Poly(meta/para-Terphenylene-Methyl Piperidinium)-Based Anion Exchange Membranes: The Effect of Backbone Structure in AEMFC Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Synthesis of Poly(meta/para-terphenylene-methyl piperidinium) Copolymers with Various Contents of m-terphenyl Units, m-p-MP-y, 6
2.2. Membrane Fabrication
2.3. Characterization and Miscellaneous Measurements
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Polymer Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Membrane Preparation
3.3. Morphological Analyses
3.4. Ion Exchange Capacity, Water Uptake, Swelling Ratio, and Density Measurements of the Membranes
3.5. Ion Conductivity
3.6. Thermal Stability and Mechanical Properties
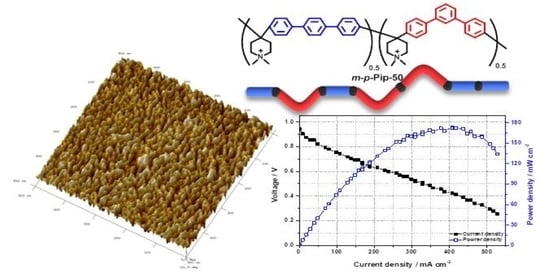
3.7. Single Cell Performance
3.8. Alkaline Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, F.; Dong, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yan, F. Base stable pyrrolidinium cations for alkaline anion exchange membrane applications. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 6740–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.N.; Wang, L.S.; Lin, C.X.; Zhuo, Y.; Zhang, Q.G.; Zhu, A.M.; Liu, Q.L. Phenolphthalein-based poly(arylene ether sulfone nitrile)s multiblock copolymers as anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8284–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, N.; Shimada, M.; Ono, H.; Akiyama, R.; Nishino, E.; Asazawa, K.; Miyake, J.; Watanabe, M.; Miyatake, K. Aromatic copolymers containing ammonium-functionalized oligophenylene moieties as highly anion conductive membranes. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 8238–8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.D.; Bae, C. Mechanistic analysis of ammonium cation stability for alkaline exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 17314–17320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Fukasawa, K.; Nishino, E.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yamada, K.; Tanaka, H.; Bae, B.; Miyatake, K.; Watanabe, M. Anion conductive block poly(arylene ether)s: Synthesis, properties, and application in alkaline fuel cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10646–10654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Pan, Z.; An, L. Recent advances in alkali-doped polybenzimidazole membranes for fuel cell applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 89, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Chen, R.; An, L.; Li, Y. Alkaline anion exchange membrane fuel cells for cogeneration of electricity and valuable chemicals. J. Power Sources 2017, 365, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayadevi, T.; Sung, S.; Chae, J.E.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, T.-H. Quaternary ammonium-functionalized poly(ether sulfone ketone) anion exchange membranes: The effect of block ratios. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 18403–18414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.; Mayadevi, T.S.; Chae, J.E.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, T.-H. Effect of increasing hydrophilic–hydrophobic block length in quaternary ammonium-functionalized poly(ether sulfone) block copolymer for anion exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 81, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.X.; Huang, X.L.; Guo, D.; Zhang, Q.G.; Zhu, A.M.; Ye, M.L.; Liu, Q. Side-chain-type anion exchange membranes bearing pendant quaternary ammonium groups via flexible spacers for fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13938–13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dang, H.-S.; Weiber, E.A.; Jannasch, P. Poly(phenylene oxide) functionalized with quaternary ammonium groups via flexible alkyl spacers for high-performance anion exchange membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 5280–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S.; Hou, J.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. A strategy to construct alkali-stable anion exchange membranes bearing ammonium groups via flexible spacers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15015–15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Lee, B.; Yun, D.; Al Munsur, A.Z.; Chae, J.E.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Nam, S.Y.; Park, C.H.; Kim, T.-H. Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide)s with various head groups: Effect of head groups on the properties of anion exchange membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41279–41292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.H.; Lin, C.X.; Hu, E.N.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Q.G.; Zhu, A.M.; Liu, Q. Anion exchange membranes with well-developed conductive channels: Effect of the functional groups. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.-S.; Jannasch, P. A comparative study of anion-exchange membranes tethered with different hetero-cycloaliphatic quaternary ammonium hydroxides. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 21965–21978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsson, J.S.; Pham, T.H.; Jannasch, P. Poly(arylene piperidinium) hydroxide ion exchange membranes: Synthesis, alkaline stability, and conductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckham, T.J.; Holdcroft, S. Structure-morphology-property relationships of non-perfluorinated proton-conducting membranes. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4667–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varcoe, J.R.; Atanassov, P.; Dekel, D.R.; Herring, A.M.; Hickner, M.A.; Kohl, P.A.; Kucernak, A.R.; Mustain, W.E.; Nijmeijer, K.; Scott, K.; et al. Anion-exchange membranes in electrochemical energy systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3135–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.Q.; Lin, C.X.; Zhang, Q.G.; Zhu, A.M.; Liu, Q. Anion exchange membranes from hydroxyl-bearing poly(ether sulfone)s with flexible spacers via ring-opening grafting for fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 19044–19055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhu, L.; Chaloux, B.L.; Hickner, M.A. Anion exchange membranes by bromination of tetramethylbiphenol-based poly(sulfone)s. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 2442–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.; Mayadevi, T.; Min, K.; Lee, J.; Chae, J.E.; Kim, T.-H. Crosslinked PPO-based anion exchange membranes: The effect of crystallinity versus hydrophilicity by oxygen-containing crosslinker chain length. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 619, 118774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chu, X.; Liao, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ge, Z.; Hickner, M.A.; Li, N. Tuning the properties of poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) anion exchange membranes and their performance in H2/O2 fuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Lee, B.-N.; Nam, S.Y. Synthesis and characterization of PEEK containing imidazole for anion exchange membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 23759–23767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lin, C.X.; Wang, X.Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Q.G.; Zhu, A.M.; Liu, Q. Highly conductive anion exchange membranes with long flexible multication spacer. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 553, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Long, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H. Chemically stable poly(meta-terphenyl piperidinium) with highly conductive side chain for alkaline fuel cell membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 598, 117797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, J.; Miyatake, K. Quaternized poly(arylene perfluoroalkylene)s (QPAFs) for alkaline fuel cells—A perspective. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2019, 3, 1916–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-H.; Kim, Y.S.; Bae, C. Robust hydroxide ion conducting poly(biphenyl alkylene)s for alkaline fuel cell membranes. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, S.; Jeon, J.Y.; Adhikari, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Bae, C. Molecular engineering of hydroxide conducting polymers for anion exchange membranes in electrochemical energy conversion technology. Accounts Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2745–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.G.; Kreuer, K.D. Alkaline stability of quaternary ammonium cations for alkaline fuel cell membranes and ionic liquids. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.-S.; Jannasch, P. Alkali-stable and highly anion conducting poly(phenylene oxide)s carrying quaternary piperidinium cations. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 11924–11938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsson, J.S.; Pham, T.H.; Jannasch, P. Tuning poly(arylene piperidinium) anion-exchange membranes by copolymerization, partial quaternization and crosslinking. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 578, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Olsson, J.S.; Jannasch, P. Effects of the N-alicyclic cation and backbone structures on the performance of poly(terphenyl)-based hydroxide exchange membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 15895–15906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matanovic, I.; Maurya, S.; Park, E.J.; Jeon, J.Y.; Bae, C.; Kim, Y.S. Adsorption of polyaromatic backbone impacts the performance of anion exchange membrane fuel cells. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 4195–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peressin, N.; Adamski, M.; Schibli, E.M.; Ye, E.; Frisken, B.J.; Holdcroft, S. Structure-property relationships in sterically congested proton-conducting poly(phenylene)s: The impact of biphenyl linearity. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 3119–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, X.; Su, X.; Gao, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, L.; Di, M.; Li, T.; Ruan, X.; He, G. Twisted ether-free polymer based alkaline membrane for high-performance water electrolysis. J. Power Sources 2020, 480, 228805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zhang, S.; Cong, Y.; Zhu, X. Highly durable and conductive poly(arylene piperidine) with a long heterocyclic ammonium side-chain for hydroxide exchange membranes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 24954–24964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Lu, C.; Li, Y.; Long, C.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H. Tunable multi-cations-crosslinked poly(arylene piperidinium)-based alkaline membranes with high ion conductivity and durability. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 588, 117120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Olsson, J.S.; Jannasch, P. Poly(arylene alkylene)s with pendant N-spirocyclic quaternary ammonium cations for anion exchange membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 16537–16547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.-H.; Park, E.J.; Han, J.; Shin, D.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Bae, C. Poly(terphenylene) anion exchange membranes: The Effect of backbone structure on morphology and membrane property. ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuli, S.K.; Roy, A.L.; Elgammal, R.A.; Tian, M.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Fujiwara, T. Effect of morphology on anion conductive properties in self-assembled polystyrene-based copolymer membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabd, Y.A.; Walker, C.W.; Beyer, F.L. Triblock copolymer ionomer membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 231, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-C.; Zhou, L.; Feng, C.-P.; Wu, X.-T.; Bao, R.-Y.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Yang, M.-B.; Yang, W. Direct modification of polyketone resin for anion exchange membrane of alkaline fuel cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.S.; Park, J.E.; Kim, S.; Han, S.-H.; Shin, S.-H.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, T.-H.; Yu, D.M.; So, S.; Hong, Y.T.; et al. Poly(carbazole)-based anion-conducting materials with high performance and durability for energy conversion devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 3633–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Munsur, A.Z.; Hossain, I.; Nam, S.Y.; Chae, J.E.; Kim, T.-H. Hydrophobic-hydrophilic comb-type quaternary ammonium-functionalized SEBS copolymers for high performance anion exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 599, 117829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X. Enhanced conductivity and stability via comb-shaped polymer anion exchange membrane incorporated with porous polymeric nanospheres. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 597, 117750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesfeld, S.; Dekel, D.R.; Page, M.; Bae, C.; Yan, Y.; Zelenay, P.; Kim, Y.S. Anion exchange membrane fuel cells: Current status and remaining challenges. J. Power Sources 2018, 375, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagesteijn, K.F.L.; Ladewig, B.P.; Ladewig, B.P. A review of the synthesis and characterization of anion exchange membranes. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 11131–11150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, N.; Lu, C.; Long, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q. Controllable physical-crosslinking poly(arylene 6-azaspiro[5.5] undecanium) for long-lifetime anion exchange membrane applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 590, 117307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, G.; Shahi, V.K. Poly(arylene ether ketone) copolymer grafted with amine groups containing a long alkyl chain by chloroacetylation for improved alkaline stability and conductivity of anion exchange membrane. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Ma, L.; Yu, Q.; Qaisrani, N.A.; Li, L.; Zhou, R.; He, G.; Zhang, F. Partially fluorinated, multication cross-linked poly(arylene piperidinium) membranes with improved conductivity and reduced swelling for fuel cell application. Ionics 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Membrane Code | IEC (meq/g) | Water Uptake (%) | Swelling Ratio (%) | Density (Dry) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calc. a | Exp. b | 20 °C | 80 °C | 20 °C (Δl) | 80 °C (Δl) | 20 °C (Δt) | 80 °C (Δt) | ||
| m-p-MP-20 | 2.80 | 2.21 ± 0.06 | 45.6 ± 0.4 | 96.4 ± 0.5 | 19.0 ± 0.3 | 28.6 ± 0.6 | 17.6 ± 0.5 | 19.0 ± 0.6 | 1.74 |
| m-p-MP-50 | 2.80 | 2.49 ± 0.01 | 49.3 ± 0.7 | 107.5 ± 1.8 | 19.0 ± 0.2 | 33.3 ± 0.3 | 11.1 ± 0.7 | 12.5 ± 0.4 | 1.66 |
| m-p-MP-60 | 2.80 | 2.30 ± 0.03 | 59.4 ± 0.8 | 201.7 ± 2.9 | 20.0 ± 0.5 | 45.0 ± 0.4 | 19.4 ± 0.6 | 23.7 ± 0.7 | 1.64 |
| Membrane Code | OH− Conductivity (mS/cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | 40 °C | 60 °C | 80 °C | |
| m-p-MP-20 | 32.76 ± 0.12 | 48.60 ± 0.01 | 72.50 ± 0.01 | 103.67 ± 0.71 |
| m-p-MP-50 | 53.53 ± 0.15 | 70.96 ± 0.37 | 99.07 ± 0.21 | 130.39 ± 0.59 |
| m-p-MP-60 | 39.18 ± 0.12 | 55.67 ± 0.11 | 77.62 ± 0.30 | 83.79 ± 1.27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayadevi, T.S.; Sung, S.; Varghese, L.; Kim, T.-H. Poly(meta/para-Terphenylene-Methyl Piperidinium)-Based Anion Exchange Membranes: The Effect of Backbone Structure in AEMFC Application. Membranes 2020, 10, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110329
Mayadevi TS, Sung S, Varghese L, Kim T-H. Poly(meta/para-Terphenylene-Methyl Piperidinium)-Based Anion Exchange Membranes: The Effect of Backbone Structure in AEMFC Application. Membranes. 2020; 10(11):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110329
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayadevi, T. S., Seounghwa Sung, Listo Varghese, and Tae-Hyun Kim. 2020. "Poly(meta/para-Terphenylene-Methyl Piperidinium)-Based Anion Exchange Membranes: The Effect of Backbone Structure in AEMFC Application" Membranes 10, no. 11: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110329
APA StyleMayadevi, T. S., Sung, S., Varghese, L., & Kim, T. -H. (2020). Poly(meta/para-Terphenylene-Methyl Piperidinium)-Based Anion Exchange Membranes: The Effect of Backbone Structure in AEMFC Application. Membranes, 10(11), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110329