Comparative Proteomics Unveils LRRFIP1 as a New Player in the DAPK1 Interactome of Neurons Exposed to Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primary Culture of Cortical Neurons
2.2. Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation (OGD)
2.3. Treatments
2.4. Assessment of Neuronal Viability
2.5. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) Procedure to Identify Protein Interactors by LC-MS/MS
2.6. Co-Immunoprecipitation Assays
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Immunocytochemistry
2.9. Transient Right Focal Cerebral Ischemia
2.10. Statistical Analysis
2.11. Antibodies
3. Results
3.1. Effects of OGD on Neuronal Death, and on DAPK1 Expression, Dephosphorylation, and Cleavage
3.2. Main Effects of OGD on the Neuronal DAPK1 Interactome
3.3. Several DAPK1 Interactors Are CTD-NR2B Binding Partners
3.4. The New Protein Candidate LRRFIP1 Is Part of the DAPK1 Protein Complex during Ischemia In Vivo and Excitotoxicity In Vitro
3.5. Colocalization of NR2B and DAPK1 with LRRFIP1
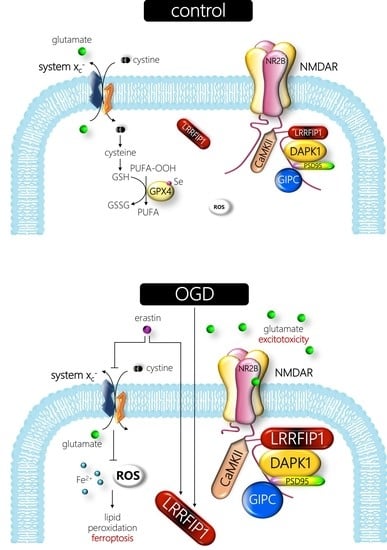
3.6. The Ferroptosis Inducer Erastin Increases Neuronal LRRFIP1 Levels Preceding Loss of Neuronal Viability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Q.; Song, W.; Xiao, W. Dioscin induces demethylation of DAPK-1 and RASSF-1α genes via the antioxidant capacity, resulting in apoptosis of bladder cancer T24 cells. EXCLI J. 2017, 16, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.T.; Chuang, M.J.; Tang, S.H.; Wu, S.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Sun, G.H.; Hsiao, P.W.; Huang, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Yu, C.P.; et al. Novel cancer therapeutics with allosteric modulation of the mitochondrial C-Raf-DAPK complex by Raf inhibitor combination therapy. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3568–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Zhai, J.; Yu, J.; Yang, Q.; Yang, J. miR-98-5p protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through anti-apoptosis and anti-oxidative stress in mice. J. Biochem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, M.A.; Ryan, T.J.; Bell, K.F.S.; Fowler, J.H.; McMahon, A.; Al-Mubarak, B.; Komiyama, N.H.; Horsburgh, K.; Kind, P.C.; Grant, S.G.N.; et al. The subtype of GluN2 C-terminal domain determines the response to excitotoxic insults. Neuron 2012, 74, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, N.; Wu, J.; Zhu, H.; Yan, H.; Guo, Y.; Cai, Y.; Yan, H.; Shi, Y.; Shu, S.; Pei, L.; et al. Genetic mutation of GluN2B protects brain cells against stroke damages. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 2979–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, A.W.; Tasker, R.A. Endothelin-1-induced ischemic damage and functional impairment is mediated primarily by NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 37, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Besshoh, S.; Arundine, M.; Gurd, J.W.; Wang, Y.T.; Salter, M.W.; Tymianski, M. Treatment of ischemic brain damage by perturbing NMDA receptor-PSD-95 protein interactions. Science 2002, 298, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Xu, X.; Peng, L.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, W.; Soundarapandian, M.M.; Balel, C.; Wang, M.; Jia, N.; Zhang, W.; et al. DAPK1 interaction with NMDA receptor NR2B subunits mediates brain damage in stroke. Cell 2010, 140, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, R.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W. Long non-coding RNA AK038897 aggravates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via acting as a ceRNA for miR-26a-5p to target DAPK1. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 314, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, J.; Ryan, T.J.; McKay, S.; Marwick, K.; Baxter, P.; Carpanini, S.M.; Wishart, T.M.; Gillingwater, T.H.; Manson, J.C.; Wyllie, D.J.A.; et al. Pro-death NMDA receptor signaling is promoted by the GluN2B C-terminus independently of Dapk1. Elife 2017, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamloo, M.; Soriano, L.; Wieloch, T.; Nikolich, K.; Urfer, R.; Oksenberg, D. Death-associated protein kinase is activated by dephosphorylation in response to cerebral ischemia. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 42290–42299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tovar, K.R.; Westbrook, G.L. The incorporation of NMDA receptors with a distinct subunit composition at nascent hippocampal synapses in vitro. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 4180–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guirao, V.; Martí-Sistac, O.; DeGregorio-Rocasolano, N.; Ponce, J.; Dávalos, A.; Gasull, T. Specific rescue by ortho-hydroxy atorvastatin of cortical GABAergic neurons from previous oxygen/glucose deprivation: Role of pCREB. J. Neurochem. 2017, 143, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeGregorio-Rocasolano, N.; Martí-Sistac, O.; Ponce, J.; Castelló-Ruiz, M.; Millán, M.; Guirao, V.; García-Yébenes, I.; Salom, J.B.; Ramos-Cabrer, P.; Alborch, E.; et al. Iron-loaded transferrin (Tf) is detrimental whereas iron-free Tf confers protection against brain ischemia by modifying blood Tf saturation and subsequent neuronal damage. Redox Biol. 2018, 15, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, J.G.; Lemasters, J.J.; Crews, F.T. Use of a multiwell fluorescence scanner with propidium iodide to assess NMDA mediated excitotoxicity in rat cortical neuronal cultures. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 221, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torregrosa, G.; Pérez-Asensio, F.J.; Burguete, M.C.; Castelló-Ruiz, M.; Salom, J.B.; Alborch, E. Chronic intracerebroventricular delivery of the secretory phospholipase A2 inhibitor, 12-epi-scalaradial, does not improve outcome after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Exp. Brain Res. 2007, 176, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Ebert, D.; Huang, X.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER version 14: More genomes, a new PANTHER GO-slim and improvements in enrichment analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D419–D426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpkins, K.L.; Guttmann, R.P.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sokol, S.; Neumar, R.W.; Lynch, D.R. Selective activation induced cleavage of the NR2B subunit by calpain. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 11322–11331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubern, C.; Camós, S.; Hurtado, O.; Rodríguez, R.; Romera, V.G.; Sobrado, M.; Cañadas, R.; Moro, M.A.; Lizasoain, I.; Serena, J.; et al. Characterization of Gcf2/Lrrfip1 in experimental cerebral ischemia and its role as a modulator of Akt, mTOR and β-catenin signaling pathways. Neuroscience 2014, 268, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, F. Ferroptosis is associated with oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced Sertoli cell death. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 3051–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeGregorio-Rocasolano, N.; Martí-Sistac, O.; Gasull, T. Deciphering the iron side of stroke: Neurodegeneration at the crossroads between iron dyshomeostasis, excitotoxicity, and ferroptosis. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bayer, K.U.; Schulman, H. CaM kinase: Still inspiring at 40. Neuron 2019, 103, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omkumar, R.V.; Kiely, M.J.; Rosenstein, A.J.; Min, K.T.; Kennedy, M.B. Identification of a phosphorylation site for calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in the NR2B subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 31670–31678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Stevens, C.; Hupp, T. Identification of a dominant negative functional domain on DAPK-1 that degrades DAPK-1 protein and stimulates TNFR-1-mediated apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 16792–16802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Stroink, A.R.; Wang, C.X. The role of DAPK-BimEL pathway in neuronal death induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation. Neuroscience 2014, 258, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, G.; Fu, T.; Yang, F.; Yao, L.; Xue, W.; Zhu, F. Prediction of GluN2B-CT1290-1310/DAPK1 interaction by protein-peptide docking and molecular dynamics simulation. Molecules 2018, 23, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swartzwelder, H.S.; Risher, M.L.; Miller, K.M.; Colbran, R.J.; Winder, D.G.; Wills, T.A. Changes in the adult GluN2B associated proteome following adolescent intermittent ethanol exposure. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, R.; Chida, K.; Lu, H.; Clendaniel, V.; Fisher, M.; Thomas, A.; Lo, E.H.; Selim, M.; Shehadah, A. Neuroprotective effects of selective inhibition of histone deacetylase 3 in experimental stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, F.; Ji, S.; Kronenberg, G.; Barco, A.; Olivares, R.; Benito, E.; Dirnagl, U.; Gertz, K.; Endres, M.; Harms, C.; et al. Histone acetylation and CREB binding protein are required for neuronal resistance against ischemic injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanzillotta, A.; Pignataro, G.; Branca, C.; Cuomo, O.; Sarnico, I.; Benarese, M.; Annunziato, L.; Spano, P.F.; Pizzi, M. Targeted acetylation of NF-kappaB/RelA and histones by epigenetic drugs reduces post-ischemic brain injury in mice with an extended therapeutic window. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 49, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zille, M.; Kumar, A.; Kundu, N.; Bourassa, M.W.; Wong, V.S.C.; Willis, D.; Karuppagounder, S.S.; Ratan, R.R. Ferroptosis in neurons and cancer cells is similar but differentially regulated by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Eneuro 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlüter, A.; Aksan, B.; Fioravanti, R.; Valente, S.; Mai, A.; Mauceri, D. Histone deacetylases contribute to excitotoxicity-triggered degeneration of retinal ganglion cells in vivo. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 8018–8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, C.; Langdon, C.; Alobid, I.; Fuentes, M.; Bonastre, M.; Mullol, J. Recovery of olfactory function after excitotoxic lesion of the olfactory bulbs is associated with increases in bulbar SIRT1 and SIRT4 expressions. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 5643–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namekata, K.; Kimura, A.; Kawamura, K.; Guo, X.; Harada, C.; Tanaka, K.; Harada, T. Dock3 attenuates neural cell death due to NMDA neurotoxicity and oxidative stress in a mouse model of normal tension glaucoma. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.Y.; Wagner, D.A.; Hsu, M.H.; Leonard, J.P. Evidence for direct protein kinase-C mediated modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor current. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Z.; Petralia, R.S.; Fu, Z.; Swanwick, C.C.; Wang, Y.-X.; Prybylowski, K.; Sans, N.; Vicini, S.; Wenthold, R.J. The role of the PDZ protein GIPC in regulating NMDA receptor trafficking. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 11663–11675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gascón, S.; Sobrado, M.; Roda, J.M.; Rodríguez-Peña, A.; Díaz-Guerra, M. Excitotoxicity and focal cerebral ischemia induce truncation of the NR2A and NR2B subunits of the NMDA receptor and cleavage of the scaffolding protein PSD-95. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Yuen, E.Y.; Lu, Y.F.; Matsushita, M.; Matsui, H.; Yan, Z.; Tomizawa, K. Regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by calpain in cortical neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 21588–21593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baudry, M.; Bi, X. Calpain-1 and calpain-2: The yin and yang of synaptic plasticity and neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Wang, S.C.; Lei, M.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, K. Regulatory role of calpain in neuronal death. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, K.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Lv, F.; Shen, H.; Pei, L. Presynaptic Caytaxin prevents apoptosis via deactivating DAPK1 in the acute phase of cerebral ischemic stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 329, 113303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, A.H.; Burns, P.; Salles, I.; Macaulay, I.C.; Jones, C.I.; Ardissino, D.; De Bono, B.; Bray, S.L.; Deckmyn, H.; Dudbridge, F.; et al. Transcription profiling in human platelets reveals LRRFIP1 as a novel protein regulating platelet function. Blood 2010, 116, 4646–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, K.S.K.; de Couet, H.G. Novel proteins interacting with the leucine-rich repeat domain of human flightless-I identified by the yeast two-hybrid system. Genomics 1999, 58, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallolas, J.; Hurtado, O.; Castellanos, M.; Blanco, M.; Sobrino, T.; Serena, J.; Vivancos, J.; Castillo, J.; Lizasoain, I.; Moro, M.A.; et al. A polymorphism in the EAAT2 promoter is associated with higher glutamate concentrations and higher frequency of progressing stroke. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordo, R.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Al-Jamal, O.; Paliogiannis, P.; Pintus, G. Resveratrol inhibits oxidative stress and prevents mitochondrial damage induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé-Carneiro, J.; Larrosa, M.; Yáñez-Gascón, M.J.; Dávalos, A.; Gil-Zamorano, J.; Gonzálvez, M.; García-Almagro, F.J.; Ruiz Ros, J.A.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Espín, J.C.; et al. One-year supplementation with a grape extract containing resveratrol modulates inflammatory-related microRNAs and cytokines expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of type 2 diabetes and hypertensive patients with coronary artery disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 72, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnerie, H.; Hsu, F.C.; Coulter, D.A.; Le Roux, P.D. Role of the NR2A/2B subunits of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor in glutamate-induced glutamic acid decarboxylase alteration in cortical GABAergic neurons in vitro. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averna, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Cervetto, C.; Pedrazzi, M.; Bavestrello, M.; De Tullio, R.; Salamino, F.; Pontremoli, S.; Melloni, E. Physiological roles of calpain 1 associated to multiprotein NMDA receptor complex. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dixon, S.J.; Patel, D.; Welsch, M.; Skouta, R.; Lee, E.; Hayano, M.; Thomas, A.G.; Gleason, C.; Tatonetti, N.; Slusher, B.S.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of cystine-glutamate exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis. Elife 2014, 2014, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, B.Y.; Pang, Y.L.; Shen, W.Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.X.; Li, W.X.; Liu, C.; Kong, X.H.; Ning, G.Z.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of deferoxamine on erastin-induced ferroptosis in primary cortical neurons. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takimoto, M. Multidisciplinary roles of LRRFIP1/GCF2 in human biological systems and diseases. Cells 2019, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
DeGregorio-Rocasolano, N.; Guirao, V.; Ponce, J.; Melià-Sorolla, M.; Aliena-Valero, A.; García-Serran, A.; Salom, J.B.; Dávalos, A.; Martí-Sistac, O.; Gasull, T. Comparative Proteomics Unveils LRRFIP1 as a New Player in the DAPK1 Interactome of Neurons Exposed to Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121202
DeGregorio-Rocasolano N, Guirao V, Ponce J, Melià-Sorolla M, Aliena-Valero A, García-Serran A, Salom JB, Dávalos A, Martí-Sistac O, Gasull T. Comparative Proteomics Unveils LRRFIP1 as a New Player in the DAPK1 Interactome of Neurons Exposed to Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(12):1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121202
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeGregorio-Rocasolano, Núria, Verónica Guirao, Jovita Ponce, Marc Melià-Sorolla, Alicia Aliena-Valero, Alexia García-Serran, Juan B. Salom, Antoni Dávalos, Octavi Martí-Sistac, and Teresa Gasull. 2020. "Comparative Proteomics Unveils LRRFIP1 as a New Player in the DAPK1 Interactome of Neurons Exposed to Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation" Antioxidants 9, no. 12: 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121202
APA StyleDeGregorio-Rocasolano, N., Guirao, V., Ponce, J., Melià-Sorolla, M., Aliena-Valero, A., García-Serran, A., Salom, J. B., Dávalos, A., Martí-Sistac, O., & Gasull, T. (2020). Comparative Proteomics Unveils LRRFIP1 as a New Player in the DAPK1 Interactome of Neurons Exposed to Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation. Antioxidants, 9(12), 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121202