Electrochemical and Electroconductive Behavior of Silk Fibroin Electrospun Membrane Coated with Gold or Silver Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
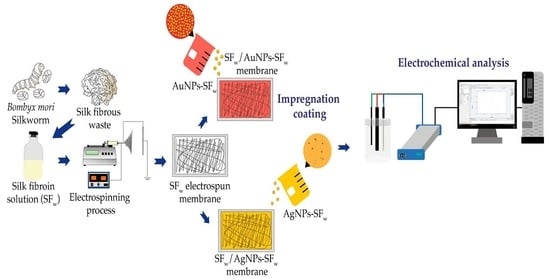
2.1. Silk Fibroin from Silk Fibrous Waste Extraction (SFw)
2.2. Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles
2.3. Preparation and Treatment of Silk Fibroin Electrospun Membranes
2.4. Impregnation Coatings of Treated Electrospun Membranes with AuNPs-SFw o AgNPs-SFw
2.5. UV-Visible Spectrophotometry and FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
2.6. Scanning Electron (SEM) and Field Emission (FESEM) Microscopy Analysis
2.7. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Analysis
2.8. MTT Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles
3.2. Preparation of Silk Fibroin Electrospun Membranes
3.3. Treatment of Electrospun Membranes
3.4. Functionalization of Treated Membranes with Metal Nanoparticles
3.5. Linear Sweep Voltammetry
3.6. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3.7. Cell Viability of Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capulli, A.; MacQueen, L.; Sheehy, S.P.; Parker, K. Fibrous scaffolds for building hearts and heart parts. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 96, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engelbrekt, C.; Sørensen, K.H.; Zhang, J.; Welinder, A.C.; Jensen, P.S.; Ulstrup, J. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles with starch-glucose and application in bioelectrochemistry. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabieva, I.; Sadriddinov, B.; Khasanova, M.; Alimova, K.; Klemola, K.; Pearson, J. Preparation of Natural Silk Waste Solutions by High Frecuency Heating. AUTEX Res. J. 2004, 4, 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Ríos, A.D.; Sánchez, S.; Álvarez-López, L.J.C.C.; Restrepo-Osorio, A. Electrospinning of silk fibroin obtained from colombian silk fibrous waste and their potential applications as biomaterials. In Proceedings of the 6th Amazon & Pacific Green Materials Congress and Sustainable Construction Materials LAT-RILEM Conference, Cali, Colombia, 27–29 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cristallini, C.; Vitale, E.; Giachino, C.; Rastaldo, R. Nanoengineering in Cardiac Regeneration: Looking Back and Going Forward. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Shi, H.; Yang, X.; Xiao, S. Self-Adhesion Conductive Sub-micron Fiber Cardiac Patch from Shape Memory Polymers to Promote Electrical Signal Transduction Function. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 19593–19602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, H.; Khalil, K.A.; Alshammari, B.A.; Abdal-Hay, A.; El-Salam, N.M.A. Development of New Bio-Composite of PEO/Silk Fibroin Blends Loaded with Piezoelectric Material. Polymers 2022, 14, 4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wu, H.; Venkataraman, V.; Hu, X. Silk fibroin-poly(lactic acid) biocomposites: Effect of protein-synthetic polymer interactions and miscibility on material properties and biological responses. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 104, 109890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo-Eraso, J.C.; Díaz-Arango, F.O.; Osorio-Alturo, A. Espectroscopia de impedancia eléctrica aplicada al control de la calidad en la industria alimentaria. Cienc. Tecnol. Agropecu. 2019, 21, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaramillo-Quiceno, N.; Restrepo-Osorio, A. Water-annealing treatment for edible silk fibroin coatings from fibrous waste. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 137, 48505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.; McCaslin, T.G.; Hazel, A.; Pagba, C.V.; Nevin, C.M.; Pavlova, A.; Barry, B.A.; Gumbart, J.C. Redox-Driven Conformational Dynamics in a Photosystem-II-Inspired β-Hairpin Maquette Determined through Spectroscopy and Simulation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 3536–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammarström, L.; Styring, S. Proton-coupled electron transfer of tyrosines in Photosystem II and model systems for artificial photosynthesis: The role of a redox-active link between catalyst and photosensitizer. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2379–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.; Bhattacharjee, R.R.; Banerjee, A.; Mandal, T.K. A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study of the Formation of Metal Nanoparticles by Using Synthetic Tyrosine-Based Oligopeptides. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2006, 12, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, S. Electrochemical Behavior and Sensitive Determination of L-Tyrosine with a Gold Nanoparticles Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Anal. Sci. 2009, 25, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soltani, N.; Saion, E.; Erfani, M.; Rezaee, K.; Bahmanrokh, G.; Drummen, G.P.C.; Bahrami, A.; Hussein, M.Z. Influence of the Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone Concentration on Particle Size and Dispersion of ZnS Nanoparticles Synthesized by Microwave Irradiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12412–12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Kedia, A.; Newmai, M.B.; Kumar, P.S. Differential role of PVP on the synthesis of plasmonic gold nanostructures and their catalytic and SERS properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 80342–80353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Janković, B.; Baumgartner, S.; Kocbek, P. The impact of relative humidity during electrospinning on the morphology and mechanical properties of nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.-K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmati, A.H.; Rashidi, A.; Ghazisaeidi, R.; Drean, J.-Y. Effect of needle length, electrospinning distance, and solution concentration on morphological properties of polyamide-6 electrospun nanowebs. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1452–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Kaplan, A.D.; Cebe, P. Determining Beta-Sheet Crystallinity in Fibrous Proteins by Thermal Analysis and Infrared Spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6161–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Nam, Y.S.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. Silk Fibroin Nanofiber. Electrospinning, Properties, and Structure. Polym. J. 2003, 35, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.-J.; Fridrikh, S.V.; Rutledge, A.G.C.; Kaplan, D.L. Electrospinning Bombyx mori Silk with Poly(ethylene oxide). Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chutipakdeevong, J.; Ruktanonchai, U.R.; Supaphol, P. Process optimization of electrospun silk fibroin fiber mat for accelerated wound healing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3634–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akturk, O.; Kismet, K.; Yasti, A.C.; Kuru, S.; Duymus, M.E.; Kaya, F.; Caydere, M.; Hucumenoglu, S.; Keskin, D. Wet electrospun silk fibroin/gold nanoparticle 3D matrices for wound healing applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 13234–13250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication of high performance silk fibroin fibers via stable jet electrospinning for potential use in anisotropic tissue regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3934–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Shao, Z. Electrospinning of reconstituted silk fiber from aqueous silk fibroin solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 2270–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.-L.; Teow, S.-Y.; Pushpamalar, J. Application of Metal Nanoparticle–Hydrogel Composites in Tissue Regeneration. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elgrishi, N.; Rountree, K.; McCarthy, B.D.; Rountree, E.; Eisenhart, T.T.; Dempsey, J.L. A Practical Beginner’s Guide to Cyclic Voltammetry. J. Chem. Educ. 2017, 95, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, C.C. Oil–oil and oil–source rock correlation. In Encyclopedia of Earth Science; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 442–444. [Google Scholar]
- Tschulik, K.; Palgrave, R.G.; Batchelor-McAuley, C.; Compton, R.G. ‘Sticky electrodes’ for the detection of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 295502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.M. Electrochemical Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Applications in Nitrate Detection, Catalysis and Antibacterial Activity. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Ireland, Maynooth, Ireland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kohl, P.A. Electrodeposition of Gold. In Modern Electroplating; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 115–130. [Google Scholar]
- Plowman, B.J.; Sidhureddy, B.; Sokolov, S.V.; Young, N.P.; Chen, A.; Compton, R.G. Electrochemical Behavior of Gold-Silver Alloy Nanoparticles. ChemElectroChem 2016, 3, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klabunde, R. Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lasia, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Its Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, S.; Ciancio, R.; Carlino, E.; Bhatti, A.S. Role of Au(NPs) in the enhanced response of Au(NPs)-decorated MWCNT electrochemical biosensor. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonanni, A.; Pumera, M.; Miyahara, Y. Influence of gold nanoparticle size (2–50 nm) upon its electrochemical behavior: An electrochemical impedance spectroscopic and voltammetric study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4980–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Le, T.-H.; Park, C.S.; Park, G.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.; Kwon, O.S.; Lim, G.T.; Yoon, H. A Solution-Processable, Nanostructured, and Conductive Graphene/Polyaniline Hybrid Coating for Metal-Corrosion Protection and Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abouzari, M.S.; Berkemeier, F.; Schmitz, G.; Wilmer, D. On the physical interpretation of constant phase elements. Solid State Ionics 2009, 180, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, A.; Genys, P.; Ramanaviciene, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Based Evaluation of 1,10-Phenanthroline-5,6-dione and Glucose Oxidase Modified Graphite Electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 146, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorcin, J.-B.; Orazem, M.E.; Pébère, N.; Tribollet, B. CPE analysis by local electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, Z.; Erkoc, P.; Sarac, A.S. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopic study of single-stranded DNA-immobilized electroactive polypyrrole-coated electrospun poly(I/I-caprolactone) nanofibers. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, B.A. Equivalent Circuit: (equivcrt.pas): Users Manual; Department of Chemical Technology, University of Twente: Enschede, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Beltran-Vargas, N.E.; Peña-Mercado, E.; Sánchez-Gómez, C.; Garcia-Lorenzana, M.; Ruiz, J.-C.; Arroyo-Maya, I.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; Campos-Terán, J. Sodium Alginate/Chitosan Scaffolds for Cardiac Tissue Engineering: The Influence of Its Three-Dimensional Material Preparation and the Use of Gold Nanoparticles. Polymers 2022, 14, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfdahl, A.; Jern, A.; Flyman, S.; Kåredal, M.; Karlsson, H.L.; Larsson-Callerfelt, A.-K. Silver Nanoparticles Alter Cell Viability Ex Vivo and in Vitro and Induce Proinflammatory Effects in Human Lung Fibroblasts. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sample | Vibrational Modes | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Amide I (cm−1) | Amide II (cm−1) | Amide III (cm−1) | |
| SFw | 1635 | 1515 | 1230 |
| F50 1d20 2—control | 1640 | 1528 | 1241 |
| F50d20—10 min | 1620 | 1509 | 1230 |
| F50d20—15 min | 1621 | 1515 | 1227 |
| F50d25—control | 1640 | 1528 | 1241 |
| F50d25—10 min | 1621 | 1513 | 1230 |
| F50d25—15 min | 1620 | 1511 | 1229 |
| Structure Type | SFw | SFw/PEO (Untreated) | F50d20 | F50d25 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d20 | d25 | 10 min | 15 min | 10 min | 15 min | ||
| β-sheets (strong, weak, intra and intermolecular) | 28% | 18% | 12% | 56% | 64% | 46% | 55% |
| β-turns | - | - | - | 33% | 2% | - | 32% |
| Side chains (Tyr) | 5% | 2% | 2% | 7% | 8% | 7% | 7% |
| Random coils | 24% | 45% | 51% | - | 8% | 37% | - |
| α-helix | 39% | - | - | - | 18% | - | - |
| turns | 4% | 35% | 35% | 4% | 1% | 10% | 5% |
| Structure Type | SFw (Control) | AuNPs-SFw | AgNPs-SFw | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UW | W | UW | W | ||||||
| 4 h | 24 h | 4 h | 24 h | 4 h | 24 h | 4 h | 24 h | ||
| β-sheets (strong, weak, intra and intermolecular) | 55% | 52% | 60% | 52% | 55% | 48% | 47% | 46% | 46% |
| β-turns | 32% | 0% | 2% | 38% | 1% | - | - | - | - |
| Side chains (Tyr) | 7% | 4% | 8% | 5% | 2% | 5% | 4% | 4% | 4% |
| Random coils | - | 4% | 11% | - | 26% | 39% | 34% | 37% | 38% |
| α-helix | - | 35% | 12% | - | 1% | - | - | - | - |
| Turns | 5% | 4% | 8% | 5% | 16% | 8% | 14% | 13% | 12% |
| Sample | Electric Potential | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 mV | 400 mV | 800 mV | |
| Graphite | 9.80 | 10.72 | 10.95 |
| Treated SFw at 20 cm | 11.39 | 12.23 | 12.54 |
| AuNPs-SFw | 9.73 | 10.57 | 10.43 |
| AgNPs-SFw | 10.01 | 10.89 | 10.82 |
| Treatred SFw at 25 cm | 7.80 | 8.49 | 8.37 |
| AuNPs-SFw | 9.36 | 10.18 | 10.12 |
| AgNPs-SFw | 11.47 | 12.58 | 12.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agudelo, W.; Montoya, Y.; Garcia-Garcia, A.; Restrepo-Osorio, A.; Bustamante, J. Electrochemical and Electroconductive Behavior of Silk Fibroin Electrospun Membrane Coated with Gold or Silver Nanoparticles. Membranes 2022, 12, 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111154
Agudelo W, Montoya Y, Garcia-Garcia A, Restrepo-Osorio A, Bustamante J. Electrochemical and Electroconductive Behavior of Silk Fibroin Electrospun Membrane Coated with Gold or Silver Nanoparticles. Membranes. 2022; 12(11):1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111154
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgudelo, Wilson, Yuliet Montoya, Alejandra Garcia-Garcia, Adriana Restrepo-Osorio, and John Bustamante. 2022. "Electrochemical and Electroconductive Behavior of Silk Fibroin Electrospun Membrane Coated with Gold or Silver Nanoparticles" Membranes 12, no. 11: 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111154
APA StyleAgudelo, W., Montoya, Y., Garcia-Garcia, A., Restrepo-Osorio, A., & Bustamante, J. (2022). Electrochemical and Electroconductive Behavior of Silk Fibroin Electrospun Membrane Coated with Gold or Silver Nanoparticles. Membranes, 12(11), 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111154