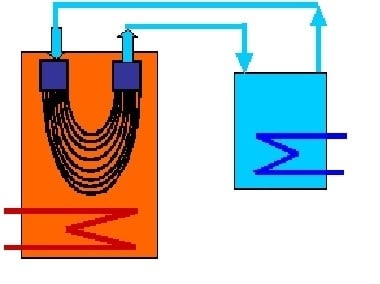
The Application of Submerged Modules for Membrane Distillation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Heat and Mass Transfer
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Influence of MD Process Parameters
4.2. The Effect of Membrane Morphology
4.3. The Effect of Capillary Membrane Length
4.4. Module Construction
4.5. Comparison of Submerged and Capillary MD Modules
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fane, A.G. Submerged membranes. In Advanced Membrane Technology and Applications; Li, N.N., Fane, A.G., Ho, W.S.W., Matsuura, T., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; Chapter 10. [Google Scholar]
- Khaing, T.H.; Li, J.F.; Li, Y.Z.; Wai, N.; Wong, F.S. Feasibility study on petrochemical wastewater treatment and reuse using a novel submerged membrane distillation bioreactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 74, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Y.; Xu, Y.P.; Chen, Z.L.; Nan, J.; Li, G.B. Air bubbling for alleviating membrane fouling of immersed hollow-fiber membrane for ultrafiltration of river water. Desalination 2010, 260, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhondi, E.; Zamani, F.; Tng, K.H.; Leslie, G.; Krantz, W.B.; Fane, A.G.; Chew, J.W. The Performance and Fouling Control of Submerged Hollow Fiber (HF) Systems: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.C.; Wang, Z.W.; Huang, S.S.; Mai, S.H.; Yang, C.F.; Wang, X.H.; Zhou, Z. Effects of various factors on critical flux in submerged membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.G.; Park, S.W.; Oh, D.K. Increase of Xylitol Productivity by Cell-Recycle Fermentation of Candida tropicalis Using Submerged Membrane Bioreactor. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.W.; Ma, J.X.; Tang, C.Y.; Kimura, K.; Wang, Q.Y.; Han, X.M. Membrane cleaning in membrane bioreactors: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 276–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.W.; Wu, Z.C. Chemical Cleaning of Membranes in a Long-Term Operated Full-Scale MBR for Restaurant Wastewater Treatment. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 2481–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, J.; Albasi, C.; Lafforgue, C. Filtration characteristics of hollow fiber microfiltration membranes used in a specific double membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2009, 48, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhondi, E.; Wicaksana, F.; Fane, A.G. Evaluation of fouling deposition, fouling reversibility and energy consumption of submerged hollow fiber membrane systems with periodic backwash. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.C.; Cooper, P.; Nelemans, B.; Cath, T.Y.; Nghiem, L.D. Optimising thermal efficiency of direct contact membrane distillation by brine recycling for small-scale seawater desalination. Desalination 2015, 374, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lokare, O.R.; Tavakkoli, S.; Khanna, V.; Vidic, R.D. Importance of feed recirculation for the overall energy consumption in membrane distillation systems. Desalination 2018, 428, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Naidu, G.; Jeong, S.; Vigneswaran, S.; Lee, S.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Experimental comparison of submerged membrane distillation configurations for concentrated brine treatment. Desalination 2017, 420, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Naidu, G.; Jeong, S.; Lee, S.; Vigneswarana, S. Fractional-submerged membrane distillation crystallizer (F-SMDC) for treatment of high salinity solution. Desalination 2018, 440, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, H.; Meng, S.; Li, H.Y.; Ye, Y.; Chen, V. Effect of operation parameters on the mass transfer and fouling in submerged vacuum membrane distillation crystallization (VMDC) for inland brine water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chung, T.S. Recent advances in membrane distillation processes: Membrane development, configuration design and application exploring. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 474, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Mavukkandy, M.O.; Bilad, M.R.; Arafat, H.A. Understanding wetting phenomena in membrane distillation and how operational parameters can affect it. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 515, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamani, H.; Matsuura, T.; Rana, D.; Lan, C.Q. Modeling of pore wetting in vacuum membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaughey, A.L.; Gustafson, R.D.; Childress, A.E. Effect of long-term operation on membrane surface characteristics and performance in membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 543, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Warsinger, D.M.; Lienhard, J.H.; Duke, M.C.; Matsuura, T.; Samhaber, W.M. Wetting phenomena in membrane distillation: Mechanisms, reversal, and prevention. Water Res. 2018, 139, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, M.; Białończyk, L. Production of ethanol from lactose in a bioreactor integrated with membrane distillation. Desalination 2013, 323, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsinger, D.M.; Servi, A.; Van Belleghem, S.; Gonzalez, J.; Swaminathan, J.; Kharraz, J.; Chung, H.W.; Arafat, H.A.; Gleason, K.K.; Lienhard, J.H. Combining air recharging and membrane superhydrophobicity for fouling prevention in membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 505, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Warsinger, D.M.; Lienhard, J.H.; Samhaber, W.M. Wetting prevention in membrane distillation through superhydrophobicity and recharging an air layer on the membrane surface. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 530, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, W.W.; Li, H.Y.; Ye, Y.; Chen, V. Evaluation of silica fouling for coal seam gas produced water in a submerged vacuum membrane distillation system. Desalination 2016, 393, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazgan-Birgi, P.; Ali, M.I.A.; Arafat, H.A. Comparative performance assessment of flat sheet and hollow fiber DCMD processes using CFD modeling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.X.; Cha-Umpong, W.; Hou, J.W.; Ji, C.; Chen, V. Open-source industrial-scale module simulation: Paving the way towards the right configuration choice for membrane distillation. Desalination 2019, 464, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, B.C.; Skibinski, B.; Koch, K.; Mancel, C.; Celestino, C.Q.; Cunha, I.L.C.; Silva, M.R.; Alvim, C.B.; Faria, C.V.; Andrade, L.H.; et al. Critical performance assessment of a submerged hybrid forward osmosis—Membrane distillation system. Desalination 2019, 468, 114082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, L.; Ghaffour, N.; Al-Saadi, A.S.; Amy, G.L. Submerged membrane distillation for seawater desalination. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 55, 2741–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alia, A.; Quist-Jensena, C.A.; Macedonioa, F.; Drioli, E. Optimization of module length for continuous direct contact membrane distillation process. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2016, 110, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Hsu, Y.C.; Ye, Y.; Chen, V. Submerged membrane distillation for inland desalination applications. Desalination 2015, 361, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Dong, X.L.; Kang, G.D.; Zhou, M.Q.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.M. Fouling behavior and scaling mitigation strategy of CaSO4 in submerged vacuum membrane distillation. Desalination 2018, 425, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, H.; Lian, B.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, Y.; Leslie, G.; Chen, V. Numerical study of CaCO3 scaling in submerged vacuum membrane distillation and crystallization (VMDC). J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 559, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, H.; Ye, Y.; Li, H.Y.; Chen, V. Scaling mitigation in submerged vacuum membrane distillation and crystallization (VMDC) with periodic air-backwash. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 547, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukanea, S.; Leeb, J.G.; Ghaffourb, N. Direct contact membrane distillation module scale-up calculations: Choosing between convective and conjugate approaches. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.; Lior, N. Study of advancement to higher temperature membrane distillation. Desalination 2017, 419, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.W.; Woo, Y.C.; Ren, J.W.; Tijing, L.D.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Shon, H.K. Volatile fatty acids and biogas recovery using thermophilic anaerobic membrane distillation bioreactor for wastewater reclamation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Naidu, G.; Lee, S.; Vigneswaran, S. Effect of inorganic and organic compounds on the performance of fractional submerged membrane distillation-crystallizer. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndinisa, N.V.; Fane, A.G.; Wiley, D.E. Fouling control in a submerged flat sheet membrane system: Part I—Bubbling and hydrodynamic effects. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 1383–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawa, J.; Kujawski, W. Driving force and activation energy in air-gap membrane distillation process. Chem. Pap. 2015, 69, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Li, L.; Obusckovic, G.; Chau, J.; Sirkar, K.K. Novel cylindrical cross-flow hollow fiber membrane module for direct contact membrane distillation-based desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 545, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, R.D.; Hiibel, S.R.; Childress, A.E. Membrane distillation driven by intermittent and variable-temperature waste heat: System arrangements for water production and heat storage. Desalination 2018, 448, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZENA Membranes Company. Available online: http://www.zena-membranes.cz/index.php/applications/membrane-distillation-md/water-desalination (accessed on 17 January 2020).
- Smallwood, J. Solvent Recovery Handbook; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1993; p. 365. [Google Scholar]
- Gryta, M.; Tomaszewska, M. Heat transport in the membrane distillation process. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 144, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKetta, J.J.; Cunningham, W.A. (Eds.) Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing and Design; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Gryta, M. Fouling in direct contact membrane distillation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, J.; Chung, H.W.; Warsinger, D.M.; Lienhard, J.H. Membrane distillation model based on heat exchanger theory and configuration comparison. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- M.W. Kellogg Company, and United States. Office of Saline Water. Saline Water Conversion Engineering Data Book, 2nd ed.; The M.W. Kellogg Company: Washington, DC, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Gryta, M.; Tomaszewska, M.; Morawski, A.W. A capillary module for membrane distillation process. Chem. Pap. 2000, 54, 370–374. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, M.Q.; Sun, D.; Li, B.B.; Li, P.X. Evaluation of commercial PTFE membranes for desalination of brine water through vacuum membrane distillation. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2016, 110, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, D.; Amigo, J.; Suárez, F. Membrane distillation: Perspectives for sustainable and improved desalination. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 238–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, A.; Ahmad, H.; Antar, M.; Laoui, T.; Khayet, M. Experimental and theoretical investigations on water desalination using direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2017, 404, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Lee, S. Influence of Hydraulic Pressure on Performance Deterioration of Direct Contact Membrane Distillation (DCMD) Process. Membranes 2019, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Gharabli, S.; Kujawski, W.; El-Rub, Z.A.; Hamad, E.M.; Kujawa, J. Enhancing membrane performance in removal of hazardous VOCs from water by modified fluorinated PVDF porous material. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 556, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Kang, G.D.; Zhou, M.Q.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.M. Submerged vacuum membrane distillation crystallization (S-VMDC) with turbulent intensification for the concentration of NaCl solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Qiang, Z.M.; Xiao, S.H.; Liu, Q.X.; Lei, Y.Q.; Zhou, T.T. Degradation of Reactive Black 5 in a submerged photocatalytic membrane distillation reactor with microwave electrodeless lamps as light source. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Naidu, G.; Johir, M.A.H.; Choi, Y.; Jeong, S.; Vigneswaran, S. Acid mine drainage treatment by integrated submerged membrane distillation-sorption system. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryta, M. Effectiveness of Water Desalination by Membrane Distillation Process. Membranes 2012, 2, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



















| Manufacturer | Membrane | Polymer | dp [µm] | Porosity [%] | Din [mm] | Wall Thickness [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EuroSep Poland | EuroSep PP | PP | 0.20 | 70 | 1.8 | 0.4 |
| PolyMem Poland | K1800 | PP | 0.20 | 74 | 1.8 | 0.35 |
| Membrana Germany | Accurel PP S6/2 | PP | 0.22 | 73 | 1.8 | 0.4 |
| Membrana Germany | Accurel PP V8/2 HF | PP | 0.20 | 73 | 5.5 | 1.5 |
| Memtek, Australia | HL310 | ECTFE | 0.40 | 75 | 0.31 | 0.17 |
| Memtek, Australia | PV370 | PVDF | 0.10 | 74 | 0.37 | 0.12 |
| Module | Membrane | Number of Capillaries | Length [cm] | Area (Inside) [cm2] | Mode (Figure 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMD1 | EuroSep PP | 3 | 85.5 | 145.0 | D |
| SMD2 | K1800 | 3 | 84.7 | 143.7 | D |
| SMD3 | Accurel PP S6/2 | 2 | 60.5 | 68.4 | D |
| SMD4 | PV370 | 19 | 120 | 265.3 | D |
| SMD5 | Accurel PP S6/2 | 4 | 22.5 | 50.9 | C |
| SMD6 | Accurel PP V8/2 HF | 1 | 26.5 | 45.8 | B |
| SMD7 | HL310 | 75 | 13.0 | 95.1 | B |
| SMD8 | PV370 | 85 | 10.1 | 73.9 | B |
| SMD9 | K1800 | 3 | 20.0 | 98.8 | B |
| SMD10 | PV370 | 55 | 7.5 | 47.9 | E |
| SMD11 | PV370 | 55 | 8.7 | 55.6 | B |
| SMD12 | Accurel PP S6/2 | 2 | 120 | 136.7 | D |
| SMD13 | Accurel PP V8/2 HF | 1 | 69 | 119.5 | B |
| Module | Membrane | Number of Capillaries | Length [cm] | Area (Inside) [cm2] | Housing Diameter [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMD1 | Accurel PP S6/2 | 8 | 65 | 294 | 12 |
| CMD2 | Accurel PP V8/2 HF | 1 | 68 | 117 | 12 |
| Process | Membrane | Din [mm] | Wall Thickness [µm] | TF [K] | TDS [g/L] | Flux [L/m2h] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VMD | Accurel PP S6/2 | 1.8 | 400 | 343 | 14.2 | 8.2 | [15] |
| VMD | Accurel PP S6/2 | 1.8 | 400 | 343 | Demi 200 | 9.0 6.0 | [30] |
| VMD | Accurel PP S6/2 | 1.8 | 400 | 343 | 6.92 | 13.0 | [55] |
| VMD | PTFE | 0.86 | 415 | 348 | 1.8 | 4.2 | [31] |
| VMD | PTFE | 0.8 | 450 | 348 | 100 | 6.23 | [32] |
| VMD | PVDF | 0.7 | 250 | 328 | demi | 14.1 | [13] |
| DCMD | Accurel PP S6/2 | 1.8 | 400 | 343 | Demi 200 | 4.6 3.0 | [30] |
| DCMD | Accurel PP S6/2 | 1.8 | 400 | - | demi | 4.6 | [56] |
| DCMD | Accurel PP S6/2 | 1.8 | 400 | - | - | 8.2 | [24] |
| DCMD | PVDF | 0.7 | 250 | 328 | demi | 8.5 | [13] |
| DCMD | PVDF | 0.7 | 250 | 328 | 12 | 2.7 | [57] |
| DCMD | PVDF | 0.7 | 250 | 328 | demi | 7.9 | [13] |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gryta, M. The Application of Submerged Modules for Membrane Distillation. Membranes 2020, 10, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10020025
Gryta M. The Application of Submerged Modules for Membrane Distillation. Membranes. 2020; 10(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleGryta, Marek. 2020. "The Application of Submerged Modules for Membrane Distillation" Membranes 10, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10020025
APA StyleGryta, M. (2020). The Application of Submerged Modules for Membrane Distillation. Membranes, 10(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10020025