Super-Resolution Microscopy Reveals an Altered Fibrin Network in Cirrhosis: The Key Role of Oxidative Stress in Fibrinogen Structural Modifications
Abstract
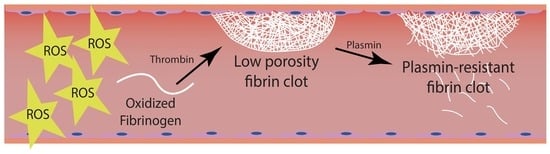
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) Assay
2.4. Plasma Lipid Peroxidation Estimation
2.5. Fibrinogen Purification
2.6. Protein Concentration Assay
2.7. Protein Carbonyl (PC) Determination
2.8. Fibrin Digestion with Plasmin and Electrophoretic Analysis of Plasmin Digests
2.9. Thrombin-Catalyzed Fibrin Polymerization Assays
2.10. Circular Dichroism Spectra of Purified Fibrinogen Extracts
2.11. Intrinsic Fluorescence Spectra of Fibrinogen
2.12. Fibrin Structure Determination by Stimulated Emission Depletion (STED) Super-Resolution and Confocal Microscopy
2.13. In Vitro Assay: AAPH-Treated Fibrinogen
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subjects
3.2. Plasma Oxidative Stress Markers in Patients and Controls
3.3. Oxidation Levels in Fibrinogen Purified from Patients and Controls
3.4. Fibrin Susceptibility to Plasmin-Induced Lysis
3.5. Fibrinogen Polymerization and Fibrin Formation
3.6. Circular Dichroism Spectra: Analysis of Secondary Structure
3.7. Intrinsic Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis
3.8. Confocal Microscopy Analysis
3.9. STED Super-Resolution Microscopy Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turco, L.; De Raucourt, E.; Valla, D.; Villa, E. Anticoagulation in the cirrhotic patient. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, S.H.; Hoffman, M.; Lisman, T.; Macik, B.G.; Northup, P.; Reddy, K.R.; Tripodi, A.; Sanyal, A.J. Coagulation in Liver Disease Group Coagulation disorders and hemostasis in liver disease: Pathophysiology and critical assessment of current management. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripodi, A.; Mannucci, P.M. Abnormalities of hemostasis in chronic liver disease: Reappraisal of their clinical significance and need for clinical and laboratory research. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talving, P.; Lustenberger, T.; Okoye, O.; Lam, L.; Smith, J.A.; Inaba, K.; Mohseni, S.; Chan, L.; Demetriades, D. The impact of liver cirrhosis on outcomes in trauma patients. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013, 75, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulley, D.; Teal, E.; Suvannasankha, A.; Chalasani, N.; Liangpunsakul, S. Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Cirrhosis Patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 3012–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, P.; Tarantino, L.; Di Minno, G.; Paternoster, M.; Graziano, V.; Petitto, M.; Nasto, A.; Di Minno, M.N.D.; Di Minno, M.N.; Di Minno, M.N.D. The risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with cirrhosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripodi, A.; Mannucci, P.M. The Coagulopathy of Chronic Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sipeki, N.; Antal-Szalmas, P.; Lakatos, P.; Papp, M. Immune dysfunction in cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 2564–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lados-Krupa, A.; Konieczynska, M.; Chmiel, A.; Undas, A. Increased Oxidation as an Additional Mechanism Underlying Reduced Clot Permeability and Impaired Fibrinolysis in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helms, C.C.; Kapadia, S.; Gilmore, A.C.; Lu, Z.; Basu, S.; Kim-Shapiro, D.B. Exposure of fibrinogen and thrombin to nitric oxide donor ProliNONOate affects fibrin clot properties. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2017, 28, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marí, M.; Colell, A.; Morales, A.; Von Montfort, C.; García-Ruiz, C.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Redox Control of Liver Function in Health and Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 12, 1295–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becatti, M.; Emmi, G.; Bettiol, A.; Silvestri, E.; Di Scala, G.; Taddei, N.; Prisco, M.; Fiorillo, C. Behçet’s syndrome as a tool to dissect the mechanisms of thrombo-inflammation: Clinical and pathogenetic aspects. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 195, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lami, D.; Cellai, A.P.; Antonucci, E.; Fiorillo, C.; Becatti, M.; Grifoni, E.; Cenci, C.; Marcucci, R.; Mannini, L.; Miniati, M.; et al. Residual perfusion defects in patients with pulmonary embolism are related to impaired fibrinolytic capacity. Thromb. Res. 2014, 134, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniati, M.; Fiorillo, C.; Becatti, M.; Monti, S.; Bottai, M.; Marini, C.; Grifoni, E.; Formichi, B.; Bauleo, C.; Arcangeli, C.; et al. Fibrin Resistance to Lysis in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Other than Thromboembolic. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becatti, M.; Marcucci, R.; Bruschi, G.; Taddei, N.; Bani, D.; Gori, A.M.; Giusti, B.; Gensini, G.F.; Abbate, R.; Fiorillo, C. Oxidative Modification of Fibrinogen Is Associated with Altered Function and Structure in the Subacute Phase of Myocardial Infarction. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Boil. 2014, 34, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becatti, M.; Emmi, G.; Silvestri, E.; Bruschi, G.; Ciucciarelli, L.; Squatrito, D.; Vaglio, A.; Taddei, N.; Abbate, R.; Emmi, L.; et al. Neutrophil Activation Promotes Fibrinogen Oxidation and Thrombus Formation in Behçet Disease. Circulation 2016, 133, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, R.N.H.; Murray-Lyon, I.M.; Dawson, J.L.; Pietroni, M.C.; Williams, R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br. J. Surg. 1973, 60, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, M.; Gitto, S.; Biselli, M. The MELD score in patients awaiting liver transplant: Strengths and weaknesses. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sofi, F.; Dinu, M.; Pagliai, G.; Cesari, F.; Gori, A.M.; Sereni, A.; Becatti, M.; Fiorillo, C.; Marcucci, R.; Casini, A. Low-Calorie Vegetarian Versus Mediterranean Diets for Reducing Body Weight and Improving Cardiovascular Risk Profile. Circulation 2018, 137, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, C.; Becatti, M.; Attanasio, M.; Lucarini, L.; Nassi, N.; Evangelisti, L.; Porciani, M.C.; Nassi, P.; Gensini, G.; Abbate, R.; et al. Evidence for oxidative stress in plasma of patients with Marfan syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. 2010, 145, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munishkina, L.A.; Phelan, C.; Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L. Conformational Behavior and Aggregation of α-Synuclein in Organic Solvents: Modeling the Effects of Membranes†. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 2720–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolberg, A.S.; Gabriel, D.A.; Hoffman, M. Analyzing fibrin clot structure using a microplate reader. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2002, 13, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, J.; Nagaswami, C. Computer modeling of fibrin polymerization kinetics correlated with electron microscope and turbidity observations: Clot structure and assembly are kinetically controlled. Biophys. J. 1992, 63, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenfield, N.J. Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2876–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, N.; Schneider, D. Hands On: Using Tryptophan Fluorescence Spectroscopy to Study Protein Structure. Breast Cancer 2019, 1958, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisman, T.; Porte, R.J. Rebalanced hemostasis in patients with liver disease: Evidence and clinical consequences. Blood 2010, 116, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollestelle, M.J.; Geertzen, H.G.M.; Straatsburg, I.H.; Van Gulik, T.M.; Van Mourik, J.A. Factor VIII expression in liver disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 91, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, J.-P.; Allali, Y.; Lesty, C.; Tanguy, M.; Silvain, J.; Ankri, A.; Blanchet, B.; Dumaine, R.; Gianetti, J.; Payot, L.; et al. Altered Fibrin Architecture Is Associated with Hypofibrinolysis and Premature Coronary Atherothrombosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Boil. 2006, 26, 2567–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Undas, A.; Zawilska, K.; Ciesla-Dul, M.; Lehmann-Kopydłowska, A.; Skubiszak, A.; Ciepłuch, K.; Tracz, W. Altered fibrin clot structure/function in patients with idiopathic venous thromboembolism and in their relatives. Blood 2009, 114, 4272–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, E.J.; Ariëns, R.A.; Grant, P.J. The influence of type 2 diabetes on fibrin structure and function. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undas, A.; Ariëns, R.A. Fibrin Clot Structure and Function. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Boil. 2011, 31, e88–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karlaftis, V.; Perera, S.; Monagle, P.; Ignjatovic, V. Importance of post-translational modifications on the function of key haemostatic proteins. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2016, 27, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shacter, E.; Williams, J.A.; Lim, M.; Levine, R.L. Differential susceptibility of plasma proteins to oxidative modification: Examination by western blot immunoassay. Free. Radic. Boil. Med. 1994, 17, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtman, E.R.; Levine, R.L. Free radical-mediated oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins. Amino Acids 2003, 25, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.-Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C.-W.; Feng, Y. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vairappan, B. Endothelial dysfunction in cirrhosis: Role of inflammation and oxidative stress. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugenholtz, G.C.; Macrae, F.L.; Adelmeijer, J.; Dulfer, S.; Porte, R.J.; Lisman, T.; Ariëns, R.A. Procoagulant changes in fibrin clot structure in patients with cirrhosis are associated with oxidative modifications of fibrinogen. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Yan, L.-J. Protein Oxidative Modifications: Beneficial Roles in Disease and Health. J. Biochem. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 1, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz, M.; Enoksson, M.; Thorpe, M.; Hellman, L.T. The Extended Cleavage Specificity of Human Thrombin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siudut, J.; Grela, M.; Wypasek, E.; Plens, K.; Undas, A. Reduced plasma fibrin clot permeability and susceptibility to lysis are associated with increased risk of postthrombotic syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, J.W.; Litvinov, R.I. Mechanisms of fibrin polymerization and clinical implications. Blood 2013, 121, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weisel, J.W. Structure of fibrin: Impact on clot stability. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridge, K.; Philippou, H.; Ariëns, R.A. Clot properties and cardiovascular disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 112, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colle, J.P.; Mishal, Z.; Lesty, C.; Mirshahi, M.; Peyne, J.; Baumelou, A.; Bensman, A.; Soria, J.; Soria, C. Abnormal fibrin clot architecture in nephrotic patients is related to hypofibrinolysis: Influence of plasma biochemical modifications: A possible mechanism for the high thrombotic tendency? Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 82, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar]
- Ariëns, R.A. Fibrin(ogen) and thrombotic disease. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undas, A. Prothrombotic Fibrin Clot Phenotype in Patients with Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: A New Risk Factor for Recurrence. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, J.W.; Litvinov, R.I. Fibrin Formation, Structure and Properties. Sub Cell. Biochem. 2017, 82, 405–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Addolorato, G.; Abenavoli, L.; Dallio, M.; Federico, A.; Germani, G.; Gitto, S.; Leandro, G.; Loguercio, C.; Marra, F.; Stasi, E. Alcohol associated liver disease 2020: A clinical practice guideline by the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF). Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 374–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovely, R.S.; Kazmierczak, S.C.; Massaro, J.M.; D’Agostino, R.B.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Farrell, D.H. γ′ Fibrinogen: Evaluation of a New Assay for Study of Associations with Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Appiah, D.; Schreiner, P.J.; MacLehose, R.F.; Folsom, A.R. Association of Plasma γ’ Fibrinogen With Incident Cardiovascular Disease: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Boil. 2015, 35, 2700–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Trilok, G.; Wang, F.; Qi, X.; Xiao, J.; Yang, C. A single hospital study on portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients—clinical characteristics & risk factors. Indian J. Med. Res. 2014, 139, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nery, F.; Chevret, S.; Condat, B.; De Raucourt, E.; Boudaoud, L.; Rautou, P.-E.; Plessier, A.; Roulot, D.; Chaffaut, C.; Bourcier, V.; et al. Causes and consequences of portal vein thrombosis in 1243 patients with cirrhosis: Results of a longitudinal study. Hepatology 2015, 61, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, H.; Okugawa, H.; Takahashi, M.; Yokosuka, O. De novo Portal Vein Thrombosis in Virus-Related Cirrhosis: Predictive Factors and Long-Term Outcomes. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Healthy Controls (n = 20) | CTP A (n = 5) | CTP B (n = 5) | CTP C (n = 5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (M/F) | 10/10 | 2/3 | 3/2 | 3/2 |
| Age (mean ± SD years) | 65 ± 7 | 65 ± 13 | 68 ± 8 | 62 ± 9 |
| Etiology | ||||
| HCV | / | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Alcohol | / | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| NASH | / | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Other | / | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Ascites | ||||
| absent | / | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| mild | / | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| moderate | / | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| severe | / | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| HE | ||||
| Grade 0 | / | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| Grade 1 | / | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Grade 2 | / | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| Grade 3 | / | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Grade 4 | / | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total bilirubin (M (range) mg/dL) | / | 0.8 (0.5–2) | 1.2 (1–2) | 4.9 (2.3–7.2) |
| Albumin (M (range) g/dL) | / | 3.7 (3.5–4.7) | 3.4 (2.5–3.6) | 3.3 (2.1–3.7) |
| INR | 1 (0.8–1.2) | 1.4 (1–1.5) | 1.3 (1.1–1.4) | 1.7 (1.2–2.2) |
| Hemoglobin (M (range) g/dL) | 13.2 (11.5–16.4) | 11.2 (10.7–12) | 10.2 (8.1–12.7) | 9.9 (8.1–13.4) |
| Hematocrit (%) | / | 34.0 (33.1–39) | 32 (25.2–38) | 28.7 (23.3–37) |
| Creatinine (M (range) mg/dL) | / | 0.8 (0.5–0.8) | 1 (0.6–1.8) | 0.7 (0.5–0.8) |
| Sodium (M (range) mmol/L) | / | 138.5 (136–145) | 136.5 (131–144) | 136 (128–145) |
| Potassium (M (range) mmol/L) | / | 4.1 (3.9–4.3) | 4.1 (3.4–5.1) | 4.2 (3.8–4.5) |
| Calcium (M (range) mg/dL) | / | 8.6 (8.1–8.8) | 7.9 (7.4–8.7) | 8.1 (7.5–9.1) |
| Prothrombin time (M (range) s) | / | 6.7 (6–7.4) | 6.2 (5–7.2) | 5.8 (5–6.8) |
| Fibrinogen (M (range) mg/dL) | 295 (233–392) | 369.5 (315–544) | 286 (162–327) | 188 (145–247) |
| MELD (mean ± SD) | / | 10 ± 1 | 11 ± 3 | 18 ± 3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Becatti, M.; Mannucci, A.; Argento, F.R.; Gitto, S.; Vizzutti, F.; Marra, F.; Taddei, N.; Fiorillo, C.; Laffi, G. Super-Resolution Microscopy Reveals an Altered Fibrin Network in Cirrhosis: The Key Role of Oxidative Stress in Fibrinogen Structural Modifications. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080737
Becatti M, Mannucci A, Argento FR, Gitto S, Vizzutti F, Marra F, Taddei N, Fiorillo C, Laffi G. Super-Resolution Microscopy Reveals an Altered Fibrin Network in Cirrhosis: The Key Role of Oxidative Stress in Fibrinogen Structural Modifications. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(8):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080737
Chicago/Turabian StyleBecatti, Matteo, Amanda Mannucci, Flavia Rita Argento, Stefano Gitto, Francesco Vizzutti, Fabio Marra, Niccolò Taddei, Claudia Fiorillo, and Giacomo Laffi. 2020. "Super-Resolution Microscopy Reveals an Altered Fibrin Network in Cirrhosis: The Key Role of Oxidative Stress in Fibrinogen Structural Modifications" Antioxidants 9, no. 8: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080737
APA StyleBecatti, M., Mannucci, A., Argento, F. R., Gitto, S., Vizzutti, F., Marra, F., Taddei, N., Fiorillo, C., & Laffi, G. (2020). Super-Resolution Microscopy Reveals an Altered Fibrin Network in Cirrhosis: The Key Role of Oxidative Stress in Fibrinogen Structural Modifications. Antioxidants, 9(8), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080737