Facilitated Structure Formation in Isoporous Block Copolymer Membranes upon Controlled Evaporation by Gas Flow
Abstract
:New Concept
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Envelope Design
2.2. Preparation of Polymer Solutions
2.3. Fabrication of Flat Sheet Membranes
2.4. Solvent Evaporation and Temperature Drop on the Surface
2.5. Morphological Investigation
3. Results and Discussions
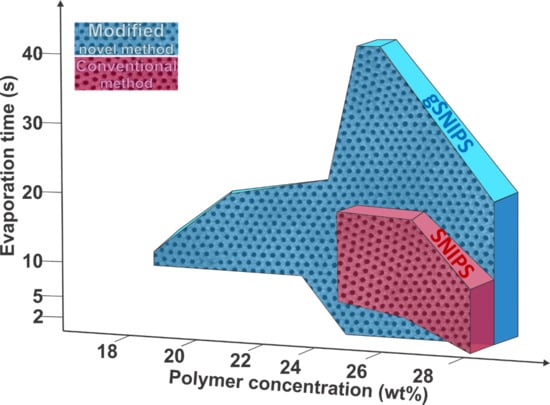
3.1. Membrane Fabrication under Normal Evaporation Conditions (by SNIPS)
3.2. Membrane Fabrication under Controlled Evaporation Conditions (by gSNIPS) and Influence of Block Copolymer Concentration
3.3. Influence of Solvents Composition on Structure Formation
3.4. Influence of Block Copolymer on Structure Formation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamley, I.W. Ordering in thin films of block copolymers: Fundamentals to potential applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 1161–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abetz, V.; Chan, C.H.; Luscombe, C.K.; Matson, J.B.; Merna, J.; Nakano, T.; Raos, G.; Russell, G.T. Quo vadis, macromolecular science? Reflections by the IUPAC polymer division on the occasion of the Staudinger centenary. Isr. J. Chem. 2020, 60, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lecommandoux, S.; Lazzari, M.; Liu, G. An introduction to block copolymer applications: State-of-the-art and future developments. In Block Copolymers in Nanoscience; Lazzari, M., Liu, G., Lecommandoux, S., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Abetz, V.; Boschetti-de-Fierro, A. 7.02—Block Copolymers in the Condensed State. In Polymer Science: A Comprehensive Reference; Matyjaszewski, K., Möller, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 7, pp. 3–44. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, Y.; Eisenberg, A. Self-assembly of block copolymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5969–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schacher, F.H.; Rupar, P.A.; Manners, I. Functional block copolymers: Nanostructured materials with emerging applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 7898–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandan, B.; Horechyy, A. Hairy core-shell polymer nano-objects from self-assembled block copolymer structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfac. 2015, 7, 12539–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epps, I.I.I.T.H.; O’Reilly, R.K. Block copolymers: Controlling nanostructure to generate functional materials—Synthesis, characterization, and engineering. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1674–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Müller, M. Process-directed self-assembly of copolymers: Results of and challenges for simulation studies. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, Y.M.; Moon, H.C. Star-shaped block copolymers: Effective polymer gelators of high-performance gel electrolytes for electrochemical devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfac. 2019, 11, 4399–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clodt, J.I.; Filiz, V.; Rangou, S.; Buhr, K.; Abetz, C.; Hoeche, D.; Hahn, J.; Jung, A.; Abetz, V. Double stimuli-responsive isoporous membranes via post-modification of pH-sensitive self-assembled diblock copolymer membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Qiu, X.; Nunes, S.P.; Peinemann, K.-V. Self-assembled isoporous block copolymer membranes with tuned pore sizes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10072–10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Rahman, M.M.; Abetz, C.; Rangou, S.; Zhang, Z.; Abetz, V. Novel post-treatment approaches to tailor the pore size of PS-b-PHEMA isoporous membranes. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1800435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Almodovar-Arbelo, N.E.; Weidman, J.L.; Corti, D.S.; Boudouris, B.W.; Phillip, W.A. Fit-for-purpose block polymer membranes molecularly engineered for water treatment. NPJ Clean Water 2018, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Rangou, S.; Abetz, C.; Filiz, V.; Abetz, V. Isoporous membranes from novel polystyrene-b-poly(4-vinylpyridine)-b-poly(solketal methacrylate) (PS-b-P4VP-b-PSMA) triblock terpolymers and their post-modification. Polymers 2019, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Rahman, M.M.; Abetz, C.; Höhme, A.-L.; Sperling, E.; Abetz, V. Chemically tailored multifunctional asymmetric isoporous triblock terpolymer membranes for selective transport. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abetz, V. Isoporous block copolymer membranes. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, G.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, J.K. Functional nanoporous membranes for drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 14814–14834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clodt, J.I.; Bajer, B.; Buhr, K.; Hahn, J.; Filiz, V.; Abetz, V. Performance study of isoporous membranes with tailored pore sizes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 495, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mulvenna, R.A.; Qu, S.; Boudouris, B.W.; Phillip, W.A. Block polymer membranes functionalized with nanoconfined polyelectrolyte brushes achieve sub-nanometer selectivity. ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abetz, V.; Kremer, K.; Müller, M.; Reiter, G. Functional macromolecular systems: Kinetic pathways to obtain tailored structures. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1800334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjabian, M.; Abetz, V. Advanced porous polymer membranes from self-assembling block copolymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinemann, K.-V.; Abetz, V.; Simon, P.F.W. Asymmetric superstructure formed in a block copolymer via phase separation. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radjabian, M.; Koll, J.; Buhr, K.; Vainio, U.; Abetz, C.; Handge, U.A.; Abetz, V. Tailoring the morphology of self-assembled block copolymer hollow fiber membranes. Polymer 2014, 55, 2986–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sankhala, K.; Koll, J.; Radjabian, M.; Handge, U.A.; Abetz, V. A pathway to fabricate hollow fiber membranes with isoporous inner surface. Adv. Mater. Interfac. 2017, 4, 1600991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangou, S.; Buhr, K.; Filiz, V.; Clodt, J.I.; Lademann, B.; Hahn, J.; Jung, A.; Abetz, V. Self-organized isoporous membranes with tailored pore sizes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 451, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radjabian, M.; Abetz, C.; Fischer, B.; Meyer, A.; Abetz, V. Influence of solvent on the structure of an amphiphilic block copolymer in solution and in formation of an integral asymmetric membrane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfac. 2017, 9, 31224–31234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegelmeier, C.; Filiz, V.; Abetz, V.; Perlich, J.; Fery, A.; Ruckdeschel, P.; Rosenfeldt, S.; Förster, S. Topological paths and transient morphologies during formation of mesoporous block copolymer membranes. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 5566–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clodt, J.I.; Rangou, S.; Schröder, A.; Buhr, K.; Hahn, J.; Jung, A.; Filiz, V.; Abetz, V. Carbohydrates as additives for the formation of isoporous PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer membranes. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallei, M.; Rangou, S.; Filiz, V.; Buhr, K.; Bolmer, S.; Abetz, C.; Abetz, V. The influence of magnesium acetate on the structure formation of polystyrene-block-poly(4-vinylpyridine)-based integral-asymmetric membranes. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Sageshima, Y.; Arai, S.; Noro, A.; Matsushita, Y. Fabrication and modification of ordered nanoporous structures from nanophase-separated block copolymer/metal salt hybrids. Langmuir 2012, 28, 17524–17529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wiesner, U. Tailoring pore size of graded mesoporous block copolymer membranes: Moving from ultrafiltration toward nanofiltration. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 6153–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.P.; Behzad, A.R.; Hooghan, B.; Sougrat, R.; Karunakaran, M.; Pradeep, N.; Vainio, U.; Peinemann, K.-V. Switchable pH-responsive polymeric membranes prepared via block copolymer micelle assembly. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3516–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.-D.; Yin, Y.-R.; Li, Z.-N.; Qiu, Y.-Y.; Yi, Z.; Gao, C.-J. Organic acids interacting with block copolymers have broadened the window that retains isoporous structures. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Zhu, G.-D.; Yi, Z.; Qiu, Y.-Y.; Liu, L.-F.; Gao, C.-J. Tailoring the pore size and permeability of isoporous membranes through blending with poly(ethylene glycol): Toward the balance of macro— and microphase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 598, 117755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Kwak, J.; Choi, C.; Seo, Y.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, B. Gyroid structures at highly asymmetric volume fractions by blending of ABC triblock terpolymer and AB diblock copolymer. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 9008–9014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, O.; Wu, M.-L.; Radjabian, M.; Abetz, C.; Abetz, V. Structure of nonsolvent-quenched block copolymer solutions after exposure to electric fields during solvent evaporation. Adv. Mater. Interfac. 2019, 6, 1900646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Q.; Jin, Y.; Qian, X.; Ma, R.; Liu, J.; Yang, D. Shear-induced parallel and transverse alignments of cylinders in thin films of diblock copolymers. Soft Matter. 2018, 14, 6635–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhala, K.; Wieland, D.C.F.; Koll, J.; Radjabian, M.; Abetz, C.; Abetz, V. Self-assembly of block copolymers during hollow fiber spinning: An in situ small-angle X-ray scattering study. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 7634–7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Böker, A.; Tsarkova, L. Temperature-controlled solvent vapor annealing of thin block copolymer films. Polymers 2019, 11, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillip, W.A.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Cussler, E.L. Cylinder orientation mechanism in block copolymer thin films upon solvent evaporation. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 7763–7770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.; Álvarez-Palacio, J.R.; Hakem, I.F.; Gu, Y.; Bockstaller, M.R.; Wiesner, U. Effect of humidity on surface structure and permeation of triblock terpolymer derived SNIPS membranes. Polymer 2017, 126, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillip, W.A.; O’Neill, B.; Rodwogin, M.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Cussler, E.L. Self-assembled block copolymer thin films as water filtration membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfac. 2010, 2, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankhala, K.; Koll, J.; Abetz, V. Setting the stage for fabrication of self-assembled structures in compact geometries: Inside-out isoporous hollow fiber membranes. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, J.; Clodt, J.I.; Abetz, C.; Filiz, V.; Abetz, V. Thin isoporous block copolymer membranes: It is all about the process. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfac. 2015, 7, 21130–21137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucher, T.; Filiz, V.; Abetz, C.; Abetz, V. Formation of thin, isoporous block copolymer membranes by an upscalable profile roller coating process—A promising way to save block copolymer. Membranes 2018, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, R.; Li, B.; Wang, Q. Self-assembly in block copolymer thin films upon solvent evaporation: A simulation study. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 4384–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.A.; Nobes, D.S.; Elliott, J.A.W. Experimental and numerical study of the evaporation of water at low pressures. Langmuir 2017, 33, 4578–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.C.; Kim, Y.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Kang, Y.S. Membrane formation by water vapor induced phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 156, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. An experimental investigation of evaporation time and the relative humidity on a novel positively charged ultrafiltration membrane via dry–wet phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Polymer Solution (in DMF/THF 1/1) | Qg | Average Pore Dimeter (nm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tg | 2 s | 5 s | 10 s | 20 s | 40 s | |
| 18 wt% PS-b-P4VP18150 | 4.5 L/min | 17.0 ± 2.8 | ||||
| 20 wt% PS-b-P4VP18150 | 1.5 L/min | 18.5 ± 2.7 | ||||
| 4.5 L/min | 15.9 ± 3.1 | 19.7 ± 2.7 | ||||
| 24 wt% PS-b-P4VP18150 | Normal | 23.0 ± 2.0 | 22.7 ± 2.4 | |||
| 1.5 L/min | 23.1 ± 2.2 | 22.9 ± 2.4 | 19.7 ± 2.4 | 19.3 ± 2.5 | ||
| 4.5 L/min | 20.5 ± 2.4 | 23.3 ± 2.4 | 23.2 ± 2.7 | 19.8 ± 2.5 | 21.5 ± 2.4 | |
| 28 wt% PS-b-P4VP18150 | Normal | 20.5 ± 2.4 | 20.8 ± 2.2 | 23.3 ± 2.5 | 22.4 ± 2.6 | |
| 1.5 L/min | 18.0 ± 2.7 | 19.1 ± 2.6 | 20.8 ± 1.7 | 22.5 ± 2.0 | ||
| 4.5 L/min | 17.1 ± 3.1 | 21.6 ± 2.6 | 22.6 ± 2.1 | |||
| Time | Evaporation under Environmental Conditions (Normal) and N2 Flow | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 1.5 L/min | 4.5 L/min | |||||||
| Polymer | DMF | THF | Polymer | DMF | THF | Polymer | DMF | THF | |
| 0 | 24.00 | 38.00 | 38.00 | 24.00 | 38.00 | 38.00 | 24.00 | 38.00 | 38.00 |
| 5 | 24.07 | 38.11 | 37.81 | 24.23 | 38.36 | 37.41 | 25.01 | 39.47 | 35.52 |
| 10 | 24.14 | 38.23 | 37.63 | 24.47 | 38.74 | 36.79 | 26.11 | 41.09 | 32.80 |
| 20 | 24.29 | 38.46 | 37.25 | 24.97 | 39.53 | 35.51 | 28.67 | 44.81 | 26.52 |
| 30 | 24.44 | 38.70 | 36.86 | 25.50 | 40.37 | 34.14 | 31.82 | 49.41 | 18.76 |
| 40 | 24.59 | 38.94 | 36.46 | 26.06 | 41.26 | 32.67 | 35.82 | 55.23 | 8.95 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sankhala, K.; Koll, J.; Abetz, V. Facilitated Structure Formation in Isoporous Block Copolymer Membranes upon Controlled Evaporation by Gas Flow. Membranes 2020, 10, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050083
Sankhala K, Koll J, Abetz V. Facilitated Structure Formation in Isoporous Block Copolymer Membranes upon Controlled Evaporation by Gas Flow. Membranes. 2020; 10(5):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050083
Chicago/Turabian StyleSankhala, Kirti, Joachim Koll, and Volker Abetz. 2020. "Facilitated Structure Formation in Isoporous Block Copolymer Membranes upon Controlled Evaporation by Gas Flow" Membranes 10, no. 5: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050083
APA StyleSankhala, K., Koll, J., & Abetz, V. (2020). Facilitated Structure Formation in Isoporous Block Copolymer Membranes upon Controlled Evaporation by Gas Flow. Membranes, 10(5), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050083