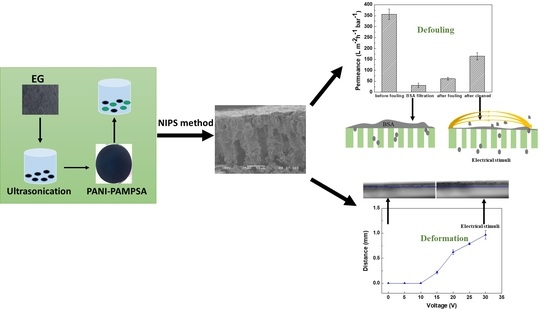
Linking the Tuneability and Defouling of Electrically Conductive Polyaniline/Exfoliated Graphite Composite Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of PANI/EG Composite Membranes
2.2.1. Synthesis of PANI-PAMPSA Complex
2.2.2. Preparation of Exfoliated Graphite
2.2.3. Membrane Fabrication
2.3. Characterisation Techniques
2.4. Membrane Transport Property
2.5. Membrane Electrical Tuneability Analysis
2.5.1. Dynamic Droplet Penetration Analysis
2.5.2. Membrane Deformation Analysis
2.6. Membrane Defouling Analysis
2.6.1. Membrane Fouling Experiment
2.6.2. Membrane Defouling Experiment
2.6.3. Defouling Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Properties, Morphology and Performance Characterisation of Membranes
3.1.1. FTIR and Electrical Conductivity of PANI/EG Composite Membranes
3.1.2. Morphology of EG and PANI/EG Composite Membranes
3.1.3. Transport Properties and Filtration Stability of PANI/EG Composite Membranes
3.2. Electrically Stimuli Response of PANI/EG Composite Membranes
3.2.1. Initial Tuneability Assessment of PANI/EG Composite Membranes
3.2.2. Deformation of PANI/EG Composite Membranes under Applied Potential
3.3. Defouling of PANI/EG Composite Membranes under Applied Potential
3.3.1. Membrane Defouling Performance in Filtration
3.3.2. Characterisation of Membrane Fouling Reduction
3.3.3. Mechanisms of Membrane Fouling Reduction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.-J.; Chu, L.-Y. Stimuli-responsive smart gating membranes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liangyin, C.; Rui, X.; Xiaojie, J. Stimuli-responsive membranes: Smart tools for controllable mass-transfer and separation processes. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 19, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formoso, P.; Pantuso, E.; De Filpo, G.; Nicoletta, F.P. Electro-Conductive Membranes for Permeation Enhancement and Fouling Mitigation: A Short Review. Membranes 2017, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, F.; Chae, S.-R.; Drews, A.; Kraume, M.; Shin, H.-S.; Yang, F. Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Membrane fouling and membrane material. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1489–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drews, A. Membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors—characterisation, contradictions, cause and cures. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 363, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaner, R.B. Gas, liquid and enantiomeric separations using polyaniline. Synth. Met. 2001, 125, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandera, D.; Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Husson, S.M. Stimuli-responsive membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 357, 6–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, M.A.C.; Huck, W.T.; Genzer, J.; Müller, M.; Ober, C.; Stamm, M.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Szleifer, I.; Tsukruk, V.V.; Urban, M. Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Wu, Z. A novel composite conductive microfiltration membrane and its anti-fouling performance with an external electric field in membrane bioreactors. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudchenko, A.V.; Rolf, J.; Russell, K.; Duan, W.; Jassby, D. Organic fouling inhibition on electrically conducting carbon nanotube–polyvinyl alcohol composite ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Vecitis, C.D. Conductive CNT-PVDF membrane for capacitive organic fouling reduction. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 459, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sairam, M.; Nataraj, S.K.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Roy, S.; Madhusoodana, C.D. Polyaniline Membranes for Separation and Purification of Gases, Liquids, and Electrolyte Solutions. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2006, 35, 249–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, J. The Use of Conducting Polymers in Membrane-Based Separations. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 984, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Xu, L.; Li, K.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Development of polyaniline conductive membrane for electrically enhanced membrane fouling mitigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Shahid, S.; Holda, A.K.; Emanuelsson, E.A.C.; Patterson, D.A. Stimuli responsive conductive polyaniline membrane: In-filtration electrical tuneability of flux and MWCO. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 552, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.L.; Shahid, S.; Patterson, D.A.; Emanuelsson, E.A.C. Flexible electro-responsive in-situ polymer acid doped polyaniline membranes for permeation enhancement and membrane fouling removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 578, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdo, S.E.; Warford, B.A.; Viswanathan, T. Electrical and thermal properties of graphite/polyaniline composites. J. Solid State Chem. 2012, 196, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćirić-Marjanović, G. Recent advances in polyaniline composites with metals, metalloids and nonmetals. Synth. Met. 2013, 170, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikzad, L.; Alibeigi, S.; Vaezi, M.R.; Yazdani, B.; Rahimipour, M.R. Synthesis of a Graphite-Polyaniline Nanocomposite and Evaluation of Its Electrochemical Properties. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2009, 32, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdo, S.; Li, Z.; Biris, A.S.; Watanabe, F.; Viswanathan, T.; Pavel, I. Structural, Electrical, and Thermal Behavior of Graphite-Polyaniline Composites with Increased Crystallinity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hao, Q.; Yang, X.; Lu, L.; Wang, X. A nanostructured graphene/polyaniline hybrid material for supercapacitors. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 2164–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mashat, L.; Shin, K.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Plessis, J.D.; Han, S.H.; Kojima, R.W.; Kaner, R.B.; Li, D.; Gou, X.; Ippolito, S.J. Graphene/polyaniline nanocomposite for hydrogen sensing. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16168–16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, K.; Mousavi, M.F.; Shamsipur, M.; Karami, H. Synthesis of polyaniline/graphite composite as a cathode of Zn-polyaniline rechargeable battery. J. Power Sources 2007, 170, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Cheung, W.; Wei, D.; Bogozi, A.; Chiu, P.L.; Wang, L.; Pontoriero, F.; Mendelsohn, R.; He, H. Improved conductivity of carbon nanotube networks by in situ polymerization of a thin skin of conducting polymer. Acs Nano 2008, 2, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Li, C.M.; Bao, S.-J.; Bao, Q.-L. Carbon nanotube/polyaniline composite as anode material for microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 170, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDiarmid, A.G.; Epstein, A.J. Secondary doping in polyaniline. Synth. Met. 1995, 69, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.-S. Effect of phenolic based polymeric secondary dopants on polyaniline. Synth. Met. 2002, 126, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweiri, R.; Sahari, J. Electrical properties of carbon-based polypropylene composites for bipolar plates in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC). J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Xiao, M.; Meng, Y. Facile synthesis of highly conductive polyaniline/graphite nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Shahid, S.; Shen, J.; Emanuelsson, E.; Patterson, D.A. A wide range and high resolution one-filtration molecular weight cut-off method for aqueous based nanofiltration and ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, W.; Ronen, A.; Walker, S.; Jassby, D. Polyaniline-Coated Carbon Nanotube Ultrafiltration Membranes: Enhanced Anodic Stability for In Situ Cleaning and Electro-Oxidation Processes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22574–22584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saveyn, H.; Van der Meeren, P.; Hofmann, R.; Stahl, W. Modelling two-sided electrofiltration of quartz suspensions: Importance of electrochemical reactions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 6768–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Ha, J.; Cho, J. Fabrication of Water-Dispersible Polyaniline-Poly (4-styrenesulfonate) Nanoparticles for Inkjet-Printed Chemical-Sensor Applications. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1772–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechavarría, L.; Hu, H.; Rincón, M.E. Polyaniline–poly (2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanosulfonic acid) composite thin films: Structure and properties. Thin Solid Film. 2003, 441, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misoon, O.; Seok, K. Effect of dodecyl benzene sulfonic acid on the preparation of polyaniline/activated carbon composites by in situ emulsion polymerization. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 59, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.-W.; O’Neal, J.; Shao, L.; Lutkenhaus, J.L. Charge storage in polymer acid-doped polyaniline-based layer-by-layer electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10127–10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Jamal, R.; Xu, F.; Ubul, A.; Abdiryim, T. The Effect of a Small Amount of Water on the Structure and Electrochemical Properties of Solid-State Synthesized Polyaniline. Materials 2012, 5, 1811–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, C.; Li, L.; Jin, S.; Zhang, B.; Qian, H.; Tong, G. Expanded graphite/polyaniline electrical conducting composites: Synthesis, conductive and dielectric properties. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1313–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Shi, H.; Chen, H.; Niu, G.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y. Synthesis of graphite nanosheets/polyaniline nanorods composites with ultrasonic and conductivity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.H.; Wu, D.J.; Weng, W.G.; Yan, W.L. Preparation of polymer/graphite conducting nanocomposite by intercalation polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 82, 2506–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Sun, H.; Peng, F.; Jiang, Z. Novel graphite-filled PVA/CS hybrid membrane for pervaporation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-K.; He, B.-I.; Zhou, W.-J.; Huang, J.; Li, X.-H.; Wu, B.; Li, H.-I. Electrochemical capacitance of well-coated single-walled carbon nanotube with polyaniline composites. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gilmore, K.J.; Moulton, S.E.; Wallace, G.G. Electrical stimulation promotes nerve cell differentiation on polypyrrole/poly (2-methoxy-5 aniline sulfonic acid) composites. J. Neural Eng. 2009, 6, 065002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Johnson, C.L.; Wang, H.-L. Preparation and characterization of monolithic polyaniline–graphite composite actuators. Polymer 2004, 45, 4769–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pile, D.; Zhang, Y.; Hillier, A.C. Electrochemically modulated permeability of poly (aniline) and composite poly (aniline)-poly (styrenesulfonate) membranes. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5925–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, F.; Lalia, B.S.; Kochkodan, V.; Hilal, N.; Hashaikeh, R. Electrically conductive polymeric membranes for fouling prevention and detection: A review. Desalination 2016, 391, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Katoh, S.; Nakajima, M.; Nabetani, H.; Abbott, T.P.; Shono, A.; Satoh, K. FT-IR analysis of BSA fouled on ultrafiltration and microfiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 192, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, H.; Dong, Y.; Mao, H.; Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Craig, V.S.J.; Hu, J. Cleaning using nanobubbles: Defouling by electrochemical generation of bubbles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 328, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecitis, C.D.; Schnoor, M.H.; Rahaman, M.S.; Schiffman, J.D.; Elimelech, M. Electrochemical multiwalled carbon nanotube filter for viral and bacterial removal and inactivation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3672–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Ng, W.J.; Liu, Y. Principle and applications of microbubble and nanobubble technology for water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Patterson, D.A. Linking the Tuneability and Defouling of Electrically Conductive Polyaniline/Exfoliated Graphite Composite Membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080631
Xu L, Wang K, Wang J, Patterson DA. Linking the Tuneability and Defouling of Electrically Conductive Polyaniline/Exfoliated Graphite Composite Membranes. Membranes. 2021; 11(8):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080631
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Lili, Kunpeng Wang, Jun Wang, and Darrell Alec Patterson. 2021. "Linking the Tuneability and Defouling of Electrically Conductive Polyaniline/Exfoliated Graphite Composite Membranes" Membranes 11, no. 8: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080631
APA StyleXu, L., Wang, K., Wang, J., & Patterson, D. A. (2021). Linking the Tuneability and Defouling of Electrically Conductive Polyaniline/Exfoliated Graphite Composite Membranes. Membranes, 11(8), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080631