular endothelial dysfunction in a rat model of endotoxic shock: Role of inducible nitric-oxide synthase and oxidative stress. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xia, T.; Nel, A.E. The role of oxidative stress in ambient particulate matter-induced lung diseases and its implications in the toxicity of engineered nanoparticles. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fredenburgh, L.E.; Perrella, M.A.; Mitsialis, S.A. The role of heme oxygenase-1 in pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryter, S.W. Heme Oxygenase-1: An anti-inflammatory effector in cardiovascular, lung, and related metabolic disorders. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoyratty, T.E.; Ai, Z.; Ballesteros, I.; Eames, H.L.; Mathie, S.; Martín-Salamanca, S.; Wang, L.; Hemmings, A.; Willemsen, N.; von Werz, V.; et al. Distinct transcription factor networks control neutrophil-driven inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 1093–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and health impacts of Air pollution: A review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, M.; Ichinose, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Arashidani, K.; Yoshida, S.; Nishikawa, M.; Takano, H.; Sun, G.; Shibamoto, T. Differences in allergic inflammatory responses between urban PM2.5 and fine particle derived from desert-dust in murine lungs. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 297, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitkus, R.J.; Powell, J.L.; Zeisler, R.; Squibb, K.S. Comparative physicochemical and biological characterization of NIST Interim Reference Material PM2.5 and SRM 1648 in human A549 and mouse RAW264.7 cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2013, 27, 2289–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, P.; Sadler, E.; Russell, V.; Young, A. The effects of clinically relevant reference agents in a mouse model of severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, OA1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polderman, J.A.W.; Farhang-Razi, V.; Dieren, S.; Kranke, P.; DeVries, J.H.; Hollmann, M.W.; Preckel, B.; Hermanides, J. Adverse side-effects of dexamethasone in surgical patients–an abridged Cochrane systematic review. Anaesthesia 2019, 74, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Piao, C.H.; Fan, Y.J.; Yu, Z.N.; Lee, S.Y.; Song, C.H.; Shin, H.S.; Chai, O.H. Artemisia gmelinii extract alleviates allergic airway inflammation via balancing TH1/TH2 homeostasis and inhibiting mast cell degranulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, P.D.; Lee, B.H.; Jeong, H.J.; An, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, H.R.; Ko, S.G.; Um, J.Y.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, H.M. Use of scopoletin to inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines through inhibition of the IκB/NF-κB signal cascade in the human mast cell line HMC-1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 555, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Luo, T.; Chai, J.; Jing, P.; Xiong, L. Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates the Inflammatory Stress of LPS-Induced BV2 Cell via Interacting with TLR4-Mediated Downstream Pathway. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 6282167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Yun, N.; Choi, J.S.; Islam, M.N.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.M. Protective effects of hyperoside against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in mice. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raineri, A.; Campagnari, R.; Toso, R.D.; Copetti, S.; Gomez-Lira, M.; Menegazzi, M. 3,5-Dicaffeoylquinic Acid Lowers 3T3-L1 Mitotic Clonal Expansion and Adipocyte Differentiation by Enhancing Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression. Molecules 2021, 26, 5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Pu, W.; Wazir, J.; Jin, X.; Wei, L.; Song, S.; Su, Z.; Li, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H. Long-term exposure to PM2.5 aggravates pulmonary fibrosis and acute lung injury by disrupting Nrf2-mediated antioxidant function. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 313, 120017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Vikash, V.; Ye, Q.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Dong, W. ROS and ROS-mediated cellular signaling. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4350965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tak, P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-kappaB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, S.; Buttari, B.; Panieri, E.; Profumo, E.; Saso, L. An overview of Nrf2 signaling pathway and its role in inflammation. Molecules 2020, 25, 5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.; Xu, F.; Shemesh, M.; Qiu, X.; Barak, Y.; Zhu, T.; Rudich, Y. Nrf2 protects against diverse PM2.5 components-induced mitochondrial oxidative damage in lung cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasper, A.E.; McIver, W.J.; Sapey, E.; Walton, G.M. Understanding the role of neutrophils in chronic inflammatory airway disease. F1000Research 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kononova, N.; Sikkeland, L.I.B.; Mahmood, F.; Vistnes, M.; Kongerud, J.; Einvik, G.; Søyseth, V. Annual decline in forced expiratory volume and airway inflammatory cells and mediators in a general population-based sample. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Branzk, N.; Papayannopoulos, V. Molecular mechanisms regulating NETosis in infection and disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 513–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manda, A.; Pruchniak, M.P.; Araźna, M.; Demkow, U.A. Neutrophil extracellular traps in physiology and pathology. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 39, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voynow, J.A.; Shinbashi, M. Neutrophil elastase and chronic lung disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbecki, J.; Barczak, K.; Gutowska, I.; Chlubek, D.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. CXCL1: Gene, Promoter, Regulation of Expression, mRNA Stability, Regulation of Activity in the Intercellular Space. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwaiz, R.; Rahman, M.; Syk, I.; Zhang, E.; Thorlacius, H. Rac1-dependent secretion of platelet-derived CCL5 regulates neutrophil recruitment via activation of alveolar macrophages in septic lung injury. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, H.-J.; Shin, D.-U.; Eom, J.-E.; Lim, K.M.; Lim, E.Y.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, H.-J.; Song, J.H.; Shim, M.; Choe, H.; et al. Artemisia gmelinii Extract Attenuates Particulate Matter-Induced Neutrophilic Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Lung Injury. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081591
Song H-J, Shin D-U, Eom J-E, Lim KM, Lim EY, Kim YI, Kim H-J, Song JH, Shim M, Choe H, et al. Artemisia gmelinii Extract Attenuates Particulate Matter-Induced Neutrophilic Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Lung Injury. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(8):1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081591
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Hyeon-Ji, Dong-Uk Shin, Ji-Eun Eom, Kyung Min Lim, Eun Yeong Lim, Young In Kim, Ha-Jung Kim, Ju Hye Song, MyeongKuk Shim, HyeonJeong Choe, and et al. 2023. "Artemisia gmelinii Extract Attenuates Particulate Matter-Induced Neutrophilic Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Lung Injury" Antioxidants 12, no. 8: 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081591
APA StyleSong, H. -J., Shin, D. -U., Eom, J. -E., Lim, K. M., Lim, E. Y., Kim, Y. I., Kim, H. -J., Song, J. H., Shim, M., Choe, H., Kim, G. -D., Lee, S. -Y., & Shin, H. S. (2023). Artemisia gmelinii Extract Attenuates Particulate Matter-Induced Neutrophilic Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Lung Injury. Antioxidants, 12(8), 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081591