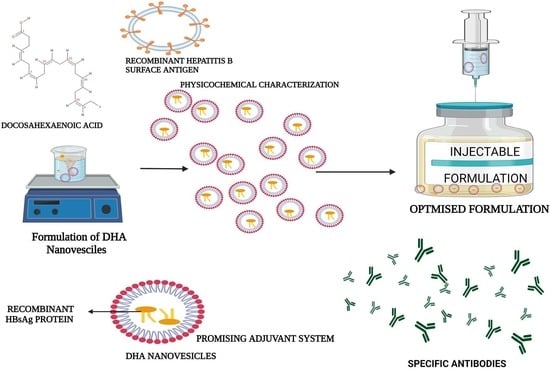
Design, Characterization, and Immune Augmentation of Docosahexaenoic Acid Nanovesicles as a Potential Delivery System for Recombinant HBsAg Protein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Formulation of DHA Nanovesicles
2.3. Lyophilization Process
2.4. Preparation of Sample Analyte
2.5. Physicochemical Characterization
2.5.1. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Analysis
2.5.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.5.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.5.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.5.6. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
2.5.7. Loading Studies
2.5.8. In Vitro Release Profile
2.6. In Vivo Study
2.6.1. Preparation of Test Sample
2.6.2. Immunogenicity Profile
2.6.3. Determination of Antibodies to HBsAg
2.6.4. Preparation and Validation of Standard Cure
2.7. Histopathological Analysis
2.8. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Characterization of LRPDNV
3.1.1. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Analysis
3.1.2. Morphological Analysis of LRPDNV
3.1.3. Thermal Analysis
3.1.4. XRD Analysis
3.1.5. NMR Studies
3.1.6. In Vitro Release Profile
3.2. In Vivo Study
3.3. Histopathology Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tripathi, N.K.; Shrivastava, A. Recent developments in recombinant protein–based dengue vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Tian, G.; Cui, Y.; Ding, C.; Deng, M.; Yu, C.; Xu, K.; Ren, J.; Yao, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Factors influencing immunologic response to hepatitis B vaccine in adults. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayman, A.A.; Faisal, M.M. Viral hepatitis in Saudi Arabia. An unfinished story. Saudi Med. J. 2015, 36, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walayat, S.; Ahmed, Z.; Martin, D.; Puli, S.; Cashman, M.; Dhillon, S. Recent advances in vaccination of non-responders to standard dose hepatitis B virus vaccine. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2503–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, A.J.; Bijker, E.M. A guide to vaccinology: From basic principles to new developments. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, I.; Garg, R.; van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk, S. Selection of adjuvants for vaccines targeting specific pathogens. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2019, 18, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizi, F.; Tarantino, A.; Castelnovo, C.; Martin, P.; Mess, P.G. Recombinant hepatitis B vaccine adjuvanted with AS04 in dialysis patients: A prospective cohort study. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2015, 40, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, S.M.; Sukumaran, N.; Nirmala, L.; Swarnalakshmi, R.; Anilbabu, B.; Siva, L.; Anbu, J.; Shanmugarajan, T.S.; Ravichandran, V. Immunopotentiation of hepatitis B vaccine using biodegradable polymers as an adjuvant. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2010, 43, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zakir, F.; Vaidya, B.; Amit, K.G.; Malik, B.; Suresh, P.V. Development and characterization of oleic acid vesicles for the topical delivery of fluconazole. Drug Delivery 2010, 17, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- William, S.; Stephen, R.W. Docosahexaenoic acid: Membrane properties of a unique fatty acid. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2003, 126, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulendran, B.S.; Arunachalam, P.; O’Hagan, D.T. Emerging concepts in the science of vaccine adjuvants. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 454–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namani, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Morigaki, K.; Walde, P. Vesicles form docosahexaenoic acid. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 54, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diego, C.; Miguel, A.M.; Ashley, F.; Lilian, S.; Kristine, O.; Juan, C.A.; Octavio, A. Immunosuppressive Mechanisms of Regulatory B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 611795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammone, M.A.; Riccioni, G.; Parrinello, G.; D’Orazio, N. Omega-3 Poly unsaturated fatty acids: Benefits and endpoints in sport. Nutrients 2018, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madkhali, O.A.; Sivakumar, S.M.; Sultan, M.H.; Bukhary, H.A.; Ghazwani, M.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Meraya, A.M.; Alshahrani, S.; Alqahtani, S.S.; Bakkari, M.A.; et al. Formulation and evaluation of injectable dextran sulfate sodium nanoparticles as a potent antibacterial agent. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, L.; Castelli, F.; Sarpietro, M.G. Differential scanning calorimetry analyses of Idebenone-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles interactions with a model of bio-membrane: A comparison with in vitro skin permeation data. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, M.F.; Safhi, M.M.; Anwer, T.; Siddiqui, R.; Khan, G.; Moni, S.S. Therapeutic potential of Vanillylacetone against CCl4 induced hepatotoxicity by suppressing the serum marker, oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines and apoptosis in Swiss albino mice. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2018, 105, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandalakshmi, K.; Venugobal, J.; Ramasamy, V. Characterization of silver nanoparticles by green synthesis method using Pedalium murex leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shnoudeh, A.J.; Hamad, I.; Abdo, R.W.; Qadumii, L.; Jaber, A.Y.; Surchi, H.S.; Alkelany, S.Z. Chapter 15—Synthesis, characterization, and applications of metal nanoparticles. In Advances in Pharmaceutical Product Development and Research, Biomaterials and Bionanotechnology; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 527–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, E.; Singhvi, G. Chapter 4—Multifunctional nanocrystals for cancer therapy: A potential nanocarrier. In Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery and Therapy; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 91–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moni, S.S.; Alam, M.F.; Safhi, M.M.; Sultan, M.H.; Makeen, H.A.; Elmobark, M.E. Development of formulation methods and physical characterization of injectable sodium selenite nanoparticles for the delivery of Sorafenib tosylate. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshyar, N.; Gray, S.; Han, H.; Bao, G. The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 673–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petithory, T.; Pieuchot, L.; Josien, L.; Ponche, A.; Anselme, K.; Vonna, L. Size-dependent internalization efficiency of macrophages from adsorbed nanoparticle-based monolayers. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Sun, L.; Bevan, M.A.; Crooks, R.M. Comparison of nano-particle size and electrophoretic mobility measurements using a carbon-nanotube-based coulter counter, dynamic light scattering, transmission electron microscopy, and phase analysis light scattering. Langmuir 2004, 20, 6940–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, V.; Destaillats, F.; Juanéda, P.; Dionisi, F.; Lambelet, P.; Jean-Louis, S.; Berdeaux, O. Thermal degradation of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids during deodorization of fish oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2006, 108, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar García, J.D.; Prieto, C.; Pardo-Figuerez, M.; Lagaron, J.M. Room temperature nanoencapsulation of bioactive eicosapentaenoic acid rich oil within whey protein microparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, H.; Mishra, D.; Mishra, P.K.; Nahar, M.; Dubey, V.; Jain, N.K. Evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticles as carriers for delivery of hepatitis B surface antigen for vaccination using subcutaneous route. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 13, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melissa, D.H.; Lu, X.; Jay, M.; Thomas, D.D. Optimization of the lyophilization process for long-term stability of solid–lipid nanoparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2012, 38, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulden, J.; Yefanov, O.M.; Mancuso, A.P.; Abramova, V.V.; Hilhorst, J.; Byelov, D.; Snigireva, I.; Snigirev, A.; Petukhov, A.V.; Vartanyants, I.A. Coherent X-ray imaging of defects in colloidal crystals. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 224105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexandri, E.; Ahmed, R.; Siddiqui, H.; Choudhary, M.L.; Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Gerothanassis, I.P. High resolution NMR spectroscopy as a structural and analytical tool for unsaturated lipids in solution. Molecules 2017, 22, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenberg, K.F. Quantitative high resolution 13C nuclear magnetic resonance of the olefinic and carbonyl carbons of edible vegetable oils. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1990, 67, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharali, D.J.; Bharali, D.J.; Elkin, G.; Qi, W.; Hutson, V.; Mousa, S.A.; Thanavala, Y. Novel nanoparticles for the delivery of recombinant hepatitis B vaccine. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2008, 4, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewangan, H.K. Different approaches for nanovaccine formulation and characterization. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1116, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Hosseini, S.N.; Khavari-Nejad, R.A.; Najafi, F.; Mahdavi, M. HBs antigen and mannose loading on the surface of iron oxide nanoparticles in order to immuno-targeting: Fabrication, characterization, cellular and humoral immunoassay. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 1543–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadian, A.; Dounighi, N.M.; Avadi, M. Enteric trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles containing hepatitis B surface antigen for oral delivery. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2015, 11, 2811–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, M.; Naser, M.D.; Seyed Mahdi, R.S.; Delaram, D.; Amir, A.; Mehdi, K.; Soheila, A.; Younes, P.S. Development and physicochemical, toxicity and immunogenicity assessments of recombinant hepatitis B surface antigen (rHBsAg) entrapped in chitosan and mannosylated chitosan nanoparticles: As a novel vaccine delivery system and adjuvant. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sreenivas, P.; Erdal, C.; Mohammed, G.Z.; Satyanarayana, S.; Oya Alpar, H. Enhancement of immune response of HBsAg loaded poly (L-lactic acid) microspheres against Hepatitis B through incorporation of alum and chitosan. J. Microencapsul. 2007, 24, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, X.; Bian, Y.; Wang, S.; Chai, Q.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, P.; Peng, H.; Yan, X.; et al. Dual-targeting nanoparticle vaccine elicits a therapeutic antibody response against chronic hepatitis B. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhalim, M.A.K.; Jarrar, B.M. Histological alterations in the liver of rats induced by different gold nanoparticle sizes, doses and exposure duration. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nobili, V.; Carpino, G.; Alisi, A.; De Vito, R.; Franchitto, A.; Alpini, G.; Onori, P.; Gaudio, E. Role of docosahexaenoic acid treatment in improving liver histology in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Zeta Potential (mV) | PDI | % PDI | Particle Size (z. d.nm) | Particle Size in Mass (r.nm) | % Mass r.nm | Mobility (µm cm/Vs) | Conductivity (mS/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −60.4 ± 10.4 | 0.201 | 74.8 | 361.4 ± 48.24 | 298.8 ± 13.4 | 50 | −3.417 | 0.728 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakkari, M.A.; Moni, S.S.; Alshammari, A.; Salawi, A.; Sultan, M.H.; Madkhali, O.A.; Alqahtani, S.S.; Alam, M.F.; Shaheen, E.S.; Elmobark, M.E. Design, Characterization, and Immune Augmentation of Docosahexaenoic Acid Nanovesicles as a Potential Delivery System for Recombinant HBsAg Protein. Vaccines 2022, 10, 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060954
Bakkari MA, Moni SS, Alshammari A, Salawi A, Sultan MH, Madkhali OA, Alqahtani SS, Alam MF, Shaheen ES, Elmobark ME. Design, Characterization, and Immune Augmentation of Docosahexaenoic Acid Nanovesicles as a Potential Delivery System for Recombinant HBsAg Protein. Vaccines. 2022; 10(6):954. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060954
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakkari, Mohammed Ali, Sivakumar S. Moni, Abdulrahman Alshammari, Ahmad Salawi, Muhammad H. Sultan, Osama A. Madkhali, Saad S. Alqahtani, Mohammad Firoz Alam, Emad Sayed Shaheen, and Mohamed Eltaib Elmobark. 2022. "Design, Characterization, and Immune Augmentation of Docosahexaenoic Acid Nanovesicles as a Potential Delivery System for Recombinant HBsAg Protein" Vaccines 10, no. 6: 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060954
APA StyleBakkari, M. A., Moni, S. S., Alshammari, A., Salawi, A., Sultan, M. H., Madkhali, O. A., Alqahtani, S. S., Alam, M. F., Shaheen, E. S., & Elmobark, M. E. (2022). Design, Characterization, and Immune Augmentation of Docosahexaenoic Acid Nanovesicles as a Potential Delivery System for Recombinant HBsAg Protein. Vaccines, 10(6), 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060954