Dual-Use Vaccine for Diarrhoeal Diseases: Cross-Protective Immunogenicity of a Cold-Chain-Free, Live-Attenuated, Oral Cholera Vaccine against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Challenge in BALB/c Mice
Abstract
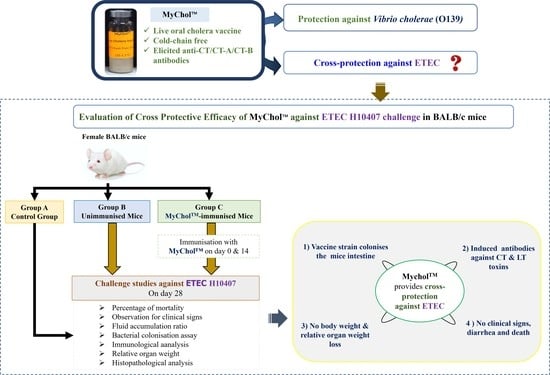
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Test Cholera Vaccine
2.3. Determination of the LD100 of ETEC H10407
2.4. Cross-Protective Efficacy of MyChol™ against ETEC H10407
2.4.1. Mice Immunisation
2.4.2. ETEC Challenge Study
2.4.3. Immunological Analysis
Detection of Anti-Cholera Toxin (Anti-CT), Anti-Heat Labile (Anti-LT) and Anti-Subunit Antibodies
Bactericidal Assay against H10407
2.4.4. Observations
Body Weight Analysis and Clinical Signs
Fluid Accumulation Ratio (FAR) in Mice after ETEC Challenge
Bacterial Colonization
Relative Organ Weight Analyses
Histopathological Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Determination of the LD100 of ETEC H10407
3.2. Cross-Protection against ETEC H10407 in Immunised Mice
3.3. Immunological Analysis
3.4. Fluid Accumulation Ratio in Mice after ETEC Challenge
3.5. Bacterial Colonisation
3.6. Relative Organ Weights
3.7. Histopathological Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- PATH. The Case for Investment in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccines. 2011. Available online: https://www.path.org/resources/the-case-for-investment-in-enterotoxigenic-escherichia-coli-vaccines/ (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- GBD 2016 Diarrhoeal Disease Collaborators. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of diarrhoea in 195 countries: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blokesch, M.; Schoolnik, G.K. Serogroup conversion of Vibrio cholerae in aquatic reservoirs. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Liu, B.; Feng, L.; Ding, P.; Guo, X.; Wang, M.; Cao, B.; Reeves, P.R.; Wang, L. Origins of the current seventh cholera pandemic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7730–E7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mutreja, A.; Kim, D.W.; Thomson, N.R.; Connor, T.R.; Lee, J.H.; Kariuki, S.; Croucher, N.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Harris, S.R.; Lebens, M.; et al. Evidence for several waves of global transmission in the seventh cholera pandemic. Nature 2011, 477, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO. The Weekly Epidemiological Record (WER). 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/journals/weekly-epidemiological-record (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- WHO. WHO Preferred Product Characteristics for Vaccines against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/who-preferred-product-characteristics-for-vaccines-against-enterotoxigenic-escherichia-coli (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Kotloff, K.L.; Nataro, J.P.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Nasrin, D.; Farag, T.H.; Panchalingam, S.; Wu, Y.; Sow, S.O.; Sur, D.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): A prospective, case-control study. Lancet 2013, 382, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAL-ED Network Investigators. Early childhood cognitive development is affected by interactions among illness, diet, enteropathogens and the home environment: Findings from the MAL-ED birth cohort study. BMJ Glob. Health 2018, 3, e000752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudden, H.; Hasso-Agopsowicz, M.; Black, R.; Troeger, C.; Reiner, R.; Breiman, R.; Jit, M.; Kang, G.; Lamberti, L.; Lanata, C.; et al. Meeting Report: WHO Workshop on modelling global mortality and aetiology estimates of enteric pathogens in children under five. Cape Town, 28–29th November 2018. Vaccine 2020, 38, 4792–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.D.; DuPont, H.L. Etiology of travellers’ diarrhea. J. Travel Med. 2017, 24 (Suppl. 1), S13–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Leung, A.A.M.; Wong, A.H.C.; Hon, K.L. Travelers’ Diarrhea: A Clinical Review. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2019, 13, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, R. Epidemiology of traveler’s diarrhea. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41 (Suppl. 8), S536–S540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffré, E.; von Mentzer, A.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Sjöling, Å. Identification of new heat-stable (STa) enterotoxin allele variants produced by human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2016, 306, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleckenstein, J.M. Confronting Challenges to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Development. Front. Trop. Dis. 2022, 2, 709907. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fitd.2021.709907 (accessed on 12 May 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, I.; Walker, R.; Porter, C.K.; Muhib, F.; Chilengi, R.; Cravioto, A.; Guerrant, R.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Qadri, F.; Baqar, S.; et al. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) vaccines: Priority activities to enable product development, licensure, and global access. Vaccine 2021, 39, 4266–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, F.; Rahman, M.A.; Begum, Y.A.; Khan, A.I.; Faruque, A.S.G.; Saha, N.C.; Baby, N.I.; Malek, M.A.; Kumar, A.R.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; et al. Impact of Rapid Urbanization on the Rates of Infection by Vibrio cholerae O1 and Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Dhaka, Bangladesh. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleckenstein, J.M.; Sheikh, A.; Qadri, F. Novel Antigens for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2014, 13, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begum, Y.A.; Rydberg, H.A.; Thorell, K.; Kwak, Y.-K.; Sun, L.; Joffré, E.; Qadri, F.; Sjöling, Å. In Situ Analyses Directly in Diarrheal Stool Reveal Large Variations in Bacterial Load and Active Toxin Expression of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. Msphere 2018, 3, e00517-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tribble, D.R. Resistant pathogens as causes of traveller’s diarrhea globally and impact(s) on treatment failure and recommendations. J. Travel Med. 2017, 24 (Suppl. 1), S6–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, J.D.; Bagamian, K.H.; Muhib, F.; Baral, R.; Laytner, L.A.; Amaya, M.; Wierzba, T.; Rheingans, R. Potential impact and cost-effectiveness of future ETEC and Shigella vaccines in 79 low- and lower middle-income countries. Vaccine X 2019, 2, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PDVAC. PDVAC Executive Summary 2020: Update on Development of Enterotoxigenic E.coli (ETEC) Vaccines. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/pdvac-executive-summary-2020-update-on-development-of-etec-vaccines (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Desai, S.N.; Pezzoli, L.; Alberti, K.P.; Martin, S.; Costa, A.; Perea, W.; Legros, D.; Desai, S.N.; Pezzoli, L.; Alberti, K.P.; et al. Achievements and challenges for the use of killed oral cholera vaccines in the global stockpile era. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmgren, J. Modern History of Cholera Vaccines and the Pivotal Role of icddr,b. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224 (Suppl. 7), S742–S748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, M.; Ali, S.A.; Rashid, N.H.A.; Lalitha, P.; Zainul, F.Z. Vibrio cholerae Strains VCUSM1 and VCUSM4, Method of Producing Same, and Vaccine Derivatives Thereof. U.S. Patent No. 7838016, 5 March 2008. Available online: https://www.mysciencework.com/patent/show/vibrio-cholerae-strains-vcusm1-vcusm4-method-producing-same-vaccine-derivatives-thereof-EP1650315B1 (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Murugaiah, C.; Noor, N.Z.N.M.; Mustafa, S.; Manickam, R.; Pattabhiraman, L. Construction and Evaluation of V. cholerae O139 Mutant, VCUSM21P, as a Safe Live Attenuated Cholera Vaccine. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e81817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, T.H.; Parasuraman, S.; Sinniah, K.; Ravichandran, M.; Prabhakaran, G. Repeated dose toxicity evaluation of a cold chain-free, live, attenuated oral cholera vaccine in Sprague Dawley rats. Vaccine 2019, 37, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, T.H.; Sinniah, K.; Yean, C.Y.; Krishnamoorthy, V.; Bahari, M.B.; Chan, Y.Y.; Prabhakaran, G. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a live, oral cholera vaccine formulation stored outside-the-cold-chain for 140 days. BMC Immunol. 2020, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Vickers, T.J.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Colonization following Intradermal, Sublingual, or Oral Vaccination with EtpA Adhesin. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. CVI 2016, 23, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parasuraman, S.; Raveendran, R.; Kesavan, R. Blood sample collection in small laboratory animals. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2010, 1, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olivier, V.; Salzman, N.H.; Satchell, K.J.F. Prolonged Colonization of Mice by Vibrio cholerae El Tor O1 Depends on Accessory Toxins. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 5043–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, N.C.; Aktories, K.; Barbieri, J.T. Novel bacterial ADP-ribosylating toxins: Structure and function. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Kocinsky, H.S.; Cha, B.; Murtazina, R.; Yang, J.; Tse, C.M.; Singh, V.; Cole, R.; Aronson, P.S.; de Jonge, H.; et al. Cyclic GMP kinase II (cGKII) inhibits NHE3 by altering its trafficking and phosphorylating NHE3 at three required sites: Identification of a multifunctional phosphorylation site. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1952–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taxt, A.M.; Diaz, Y.; Aasland, R.; Clements, J.D.; Nataro, J.P.; Sommerfelt, H.; Puntervoll, P. Towards Rational Design of a Toxoid Vaccine against the Heat-Stable Toxin of Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qadri, F.; Khan, A.I.; Faruque, A.S.G.; Begum, Y.A.; Chowdhury, F.; Nair, G.B.; Salam, M.A.; Sack, D.A.; Svennerholm, A.-M. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae diarrhea, Bangladesh, 2004. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1104–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid-Hempel, P.; Frank, S.A. Pathogenesis, Virulence, and Infective Dose. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hickman, D.L.; Johnson, J.; Vemulapalli, T.H.; Crisler, J.R.; Shepherd, R. Commonly Used Animal Models. Princ. Anim. Res. Grad. Undergrad. Stud. 2017, 117–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, W.; Cassels, F.J. Mucosal immunization of BALB/c mice using enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli colonization factors CFA/I and CS6 administered with and without a mutant heat-labile enterotoxin. Vaccine 2003, 21, 1884–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, W.; Cassels, F.J. Long-term systemic and mucosal antibody responses measured in BALB/c mice following intranasal challenge with viable enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 46, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hays, M.P.; Kumar, A.; Martinez-Becerra, F.J.; Hardwidge, P.R. Immunization with the MipA, Skp, or ETEC_2479 Antigens Confers Protection against Enterotoxigenic E. coli Strains Expressing Different Colonization Factors in a Mouse Pulmonary Challenge Model. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen, K.P.; Randolph, M.M.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Importance of heat-labile enterotoxin in colonization of the adult mouse small intestine by human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veena, H.; Gowda, S.K.; Achur, R.N.; Thippeswamy, N.B. Molecular mechanism of Escherichia coli H10407 induced diarrhoea and its control through immunomodulatory action of bioactives from Simarouba amara (Aubl.). J. Microbiol. Seoul Korea 2021, 59, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.K.; Riddle, M.S.; Tibble, D.R.; Bougeois, A.L.; McKenzie, R.; Isidean, S.D.; Sebeny, P.; Savarino, S.J. A systematic review of experimental infections with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Vaccine 2011, 29, 5869–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenzie, R.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Frech, S.A.; Flyer, D.C.; Bloom, A.; Kazempour, K.; Glenn, G.M. Transcutaneous immunization with the heat-labile toxin (LT) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC): Protective efficacy in a double-blind, placebo-controlled challenge study. Vaccine 2007, 25, 3684–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossman, L.C.; Chaudhuri, R.R.; Beatson, S.A.; Wells, T.J.; Desvaux, M.; Cunningham, A.F.; Petty, N.K.; Mahon, V.; Brinkley, C.; Hobman, J.L.; et al. A Commensal Gone Bad: Complete Genome Sequence of the Prototypical Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Strain H10407. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5822–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, L.T.; Hahn, R.W.; Thompson, C.C.; Bauer, D.L.; Norton, E.B.; Clements, J.D. Simultaneous Exposure to Escherichia coli Heat-Labile and Heat-Stable Enterotoxins Increases Fluid Secretion and Alters Cyclic Nucleotide and Cytokine Production by Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 5308–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azer, S.A.; Tuma, F. Infectious Colitis; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544325/ (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, P.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: Intestinal pathogenesis mechanisms and colonization resistance by gut microbiota. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2055943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, F.; Chen, S.; Tang, W.; Zhang, D.; Liu, S. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection alters intestinal immunity in mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xi, M.; Yao, Q.; Ge, W.; Chen, Y.; Cao, B.; Wang, Z.; Cui, X.; Sun, Q. Effects of stachyose on intestinal microbiota and immunity in mice infected with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Bai, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) total RNA against ETEC challenge in a mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, L. Protective efficacy of a novel multivalent vaccine in the prevention of diarrhea induced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in a murine model. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 23, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-S.; Yang, J.S.; Kim, K.W.; Yun, C.-H.; Holmgren, J.; Czerkinsky, C.; Han, S.H. Anti-bacterial and anti-toxic immunity induced by a killed whole-cell-cholera toxin B subunit cholera vaccine is essential for protection against lethal bacterial infection in mouse pulmonary cholera model. Mucosal Immunol. 2013, 6, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.Y.; Lee, S.; Rho, S.; Kim, J.-O.; Choi, S.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, J.Y.; Song, M.; Yang, J.S. Immunogenicity of a bivalent killed thimerosal-free oral cholera vaccine, Euvichol, in an animal model. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2018, 7, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sit, B.; Zhang, T.; Fakoya, B.; Akter, A.; Biswas, R.; Ryan, E.T.; Waldor, M.K. Oral immunization with a probiotic cholera vaccine induces broad protective immunity against Vibrio cholerae colonization and disease in mice. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.H.; Garza, J.; Choquette, M.; Hawkins, J.; Hoeper, A.; Bernstein, D.I.; Cohen, M.B. Safety and Immunogenicity of Escalating Dosages of a Single Oral Administration of Peru-15 pCTB, a Candidate Live, Attenuated Vaccine against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. CVI 2015, 22, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Lu, T.; Mani, S.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Walker, R.; Sack, D.A.; Zhang, W. Adjuvant effect of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) double-mutant heat-labile toxin (dmLT) on systemic immunogenicity induced by the CFA/I/II/IV MEFA ETEC vaccine: Dose-related enhancement of antibody responses to seven ETEC adhesins (CFA/I, CS1-CS6). Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 16, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, H.; Garcia, C.; Ruan, X.; Duan, Q.; Sack, D.A.; Zhang, W. Preclinical Characterization of Immunogenicity and Efficacy against Diarrhea from MecVax, a Multivalent Enterotoxigenic E. coli Vaccine Candidate. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00106-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, M., Jr.; Smith, M.; Poole, S.T.; Laird, R.M.; Rollenhagen, J.E.; Kaminski, R.W.; Wenzel, H.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Savarino, S.J. Evaluation of the reactogenicity, adjuvanticity and antigenicity of LT(R192G) and LT(R192G/L211A) by intradermal immunization in mice. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, W.; Boedeker, E.C. Attenuated Escherichia coli strains expressing the colonization factor antigen I (CFA/I) and a detoxified heat-labile enterotoxin (LThK63) enhance clearance of ETEC from the lungs of mice and protect mice from intestinal ETEC colonization and LT-induced fluid accumulation. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 152, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macpherson, A.J.; McCoy, K.D.; Johansen, F.-E.; Brandtzaeg, P. The immune geography of IgA induction and function. Mucosal. Immunol. 2008, 1, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riaz, S.; Steinsland, H.; Hanevik, K. Human Mucosal IgA Immune Responses against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Pathogens 2020, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Organs | Groups | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Group A (Control Group) | Group B (Unimmunized Mice Challenged) | Group C (Immunized Mice Challenged) | |
| Brain | Within normal limit | Gliosis and necrotic area are noted | Within normal limit |
| Heart | Within normal limit | Mild degeneration of myocytes with mild interstitial oedema | Within normal limit |
| Lung | Within normal limit | Extensive lymphocytic infiltration, congestion, and oedema of the interstitium with focal alveoli oedema and type II pneumocytes hyperplasia | Mild lymphocytic infiltration, congestion, and oedema of the interstitium with focal alveoli oedema and type II pneumocytes hyperplasia |
| Spleen | Within normal limit | Moderate focal parenchymal congestion with enlarged germinal centres, and focal white pulp disintegration and apoptosis | Mild focal parenchymal congestion and focal apoptosis |
| Kidney | Within normal limit | Mild degeneration of tubules Mild congestion Moderate inflammation of the interstitium | Mild degeneration of tubules Mild congestion Mild inflammation of the interstitium |
| Liver | Within normal limit | Mild degeneration of hepatocytes Severe sinusoidal congestion Mild Kupfer cell hyperplasia Moderate portal inflammation Moderate bile duct hyperplasia | Mild degeneration of hepatocytes Mild sinusoidal congestion Mild Kupfer cell hyperplasia Mild portal inflammation |
| Pancreas | Within normal limit | Within normal limit | Within normal limit |
| Intestines | Within normal limit | Severe necrosis, congestion and haemorrhage, and neutrophil infiltration | Within normal limit |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hui Xian, T.; Parasuraman, S.; Ravichandran, M.; Prabhakaran, G. Dual-Use Vaccine for Diarrhoeal Diseases: Cross-Protective Immunogenicity of a Cold-Chain-Free, Live-Attenuated, Oral Cholera Vaccine against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Challenge in BALB/c Mice. Vaccines 2022, 10, 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10122161
Hui Xian T, Parasuraman S, Ravichandran M, Prabhakaran G. Dual-Use Vaccine for Diarrhoeal Diseases: Cross-Protective Immunogenicity of a Cold-Chain-Free, Live-Attenuated, Oral Cholera Vaccine against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Challenge in BALB/c Mice. Vaccines. 2022; 10(12):2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10122161
Chicago/Turabian StyleHui Xian, Tew, Subramani Parasuraman, Manickam Ravichandran, and Guruswamy Prabhakaran. 2022. "Dual-Use Vaccine for Diarrhoeal Diseases: Cross-Protective Immunogenicity of a Cold-Chain-Free, Live-Attenuated, Oral Cholera Vaccine against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Challenge in BALB/c Mice" Vaccines 10, no. 12: 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10122161
APA StyleHui Xian, T., Parasuraman, S., Ravichandran, M., & Prabhakaran, G. (2022). Dual-Use Vaccine for Diarrhoeal Diseases: Cross-Protective Immunogenicity of a Cold-Chain-Free, Live-Attenuated, Oral Cholera Vaccine against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Challenge in BALB/c Mice. Vaccines, 10(12), 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10122161